莫里斯遍历和为SortedMap的
介绍一种时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度为O(1)的二叉树的遍历方式,N为二叉树的节点个数
当前节点小人,小人初始时来到头:
- 如果CUR没有左子树,CUR向右移动,CUR = cur.right
- 如果CUR有左子树,找到左子树最右节点,记为mostright
- 如果mostright的右指针指向空,让它指向CUR,然后CUR向左移动,CUR = cur.left
- 如果mostright的右指针指向CUR,让它指回零,然后CUR向右移动,CUR = cur.right
莫里斯遍历过程中,有左子树的节点能够被遍历两次,没有左子树的节点被遍历一次
递归函数实现先序,中序,后续遍历的本质是系统栈三次达到每个节点的状态实现的
莫里斯遍历:利用莫里斯遍历实现二叉树的先序,中序,后续遍历,时间复杂度为O(N),额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
思考:莫里斯遍历的是指就是避免用栈结构,而是让下层到上层有指针,具体是通过让底层节点指向空的空闲指针指回上层的某个节点,从而完成下层到上层的移动。
以莫里斯中序遍历的过程为例;
- 假设当前子树的头节点为小时,让ħ的左子树中最右节点的右指针指向小时,然后ħ的左子树继续步骤1的处理过程,直到遇到某一个节点没有左子树时记为节点,进入步骤2。
- 从节点开始通过每个节点的右指针进行移动,并依次打印,假设移动到的节点为小人。对每一个小人节点都判断CUR节点的左子树中最右节点是否指向CUR。
- 如果是,让CUR节点的左子树中最右节点的右指针指向空,也就是把步骤1的调整后再逐渐调整回来,然后打印CUR,继续通过CUR的右指针移动到下一个节点,重复步骤2。
- 如果不是,以CUR为头的子树重回步骤1执行。
- 步骤2最终移动到空,整个过程结束。
莫里斯先序遍历的实现就是莫里斯中序遍历实现的简单改写。先序遍历的打印时机放在了步骤2所描述的移动过程中,而先序遍历只要把打印时机放在步骤1发生的时候即可。步骤1发生的时候,正在处理以ħ为头的子树,并且是以ħ为头的子树首次进入调整过程,此时直接打印小时,就可以做到先根打印。
莫里斯后序遍历的实现也是莫里斯中序遍历实现的改写,但包含更复杂的调整过程。总的来说,逻辑很简单,就是依次逆序打印所有节点的左子树的右边界,打印的时机放在步骤2的条件1被触发的时候,也就是调回去的过程发生的时候。
代码:
public class MorrisTraversal {
/**
* 使用递归的方式实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历
* 将打印置于不同位置可以实现不同的遍历效果
*
* @param head
*/
public static void process(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
// 1
//System.out.println(head.value);
process(head.left);
// 2
//System.out.println(head.value);
process(head.right);
// 3
//System.out.println(head.value);
}
public static class Node {
public int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
/**
* Morris遍历实现二叉树的先序遍历
*
* @param head
*/
public static void morrisIn(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur1 = head;
Node cur2 = null;
while (cur1 != null) {
cur2 = cur1.left;
if (cur2 != null) {
while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {
cur2 = cur2.right;
}
if (cur2.right == null) {//第一次到达有左子树的节点
cur2.right = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.left;
continue;
} else {
cur2.right = null;
}
}
System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");//将打印语句放在第二次达到有左子树的节点
cur1 = cur1.right;
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* Morris遍历的先序遍历
*
* @param head
*/
public static void morrisPre(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur1 = head;
Node cur2 = null;
while (cur1 != null) {
cur2 = cur1.left;
if (cur2 != null) {
while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {
cur2 = cur2.right;
}
if (cur2.right == null) {
cur2.right = cur1;
System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");
cur1 = cur1.left;
continue;
} else {
cur2.right = null;
}
} else {
System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");
}
cur1 = cur1.right;
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* Morris遍历的后序遍历
*
* @param head
*/
public static void morrisPos(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur1 = head;
Node cur2 = null;
while (cur1 != null) {
cur2 = cur1.left;
if (cur2 != null) {
while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {
cur2 = cur2.right;
}
if (cur2.right == null) {
cur2.right = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.left;
continue;
} else {
cur2.right = null;
printEdge(cur1.left);
}
}
cur1 = cur1.right;
}
printEdge(head);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printEdge(Node head) {
Node tail = reverseEdge(head);
Node cur = tail;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
reverseEdge(tail);
}
public static Node reverseEdge(Node from) {
Node pre = null;
Node next = null;
while (from != null) {
next = from.right;
from.right = pre;
pre = from;
from = next;
}
return pre;
}
// for test -- print tree
public static void printTree(Node head) {
System.out.println("Binary Tree:");
printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "v", len);
String val = to + head.value + to;
int lenM = val.length();
int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2;
int lenR = len - lenM - lenL;
val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR);
System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val);
printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "^", len);
}
public static String getSpace(int num) {
String space = " ";
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer("");
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
buf.append(space);
}
return buf.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(4);
head.left = new Node(2);
head.right = new Node(6);
head.left.left = new Node(1);
head.left.right = new Node(3);
head.right.left = new Node(5);
head.right.right = new Node(7);
printTree(head);
morrisIn(head);
morrisPre(head);
morrisPos(head);
printTree(head);
}
}
在二叉树上,何为一个节点的后继节点?何为搜索二叉树?
题目描述:现在有一种新的二叉树节点类型如下:
public class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}该结构比普通二叉树节点结构多了一个指向父结点的父指针。假设有一棵节点类型的节点组成的二叉树,树中每个节点的父指针都正确地指向自己的父结点,头节点的父指向空。只给一个在二叉树中的某个节点的节点,请实现返回节点的后继节点的函数。在二叉树的中序遍历的序列中,节点的下一个节点叫作节点的后继节点。
思考:简答的解法:既然新类型的二叉树节点有指向父节点的指针,那么一直往上移动,自然可以找到头节点找到头节点之后,再进行二叉树的中序遍历,生成中序遍历序列, 。然后在这个序列中找到节点节点的下一个节点返回即可如果二叉树的节点数为N,这种方法要把二叉树的所有节点至少遍历一遍,生成中序遍历的序列还需要大小为ñ的空间,所以该方法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度都为O(N)。
最优的解法不必遍历所有的节点,如果节点节点和节点后继节点之间的实际距离为L,最优解法只用走过大号个节点,时间复杂度为O(L),空间复杂度为ö(1)。接下来详细说明最优解法是如何找到节点的后继节点的。
- 情况1:如果节点有右子树,那么后继节点就是右子树最左边的节点。
- 情况2:如果节点没有右子树,那么先看节点是不是节点父结点的左孩子,如果是,那么此时节点的父节点就是节点的后继节点;如果是右孩子,就向上寻找节点的后继节点,假设向上移动到的节点记为S,S的父节点记为p,如果发现小号是p的左孩子,那么节点p就是节点节点的后继节点,否则就一直向上移动。
- 情况3:如果在情况2中一直向上寻找,都移动到空节点时还是没有发现节点的后继节点,说明节点根本不存在后继节点。
代码如下:
public Node getNextNode(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
if (node.right != null) { //情况1
return getLeftMost(node.right);
} else { //情况2
Node parent = node.parent;
while (parent != null && parent.left != node) {
node = parent;
parent = node.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
private Node getLeftMost(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}根据后序数组重建搜索二叉树
题目:给定一个整型数组改编,已知其中没有重复值,判断ARR是否可能是节点值类型为整型的搜索二叉树后序遍历的结果。
进阶:如果整型数组编曲中没有重复值,且已知是一棵搜索二叉树的后序遍历结果,通过数组ARR重构二叉树。
解法:原问题的解法:二叉树的后序遍历为先左,再右,最后根的顺序,所以,如果一个数组是二叉树后序遍历结果,那么头节点的值一定会是数组的最后一个元素。搜索二叉树的性质,所有比后序数组最后一个元素值小的数组会在数组的左边,比数组最后一个元素值大的数组会在数组的右边。如果不满足这种情况,说明这个数组一定不可能是搜索二叉树后续遍历的结果,接下来数组划分成左边数组和右边数组,相当于二叉树分出了左子树和右子树,只要递归地进行如上判断即可。
代码:
/**
* 根据后序数组重建搜索二叉树
*/
public class IsPostArray {
public boolean isPostArray(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return false;
}
return isPost(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
public boolean isPost(int[] arr, int start, int end) {
if (start == end) {
return true;
}
int less = -1;
int more = end;
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (arr[end] > arr[i]) {
less = i;
} else {
more = more == end ? i : more;
}
}
if (less == -1 || more == end) {
return isPost(arr, start, end - 1);
}
if (less != more - 1) {
return false;
}
return isPost(arr, start, less) && isPost(arr, more, end - 1);
}
}
进阶问题的分析与原问题同理,一棵树的后序数组中最后一个值为二叉树头节点的数组左部分都比头节点的值小,用来生成头节点的左子树,剩下的部分用来生成右子树。
/**
* 已知一棵搜索二叉树的后序遍历结果,通过数组arr重构二叉树
*/
public class PosArrayToBST {
public class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public Node posArrayToBST(int[] posArr) {
if (posArr == null) {
return null;
}
return posToBST(posArr, 0, posArr.length - 1);
}
private Node posToBST(int[] posArr, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return null;
}
Node head = new Node(posArr[end]);
int less = -1;
int more = end;
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (posArr[end] > posArr[i]) {
less = i;
} else {
more = more == end ? i : more;
}
}
head.left = posToBST(posArr, start, less);
head.right = posToBST(posArr, more, end - 1);
return head;
}
}
如何实现搜索二叉树的查找?插入?删除?
