还有兄弟不知道网络安全面试可以提前刷题吗?费时一周整理的160+网络安全面试题,金九银十,做网络安全面试里的显眼包!
王岚嵚工程师面试题(附答案),只能帮兄弟们到这儿了!如果你能答对70%,找一个安全工作,问题不大。
对于有1-3年工作经验,想要跳槽的朋友来说,也是很好的温习资料!
【完整版领取方式在文末!!】
93道网络安全面试题



内容实在太多,不一一截图了
黑客学习资源推荐
最后给大家分享一份全套的网络安全学习资料,给那些想学习 网络安全的小伙伴们一点帮助!
对于从来没有接触过网络安全的同学,我们帮你准备了详细的学习成长路线图。可以说是最科学最系统的学习路线,大家跟着这个大的方向学习准没问题。
1️⃣零基础入门
① 学习路线
对于从来没有接触过网络安全的同学,我们帮你准备了详细的学习成长路线图。可以说是最科学最系统的学习路线,大家跟着这个大的方向学习准没问题。

② 路线对应学习视频
同时每个成长路线对应的板块都有配套的视频提供:

网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
}
public Object getData(){
return this.data;
}
public void setNext(Node next){
this.next = next;
}
public Node getNext(){
return this.next;
}
}
public class TestLinkDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
//1.封装几个节点
Node root = new Node(“火车头”);
Node n1 = new Node(“车厢1”);
Node n2 = new Node(“车厢2”);
Node n3 = new Node(“车厢3”);
//2.设置节点关系
root.setNext(n1);
n1.setNext(n2);
n2.setNext(n3);
//3.输出链表
print(root);
}
public static void print(Node node){
if(node != null){//表示当前是有节点的
System.out.println(node.getData());
print(node.getNext());//继续向下取出
}
}
}
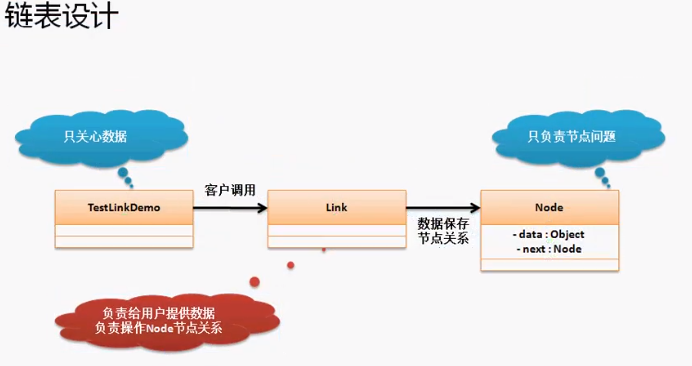
在整个链表的实现过程中,Node类的作用:保存数据和保存下一个节点,但是我们发现客户端需要自己来进行节点的创建操作以及关系的配置。所谓的链表就是需要有一个单独的类,假设叫Link,通过Link类来实现Node的数据保存和关系处理。
###### 2.2 链表实现结构说明
通过之前的分析,可以发现链表的最大作用类就是Node,但是以上程序都是由用户自己去匹配节点关系的,但是这些节点的匹配工作不应该由用户完成,应该由一个程序专门去负责。
那么专门负责几点操作的类,就成为链表类——Link,负责处理几点关系,而用户不用关心节点的问题,只需关心Link的处理操作即可。
**真实开发——标准过程**

class Link{//负责对链表的操作
//将Node定义内部类,表示Node类只能为Link类提供服务
private class Node{//负责数据与节点的关系匹配
private Object data;//真正要保存的数据
private Node next;//定义下一个节点
public Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public void setData(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData(){
return this.data;
}
}
//以下为Link类
}
public class TestLinkDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
}
}
###### 2.3 增加链表数据—public void add(数据)
通过上面程序的分析,可以发下,对于链表的实现,Node类是整个操作的关键,但是首先来研究一下之前程序的问题:Node是一个单独的类是可以被用户直接使用的,但是这个类由用户直接去使用,没有任何意义,即:这个类有用,但不能让用户去使用,让Link类去使用。
class Link{//负责对链表的操作
//将Node定义内部类,表示Node类只能为Link类提供服务
private class Node{//负责数据与节点的关系匹配
private Object data;//真正要保存的数据
private Node next;//定义下一个节点
public Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public void setData(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData(){
return this.data;
}
public void setNext(Node next){
this.next = next;
}
public Node getNext(){
return this.next;
}
//第一次调用:this = Link.root
//第二次调用:this = Link.root.next
//第三次调用:this = Link.root.next.next
public void addNode(Node newNode){//处理节点关系
if(this.next == null){ //当前节点下一个为空
this.next = newNode;
}else{//当前节点的下一个不为空
this.next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
public void nodePrint(){
System.out.println(this.getData());
if (this.getNext()==null)
{
return;
}else{
this.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
}
//以下为Link类------------------------------------------------
