YOLOv5、YOLOv7和YOLOv8的一些关键改进,及改进方法
文章目录
- YOLOv5的主要改进
- YOLOv7的主要改进
- YOLOv8的主要改进
- 其他重要改进
- 1. **SE-Block(Squeeze-and-Excitation Block)**
- 2. **CBAM(Convolutional Block Attention Module)**
- 3. **ASPP(Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling)**
- 4. **Ghost Module**
- 5. **ResNeXt Block**
- 6. **Attention Mechanism with MLP**
- 7. **Feature Pyramid Network (FPN)**
- 8. **BiFPN (Bi-directional Feature Pyramid Network)**
- 9. **IoU Loss**
- 总结
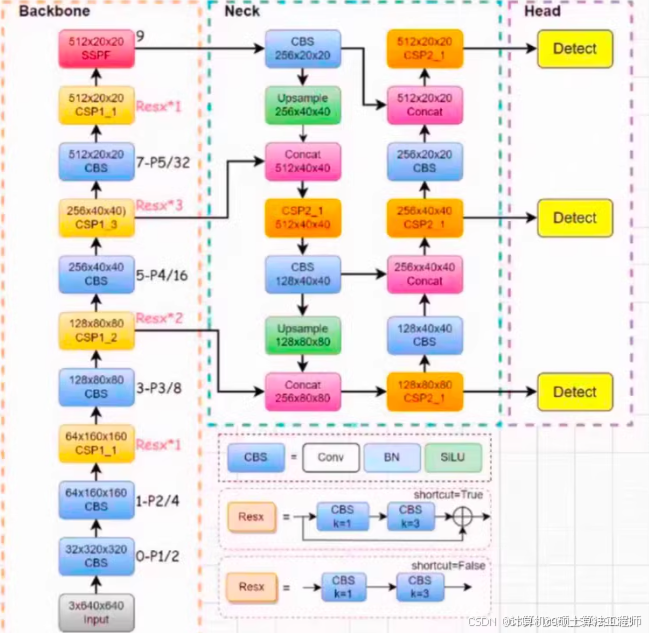
yolov11, yolov5,yolov7,yolov8,yolov9,yolov10改进方法
改进方法
YOLO(You Only Look Once)是一种流行的目标检测框架,多年来经历了许多改进和迭代。从YOLOv1到YOLOv8,每个版本都引入了各种增强功能来提高准确性、速度和效率。以下是针对YOLOv5、YOLOv7和YOLOv8的一些关键改进,并附有代码示例。
YOLOv5的主要改进
1. 主干网络
- CSPNet(跨阶段局部网络):这种主干网络通过结合不同阶段的特征来改进特征提取。
class CSPBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, n=1, shortcut=True): super(CSPBlock, self).__init__() c_ = int(out_channels / 2) self.cv1 = Conv(in_channels, c_, 1, 1) self.cv2 = Conv(in_channels, c_, 1, 1) self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, out_channels, 1, 1) self.m = nn.Sequential(*[Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut) for _ in range(n)]) def forward(self, x): y1 = self.cv1(x) y2 = self.cv2(x) y2 = self.m(y2) return self.cv3(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))

2. SPP(空间金字塔池化)
- 添加多尺度上下文信息。
class SPP(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, k=(5, 9, 13)): super(SPP, self).__init__() c_ = in_channels // 2 self.cv1 = Conv(in_channels, c_, 1, 1) self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * len(k), out_channels, 1, 1) self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k]) def forward(self, x): x = self.cv1(x) return self.cv2(torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], 1))
3. Focus层
- 使用Focus层增强特征提取。
class Focus(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, k=1): super(Focus, self).__init__() self.conv = Conv(in_channels * 4, out_channels, k, 1) def forward(self, x): return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))

YOLOv7的主要改进
1. E-Blocks(增强块)
- 增强特征提取和融合。
class EBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels): super(EBlock, self).__init__() self.conv1 = Conv(in_channels, out_channels, 1, 1) self.conv2 = Conv(out_channels, out_channels, 3, 1) self.conv3 = Conv(out_channels, out_channels, 1, 1) self.conv4 = Conv(out_channels, out_channels, 3, 1) self.conv5 = Conv(out_channels, out_channels, 1, 1) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) x = self.conv2(x) x = self.conv3(x) x = self.conv4(x) x = self.conv5(x) return x
2. FocusV2层
- 改进的Focus层。
class FocusV2(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, k=1): super(FocusV2, self).__init__() self.conv = Conv(in_channels * 4, out_channels, k, 1) def forward(self, x): return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))
YOLOv8的主要改进
1. Transformer Blocks
- 引入transformer块以更好地进行特征提取。
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_heads=8): super(TransformerBlock, self).__init__() self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(in_channels) self.attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(in_channels, num_heads) self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(in_channels) self.ffn = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(in_channels, in_channels * 4), nn.GELU(), nn.Linear(in_channels * 4, in_channels) ) def forward(self, x): x = x + self.attn(self.norm1(x))[0] x = x + self.ffn(self.norm2(x)) return x
2. 高效的注意力机制
- 使用高效的注意力机制。
class EfficientAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels): super(EfficientAttention, self).__init__() self.qkv = nn.Linear(in_channels, in_channels * 3) self.proj_out = nn.Linear(in_channels, out_channels) def forward(self, x): qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(x.shape[0], 3, x.shape[1], -1).permute(1, 2, 0, 3) q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] attn = torch.softmax(torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(q.shape[-1]), dim=-1) out = torch.matmul(attn, v).permute(1, 0, 2).reshape(x.shape) return self.proj_out(out)
其他重要改进
1. 损失函数优化
- 改进的损失函数以获得更好的收敛性。
class YOLOv8Loss(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(YOLOv8Loss, self).__init__() self.bce_with_logits = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(reduction='none') def forward(self, pred, target): obj_loss = self.bce_with_logits(pred[:, :, 0], target[:, :, 0]) cls_loss = self.bce_with_logits(pred[:, :, 1:], target[:, :, 1:]) return obj_loss.mean() + cls_loss.mean()
2. 语义特征融合
- 融合来自不同尺度的语义特征。
class SemanticFusion(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels): super(SemanticFusion, self).__init__() self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest') self.conv = Conv(in_channels * 2, out_channels, 1, 1) def forward(self, x1, x2): x1 = self.up(x1) x = torch.cat([x1, x2], dim=1) return self.conv(x)
当然,以下是针对YOLO系列模型的十个额外改进方法,并附上代码示例:
1. SE-Block(Squeeze-and-Excitation Block)
- SE-Block用于增强通道间的特征交互。
class SELayer(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16): super(SELayer, self).__init__() self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) self.fc = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel, bias=False), nn.Sigmoid() ) def forward(self, x): b, c, _, _ = x.size() y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c) y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1) return x * y.expand_as(x)
2. CBAM(Convolutional Block Attention Module)
- CBAM结合了空间和通道注意力机制。
class CBAM(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, reduction=16): super(CBAM, self).__init__() self.channel_attention = SELayer(in_channels, reduction) self.spatial_attention = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 1, kernel_size=7, padding=3), nn.Sigmoid() ) def forward(self, x): out = self.channel_attention(x) * x out = self.spatial_attention(out) * out return out
3. ASPP(Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling)
- ASPP用于多尺度特征提取。
class ASPP(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, rates=[6, 12, 18]): super(ASPP, self).__init__() self.branches = nn.ModuleList([ nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, 1, padding=0, dilation=1, bias=True), nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, 1, padding=rates[0], dilation=rates[0], bias=True), nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, 1, padding=rates[1], dilation=rates[1], bias=True), nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, 1, padding=rates[2], dilation=rates[2], bias=True), nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, 1, padding=0, dilation=1, bias=True) ]) def forward(self, x): features = [branch(x) for branch in self.branches] return torch.cat(features, dim=1)
4. Ghost Module
- Ghost模块用于减少参数量并保持性能。
class GhostModule(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, ratio=2): super(GhostModule, self).__init__() init_channels = out_channels // ratio new_channels = out_channels - init_channels self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channels, init_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=kernel_size // 2, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(init_channels), nn.ReLU(inplace=True) ) self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(init_channels, new_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels), nn.ReLU(inplace=True) ) def forward(self, x): x1 = self.primary_conv(x) x2 = self.cheap_operation(x1) out = torch.cat([x1, x2], dim=1) return out