定义:二叉搜索树是这样的一种二叉树:
(1)每个元素都有一个关键值,并且没有任意两个元素有相同的关键值
(2)根节点的左子树中任意元素的关键值小于根节点的关键值。
(3)根节点的右子树中任意元素的关键值大于根节点的关键值。
(4)根节点的左右子树也是二叉搜索树。
从定义看出,二叉搜索树是一种特殊的二叉树,它给每个元素加上了序的概念,但又不同于最大最小堆,它总是左<根<右的。
查找:
从根元素开始遍历,如果找到匹配的,则直接将其对应元素的值返回。
如果关键值比当前查找元素的关键值小,那么关键值一定在左子树中,所以递归的在左子树中查找。
如果关键值比当前查找元素的关键值大,那么关键值一定在右子树中,所以递归的在右子树中查找。
上述递归跳出的条件就是当前查找元素为空,一旦为空都找不到匹配,则说明该二叉搜索树中没有匹配值。
插入:
插入之前必须保证二叉搜索树的第一条定义,所以先找下是否有匹配元素,如果有,则不执行插入动作。
然后从根开始折半找,根据子元素的值来确定这个值插入左边还是右边,直到选择到一个精确的位置,使得待插元素的关键值刚好落在当前元素和其某个子元素之间(或者没有子元素)
删除:
删除复杂多了,先遍历找到要删除的元素,
分为3种情况:
- 如果该元素左,右子树都不为空,则把该元素替换为其左子树中的最大元素或者右子树的最小元素(因为这2个元素刚好是与当前元素最近的2个元素)
- 如果该元素左,右子树都为空(也就是叶节点),那么直接丢弃,当然也要考虑根节点的情况。
- 如果该元素左或者右子树不为空,那么需要找到该元素的父亲元素,然后把其不为空的这个分支的根元素设为父亲元素的直接子元素,当然也要考虑根节点的情况。
public class AbstractBinarySearchTree {
public static class Node {
public Integer value;
public Node parent;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(Integer value, Node parent, Node left, Node right) {
super();
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return left == null && right == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((value == null) ? 0 : value.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Node other = (Node) obj;
if (value == null) {
if (other.value != null)
return false;
} else if (!value.equals(other.value))
return false;
return true;
}
}
/**
* 整个树开始的根节点.
*/
public Node root;
/**
* 树的大小.
*/
protected int size;
/**
* 因为这是抽象类,并且各种树在不同节点上具有不同的附加信息,
* 所以子类使用该抽象方法来创建节点。
* (maybe of class {@link Node} or maybe some
* different node sub class).
*
* @param value Value that node will have.
* @param parent Node's parent.
* @param left Node's left child.
* @param right Node's right child.
* @return Created node instance.
*/
protected Node createNode(int value, Node parent, Node left, Node right) {
return new Node(value, parent, left, right);
}
/**
* 查找具有特定值的节点。 如果未找到,则返回null。
*
* @param element Element value.
* @return Node with value provided, or null if not found.
*/
public Node search(int element) {
Node node = root;
while (node != null && node.value != null && node.value != element) {
if (element < node.value) {
node = node.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
return node;
}
/**
* 插入新元素.
*
* @param element Element to insert.
*/
public Node insert(int element) {
if (root == null) {
root = createNode(element, null, null, null);
size++;
return root;
}
Node insertParentNode = null;
Node searchTempNode = root;
while (searchTempNode != null && searchTempNode.value != null) {
insertParentNode = searchTempNode;
if (element < searchTempNode.value) {
searchTempNode = searchTempNode.left;
} else {
searchTempNode = searchTempNode.right;
}
}
Node newNode = createNode(element, insertParentNode, null, null);
if (insertParentNode.value > newNode.value) {
insertParentNode.left = newNode;
} else {
insertParentNode.right = newNode;
}
size++;
return newNode;
}
/**
* 如果存在具有此值的节点,则删除元素.
*
* @param element Element value to remove.
* @return New node that is in place of deleted node. Or null if element for
* delete was not found.
*/
public Node delete(int element) {
Node deleteNode = search(element);
if (deleteNode != null) {
return delete(deleteNode);
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 找到节点时删除逻辑.
*
* @param deleteNode Node that needs to be deleted.
* @return 用于替换已删除节点的新节点。 如果未找到要删除的元素,则返回null。
*/
protected Node delete(Node deleteNode) {
if (deleteNode != null) {
Node nodeToReturn = null;
if (deleteNode != null) {
if (deleteNode.left == null) {
nodeToReturn = transplant(deleteNode, deleteNode.right);
} else if (deleteNode.right == null) {
nodeToReturn = transplant(deleteNode, deleteNode.left);
} else {
Node successorNode = getMinimum(deleteNode.right);
if (successorNode.parent != deleteNode) {
transplant(successorNode, successorNode.right);
successorNode.right = deleteNode.right;
successorNode.right.parent = successorNode;
}
transplant(deleteNode, successorNode);
successorNode.left = deleteNode.left;
successorNode.left.parent = successorNode;
nodeToReturn = successorNode;
}
size--;
}
return nodeToReturn;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 将一个节点从树(newNode)放到另一个节点(nodeToReplace).
*
* @param nodeToReplace Node which is replaced by newNode and removed from tree.
* @param newNode New node.
* @return New replaced node.
*/
private Node transplant(Node nodeToReplace, Node newNode) {
if (nodeToReplace.parent == null) {
this.root = newNode;
} else if (nodeToReplace == nodeToReplace.parent.left) {
nodeToReplace.parent.left = newNode;
} else {
nodeToReplace.parent.right = newNode;
}
if (newNode != null) {
newNode.parent = nodeToReplace.parent;
}
return newNode;
}
/**
* @param element
* @return true if tree contains element.
*/
public boolean contains(int element) {
return search(element) != null;
}
/**
* @return Minimum element in tree.
*/
public int getMinimum() {
return getMinimum(root).value;
}
/**
* @return Maximum element in tree.
*/
public int getMaximum() {
return getMaximum(root).value;
}
/**
* Get next element element who is bigger than provided element.
*
* @param element Element for whom descendand element is searched
* @return Successor value.
*/
// TODO Predecessor
public int getSuccessor(int element) {
return getSuccessor(search(element)).value;
}
/**
* @return Number of elements in the tree.
*/
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
/**
* Tree traversal with printing element values. In order method.
*/
public void printTreeInOrder() {
printTreeInOrder(root);
}
/**
* Tree traversal with printing element values. Pre order method.
*/
public void printTreePreOrder() {
printTreePreOrder(root);
}
/**
* Tree traversal with printing element values. Post order method.
*/
public void printTreePostOrder() {
printTreePostOrder(root);
}
/*-------------------PRIVATE HELPER METHODS-------------------*/
private void printTreeInOrder(Node entry) {
if (entry != null) {
printTreeInOrder(entry.left);
if (entry.value != null) {
System.out.println(entry.value);
}
printTreeInOrder(entry.right);
}
}
private void printTreePreOrder(Node entry) {
if (entry != null) {
if (entry.value != null) {
System.out.println(entry.value);
}
printTreeInOrder(entry.left);
printTreeInOrder(entry.right);
}
}
private void printTreePostOrder(Node entry) {
if (entry != null) {
printTreeInOrder(entry.left);
printTreeInOrder(entry.right);
if (entry.value != null) {
System.out.println(entry.value);
}
}
}
protected Node getMinimum(Node node) {
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
protected Node getMaximum(Node node) {
while (node.right != null) {
node = node.right;
}
return node;
}
protected Node getSuccessor(Node node) {
// 如果有右子树,则后继是该子树的最左边节点
if (node.right != null) {
return getMinimum(node.right);
} else { // 否则它是最低的祖先,其左孩子也是节点的祖先
Node currentNode = node;
Node parentNode = node.parent;
while (parentNode != null && currentNode == parentNode.right) {
// 直到我们发现父节点currentNode不在右子树中。
currentNode = parentNode;
parentNode = parentNode.parent;
}
return parentNode;
