
文章目录
由于近期需要提高网络训练的速度,所以去找了一条捷径,想走快点,就找到了Horovod框架,对TensorFlow搭建的网络训练提速特别有效,好吧,让我们一起开启愉快的Horovod之旅吧. Oh, no 是痛苦的Horovod之旅吧 !!!
一、Horovod简介
- Horovod名字的来源
Horovod,它的名字来自于俄国传统民间舞蹈,舞者手牵手围成一个圈跳舞,与分布式 TensorFlow 流程使用 Horovod 互相通信的场景很像。
- Horovod发展史
Horovod是Uber(优步)开源的又一个深度学习工,Horovod在2017年10月,Uber以Apache 2.0授权许可开源发布。Horovod是优步跨多台机器的分布式训练框架,现已加入开源计划LF Deep Learning Foundation。
Uber利用Horovod来支持自动驾驶汽车,欺诈检测和出行预测。该项目的贡献者包括亚马逊,IBM,英特尔和Nvidia。除了优步,阿里巴巴,亚马逊和Nvidia也在使用Horovod。Horovod项目可以与TensorFlow,Keras和PyTorch等流行框架一起使用。优步于上个月加入了Linux基金会,并加入了其他科技公司,如AT&T和诺基亚,他们出面支持LF Deep Learning Foundation开源项目。LF深度学习基金会成立于3月,旨在支持深度学习和机器学习的开源项目,并且是Linux基金会的一部分。在推出Acumos(用于训练和部署AI模型)和Acumos Marketplace(AI模型的开放式交易所)推出一个月后,Horovod正式推出。自该基金会启动以来,开展的其他项目包括机器学习平台Angel and Elastic Deep Learning,该项目旨在帮助云服务提供商利用TensorFlow等框架制作云集群服务。百度和腾讯分别于八月份加入这些项目,它们也是LF深度学习基金会的创始成员。
- Horovod优点
Horovod能让人工智能开发者轻松的使用TensorFlow、Keras和PyTorch机器学习框架,训练分布式深度学习模型。不少云计算服务都已经集成了Horovod,包括AWS深度学习服务AMI、Azure数据科学虚拟机、Databricks Runtime、GCP深度学习虚拟机、IBM FfDL、IBM Watson Studio和NVIDIA GPU Cloud等。
- 其他详细介绍:
- Horovod开源项目的github地址
去你的吧 大哥,前面是一个链接,你要点它呀,好吧,我错啦 !
二、Horovod框架的安装 Install
Horovod的安装分成两个步骤:
- 安装OpenMPI
- 安装horovod
1、安装OpenMPI
详细参考这里: ——>去你的吧
- OpenMPI 1.0.0版本下载
下载地址:点我,我带你走!
下载好的压缩包: 
- OpenMPI 安装步骤
1)解压并进行配置
tar -zxvf openmpi-1.8.4.tar.gz
cd openmpi-1.8.4
./configure --prefix="/usr/local/openmpi"
注意最后一行是将其安装到 /usr/local/openmpi目录下,可以指定为其他目录,如,用户目录下。
2)Build 并安装
make # 编译时间需要耐心等待一会,最好是在后面加上 -j8 参数吧,会快一些,具体是几核,根据自己的PC选择
sudo make install
可以在make后加参数-j8, 表示用8核编译
3)添加环境变量
在.bashrc文件中添加下列几行
export PATH="$PATH:/usr/local/openmpi/bin"
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/openmpi/lib/"
保存后,执行
sudo ldconfig
打开新的终端,使环境变量生效。
注意:
可能你去添加环境变量的时候,发现上面的LD_LIBRARY_PATH、PATH 变量中已经有值了,此时只要加个冒号,再添加即可,类似windows添加变量用分号隔开一个道理。eg: export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda-8.0/lib64:/usr/local/cuda/extras/CUPTI/lib64:/usr/local/openmpi/lib/"
4) 测试是否安装成功
mpirun 或 which mpirun
在测试样例中进行测试:
cd examples
make
mpirun -np 8 hello_c
结果如下

2、安装Horovod
这个安装比较简单,第二种是采用国内清华的镜像安装,速度那不是快一点,好吧,你开心就好!!!
pip install horovod
或
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple horovod
安装完毕,下面开始痛苦之旅吧
三、Horovod框架的使用
下面让我带你一起,来看看Horovod的用法吧
1、在项目中使用Horovod框架
Usage: github上给出这样使用
To use Horovod, make the following additions to your program:
- Run hvd.init().
- Pin a server GPU to be used by this process using config.gpu_options.visible_device_list. With the typical setup of one GPU per process, this can be set to local rank. In that case, the first process on the server will be allocated the first GPU, second process will be allocated the second GPU and so forth.
- Scale the learning rate by number of workers. Effective batch size in synchronous distributed training is scaled by the number of workers. An increase in learning rate compensates for the increased batch size.
- Wrap optimizer in hvd.DistributedOptimizer. The distributed optimizer delegates gradient computation to the original optimizer, averages gradients using allreduce or allgather, and then applies those averaged gradients.
- Add hvd.BroadcastGlobalVariablesHook(0) to broadcast initial variable states from rank 0 to all other processes. This is necessary to ensure consistent initialization of all workers when training is started with random weights or restored from a checkpoint. Alternatively, if you’re not using MonitoredTrainingSession, you can simply execute the hvd.broadcast_global_variables op after global variables have been initialized.
- Modify your code to save checkpoints only on worker 0 to prevent other workers from corrupting them. This can be accomplished by passing checkpoint_dir=None to tf.train.MonitoredTrainingSession if hvd.rank() != 0.
Do you understand ?
好吧,我就知道你看不懂,还是我来吧
2、Horovod使用样例
import tensorflow as tf
import horovod.tensorflow as hvd
# 1、初始化 Horovod
hvd.init()
# 2、使用GPU来处理本地队列(向每个TensorFlow进分配一个进程)
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.visible_device_list = str(hvd.local_rank())
# 3、建立模型
loss = ...
opt = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(0.01 * hvd.size())
# 4、添加Horovod分布式优化器
opt = hvd.DistributedOptimizer(opt)
# 5、Add hook to broadcast variables from rank 0 to all other processes during
# initialization.
hooks = [hvd.BroadcastGlobalVariablesHook(0)]
# Make training operation
train_op = opt.minimize(loss)
# Save checkpoints only on worker 0 to prevent other workers from corrupting them.
checkpoint_dir = '/tmp/train_logs' if hvd.rank() == 0 else None
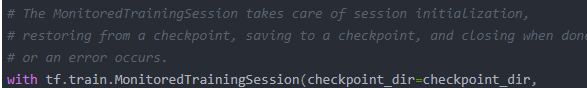
# The MonitoredTrainingSession takes care of session initialization,
# restoring from a checkpoint, saving to a checkpoint, and closing when done
# or an error occurs.
with tf.train.MonitoredTrainingSession(checkpoint_dir=checkpoint_dir,
config=config,
hooks=hooks) as mon_sess:
while not mon_sess.should_stop():
# Perform synchronous training.
mon_sess.run(train_op)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/43942234
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/40578792
https://docs.amazonaws.cn/dlami/latest/devguide/tutorial-horovod.html

sfasf



♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠
























 1040
1040

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








