Channel
设计原理
不要通过共享内存的方式进行通信,而是应该通过通信的方式共享内存。
在主流编程语言中,多个线程传递数据的方式一般都是共享内存。
Go 可以使用共享内存加互斥锁进行通信,同时也提供了一种不同的并发模型,即通信顺序进程(Communicating sequential processes,CSP)。Goroutine 和 Channel 分别对应 CSP 中的实体和传递信息的媒介,Goroutine 之间会通过 Channel 传递数据。
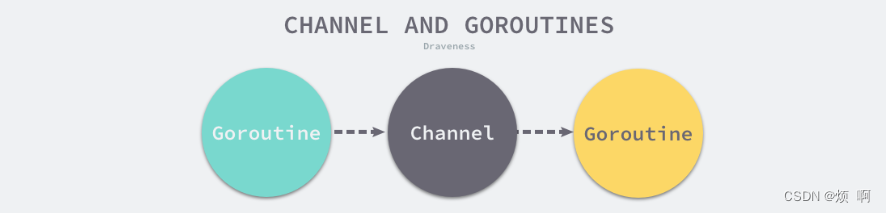
上图中的两个 Goroutine,一个会向 Channel 中发送数据,另一个会从 Channel 中接收数据,它们两者能够独立运行并不存在直接关联,但是能通过 Channel 间接完成通信。
数据结构
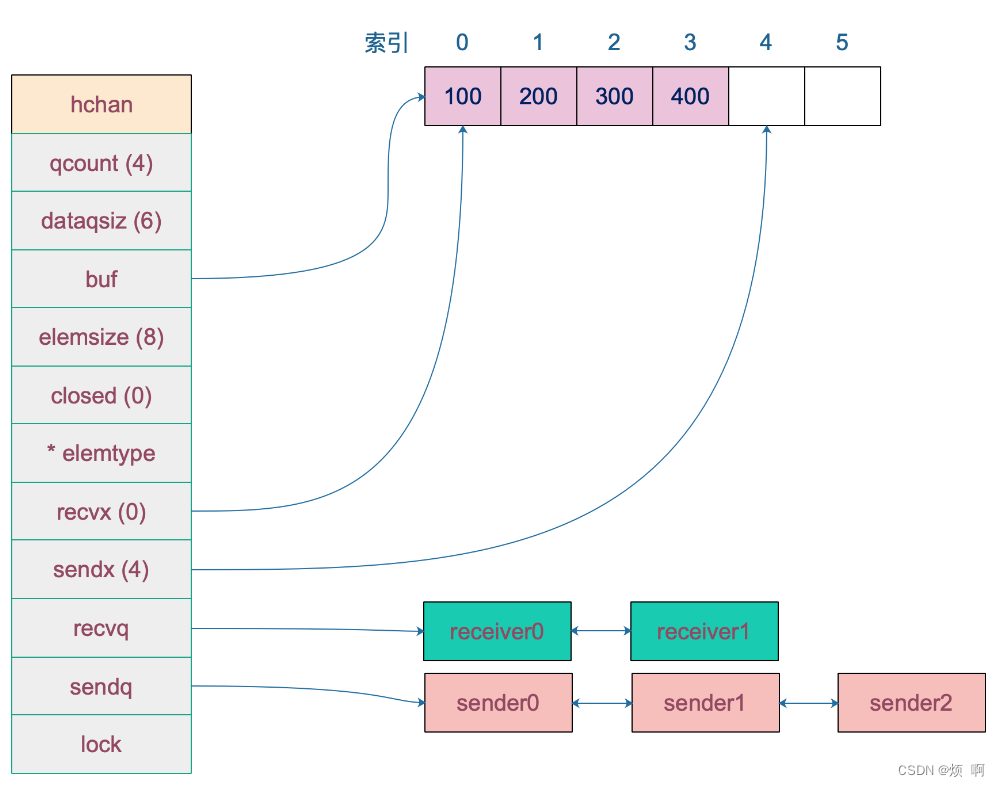
type hchan struct {
// 循环队列
// 元素数量
qcount uint // total data in the queue
// 队列的长度
dataqsiz uint // size of the circular queue
// 缓冲区大小 有缓冲的 channel 才有
buf unsafe.Pointer // points to an array of dataqsiz elements
// 已发送和接收元素在队列中的索引
sendx uint // send index
recvx uint // receive index
// 元素类型和大小
elemsize uint16
elemtype *_type // element type
// channel 是否已关闭
closed uint32
// 等待接受和发送的 goroutine 队列
recvq waitq // list of recv waiters
sendq waitq // list of send waiters
// lock protects all fields in hchan, as well as several
// fields in sudogs blocked on this channel.
//
// Do not change another G's status while holding this lock
// (in particular, do not ready a G), as this can deadlock
// with stack shrinking.
lock mutex
}
sendq 和 recvq 存储了当前 Channel 由于缓冲区空间不足而阻塞的 Goroutine 列表,这些等待队列使用双向链表 runtime.waitq 表示,链表中所有的元素都是 runtime.sudog 结构,runtime.sudog 表示一个在等待列表中的 Goroutine。
type waitq struct {
first *sudog
last *sudog
}
创建 channel
通道有两个方向,发送和接收。
一般而言,使用 make 创建一个能收能发的通道:
// 无缓冲通道
ch1 := make(chan int)
// 有缓冲通道
ch2 := make(chan int, 10)
创建 chan 的函数是 makechan:
func makechan(t *chantype, size int64) *hchan
创建的 chan 是一个指针,所以我们能在函数间直接传递 channel,而不用传递 channel 的指针。
const hchanSize = unsafe.Sizeof(hchan{}) + uintptr(-int(unsafe.Sizeof(hchan{}))&(maxAlign-1))
func makechan(t *chantype, size int64) *hchan {
elem := t.elem
// 省略了检查 channel size,align 的代码
// ……
var c *hchan
// 如果元素类型不含指针 或者 size 大小为 0(无缓冲类型)
// 只进行一次内存分配
if elem.kind&kindNoPointers != 0 || size == 0 {
// 如果 hchan 结构体中不含指针,GC 就不会扫描 chan 中的元素
// 只分配 "hchan 结构体大小 + 元素大小*个数" 的内存
c = (*hchan)(mallocgc(hchanSize+uintptr(size)*elem.size, nil, true))
// 如果是缓冲型 channel 且元素大小不等于 0(大小等于 0的元素类型:struct{})
if size > 0 && elem.size != 0 {
c.buf = add(unsafe.Pointer(c), hchanSize)
} else {
// race detector uses this location for synchronization
// Also prevents us from pointing beyond the allocation (see issue 9401).
// 1. 非缓冲型的,buf 没用,直接指向 chan 起始地址处
// 2. 缓冲型的,能进入到这里,说明元素无指针且元素类型为 struct{},也无影响
// 因为只会用到接收和发送游标,不会真正拷贝东西到 c.buf 处(这会覆盖 chan的内容)
c.buf = unsafe.Pointer(c)
}
} else {
// 进行两次内存分配操作
c = new(hchan)
c.buf = newarray(elem, int(size))
}
// 更新字段
c.elemsize = uint16(elem.size)
c.elemtype = elem
c.dataqsiz = uint(size)
return c
}





















 2807
2807

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