}
}
// -------------------------------- TREE PRINTING
// ------------------------------------
public void printTree() {
printSubtree(root);
}
public void printSubtree(Node node) {
if (node.right != null) {
printTree(node.right, true, "");
}
printNodeValue(node);
if (node.left != null) {
printTree(node.left, false, "");
}
}
private void printNodeValue(Node node) {
if (node.value == null) {
System.out.print("<null>");
} else {
System.out.print(node.value.toString());
}
System.out.println();
}
private void printTree(Node node, boolean isRight, String indent) {
if (node.right != null) {
printTree(node.right, true, indent + (isRight ? " " : " | "));
}
System.out.print(indent);
if (isRight) {
System.out.print(" /");
} else {
System.out.print(" \\");
}
System.out.print("----- ");
printNodeValue(node);
if (node.left != null) {
printTree(node.left, false, indent + (isRight ? " | " : " "));
}
}
}
扩展:
- 如何实现在搜索二叉树上查找与给定值的目标最近的值
- 如何实现在搜索二叉树上查找<=给定值的目标最近的值
- 如何实现在搜索二叉树上查找> =给定值的目标最近的值
思考:
问题1:使用递归查找,如果当前节点值小于目标值,则结果只可能是当前节点值或者右子树中的值;如果当前节点值大于目标值,则结果只可能是当前节点值或者左子树中的值。
代码:
/**
* 二叉搜索树最接近值查找
*/
public class ClosestValue {
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
private int value;
public int closestValue(TreeNode root, double target) {
if (root.val == target)
return root.val;
if (root.val < target) {
if (root.right == null)
return root.val;
int right = closestValue(root.right, target);
if (Math.abs(root.val - target) <= Math.abs(right - target))
return root.val;
return right;
} else {
if (root.left == null)
return root.val;
int left = closestValue(root.left, target);
if (Math.abs(root.val - target) <= Math.abs(left - target))
return root.val;
return left;
}
}
}
问题2:同理,如果在二叉搜索树中查找小于等于目标的最大值,则
- 如果当前节点值等于目标值,则返回该节点的值
- 如果当前节点值小于目标值,则结果只可能是当前节点值或者其存在于其左子树中
- 如果当前节点值大于目标值,则结果只可能存在与其左子树中
代码:
/**
* 在二叉搜索树中找最大的小于某个key值的节点
* 迭代实现
*
* @param root
* @param key
* @return
*/
public TreeNode FindCeiling3(TreeNode root, int key) {
TreeNode ceiling = null;
TreeNode current = root;
while (current != null) {
if (current.val >= key) {
current = current.left;
} else {
ceiling = current;
current = current.right;
}
}
return ceiling;
}问题3:如果在二叉搜索树中查找大于等于目标的最小值,则
- 如果当前节点值等于目标值,则返回该节点的值
- 如果当前节点值小于目标值,则结果只可能存在于其右子树中
- 如果当前节点值大于目标值,则结果只可能是当前节点值或者其左子树中的值。
代码:
/**
* 在二叉搜索树中找最小的大于某个key值的节点
* 迭代实现
*
* @param root
* @param key
* @return
*/
public TreeNode FindCeiling1(TreeNode root, int key) {
TreeNode ceiling = null;
TreeNode current = root;
while (current != null) {
if (current.val <= key) {
current = current.right;
} else {
ceiling = current;
current = current.left;
}
}
return ceiling;
}
/**
* 递归实现
*
* @param root
* @param key
* @return
*/
public TreeNode FindCeiling2(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
if (root.val <= key) {
return FindCeiling2(root.right, key);
} else {
TreeNode ceiling = FindCeiling2(root.left, key);
return ceiling != null ? ceiling : root;
}
}判断一棵二叉树是否为平衡二叉树
题目:平衡二叉树的性质为:要么是一棵空树,要么任何一个节点的左右子树高度差的绝对值不超过1给定一棵二叉树的头节点的头,判断这棵二叉树是否为平衡二叉树。
要求:如果二叉树的节点数为N,要求时间复杂度为O(N)。
解法:解法的整体过程为二叉树的后序遍历,对任何一个节点的节点来说,先遍历节点的左子树,遍历过程中收集两个信息,节点的左子树是否为平衡二叉树,节点的左子树最深到哪一层记为LH。如果发现节点的左子树不是平衡二叉树,无序进行任何后续过程,此时返回什么已不重要,因为已经发现整棵树不是平衡二叉树,退出遍历过程;如果节点的左子树是平衡二叉树,再遍历节点的右子树,遍历过程中再收集两个信息,节点的右子树是否为平衡二叉树,节点的右子树最深到哪一层记为的的rH如果发现节点的右子树不是平衡二叉树,无须进行任何后续过程,返回什么也不重要,因为已经发现整棵树不是平衡二叉树,退出遍历过程;如果节点的右子树也是平衡二叉树,就看LH和的的rH差的绝对值是否大于1,如果大于1,说明已经发现整棵树不是平衡二叉树,果不大于1,则返回LH和的的rH较大的一个。
代码:
public class IsBalance {
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
public boolean isBalance(TreeNode head) {
boolean[] res = new boolean[1];
res[0] = true;
getHeight(head, 1, res);
return res[0];
}
/**
* 一旦发现不符合平衡二叉树的性质,递归过程会迅速推出
* 整个后序遍历的过程中,每个节点最多遍历一次,如果中途发现不满足平衡二叉树的性质,整个过程会迅速退出,没遍历的节点也不用遍历了,
* 所以时间复杂度为O(N)
*
* @param head
* @param level
* @param res 长度为1,功能相当于一个全局的Boolean变量
* @return
*/
private int getHeight(TreeNode head, int level, boolean[] res) {
if (head == null) {
return level;
}
int lH = getHeight(head.left, level + 1, res);
if (!res[0]) {
return level;
}
int rH = getHeight(head.right, level + 1, res);
if (!res[0]) {
return level;
}
if (Math.abs(lH - rH) > 1) {
res[0] = false;
}
return Math.max(lH, rH);
}
}
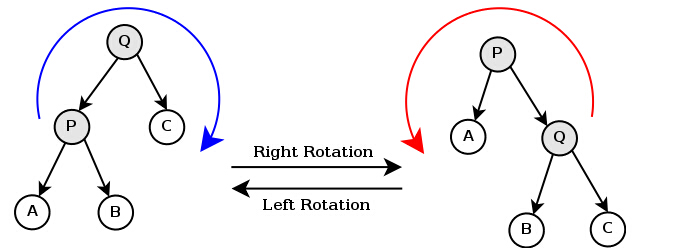
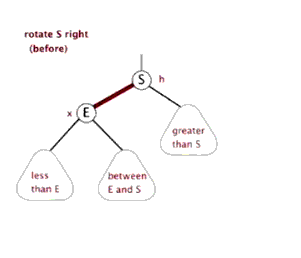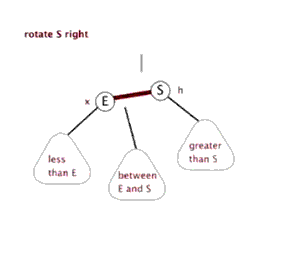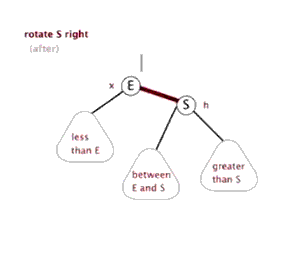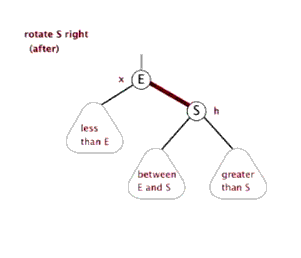
树的左旋与右旋
- 介绍调整树的左旋操作
- 介绍调整树的右旋操作
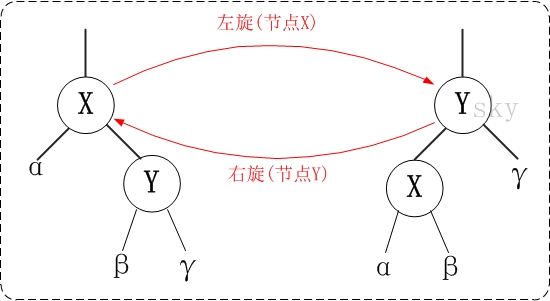
思考:如下图所示的操作中,对节点Q的操作为右旋,对节点P的操作为左旋,二者互为逆操作简单地讲:
- 右旋:自己变为左孩子的右孩子
- 左旋:自己变为右孩子的左孩子
代码:
public class BinTree {
/**
* 定义二叉树节点
*/
private class Node {
int val;
Node lchild;
Node rchild;
Node parent;
Node(int data) {
this.val = data;
}
}
public Node root;//根节点
public void rightRotate(Node node) {
Node p = node.lchild;
Node b = p.rchild;
Node fa = node.parent;
b.parent = node;
node.lchild = b;
node.parent = p;
p.rchild = node;
if (root == node) {
root = p;
} else {
p.parent = fa;
if (fa.lchild == node)
fa.lchild = p;
else
fa.rchild = p;
}
}
public void leftRoate(Node node) {
Node q = node.rchild;
Node b = q.lchild;
Node fa = node.parent;
b.parent = node;
node.rchild = b;
node.parent = q;
q.lchild = node;
if (node == root) {
root = node;
} else {
q.parent = fa;
if (fa.lchild == node)
fa.lchild = q;
else
fa.rchild = q;
}
}
}
#include
class BinTree{
private:
typedef struct node{
int data;
node*lchild,*rchild,*parent;
}*tree;
tree root;
public:
void right_rotate(node *p);
void left_rotate(node *p);
};
void BinTree::right_rotate(node *q){
node* p=q->lchild;
node* b=p->rchild;
node* fa=q->parent;
b->parent=q;
q->lchild=b;
q->parent=p;
p->rchild=q;
if(q==root)
root=p;//此时p->parent==q 但没关系,已经标记了根为p
else{
p->parent=fa;
if(fa->lchild==q) fa->lchild=p;
else fa->rchild=p;
}
}
void BinTree::left_rotate(node *p){
tree q=p->rchild;
tree b=q->lchild;
node* fa=p->parent;
b->parent=p;
p->rchild=b;
p->parent=q;
q->lchild=p;
if(p==root)
root=q;//此时q->parent==p 但没关系,已经标记了根为q
else{
q->parent=fa;
if(fa->lchild==p) fa->lchild=q;
else fa->rchild=q;
}
}
/**
* Abstract class for self balancing binary search trees. Contains some methods
* that is used for self balancing trees.
*
* @author Ignas Lelys
* @created Jul 24, 2011
*/
public abstract class AbstractSelfBalancingBinarySearchTree extends AbstractBinarySearchTree {
/**
* Rotate to the left.
* 左旋
*
* @param node Node on which to rotate.
* @return Node that is in place of provided node after rotation.
*/
protected Node rotateLeft(Node node) {
Node temp = node.right;
temp.parent = node.parent;
node.right = temp.left;
if (node.right != null) {
node.right.parent = node;
}
temp.left = node;
node.parent = temp;
// temp took over node's place so now its parent should point to temp
if (temp.parent != null) {
if (node == temp.parent.left) {
temp.parent.left = temp;
} else {
temp.parent.right = temp;
}
} else {
root = temp;
}
return temp;
}
/**
* Rotate to the right.
* 右旋
*
* @param node Node on which to rotate.
* @return Node that is in place of provided node after rotation.