private Node root; //属于根节点,没有根节点就无法数据的保存
//增加数据
public void add(Object data){
if(data == null){//人为追加规定,不允许存放null值
return ;//结束方法调用
}
//如果要想进行数据的保存,那么必须将数据封装在Node类里面
//如果没有封装,则无法确认好节点的先后顺序
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;//第一个节点设置为根节点
}else{//根节点存在了
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
}
//输出数据
public void print(){
if (this.root == null){
return;
}
System.out.println(this.root.getData());
if (this.root.getNext()==null){
return;
}
else{
this.root.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
}
public class TestLinkDemo1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Link link = new Link();
link.add(“Hello”);
link.add(“World”);
link.print();
}
}
###### 2.4 增加多个数据—public void addAll(数据数组)
public void addAll(String date[]){
for(int x = 0;x<date.length;x++){
this.add(date[x]);
}
}
###### 2.5 统计数据个数—public int size()
在Link类中定义
private int count;//统计个数
在增加数据的最后一行添加count++
public void add(Object data){
if(data == null){//人为追加规定,不允许存放null值
return ;//结束方法调用
}
//如果要想进行数据的保存,那么必须将数据封装在Node类里面
//如果没有封装,则无法确认好节点的先后顺序
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;//第一个节点设置为根节点
}else{//根节点存在了
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
count++;
}
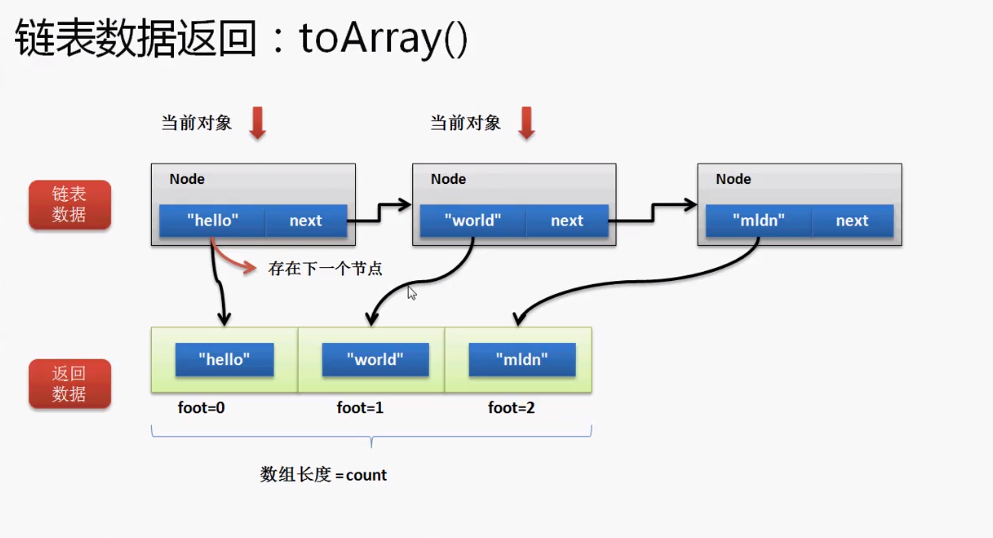
###### 2.6 链表数据转换为对象数组—public Object[] toArray()
对于链表的这种数据结构,最为关键的是两个操作:删除和取得全部数据。
在Link类中定义一个操作数组的脚标:
private int foot = 0;
要把数据保存的数组,Link类和Node类都需要使用,那么可以在Link类中定义返回数组,必须以属性的形式出现,只有这样,Node类才可以访问这个数组并进行操作。
private Object [] retData ; //返回类型
在Link类中增加toArray()方法:
//链表数据转换为对象数组
public Object[] toArray(){
if(this.count == 0){
return null;
}
this.retData = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
this.foot = 0;//下表清零操作
return this.retData;
}
在Node中增加toArrayNode()方法:
public void toArrayNode(){
Link.this.retData[Link.this.foot++] = this.data;
if(this.next != null){
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
不过按照以上的方式进行开发,每一次调用toArray()方法,都要重复的进行数据的的遍历,如果在数据没有修改的情况下,这种做法是一种低效的做法,最好的方法是增加一个修改标记,如果发现数据增加了或删除的话,表示要重新遍历数据。
###### 2.7 链表查询数据—public boolean contains(查找对象)
现在如果想查询某个数据是否存在,那么基本的操作原理:逐个盘查,盘查的具体对象应该交给Node去完成,前提是:有数据存在。
在Link类之中,增加查询操作:
//查找链表的指定数据是否存在
public boolean contains(Object search){
if(search == null && this.root == null)
return false;
return this.root.containsNode(search);
}
在Node类中,完成具体查询,查询流程为:
判断当前节点的内容是否满足于查询内容,如果满足返回ture;
如果当前节点内容不满足,则向后继续查询,如果没有后续节点了,则返回false。
public boolean containsNode(Object search){
if(search.equals(this.data))
return true;
else{
if(this.next != null){//判断下一个节点是否为空
return this.next.containsNode(search);
}
return false;
}
}
###### 2.8 根据索引取得数据—public Object get(int index)
在一个链表之中会有多个节点保存数据,现在要求可以取得指定节点的数据。但是在进行这一操作的过程之中,有一个小问题:如果要取得数据的索引超过了数据的保存个数,那么是无法取得的。
在Link类之中增加一个get(int index)方法:
//根据索引取得数据
public Object get(int index){
if(index >= this.count){
return null;
}
this.foot = 0;