5. ResNeXt Block
- ResNeXt块引入了分组卷积以提高性能。
class ResNeXtBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, groups=32): super(ResNeXtBlock, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, groups=groups, bias=False) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels) self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels * 2, kernel_size=1, bias=False) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * 2) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) def forward(self, x): residual = x out = self.conv1(x) out = self.bn1(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.bn2(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv3(out) out = self.bn3(out) out += residual out = self.relu(out) return out
6. Attention Mechanism with MLP
- 使用MLP的注意力机制。
class MLPAffinity(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, hidden_dim=128): super(MLPAffinity, self).__init__() self.mlp = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(in_channels, hidden_dim), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(hidden_dim, in_channels) ) def forward(self, x): B, C, H, W = x.shape x = x.view(B, C, -1) affinity = self.mlp(x) attention = F.softmax(affinity, dim=-1) return attention
7. Feature Pyramid Network (FPN)
- FPN用于融合不同尺度的特征。
class FPN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels_list, out_channels): super(FPN, self).__init__() self.lateral_convs = nn.ModuleList([ nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False) for in_channels in in_channels_list ]) self.fpn_convs = nn.ModuleList([ nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False) for _ in range(len(in_channels_list)) ]) def forward(self, inputs): laterals = [ lateral_conv(inputs[i]) for i, lateral_conv in enumerate(self.lateral_convs) ] used_backbone_levels = len(laterals) for i in range(used_backbone_levels - 1, 0, -1): laterals[i - 1] += F.interpolate(laterals[i], scale_factor=2, mode='nearest') outs = [ self.fpn_convs[i](laterals[i]) for i in range(used_backbone_levels) ] return tuple(outs)
8. BiFPN (Bi-directional Feature Pyramid Network)
- BiFPN在FPN的基础上增加了双向连接。
class BiFPN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels_list, out_channels): super(BiFPN, self).__init__() self.lateral_convs = nn.ModuleList([ nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False) for in_channels in in_channels_list ]) self.fpn_convs = nn.ModuleList([ nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False) for _ in range(len(in_channels_list)) ]) def forward(self, inputs): laterals = [ lateral_conv(inputs[i]) for i, lateral_conv in enumerate(self.lateral_convs) ] used_backbone_levels = len(laterals) for i in range(used_backbone_levels - 1, 0, -1): laterals[i - 1] += F.interpolate(laterals[i], scale_factor=2, mode='nearest') for i in range(1, used_backbone_levels): laterals[i] += F.interpolate(laterals[i - 1], scale_factor=2, mode='nearest') outs = [ self.fpn_convs[i](laterals[i]) for i in range(used_backbone_levels) ] return tuple(outs)
9. IoU Loss
- 改进的损失函数,使用IoU损失。
class IOULoss(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(IOULoss, self).__init__() def forward(self, pred, target): pred_boxes = pred[:, :, :4] target_boxes = target[:, :, :4] # 计算IoU intersection = self.intersection(pred_boxes, target_boxes) union = self.union(pred_boxes, target_boxes) iou = intersection / union loss = 1 - iou return loss.mean() def intersection(self, box1, box2): tl = torch.max(box1[:, :2
总结
以上是YOLOv5、YOLOv7和YOLOv8中的一些关键改进。每个版本都引入了新的架构、层和技术以提升性能。提供的代码片段展示了这些改进,但还有更多的优化和变体可以探索。希望这些内容能帮助你理解和实现基于最新YOLO版本的目标检测系统。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