*/
protected Node rotateRight(Node node) {
Node temp = node.left;
temp.parent = node.parent;
node.left = temp.right;
if (node.left != null) {
node.left.parent = node;
}
temp.right = node;
node.parent = temp;
// temp took over node's place so now its parent should point to temp
if (temp.parent != null) {
if (node == temp.parent.left) {
temp.parent.left = temp;
} else {
temp.parent.right = temp;
}
} else {
root = temp;
}
return temp;
}
}
介绍AVL树
- 当插入或删除一个节点时,可能会让整棵AVL不平衡。此时,只需要把最小不平衡子树调整即可恢复整体的平衡性。
- 介绍树的LL,RR,LR,RL调整
- 介绍插入节点时的调整细节
- 介绍删除节点时的调整细节
AVL树是带有平衡条件的二叉查找树。这个平衡条件必须容易保持,而且它保证树的深度必须是O(log N)。一颗AVL树是其每个节点的左子树和右子树的高度最多差1的二叉查找树(空树的高度定义为-1)。对AVL树进行插入操作可能会使其失去平衡的条件,但这可以通过对树进行简单的修正来保持其平衡的属性,这种操作称之为旋转。
一颗平衡二叉树,如果有n个结点,其高度可保持O(log2 ^ n),平均搜索长度也可以保持在O(log2 ^ n)
平衡化旋转
AVL树相较于普通的二叉搜索树,最主要的就是做了平衡化处理,使得二叉树变的平衡,高度降低。
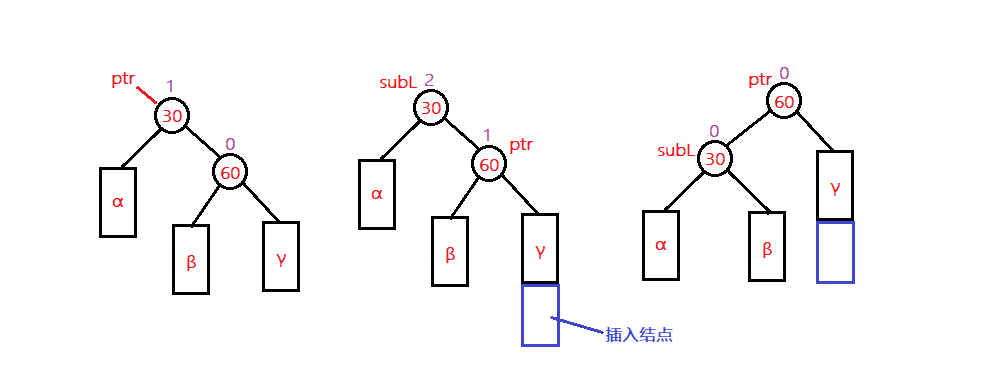
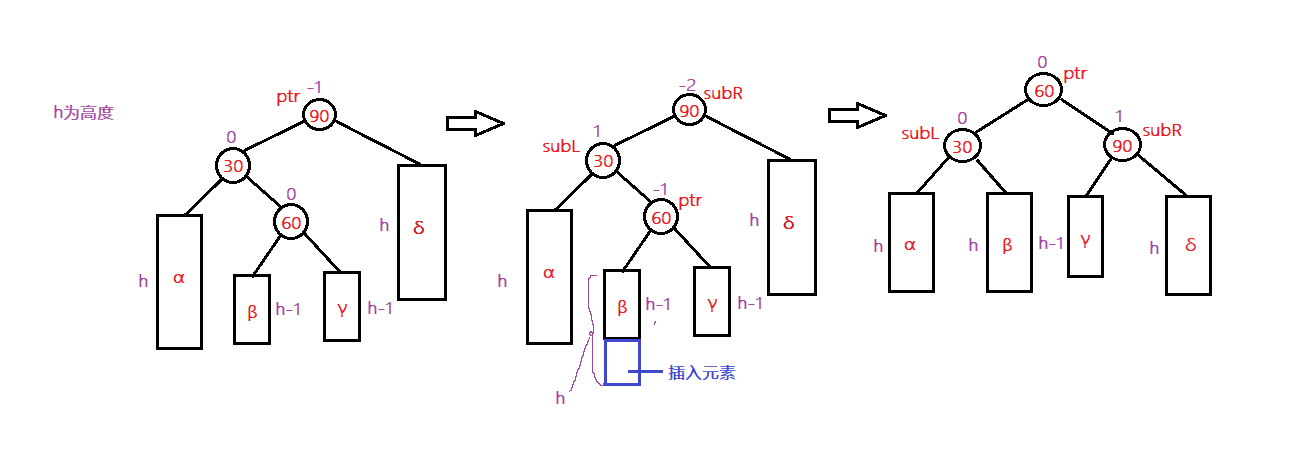
在插入一个结点后应该沿搜索路径将路径上的结点平衡因子进行修改,当平衡因子大于1时,就需要进行平衡化处理。从发生不平衡的结点起,沿刚才回溯的路径取直接下两层的结点,如果这三个结点在一条直线上,则采用单旋转进行平衡化,如果这三个结点位于一条折线上,则采用双旋转进行平衡化。
单旋转
- 左单旋
如下图的动画演示:将右子树的左子树链接到父结点的右孩子节点,父结点作为PTR节点的左孩子节点便完成了旋转。
- 右单旋
如下图动画演示:右单旋是左单旋的镜像旋转,当前节点PTR,与父结点和当前节点的左孩子节点位于一条直线上时,使用右单旋进行平衡。
双旋转
当在PTR的左子树的右子树中插入一个结点后,造成了PTR平衡因子为-2的不平衡,将PTR向下找到当前节点的左孩子的右孩子,先进行左单旋的ptr - >左= subL,然后将PTR的右子树断开指向SUBR,此时便完成了旋转,最后将平衡因子进行更新。
分为先右单旋再左单旋和先左单旋后右单旋两种方式,互为镜像旋转。
详细过程的代码如下
/**
* AVL tree implementation.
*
* In computer science, an AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree, and
* it was the first such data structure to be invented.[1] In an AVL tree, the
* heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one. Lookup,
* insertion, and deletion all take O(log n) time in both the average and worst
* cases, where n is the number of nodes in the tree prior to the operation.
* Insertions and deletions may require the tree to be rebalanced by one or more
* tree rotations.
*
* @author Ignas Lelys
* @created Jun 28, 2011
*
*/
public class AVLTree extends AbstractSelfBalancingBinarySearchTree {
/**
* @see trees.AbstractBinarySearchTree#insert(int)
*
* AVL tree insert method also balances tree if needed. Additional
* height parameter on node is used to track if one subtree is higher
* than other by more than one, if so AVL tree rotations is performed
* to regain balance of the tree.
*/
@Override
public Node insert(int element) {
Node newNode = super.insert(element);
rebalance((AVLNode)newNode);
return newNode;
}
/**
* @see trees.AbstractBinarySearchTree#delete(int)
*/
@Override
public Node delete(int element) {
Node deleteNode = super.search(element);
if (deleteNode != null) {
Node successorNode = super.delete(deleteNode);
if (successorNode != null) {
// if replaced from getMinimum(deleteNode.right) then come back there and update heights
AVLNode minimum = successorNode.right != null ? (AVLNode)getMinimum(successorNode.right) : (AVLNode)successorNode;
recomputeHeight(minimum);
rebalance((AVLNode)minimum);
} else {
recomputeHeight((AVLNode)deleteNode.parent);
rebalance((AVLNode)deleteNode.parent);
}
return successorNode;
}
return null;
}
/**
* @see trees.AbstractBinarySearchTree#createNode(int, trees.AbstractBinarySearchTree.Node, trees.AbstractBinarySearchTree.Node, trees.AbstractBinarySearchTree.Node)
*/
@Override
protected Node createNode(int value, Node parent, Node left, Node right) {
return new AVLNode(value, parent, left, right);
}
/**
* Go up from inserted node, and update height and balance informations if needed.
* If some node balance reaches 2 or -2 that means that subtree must be rebalanced.
*
* @param node Inserted Node.
*/
private void rebalance(AVLNode node) {
while (node != null) {
Node parent = node.parent;
int leftHeight = (node.left == null) ? -1 : ((AVLNode) node.left).height;
int rightHeight = (node.right == null) ? -1 : ((AVLNode) node.right).height;
int nodeBalance = rightHeight - leftHeight;
// rebalance (-2 means left subtree outgrow, 2 means right subtree)
if (nodeBalance == 2) {
if (node.right.right != null) {
node = (AVLNode)avlRotateLeft(node); //左单旋
break;
} else {
node = (AVLNode)doubleRotateRightLeft(node); //先右旋后左旋的双旋转
break;
}
} else if (nodeBalance == -2) {
if (node.left.left != null) {
node = (AVLNode)avlRotateRight(node); //右单旋
break;
} else {
node = (AVLNode)doubleRotateLeftRight(node); //先左旋后右旋的双旋转
break;
}
} else {
updateHeight(node);
}
node = (AVLNode)parent;
}
}
/**
* Rotates to left side.左单旋
*/
private Node avlRotateLeft(Node node) {
Node temp = super.rotateLeft(node);
updateHeight((AVLNode)temp.left);
updateHeight((AVLNode)temp);
return temp;
}
/**
* Rotates to right side.右单旋
*/
private Node avlRotateRight(Node node) {
Node temp = super.rotateRight(node);
updateHeight((AVLNode)temp.right);
updateHeight((AVLNode)temp);
return temp;
}
/**
* Take right child and rotate it to the right side first and then rotate
* node to the left side.
* 先右旋后左旋
*/
protected Node doubleRotateRightLeft(Node node) {
node.right = avlRotateRight(node.right);
return avlRotateLeft(node);
}
/**
* Take right child and rotate it to the right side first and then rotate
* node to the left side.
* 先左旋后右旋
*/
protected Node doubleRotateLeftRight(Node node) {
node.left = avlRotateLeft(node.left);
return avlRotateRight(node);
}
/**
* Recomputes height information from the node and up for all of parents.
* It needs to be done after delete.
*/
private void recomputeHeight(AVLNode node) {
while (node != null) {
node.height = maxHeight((AVLNode)node.left, (AVLNode)node.right) + 1;
node = (AVLNode)node.parent;
}
}
/**
* Returns higher height of 2 nodes.
*/
private int maxHeight(AVLNode node1, AVLNode node2) {
if (node1 != null && node2 != null) {
return node1.height > node2.height ? node1.height : node2.height;
} else if (node1 == null) {
return node2 != null ? node2.height : -1;
} else if (node2 == null) {
return node1 != null ? node1.height : -1;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Updates height and balance of the node.
*
* @param node Node for which height and balance must be updated.