return this.root.getNode(index);
}
在Node类之中增加一个getNdoe(int index)方法:
//第一次this == Link.root
//第二次this == Link.root.next
public Object getNode(int index){
if(Link.this.foot++ == index){
return this.data;
}else{
return this.next.getNode(index);
}
}
###### 2.9 修改指定索引数据—public void set(int index,Object newData)
如果修改数据只需要进行数据的替换。
在Link类之中增加一个set(int index,Object newData)方法:
//修改指定索引数据
public void set(int index,Object newData){
if(index >= this.count){
return ;
}
this.foot = 0;
this.root.setNode(index,newData);
}
在Node类之中增加一个getNode(int index)方法:
public void setNode(int index, Object newData){
if(Link.this.foot ++ == index){//索引相同
this.data = newData;
}else{
if(this.next != null){
this.next.setNode(index,newData);
}
}
}
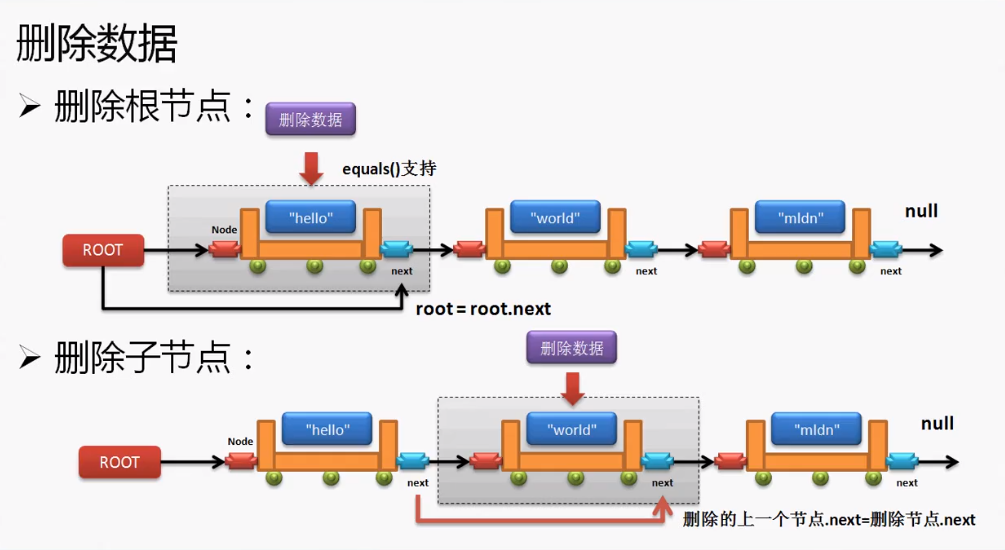
###### 2.10 删除数据—public void remove(数据)
对于链表之中的内容,之前完成的是增加操作和查询操作,但是从链表之中也会存在删除数据的操作,可是删除数据的操作要分为两种情况讨论:
情况一:删除的数据不是根节点,待删节点的上一个next指向待删节点的next。
所有的处理操作应该交给Node进行处理。
情况二:删除的数据是根节点,下一个节点保存为跟节点。
如果删除的是根节点,意味着Link中的根节点的保存需要发生变化,该操作主要在Link中处理。
在Link中增加一个删除remove(Object data)方法
//删除数据
public void remove(Object data){
if(this.contains(data)){//如果数据存在则进行数据处理
if(this.root.data.equals(data)){//首先需要判断要删除的数据是否为根节点数据
this.root = this.root.next;//根节点变为下一个节点
}else{//不是根节点
this.root.next.removeNode(this.root,data);
}
this.count --;
}
}
在Node类之中增加一个removeNode(Node previous, Object data)方法:
//第一次:this = Link.root.next、previous= Link.root;
//第二次:this = Link.root.next.next、previous= Link.root.next;
public void removeNode(Node previous, Object data){
if(this.data.equals(data)){//当前节点为要删除的节点
previous.next = this.next;
}else{
this.next.removeNode(this,data);
}
}
#### Link链表类模板
class Link{//负责链表的操作
//将Node定义内部类,表示Node类只能为Link类提供服务
private class Node{//负责数据与节点的关系匹配
private Object data;//真正要保存的数据
private Node next;//定义下一个节点
public Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public void setData(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData(){
return this.data;
}
public void setNext(Node next){
this.next = next;
}
public Node getNext(){
return this.next;
}
//第一次调用:this = Link.root
//第二次调用:this = Link.root.next
//第三次调用:this = Link.root.next.next
public void addNode(Node newNode){//处理节点关系
if(this.next == null){ //当前节点下一个为空
this.next = newNode;
}else{//当前节点的下一个不为空
this.next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
public void nodePrint(){
System.out.println(this.getData());
if (this.getNext()==null)
{
return;
}else{
this.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
public void toArrayNode(){
Link.this.retData[Link.this.foot++] = this.data;
if(this.next != null){
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
public boolean containsNode(Object search){
if(search.equals(this.data))
return true;
else{
if(this.next != null){//判断下一个节点是否为空
return this.next.containsNode(search);
}
return false;
}
}
//第一次this == Link.root
//第二次this == Link.root.next
