案例一
import tensorflow as tf
a=3
w=tf.Variable([[0.5, 1.0 ]])
x=tf.Variable([ [2, 0], [1, 0] ])
y=tf.matmul(w,x)
print(y)
init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
print(y.eval())
最终得出两个结果:
Tersor("Variable_9/read:0",shape(1,2), dtype=float32)
[[2.]]
案例二:
input1=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
input2=tf.placeholder(tf.float32) #先占上一个地
output=tf.mul(input1,input2)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run([ output ],feed_dict={input1:[7.],input2:[2.] } ) )
输出:
[array([14.], dtype=float32)]
案例三:通过tensorflow构造一个线性回归模型
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
num_points=1000
vectors_set=[]
for i in range(num_points):
x1=np.random.normal(0.0,0.55)#对1进行高斯均值初始化,以0为均值,0.55为标准差
y1=x1*0.1+0.3+np.random.normal(0.0,0.03)
vectors_set.append([x1,y1])
x_data=[v[0] for v in vectors_set]
y_data=[v[1] for v in vectors_set]
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data,c='y')
plt.show()
#生成1维的W矩阵,取值是[-1,1]之间的随机数
W=tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1],-1.0,1.0),name='W')
#生成1维的b矩阵,初始值是0
b=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]),name='b')
#经过计算得出预估值y 找到最合适的W和b
y=W*x_data+b
#以估计值y和实际值y_data之间的均方误差作为损失
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_data),name='loss')
#采用梯度下降法来优化参数-------优化器
optimizer=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5)
#训练的过程就是最下化这个误差值
train=optimizer.minimize(loss,name='train')
sess=tf.Session()
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
#初始化的W和b是多少
print("W=",sess.run(W),"b=",sess.run(b),"loss=",sess.run(loss))
#执行20次训练
for step in range(20):
sess.run(train)
#输出训练好的W和b
print("W=",sess.run(W),"b=",sess.run(b),"loss=",sess.run(loss))
输出:
随着迭代的进行,W越来越接近0.1,b越来越接近0.3,loss值越来越小
案例三:Mnist手写字符识别
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import input_data
print("packs loaded")
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('data/',one_hot=True)
trainimg =mnist.train.images
trainlabel=mnist.train.labels
testimg = mnist.test.images
testlabel= mnist.test.labels
print("MNIST loaded")
print (trainimg.shape)
print (trainlabel.shape)
print (testimg.shape)
print (testlabel.shape)
print (testlabel[0])
x= tf.placeholder("float",[None,784])
y= tf.placeholder("float",[None,10])
W=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]))
b=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
actv=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W)+b) #Wx+b softmax输出结果是概率值
#y*tf.log(actv) 表示真实分类的概率值
cost=tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y*tf.log(actv),reduction_indices=1))
learning_rate=0.01
optm=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
#其中tf.argmax(actv,1) 代表预测值第一行最大数对应的索引值 ,tf.argmax(y,1)真实值对应的索引
#其中tf.argmax(actv,0) 代表预测值第一列最大数对应的索引值 ,tf.argmax(y,0)真实值对应的索引
pred=tf.equal(tf.argmax(actv,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
#pred返回值是True 或者 False
accr=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(pred,"float")) #准确率衡量
init= tf.global_variables_initializer()
training_epochs=50 #所有样本进行50次迭代
batch_size=100 #每一次迭代100个样本,每一个batch有100个样本
display_step=5
sess=tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
#MINI-BATCH LEARNING 每一个epoch进行迭代
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost=0.
num_batch=int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
for i in range(num_batch): #每一个batch进行选择
#其中batch_xs代表样本,batch_ys代表标签
batch_xs,batch_ys=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(optm,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})
feeds={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys}
#损失函数值
avg_cost+=sess.run(cost,feed_dict=feeds)/num_batch
#DISPLAY
if epoch%display_step==0:#每5个epoch打印一下,分别是第5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,45,50次
feeds_train={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys}
feeds_test ={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels}
train_acc =sess.run(accr,feed_dict=feeds_train) #训练的准确率
test_acc=sess.run(accr,feed_dict=feeds_test) #测试的准确率
print("Epch: %03d/%03d cost:%.9f train_acc: %.3f test_acc:%.3f"
%(epoch,training_epochs,avg_cost,train_acc,test_acc))
print("Done")
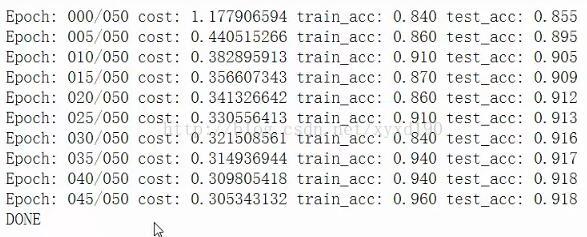
输出结果:
案例四:通过tensorflow实现一个简单的神经网络
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('data/', one_hot=True)
# NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
n_hidden_1 = 256 #第一层有256个神经元
n_hidden_2 = 128 #第二层有128个神经元
n_input = 784
n_classes = 10
# INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, n_input])
y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, n_classes])
# NETWORK PARAMETERS
stddev = 0.1
weights = {
'w1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input, n_hidden_1], stddev=stddev)), #w1是784*256
'w2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1, n_hidden_2], stddev=stddev)), #w2是256*128
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2, n_classes], stddev=stddev)) #out是128*10
}
biases = {
'b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])), #b1是256维
'b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2])), #b2是128维
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes])) #out是10维
}
print ("NETWORK READY")
def multilayer_perceptron(_X, _weights, _biases):
layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(_X, _weights['w1']), _biases['b1']))
layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, _weights['w2']), _biases['b2']))
return (tf.matmul(layer_2, _weights['out']) + _biases['out'])
# PREDICTION
pred = multilayer_perceptron(x, weights, biases)
# LOSS AND OPTIMIZER
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred, y))
optm = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001).minimize(cost) #通过梯度下降法是的Loss函数最小
corr = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1)) #corr只用两个值,TRUE和FALSE
accr = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(corr, "float")) #将准确率转换成float类型
# INITIALIZER
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
print ("FUNCTIONS READY")
training_epochs = 20 #训练迭代20次
batch_size = 100 #每一个batch有100个样本
display_step = 4
# LAUNCH THE GRAPH
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
# OPTIMIZE
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0.
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
# ITERATION
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
feeds = {x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys}
sess.run(optm, feed_dict=feeds)
avg_cost += sess.run(cost, feed_dict=feeds)
avg_cost = avg_cost / total_batch
# DISPLAY
if (epoch+1) % display_step == 0:
print ("Epoch: %03d/%03d cost: %.9f" % (epoch, training_epochs, avg_cost))
feeds = {x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys}
train_acc = sess.run(accr, feed_dict=feeds)
print ("TRAIN ACCURACY: %.3f" % (train_acc))
feeds = {x: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels}
test_acc = sess.run(accr, feed_dict=feeds)
print ("TEST ACCURACY: %.3f" % (test_acc))
print ("OPTIMIZATION FINISHED")






















 8万+
8万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