*/
private static final void updateHeight(AVLNode node) {
int leftHeight = (node.left == null) ? -1 : ((AVLNode) node.left).height;
int rightHeight = (node.right == null) ? -1 : ((AVLNode) node.right).height;
node.height = 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
/**
* Node of AVL tree has height and balance additional properties. If balance
* equals 2 (or -2) that node needs to be re balanced. (Height is height of
* the subtree starting with this node, and balance is difference between
* left and right nodes heights).
*
* @author Ignas Lelys
* @created Jun 30, 2011
*
*/
protected static class AVLNode extends Node {
public int height;
public AVLNode(int value, Node parent, Node left, Node right) {
super(value, parent, left, right);
}
}
}
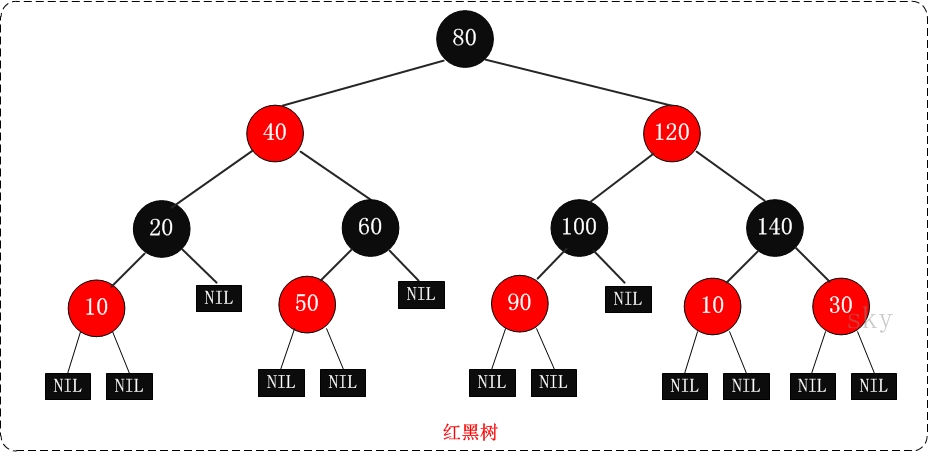
何为红黑树?
红黑树的定义是含有红黑连接并满足下列条件的二叉查找树:
- 红链接均为左链接
- 没有任何一个结点同时和两条红链接相连
- 该树是完美黑色平衡的,即任意空链接到根结点的路径上的黑链接数量相同。
上述定义摘自“算法”第四版
RB Tree,全称是Red-Black Tree,又称为“红黑树”,它一种特殊的二叉查找树。红黑树的每个节点上都有存储位表示节点的颜色,可以是红(红)或黑(黑)。
红黑树的特性:
(1)每个节点或者是黑色,或者是红色。
(2)根节点是黑色。
(3)每个叶子节点(NIL)是黑色。[注意:这里叶子节点,是指为空(NIL或NULL) ))的叶子节点!]
(4)如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
(5)从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑节点。
注意:
(01)特性(3)中的叶子节点,是只为空(NIL或null)的节点。
(02)特性(5),确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出两倍。因而,红黑树是相对是接近平衡的二叉树。
红黑树的应用
红黑树的应用比较广泛,主要是用它来存储有序的数据,它的时间复杂度是O(logN),效率非常之高。
例如,Java集合中的TreeSet和TreeMap,C ++ STL中的集合,地图,以及Linux的虚拟内存的管理,都是通过红黑树去实现的。
红黑树的时间复杂度为:O(lgn)
定理:一棵含有Ñ个节点的红黑树的高度至多为2log(N + 1)。
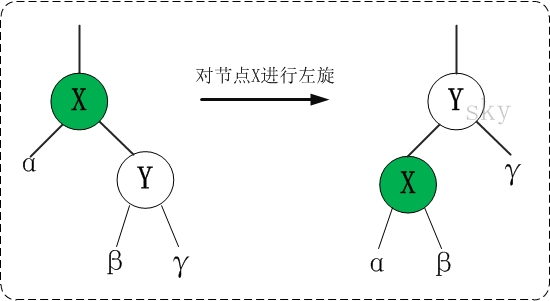
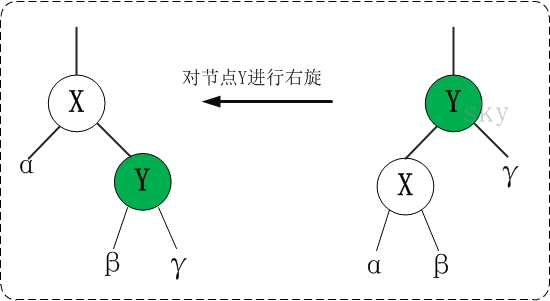
红黑树的基本操作(一)左旋和右旋
红黑树的基本操作是添加、删除。在对红黑树进行添加或删除之后,都会用到旋转方法。为什么呢?道理很简单,添加或删除红黑树中的节点之后,红黑树就发生了变化,可能不满足红黑树的5条性质,也就不再是一颗红黑树了,而是一颗普通的树。而通过旋转,可以使这颗树重新成为红黑树。简单点说,旋转的目的是让树保持红黑树的特性。
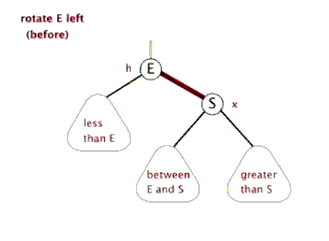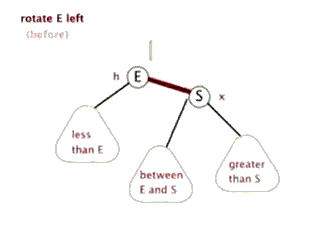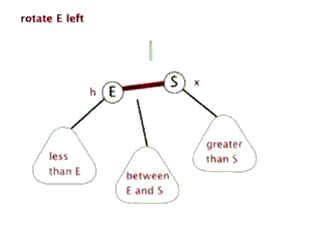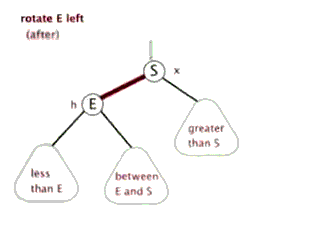
旋转包括两种:左旋 和 右旋。下面分别对它们进行介绍。
(1)左旋
对x进行左旋,意味着”将x变成一个左节点”。
(2)右旋
对x进行左旋,意味着”将x变成一个左节点”。
区分“左旋”和“右旋”
仔细观察上面”左旋”和”右旋”的示意图。能清晰的发现,它们是对称的。无论是左旋还是右旋,被旋转的树,在旋转前是二叉查找树,并且旋转之后仍然是一颗二叉查找树。
左旋示例图(以x为节点进行左旋):
z
x /
/ \ --(左旋)--> x
y z /
y对x进行左旋,意味着,将“x的右孩子”设为“x的父亲节点”;即,将 x变成了一个左节点(x成了为z的左孩子)!。 因此,左旋中的“左”,意味着“被旋转的节点将变成一个左节点”。
右旋示例图(以x为节点进行右旋):
y
x \
/ \ --(右旋)--> x
y z \
z对x进行右旋,意味着,将“x的左孩子”设为“x的父亲节点”;即,将 x变成了一个右节点(x成了为y的右孩子)! 因此,右旋中的“右”,意味着“被旋转的节点将变成一个右节点”。
红黑树的基本操作(二) 添加
将一个节点插入到红黑树中,需要执行哪些步骤呢?首先,将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点插入;然后,将节点着色为红色;最后,通过旋转和重新着色等方法来修正该树,使之重新成为一颗红黑树。详细描述如下:
第一步: 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点插入。
红黑树本身就是一颗二叉查找树,将节点插入后,该树仍然是一颗二叉查找树。也就意味着,树的键值仍然是有序的。此外,无论是左旋还是右旋,若旋转之前这棵树是二叉查找树,旋转之后它一定还是二叉查找树。这也就意味着,任何的旋转和重新着色操作,都不会改变它仍然是一颗二叉查找树的事实。
好吧?那接下来,我们就来想方设法的旋转以及重新着色,使这颗树重新成为红黑树!
第二步:将插入的节点着色为”红色”。
为什么着色成红色,而不是黑色呢?为什么呢?在回答之前,需要重新温习一下红黑树的特性:
(1) 每个节点或者是黑色,或者是红色。
(2) 根节点是黑色。
(3) 每个叶子节点是黑色。 [注意:这里叶子节点,是指为空的叶子节点!]
(4) 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
(5) 从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑节点。
将插入的节点着色为红色,不会违背”特性(5)”!少违背一条特性,就意味着我们需要处理的情况越少。接下来,就要努力的让这棵树满足其它性质即可;满足了的话,它就又是一颗红黑树了。
第三步:通过一系列的旋转或着色等操作,使之重新成为一颗红黑树。
第二步中,将插入节点着色为“红色”之后,不会违背“特性(5)”。那它到底会违背哪些特性呢?
对于”特性(1)”,显然不会违背了。因为我们已经将它涂成红色了。
对于”特性(2)”,显然也不会违背。在第一步中,我们是将红黑树当作二叉查找树,然后执行的插入操作。而根据二叉查找数的特点,插入操作不会改变根节点。所以,根节点仍然是黑色。
对于”特性( 3)”,显然不会违背了。这里的叶子节点是指的空叶子节点,插入非空节点并不会对它们造成影响。
对于”特性(4)”,是有可能违背的!