public Object getNode(int index){
if(Link.this.foot++ == index){
return this.data;
}else{
return this.next.getNode(index);
}
}
public void setNode(int index, Object newData){
if(Link.this.foot ++ == index){//索引相同
this.data = newData;
}else{
if(this.next != null){
this.next.setNode(index,newData);
}
}
}
//第一次:this = Link.root.next、previous= Link.root;
//第二次:this = Link.root.next.next、previous= Link.root.next;
public void removeNode(Node previous, Object data){
if(this.data.equals(data)){//当前节点为要删除的节点
previous.next = this.next;
}else{
this.next.removeNode(this,data);
}
}
}
//以下为Link类------------------------------------------------
private Object [] retData ; //返回类型
private int foot = 0;//操作下标
private int count;//统计个数
private Node root; //属于根节点,没有根节点就无法数据的保存
//增加数据
public void add(Object data){
if(data == null){//人为追加规定,不允许存放null值
return ;//结束方法调用
}
//如果要想进行数据的保存,那么必须将数据封装在Node类里面
//如果没有封装,则无法确认好节点的先后顺序
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;//第一个节点设置为根节点
}else{//根节点存在了
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
count++;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
this.count=0;
return false;
}
//增加多个数据
public void addAll(String date[]){
for(int x = 0;x<date.length;x++){
this.add(date[x]);
}
}
public int size(){
return this.count;
}
//输出数据
public void print(){
if (this.root == null){
return;
}
System.out.println(this.root.getData());
if (this.root.getNext()==null){
return;
}
else{
this.root.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
//链表数据转换为对象数组
public Object[] toArray(){
if(this.count == 0){
return null;
}
this.retData = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
this.foot = 0;//下表清零操作
return this.retData;
}
//查找链表的指定数据是否存在
public boolean contains(Object search){
if(search == null && this.root == null)
return false;
return this.root.containsNode(search);
}
//根据索引取得数据
public Object get(int index){
if(index >= this.count){
return null;
}
this.foot = 0;
return this.root.getNode(index);
}
//修改指定索引数据
public void set(int index,Object newData){
if(index >= this.count){
return ;
}
this.foot = 0;
this.root.setNode(index,newData);
}
//删除数据
public void remove(Object data){
if(this.contains(data)){//如果数据存在则进行数据处理
if(this.root.data.equals(data)){//首先需要判断要删除的数据是否为根节点数据
this.root = this.root.next;//根节点变为下一个节点
}else{//不是根节点
this.root.next.removeNode(this.root,data);
}
this.count --;
}
}
}
#### 综合案例
建立宠物商店,包括销售宠物上架、下架、关键字查询,要求程序的关系即可,对于宠物的信息只要有三项:名字、年龄、颜色。
对应的关系:一个宠物商店有多种宠物,如果按照表设计应该属于一对多关系映射,但是现在问题,一方是宠物商店,多方是宠物,但是宠物又分为猫、狗、猪、驴、鱼等。
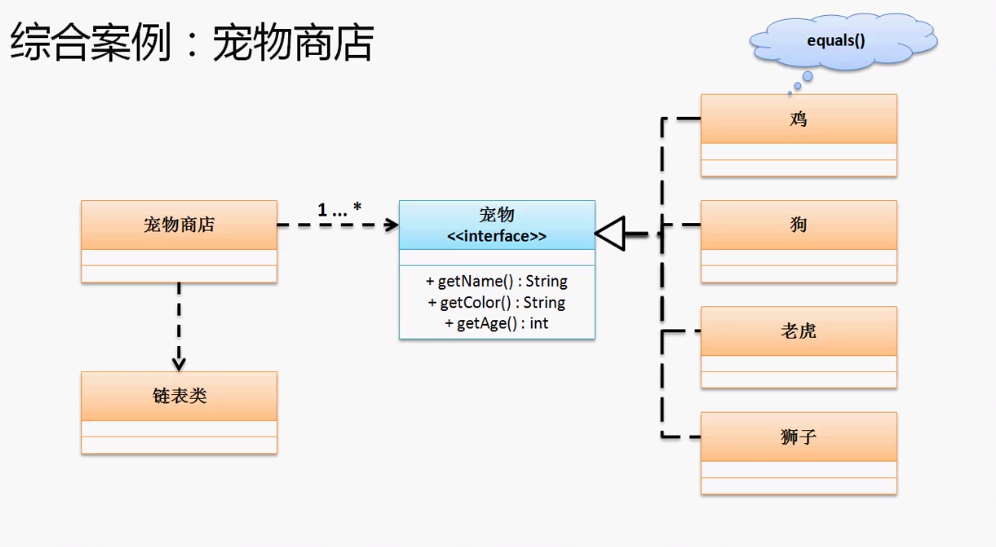
1、建立宠物标准
interface Pet{//定义宠物
public String getName();
public String getColor();
public int getAge();
}
2、对于宠物商店,只关注于宠物的标准,而不关心具体是那种宠物
class PetShop{
private Link pets = new Link();//开辟一个链表,保存宠物信息
public void add(Pet pet){//上架宠物
this.pets.add(pet);
}
public void delete(Pet pet){//下架宠物
