>- **🍨 本文为[🔗365天深度学习训练营](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pgg8O9Hv8fiLBc8xbFm4HQ) 中的学习记录博客**
>- **🍖 原作者:[K同学啊 | 接辅导、项目定制](https://mtyjkh.blog.csdn.net/)*
一 前期准备
1.设置GPU
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import os,PIL,pathlib,warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
devicedevice(type='cpu')
2.导入数据
import os,PIL,random,pathlib
data_dir = './coffee/'
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[1] for path in data_paths]
classeNames还是了解一下数据集的结构。本周做的是咖啡豆识别。有一个主文件夹叫coffee,在coffee文件夹下还有四个分类文件夹,分别是:'Dark', 'Green', 'Light', 'Medium'。每类对应着图片数据。
['Dark', 'Green', 'Light', 'Medium']
3.统一调整图片格式,转换为需要的数据
# 关于transforms.Compose的更多介绍可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38251616/article/details/124878863
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
# transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 随机水平翻转
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
test_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
total_data = datasets.ImageFolder("./coffee/",transform=train_transforms)
total_dataDataset ImageFolder
Number of datapoints: 1200
Root location: ./coffee/
StandardTransform
Transform: Compose(
Resize(size=[224, 224], interpolation=bilinear, max_size=None, antialias=warn)
ToTensor()
Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
)
total_data.class_to_idx{'Dark': 0, 'Green': 1, 'Light': 2, 'Medium': 3}
4.划分数据集
train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
train_dataset, test_dataset
batch_size = 16
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
for X, y in test_dl:
print("Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: ", X.shape)
print("Shape of y: ", y.shape, y.dtype)
breakShape of X [N, C, H, W]: torch.Size([16, 3, 224, 224]) Shape of y: torch.Size([16]) torch.int64
二 搭建VGG-16模型
VGG-16结构说明:
- 13个卷积层(Convolutional Layer),分别用
blockX_convX表示- 3个全连接层(Fully connected Layer),分别用
fcX与predictions表示- 5个池化层(Pool layer),分别用
blockX_pool表示
VGG-16包含了16个隐藏层(13个卷积层和3个全连接层),故称为VGG-16
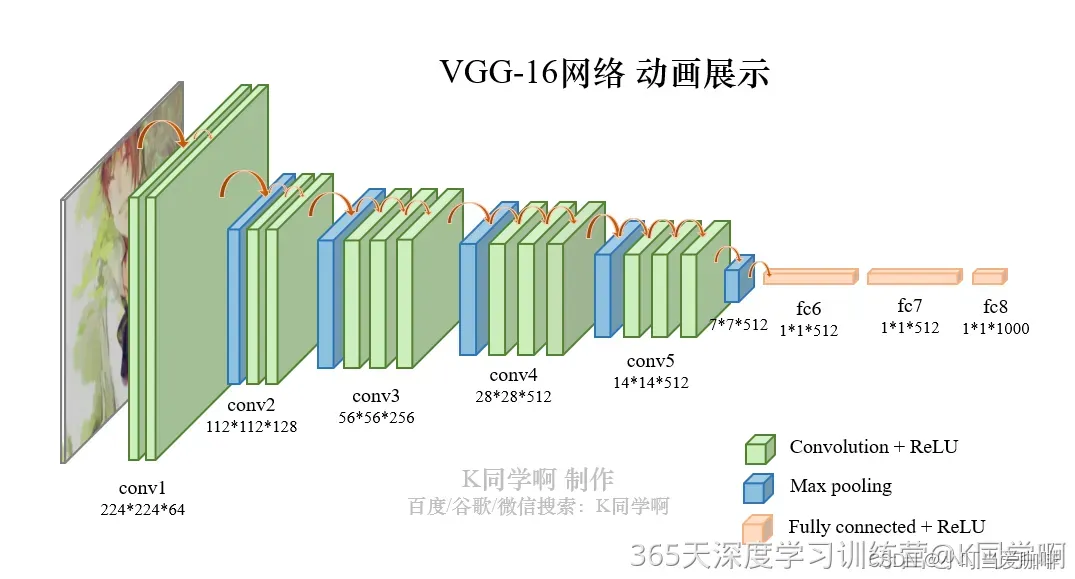
这里分为2种方式:1.调用内置VGG-16函数;2.手动搭建vgg-16模型
1.调库搭建模型
from torchvision.models import vgg16
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
# 加载预训练模型,并且对模型进行微调
model = vgg16(pretrained = True).to(device) # 加载预训练的vgg16模型
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False # 冻结模型的参数,这样子在训练的时候只训练最后一层的参数
# 修改classifier模块的第6层(即:(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=2, bias=True))
# 注意查看我们下方打印出来的模型
model.classifier._modules['6'] = nn.Linear(4096,len(classeNames)) # 修改vgg16模型中最后一层全连接层,输出目标类别个数
model.to(device)
modelUsing cpu device
VGG(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(5): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(6): ReLU(inplace=True)
(7): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(8): ReLU(inplace=True)
(9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(10): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(13): ReLU(inplace=True)
(14): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(15): ReLU(inplace=True)
(16): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(17): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(18): ReLU(inplace=True)
(19): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(20): ReLU(inplace=True)
(21): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(22): ReLU(inplace=True)
(23): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(24): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(25): ReLU(inplace=True)
(26): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(27): ReLU(inplace=True)
(28): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(29): ReLU(inplace=True)
(30): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(avgpool): AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(7, 7))
(classifier): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4, bias=True)