那接下来,想办法使之”满足特性(4)”,就可以将树重新构造成红黑树了。
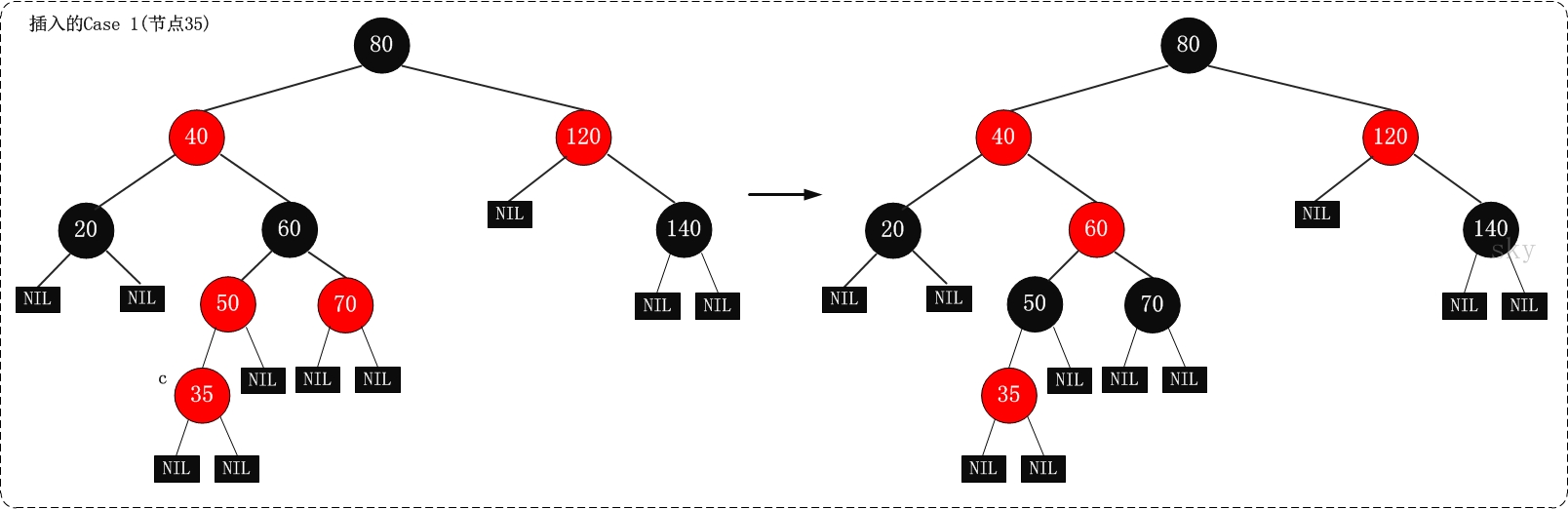
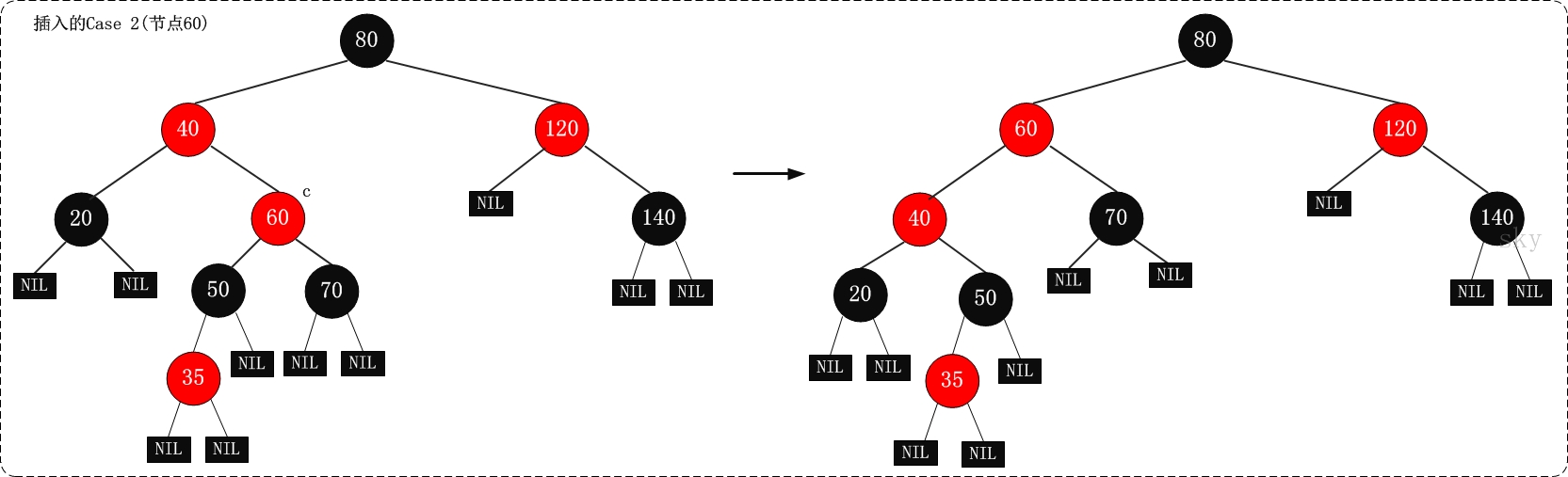
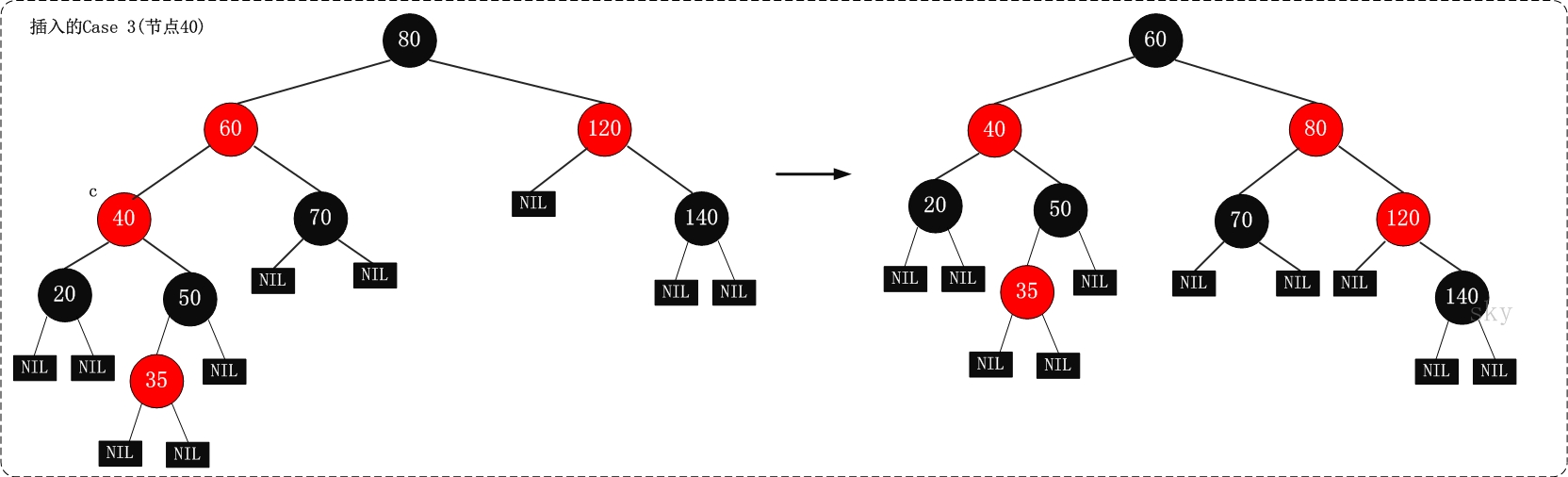
根据被插入节点的父节点的情况,可以将“当节点z被着色为红色节点,并插入二叉树”划分为三种情况来处理.①
情况说明:被插入的节点是根节点。
处理方法:直接把此节点涂为黑色
.②情况说明:被插入的节点的父节点是黑色。
处理方法:什么也不需要做。节点被插入后,仍然是红黑树
.③情况说明:被插入的节点的父节点是红色。
处理方法:那么,该情况与红黑树的“特性(5)”相冲突这种情况下,被插入节点是一定存在非空祖父节点的;进一步的讲,被插入节点也一定存在叔叔节点(即使叔叔节点为空,我们也视之为存在,空节点本身就是黑色节点)。理解这点之后,我们依据”叔叔节点的情况”,将这种情况进一步划分为3种情况(情况)。
| 现象说明 | 处理策略 | |
|---|---|---|
| 情况1 | 当前节点的父节点是红色,且当前节点的祖父节点的另一个子节点(叔叔节点)也是红色。 | (01)将“父节点”设为黑色。 (02)将“叔叔节点”设为黑色。 (03)将“祖父节点”设为“红色”。 (04)将“祖父节点”设为“当前”节点”(红色节点);即,之后继续对‘当前节点’进行操作。 |
| 案例2 | 当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是其父节点的右孩子 | (01)将“父节点”作为“新的当前节点”。 (02)以“新的当前节点”为支点进行左旋。 |
| 案例3 | 当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是其父节点的左孩子 | (01)将“父节点”设为“黑色”。 (02)将“祖父节点”设为“红色”。 (03)以“祖父节点”为支点进行右旋。 |
上面三种情况(CASE)处理问题的核心思路都是:将红色的节点移到根节点;然后,将根节点设为黑色。
案例1示意图:
案例2示意图:
情形3示意图:
红黑树的基本操作(三)删除
将红黑树内的某一个节点删除需要执行的操作依次是:首先,将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将该节点从二叉查找树中删除;然后,通过”旋转和重新着色”等一系列来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树详细描述如下:
第一步:将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点删除。
这和”删除常规二叉查找树中删除节点的方法是一样的”。分3种情况:
① 被删除节点没有儿子,即为叶节点。那么,直接将该节点删除就OK了。
② 被删除节点只有一个儿子。那么,直接删除该节点,并用该节点的唯一子节点顶替它的位置。
③ 被删除节点有两个儿子。那么,先找出它的后继节点;然后把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。在这里,后继节点相当于替身,在将后继节点的内容复制给”被删除节点”之后,再将后继节点删除。这样就巧妙的将问题转换为”删除后继节点”的情况了,下面就考虑后继节点。 在”被删除节点”有两个非空子节点的情况下,它的后继节点不可能是双子非空。既然”的后继节点”不可能双子都非空,就意味着”该节点的后继节点”要么没有儿子,要么只有一个儿子。若没有儿子,则按”情况① “进行处理;若只有一个儿子,则按”情况② “进行处理。
第二步:通过”旋转和重新着色”等一系列来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。
因为”第一步”中删除节点之后,可能会违背红黑树的特性。所以需要通过”旋转和重新着色”来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。
红黑树的Java实现(完整源码)
下面是红黑树实现的完整代码和相应的测试程序。
(1)除了上面所说的“左旋”,“右旋”,“添加”,“删除”等基本操作之后,还实现了“遍历” ,“查找”,“打印”,“最小值”,“最大值”,“创建”,“销毁”等接口。
(2)函数接口大多分为内部接口和外部接口。内部接口是私人函数,外部接口则是公共函数。
(3)测试代码中提供了“插入”和“删除”动作的检测开关。默认是关闭的,打开方法可以参考“代码中的说明”。建议在打开开关后,在草稿上自己动手绘制一下红黑树。
package NowCoder2.Class03;
/**
* 红黑树
*
* @param <T>
*/
public class RBTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private RBTNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
public class RBTNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {
boolean color; // 颜色
T key; // 关键字(键值)
RBTNode<T> left; // 左孩子
RBTNode<T> right; // 右孩子
RBTNode<T> parent; // 父结点
public RBTNode(T key, boolean color, RBTNode<T> parent, RBTNode<T> left, RBTNode<T> right) {
this.key = key;
this.color = color;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public T getKey() {
return key;
}
public String toString() {
return "" + key + (this.color == RED ? "(R)" : "B");
}
}
public RBTree() {
mRoot = null;
}
private RBTNode<T> parentOf(RBTNode<T> node) {
return node != null ? node.parent : null;
}
private boolean colorOf(RBTNode<T> node) {
return node != null ? node.color : BLACK;
}
private boolean isRed(RBTNode<T> node) {
return ((node != null) && (node.color == RED)) ? true : false;
}
private boolean isBlack(RBTNode<T> node) {
return !isRed(node);
}
private void setBlack(RBTNode<T> node) {
if (node != null)
node.color = BLACK;
}
private void setRed(RBTNode<T> node) {
if (node != null)
node.color = RED;
}
private void setParent(RBTNode<T> node, RBTNode<T> parent) {
if (node != null)
node.parent = parent;
}
private void setColor(RBTNode<T> node, boolean color) {
if (node != null)
node.color = color;
}
/**
* 前序遍历“红黑树”
*
* @param tree
*/
private void preOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
preOrder(tree.left);
preOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void preOrder() {
preOrder(mRoot);
}
/**
* 中序遍历“红黑树”
*
* @param tree
*/
private void inOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
inOrder(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
inOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void inOrder() {
inOrder(mRoot);
}
/**
* 后序遍历“红黑树”
*
* @param tree
*/
private void postOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
postOrder(tree.left);
postOrder(tree.right);
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
}
}
public void postOrder() {
postOrder(mRoot);
}
/**
* (递归实现)查找“红黑树x”中键值为key的节点
*
* @param x
* @param key
* @return
*/
private RBTNode<T> search(RBTNode<T> x, T key) {
if (x == null)
return x;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
return search(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0)
return search(x.right, key);
else
return x;
}
public RBTNode<T> search(T key) {
return search(mRoot, key);
}
/**
* (非递归实现)查找“红黑树x”中键值为key的节点
*
* @param x
* @param key
* @return
*/
private RBTNode<T> iterativeSearch(RBTNode<T> x, T key) {
while (x != null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
x = x.right;
else
return x;
}
return x;
}
private RBTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) {
return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key);
}
/**
* 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最小结点
*
* @param tree
* @return
*/
private RBTNode<T> minimum(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null)
return null;
while (tree.left != null)
tree = tree.left;
return tree;
}
public T minimum() {
RBTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot);
if (p != null)
return p.key;
return null;
}
/**
* 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最大结点
*
* @param tree
* @return
*/
private RBTNode<T> maximum(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null)
return null;
while (tree.right != null)
tree = tree.right;
return tree;
}
public T maximum() {
RBTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot);
if (p != null)
return p.key;
return null;
}
/**
* 找节点(x)的后继节点。即,查找“红黑树中数据值大于该节点”的“最小结点”.
*
* @param x
* @return
*/
public RBTNode<T> successor(RBTNode<T> x) {
//如果x存在右孩子,则“x”的后继结点为“以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点”。
if (x.right != null)
return minimum(x.right);
//如果x没有右孩子,则x有以下两种可能:
//(01)x是“一个左孩子”,则“x”的后继结点“为”它的父结点“。
//(02)x是一个“右孩子”,则查找“x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子“,找到的这个”最低的父结点“就是”x的后继节点“。
RBTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y != null) && (x == y.right)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/**
* 找节点(x)的前驱结点,即,查找“红黑树中数据值小于该节点”的“最大结点”。
*
* @param x
* @return
*/
public RBTNode<T> predecessor(RBTNode<T> x) {
//如果x存在左孩子,则“x的前驱结点”为“以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点”。
if (x.left != null)
return maximum(x.left);
//如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
//(01)x是“一个右孩子”,则“x的前驱结点”为“它的父结点”.
//(02)x是“一个左孩子”,则查找“x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子”,找到的这个“最低的父结点”,就是“x的前驱结点”。
RBTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y != null) && (x == y.left)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/**
* 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转
* <p>
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋):
* * px px
* * / /
* * x y
* * / \ --(左旋)-. / \ #
* * lx y x ry
* * / \ / \
* * ly ry lx ly
*
* @param x
*/
private void leftRotate(RBTNode<T> x) {
//设置x的右孩子为y
RBTNode<T> y = x.right;
//将“y的左孩子”设为“x的右孩子”;
//如果y的左孩子非空,将“x”设为“y的左孩子的父亲”
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != null)
y.left.parent = x;
//将“x的父亲”设为“y的父亲”
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
this.mRoot = y;//如果“x的父亲”是空节点,则将y设置为根节点
} else {
if (x.parent.left == x)
x.parent.left = y;//如果x是它父结点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父结点的左孩子”
else
x.parent.right = y;//如果x是它父结点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父结点的左孩子”
}
//将“x”设为“y的左孩子”
y.left = x;
//将“x的父结点”设为“y”
x.parent = y;
}
/**
* 对红黑树的节点(y)进行右旋转
* 右旋示意图(对节点y进行左旋):
* * py py
* * / /
* * y x
* * / \ --(右旋)-. / \ #
* * x ry lx y
* * / \ / \ #
* * lx rx rx ry
* *
*
* @param y
*/
private void rightRotate(RBTNode<T> y) {
//设置x是当前节点的左孩子
RBTNode<T> x = y.left;
//将“x的右孩子”设为“y的左孩子”
//如果“x的右孩子”不为空的话,将“y”设为“x的右孩子的父亲”
y.left = x.right;
if (x.right != null)
x.right.parent = y;
//将“y的父亲“设为”x的父亲“
x.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent == null) {
this.mRoot = x;//如果“y的父亲”是空节点,则将x设为根节点
} else {
if (y == y.parent.right)
y.parent.right = x;//如果y是它父结点的右孩子,则将x设为“y的父结点的右孩子”
else
y.parent.left = x;//(y是它父结点的左孩子)将x设为“x的父结点的左孩子”
}
//将“y”设为“x的右孩子”
x.right = y;
//将“y的父结点”设为“x”
y.parent = x;
}
/**
* 红黑树插入修正函数
* <p>
* 在向红黑树中插入节点之后(失去平衡),再调用函数
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一棵红黑树。
*
* @param node 插入的节点
*/
private void insertFixUp(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> parent, gparent;
//若“父结点存在。并且父结点的颜色是红色”
while (((parent = parentOf(node)) != null) && isRed(parent)) {
gparent = parentOf(parent);
//若“父结点”是“祖父节点的左孩子”
if (parent == gparent.left) {
//case1条件:叔叔节点是红色
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.right;
if ((uncle != null) && isRed(uncle)) {
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
//case2条件:叔叔是黑色的,且当前节点是右孩子
if (parent.right == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
leftRotate(parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
//case3条件:叔叔是黑色的,且当前节点是左孩子。
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
rightRotate(gparent);
} else {//若“z的父结点”是“z的祖父节点的右孩子”
//case1条件:叔叔节点是红色
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.left;
if ((uncle != null) && isRed(uncle)) {
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
//case2条件:叔叔是黑色的,且当前节点是左孩子
if (parent.left == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
rightRotate(parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
//case3条件:叔叔是黑色的,且当前节点是右孩子
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
leftRotate(gparent);
}
}
//将根节点设为黑色
setBlack(this.mRoot);
}
/**
* 将节点插入到红黑树中
*
* @param node 插入的节点
*/
private void insert(RBTNode<T> node) {
int cmp;
RBTNode<T> y = null;
RBTNode<T> x = this.mRoot;
//1.将红黑树当做一棵二叉查找树,将节点添加到二叉查找树中
while (x != null) {
y = x;
cmp = node.key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else
x = x.right;
}
node.parent = y;
if (y != null) {
cmp = node.key.compareTo(y.key);
if (cmp < 0)
y.left = node;
else
y.right = node;
} else {
this.mRoot = node;
}
//2.设置结点的颜色为红色
node.color = RED;
//3.将它重新修正为一棵二叉查找树
insertFixUp(node);
}
/**
* 新建节点(key),并将其插入到红黑树中
*
* @param key
*/
public void insert(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node = new RBTNode<T>(key, BLACK, null, null, null);
//如果新建节点失败,则返回
if (node != null)
insert(node);
}
/**
* 红黑树删除修正函数
* <p>
* 在从红黑树中删除插入结点之后(红黑树失去平衡),在调用该函数
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一棵红黑树
*
* @param node
* @param parent
*/
private void removeFixUp(RBTNode<T> node, RBTNode<T> parent) {
RBTNode<T> other;
while ((node == null || isBlack(node)) && (node != this.mRoot)) {
if (parent.left == node) {
other = parent.right;
if (isRed(other)) {
//Case1:x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
leftRotate(parent);
other = parent.right;
}
if ((other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) && (other.right == null || isBlack(other.right))) {
//case2:x的兄弟w是黑色的,且w的两个孩子也都是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.right == null || isBlack(other.right)) {
//case3.x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色的,右孩子为黑色
setBlack(other.left);
setRed(other);
rightRotate(other);
other = parent.right;
}
//case4:x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.right);
leftRotate(parent);
node = this.mRoot;
break;
}
} else {
other = parent.left;
if (isRed(other)) {
//case1:x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
rightRotate(parent);
other = parent.left;
}
if ((other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) && (other.right == null || isBlack(other.right))) {
//case2:x的兄弟w是黑色的,且w的两个孩子也是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) {
//case3:x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色的,右孩子为黑色
setBlack(other.right);
setRed(other);
leftRotate(other);
other = parent.left;
}
//case4:x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.left);
rightRotate(parent);
node = this.mRoot;
break;
}
}
}
if (node != null)
setBlack(node);
}
/**
* 删除节点(node),并返回被删除的节点
*
* @param node 删除的节点
*/
private void remove(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> child, parent;
boolean color;
//被删除节点的“左右孩子都不为空”的情况
if ((node.left != null) && (node.right != null)) {
//被删除节点的后继节点。
//用它来取代“被删除节点”的位置,然后再将“被删节点”去掉
RBTNode<T> replace = node;
//获取后继节点
replace = replace.right;
while (replace.left != null)
replace = replace.left;
//“node节点”不是根节点(只有根节点不存在父结点)
if (parentOf(node) != null) {
if (parentOf(node).left == node)
parentOf(node).left = replace;
else
parentOf(node).right = replace;
} else {
//“node节点”是根节点,更新根节点
this.mRoot = replace;
}
//child是“取代节点”的右孩子,也是需要“调整的节点”
//“取代节点”肯定不存在左孩子!因为它是一个后继节点
child = replace.right;
parent = parentOf(replace);
//保存“取代节点”的颜色
color = colorOf(replace);
//“被删除节点”是“它的后继节点的父结点”
if (parent == node) {
parent = replace;
} else {
//child不为空
if (child != null)
setParent(child, parent);
parent.left = child;
replace.right = node.right;
setParent(node.right, replace);
}
replace.parent = node.parent;
replace.color = node.color;
replace.left = node.left;
node.left.parent = replace;
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
return;
}
if (node.left != null) {
child = node.left;
} else {
child = node.right;
}
parent = node.parent;
//保存“取代节点”的颜色
color = node.color;
if (child != null)