this.pets.delete(pet);
}
public Link getPets(){ //得到全部宠物
return this.pets;
}
public Link search(String keyword){//关键字查找
Link result = new Link();
Object [] data = this.pets.toArray();
for(int i = 0; i < data.length ; i++){
Pet pet = (Pet) data[i];
if(pet.getName().contains(keyword) || pet.getColor().contains(keyword)){
result.add(pet); //满足查询结果
}
}
return result;
}
}
3、定义宠物狗
class Dog implements Pet{
private String name;
private String color;
private int age;
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public String getColor(){
return this.color;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
if(this == obj){
return false;
}
if(!(obj instanceof Dog)){
return false;
}
Dog pet = (Dog) obj;
return this.name.equals(pet.name) && this.color.equals(pet.color) && this.age.equals(pet.age);
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
public Dog(String name, String color, int age){
this.name = name ;
this.color = color;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return "【狗】名字 = " + this.name +
"颜色 = " + this.color +
"年龄 = " +this.age;
}
}
定义宠物猫
class Cat implements Pet{
private String name;
private String color;
private int age;
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public String getColor(){
return this.color;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
if(this == obj){
return false;
}
if(!(obj instanceof Cat)){
return false;
}
Cat pet = (Cat) obj;
return this.name.equals(pet.name) && this.color.equals(pet.color) && this.age.equals(pet.age);
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
public Cat(String name, String color, int age){
this.name = name ;
this.color = color;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return "【猫】名字 = " + this.name +
"颜色 = " + this.color +
"年龄 = " +this.age;
}
}
5、测试类
public class Pets{
public static void main(String args[]){
PetShop ps = new PetShop();
ps.add(new Dog(“小黑”,“黑色”,1));
ps.add(new Dog(“金毛”,“金色”,2));
ps.add(new Dog(“拉布拉多”,“白色”,3));
ps.add(new Dog(“萨摩耶”,“白色”,2));
ps.add(new Cat(“加菲猫”,“黄色”,3));
ps.add(new Dog(“波斯猫”,“金色”,4));
ps.delete(new Dog(“萨摩耶”,“白色”,2));
Link all = ps.search(“白”);
Object [] data = all.toArray();
for(int i = 0 ; i < data.length ; i++){
System.out.println(data[i]);
}
}
}
6、完整代码
class Link{//负责链表的操作
//将Node定义内部类,表示Node类只能为Link类提供服务
private class Node{//负责数据与节点的关系匹配
private Object data;//真正要保存的数据
private Node next;//定义下一个节点
public Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public void setData(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData(){
return this.data;
}
public void setNext(Node next){
this.next = next;
}
public Node getNext(){
return this.next;
}
//第一次调用:this = Link.root
//第二次调用:this = Link.root.next
//第三次调用:this = Link.root.next.next
public void addNode(Node newNode){//处理节点关系
if(this.next == null){ //当前节点下一个为空
this.next = newNode;
}else{//当前节点的下一个不为空