)
)
# 统计模型参数量以及其他指标
import torchsummary as summary
summary.summary(model, (3, 224, 224))----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 1,792
ReLU-2 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 0
Conv2d-3 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 36,928
ReLU-4 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 0
MaxPool2d-5 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-6 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 73,856
ReLU-7 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-8 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 147,584
ReLU-9 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 0
MaxPool2d-10 [-1, 128, 56, 56] 0
Conv2d-11 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 295,168
ReLU-12 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 0
Conv2d-13 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 590,080
ReLU-14 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 0
Conv2d-15 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 590,080
ReLU-16 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 0
MaxPool2d-17 [-1, 256, 28, 28] 0
Conv2d-18 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 1,180,160
ReLU-19 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 0
Conv2d-20 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 2,359,808
ReLU-21 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 0
Conv2d-22 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 2,359,808
ReLU-23 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 0
MaxPool2d-24 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 0
Conv2d-25 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 2,359,808
ReLU-26 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 0
Conv2d-27 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 2,359,808
ReLU-28 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 0
Conv2d-29 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 2,359,808
ReLU-30 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 0
MaxPool2d-31 [-1, 512, 7, 7] 0
AdaptiveAvgPool2d-32 [-1, 512, 7, 7] 0
Linear-33 [-1, 4096] 102,764,544
ReLU-34 [-1, 4096] 0
Dropout-35 [-1, 4096] 0
Linear-36 [-1, 4096] 16,781,312
ReLU-37 [-1, 4096] 0
Dropout-38 [-1, 4096] 0
Linear-39 [-1, 4] 16,388
================================================================
Total params: 134,276,932
Trainable params: 16,388
Non-trainable params: 134,260,544
----------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 0.57
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 218.77
Params size (MB): 512.23
Estimated Total Size (MB): 731.57
----------------------------------------------------------------
2.手动搭建模型
import torch.nn.functional as F
class vgg16(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(vgg16, self).__init__()
# 卷积块1
self.block1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
)
# 卷积块2
self.block2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
)
# 卷积块3
self.block3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
)
# 卷积块4
self.block4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
)
# 卷积块5
self.block5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
)
# 全连接网络层,用于分类
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=512*7*7, out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=len(classeNames))
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.block1(x)
x = self.block2(x)
x = self.block3(x)
x = self.block4(x)
x = self.block5(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
model = vgg16().to(device)
model# 统计模型参数量以及其他指标
import torchsummary as summary
summary.summary(model, (3, 224, 224))三、 训练模型
1. 编写训练函数
# 训练循环
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 训练集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # 初始化训练损失和正确率
for X, y in dataloader: # 获取图片及其标签
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 计算预测误差