child.parent = parent;
//“node节点”不是根节点
if (parent != null) {
if (parent.left == node)
parent.left = child;
else
parent.right = child;
} else {
this.mRoot = child;
}
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
}
/**
* 删除节点(z),并返回被删除的节点
*
* @param key
*/
public void remove(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node;
if ((node = search(mRoot, key)) != null)
remove(node);
}
/**
* 销毁红黑树
*
* @param tree
*/
private void destory(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null)
return;
if (tree.left != null)
destory(tree.left);
if (tree.right != null)
destory(tree.right);
tree = null;
}
public void clear() {
destory(mRoot);
mRoot = null;
}
/**
* 打印“红黑树”
*
* @param tree
* @param key 节点的键值
* @param direction 0 表示该节点是根节点
* -1 表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子
* 1 表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子
*/
private void print(RBTNode<T> tree, T key, int direction) {
if (tree != null) {
if (direction == 0)
System.out.printf("%2d(B) is root\n", tree.key);
else
System.out.printf("%2d(%s) is %2d's %6s child\n", tree.key, isRed(tree) ? "R" : "B", key, direction == 1 ? "right" : "left");
print(tree.left, tree.key, -1);
print(tree.right, tree.key, 1);
}
}
public void print() {
if (mRoot != null)
print(mRoot, mRoot.key, 0);
}
}
红黑树的的Java测试代码
package NowCoder2.Class03;
public class RBTreeTest {
private static final int a[] = {10, 40, 30, 60, 90, 70, 20, 50, 80};
private static final boolean mDebugInsert = false; // "插入"动作的检测开关(false,关闭;true,打开)
private static final boolean mDebugDelete = false; // "删除"动作的检测开关(false,关闭;true,打开)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i, ilen = a.length;
RBTree<Integer> tree = new RBTree<Integer>();
System.out.printf("== 原始数据: ");
for (i = 0; i < ilen; i++)
System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]);
System.out.printf("\n");
for (i = 0; i < ilen; i++) {
tree.insert(a[i]);
// 设置mDebugInsert=true,测试"添加函数"
if (mDebugInsert) {
System.out.printf("== 添加节点: %d\n", a[i]);
System.out.printf("== 树的详细信息: \n");
tree.print();
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
System.out.printf("== 前序遍历: ");
tree.preOrder();
System.out.printf("\n== 中序遍历: ");
tree.inOrder();
System.out.printf("\n== 后序遍历: ");
tree.postOrder();
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 最小值: %s\n", tree.minimum());
System.out.printf("== 最大值: %s\n", tree.maximum());
System.out.printf("== 树的详细信息: \n");
tree.print();
System.out.printf("\n");
// 设置mDebugDelete=true,测试"删除函数"
if (mDebugDelete) {
for (i = 0; i < ilen; i++) {
tree.remove(a[i]);
System.out.printf("== 删除节点: %d\n", a[i]);
System.out.printf("== 树的详细信息: \n");
tree.print();
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
// 销毁二叉树
tree.clear();
}
}
测试结果

何为SB树?
每棵子树的大小,不小于其兄弟的子树大小(即每棵叔叔树的大小,不小于侄子树的大小)。(陈启峰发明与2006年底完成的论文“Size Balanced Tree”,并于2007年的全国青少年信息学奥林匹克竞赛冬令营中发表)
Size Balanced Tree(SBT)是一种通过大小(Size)域来保持平衡的二叉搜索树。它支持许多运算时间级别为O(logN)的主要操作。

通常SBT的每一个结点包含key,left,right和size等域。size是一个额外但是十分有用的数据域,它一直在更新,它在前面已经定义了。
每一个在SBT中的结点t,我们保证:
- 性质A:
- 性质B:
详细介绍可参考:SBT中文 - 百度文库
它的平衡性是这样规定的

任何一个叔叔节点的个数,不低于侄子节点的整棵树
它所有的操作都是为了保证这个平衡性,详细介绍可参考这位大神的博客
Size Balanced Tree(SBT)平衡二叉树_xkey的博客-CSDN博客
何为跳表?
跳表并不是树结构的,它的每个节点是一个值加一个数组的结构,通过概率而实现的一种和平衡搜索二叉树功能相似的结构,它使用随机的平衡策略取代平衡树严格的强制。因此它具有更简单有效的插入、删除方法以及更快的搜索速度。目前开源软件Redis和LevelDB都有用到。
package NowCoder2.Class03;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class SkipListClass {
public static class SkipListNode {
public Integer value;
public ArrayList<SkipListNode> nextNodes;
public SkipListNode(Integer value) {
this.value = value;
nextNodes = new ArrayList<SkipListNode>();
}
}
public static class SkipListIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {
SkipList list;
SkipListNode current;
public SkipListIterator(SkipList list) {
this.list = list;
this.current = list.getHead();
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return current.nextNodes.get(0) != null;
}
public Integer next() {
current = current.nextNodes.get(0);
return current.value;
}
}
public static class SkipList {
private SkipListNode head;
private int maxLevel;
private int size;
private static final double PROBABILITY = 0.5;
public SkipList() {
size = 0;
maxLevel = 0;
head = new SkipListNode(null);
head.nextNodes.add(null);
}
public SkipListNode getHead() {
return head;
}
public void add(Integer newValue) {
if (!contains(newValue)) {
size++;
int level = 0;
while (Math.random() < PROBABILITY) {
level++;
}
while (level > maxLevel) {
head.nextNodes.add(null);
maxLevel++;
}
SkipListNode newNode = new SkipListNode(newValue);
SkipListNode current = head;
do {
current = findNext(newValue, current, level);
newNode.nextNodes.add(0, current.nextNodes.get(level));
current.nextNodes.set(level, newNode);
} while (level-- > 0);
}
}
public void delete(Integer deleteValue) {
if (contains(deleteValue)) {
SkipListNode deleteNode = find(deleteValue);
size--;
int level = maxLevel;
SkipListNode current = head;
do {
current = findNext(deleteNode.value, current, level);
if (deleteNode.nextNodes.size() > level) {
current.nextNodes.set(level, deleteNode.nextNodes.get(level));
}
} while (level-- > 0);
}
}
/**
* 返回最大值小于等于e的跳表节点
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
private SkipListNode find(Integer e) {
return find(e, head, maxLevel);
}
/**
* 返回最大值小于等于e的跳表节点
* 从节点起始位置和层次开始
*
* @param e
* @param current
* @param level
* @return
*/
private SkipListNode find(Integer e, SkipListNode current, int level) {
do {
current = findNext(e, current, level);
} while (level-- > 0);
return current;
}
/**
* 返回给定级别的节点,其最大值小于e
*
* @param e
* @param current
* @param level
* @return
*/
private SkipListNode findNext(Integer e, SkipListNode current, int level) {
SkipListNode next = current.nextNodes.get(level);
while (next != null) {
Integer value = next.value;
if (lessThan(e, value)) {
break;
}
current = next;
next = current.nextNodes.get(level);
}
return current;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean contains(Integer value) {
SkipListNode node = find(value);
return node != null && node.value != null && equalTo(node.value, value);
}
public Iterator<Integer> iterator() {
return new SkipListIterator(this);
}
/******************************************************************************
* 效用函数 *
******************************************************************************/
private boolean lessThan(Integer a, Integer b) {
return a.compareTo(b) < 0;
}
private boolean equalTo(Integer a, Integer b) {
return a.compareTo(b) == 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}






















 1020
1020











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