this.next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
public void nodePrint(){
System.out.println(this.getData());
if (this.getNext()==null)
{
return;
}else{
this.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
public void toArrayNode(){
Link.this.retData[Link.this.foot++] = this.data;
if(this.next != null){
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
public boolean containsNode(Object search){
if(search.equals(this.data))
return true;
else{
if(this.next != null){//判断下一个节点是否为空
return this.next.containsNode(search);
}
return false;
}
}
//第一次this == Link.root
//第二次this == Link.root.next
public Object getNode(int index){
if(Link.this.foot++ == index){
return this.data;
}else{
return this.next.getNode(index);
}
}
public void setNode(int index, Object newData){
if(Link.this.foot ++ == index){//索引相同
this.data = newData;
}else{
if(this.next != null){
this.next.setNode(index,newData);
}
}
}
//第一次:this = Link.root.next、previous= Link.root;
//第二次:this = Link.root.next.next、previous= Link.root.next;
public void removeNode(Node previous, Object data){
if(this.data.equals(data)){//当前节点为要删除的节点
previous.next = this.next;
}else{
this.next.removeNode(this,data);
}
}
}
//以下为Link类------------------------------------------------
private Object [] retData ; //返回类型
private int foot = 0;//操作下标
private int count;//统计个数
private Node root; //属于根节点,没有根节点就无法数据的保存
//增加数据
public void add(Object data){
if(data == null){//人为追加规定,不允许存放null值
return ;//结束方法调用
}
//如果要想进行数据的保存,那么必须将数据封装在Node类里面
//如果没有封装,则无法确认好节点的先后顺序
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;//第一个节点设置为根节点
}else{//根节点存在了
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
count++;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
this.count=0;
return false;
}
//增加多个数据
public void addAll(String date[]){
for(int x = 0;x<date.length;x++){
this.add(date[x]);
}
}
public int size(){
return this.count;
}
//输出数据
public void print(){
if (this.root == null){
return;
}
System.out.println(this.root.getData());
if (this.root.getNext()==null){
return;
}
else{
this.root.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
//链表数据转换为对象数组
public Object[] toArray(){
if(this.count == 0){
return null;
}
this.retData = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
this.foot = 0;//下表清零操作
return this.retData;
}
//查找链表的指定数据是否存在
public boolean contains(Object search){
if(search == null && this.root == null)
return false;
return this.root.containsNode(search);
}
//根据索引取得数据
public Object get(int index){
if(index >= this.count){
return null;
}
this.foot = 0;
return this.root.getNode(index);
}
//修改指定索引数据
public void set(int index,Object newData){
if(index >= this.count){
return ;
}
this.foot = 0;
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!






















 12万+
12万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