pred = model(X) # 网络输出
loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # 计算网络输出和真实值之间的差距,targets为真实值,计算二者差值即为损失
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
# 记录acc与loss
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss2.编写测试函数
def test (dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 测试集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
with torch.no_grad():
for imgs, target in dataloader:
imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
# 计算loss
target_pred = model(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss3.正式训练
import copy
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr= 1e-4)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建损失函数
epochs = 40
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
best_acc = 0 # 设置一个最佳准确率,作为最佳模型的判别指标
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
# 保存最佳模型到 best_model
if epoch_test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_test_acc
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
# 获取当前的学习率
lr = optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}, Lr:{:.2E}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss,
epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
# 保存最佳模型到文件中
PATH = './best_model.pth' # 保存的参数文件名
torch.save(model.state_dict(), PATH)
print('Done')Epoch: 1, Train_acc:86.1%, Train_loss:0.551, Test_acc:92.9%, Test_loss:0.462, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 2, Train_acc:89.2%, Train_loss:0.426, Test_acc:95.0%, Test_loss:0.383, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 3, Train_acc:90.9%, Train_loss:0.362, Test_acc:94.6%, Test_loss:0.336, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 4, Train_acc:91.0%, Train_loss:0.325, Test_acc:95.0%, Test_loss:0.301, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 5, Train_acc:92.5%, Train_loss:0.283, Test_acc:95.0%, Test_loss:0.275, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 6, Train_acc:93.0%, Train_loss:0.280, Test_acc:96.2%, Test_loss:0.256, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 7, Train_acc:93.0%, Train_loss:0.256, Test_acc:96.7%, Test_loss:0.241, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 8, Train_acc:93.6%, Train_loss:0.237, Test_acc:97.1%, Test_loss:0.229, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 9, Train_acc:93.6%, Train_loss:0.240, Test_acc:97.1%, Test_loss:0.218, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:10, Train_acc:93.5%, Train_loss:0.215, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.209, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:11, Train_acc:94.0%, Train_loss:0.206, Test_acc:97.1%, Test_loss:0.202, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:12, Train_acc:94.7%, Train_loss:0.201, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.197, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:13, Train_acc:95.8%, Train_loss:0.183, Test_acc:97.1%, Test_loss:0.191, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:14, Train_acc:94.3%, Train_loss:0.192, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.183, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:15, Train_acc:93.8%, Train_loss:0.189, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.184, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:16, Train_acc:94.7%, Train_loss:0.180, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.176, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:17, Train_acc:95.8%, Train_loss:0.168, Test_acc:97.1%, Test_loss:0.176, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:18, Train_acc:95.3%, Train_loss:0.164, Test_acc:97.1%, Test_loss:0.168, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:19, Train_acc:95.4%, Train_loss:0.157, Test_acc:97.1%, Test_loss:0.165, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:20, Train_acc:95.7%, Train_loss:0.157, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.164, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:21, Train_acc:95.1%, Train_loss:0.159, Test_acc:97.1%, Test_loss:0.161, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:22, Train_acc:94.7%, Train_loss:0.170, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.158, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:23, Train_acc:96.0%, Train_loss:0.148, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.157, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:24, Train_acc:95.9%, Train_loss:0.139, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.153, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:25, Train_acc:95.9%, Train_loss:0.139, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.152, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:26, Train_acc:96.2%, Train_loss:0.128, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.152, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:27, Train_acc:95.9%, Train_loss:0.132, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.147, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:28, Train_acc:95.7%, Train_loss:0.131, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.149, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:29, Train_acc:95.7%, Train_loss:0.138, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.144, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:30, Train_acc:95.7%, Train_loss:0.135, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.144, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:31, Train_acc:96.7%, Train_loss:0.132, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.143, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:32, Train_acc:96.2%, Train_loss:0.125, Test_acc:97.9%, Test_loss:0.142, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:33, Train_acc:96.2%, Train_loss:0.124, Test_acc:96.7%, Test_loss:0.149, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:34, Train_acc:95.8%, Train_loss:0.134, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.138, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:35, Train_acc:95.9%, Train_loss:0.124, Test_acc:97.9%, Test_loss:0.139, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:36, Train_acc:95.9%, Train_loss:0.135, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.139, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:37, Train_acc:96.6%, Train_loss:0.116, Test_acc:97.9%, Test_loss:0.138, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:38, Train_acc:96.7%, Train_loss:0.120, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.135, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:39, Train_acc:95.9%, Train_loss:0.121, Test_acc:97.5%, Test_loss:0.135, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:40, Train_acc:96.4%, Train_loss:0.121, Test_acc:96.2%, Test_loss:0.151, Lr:1.00E-04
四 结果可视化
1. Loss与Accuracy图
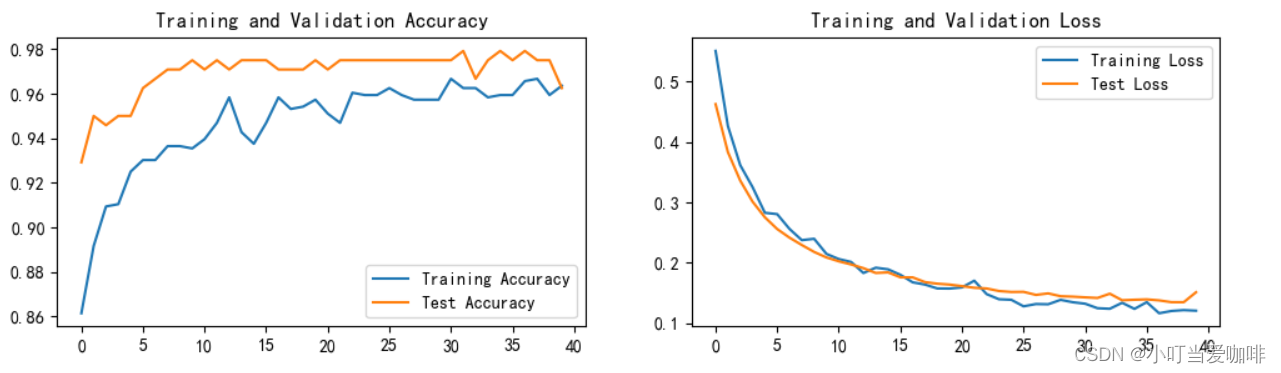
2.指定图片预测
from PIL import Image
classes = list(total_data.class_to_idx)
def predict_one_image(image_path, model, transform, classes):
test_img = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
plt.imshow(test_img) # 展示预测的图片
test_img = transform(test_img)
img = test_img.to(device).unsqueeze(0)
model.eval()
output = model(img)
_,pred = torch.max(output,1)
pred_class = classes[pred]
print(f'预测结果是:{pred_class}')# 预测训练集中的某张照片
predict_one_image(image_path='./coffee/Dark/dark (1).png',
model=model,
transform=train_transforms,
classes=classes)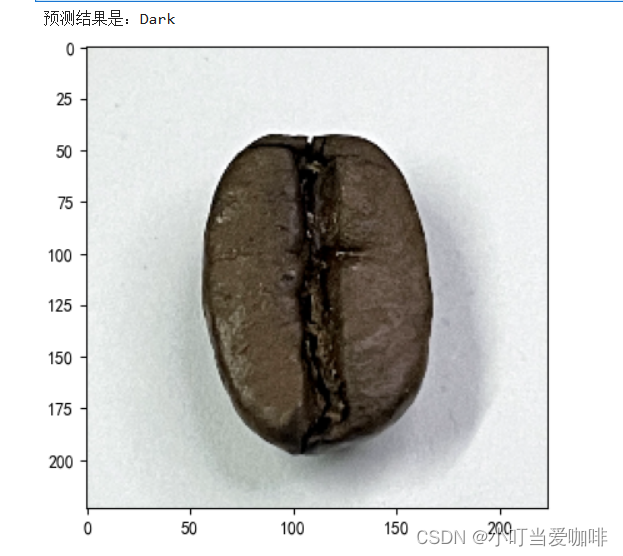
3.模型与评估
best_model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, best_model, loss_fn)
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss(0.9791666666666666, 0.14160602341095607)
五 总结心得
1.对相同结构的不同数据集,掌握如何调用和手写vgg16函数进行深度学习分析
2.准确率高达98%
3 初步掌握了vgg16的网络原理和结构





















 7万+
7万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








