转载地址:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/384902839
接着上一章的分析,LeGO-LOAM进行点云分割之后,接着会对分割后的点云进行特征提取,下面我们首先回顾下点云分割的过程,然后开始分析特征提取。
点云分割
LeGO-LOAM首先进行地面分割,找到地面之后,对地面之上的点进行聚类。聚类的算法如下图,主要是根据斜率对物体做切割,最后得到地面和分割后的点云。上述步骤的关键是要理解如何进行地面分割和点云分割。

特征提取
点云分割完成之后,接下来对分割后的点云提取特征,提取的特征的目的是进行点云配准,从而得出当前位姿。
LeGO-LOAM的特征提取和点云配准的过程都在LeGO-LOAM\src\featureAssociation.cpp中。下面我们开始逐步分析代码。
和点云分割一样,特征提取也是单独的ROS执行程序,函数入口在main函数中。也是在构造函数FeatureAssociation()中申明订阅消息和回调函数,与点云分割不同的是,在主函数中通过循环调用runFeatureAssociation来提取特征和特征匹配。
主函数
总结一下,LeGO-LOAM特征提取的实现分为2个步骤
- 消息订阅和回调,在构造函数中申明。
- 接收到消息之后,循环调用runFeatureAssociation提取特征,并且进行特征匹配,获取位姿。
也就是说主要的执行步骤在runFeatureAssociation中。
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "lego_loam");
ROS_INFO("\033[1;32m---->\033[0m Feature Association Started.");
// 1. 在构造函数中订阅消息和消息回调函数
FeatureAssociation FA;
ros::Rate rate(200);
// 2. 循环调用runFeatureAssociation,函数的主流程所在
while (ros::ok())
{
ros::spinOnce();
FA.runFeatureAssociation();
rate.sleep();
}
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
接下来我们先看消息回调,然后再看主流程runFeatureAssociation。
消息回调
消息回调主要是接收上一个步骤(点云分割)中分割好的点云消息。
FeatureAssociation():
nh("~")
{
// 1. 接收消息,上一步分割好的点云
subLaserCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/segmented_cloud", 1, &FeatureAssociation::laserCloudHandler, this);
subLaserCloudInfo = nh.subscribe<cloud_msgs::cloud_info>("/segmented_cloud_info", 1, &FeatureAssociation::laserCloudInfoHandler, this);
subOutlierCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/outlier_cloud", 1, &FeatureAssociation::outlierCloudHandler, this);
subImu = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::Imu>(imuTopic, 50, &FeatureAssociation::imuHandler, this);
// 2. 发布消息
pubCornerPointsSharp = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_sharp", 1);
pubCornerPointsLessSharp = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_less_sharp", 1);
pubSurfPointsFlat = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_flat", 1);
pubSurfPointsLessFlat = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_less_flat", 1);
pubLaserCloudCornerLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_corner_last", 2);
pubLaserCloudSurfLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_surf_last", 2);
pubOutlierCloudLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/outlier_cloud_last", 2);
pubLaserOdometry = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry> ("/laser_odom_to_init", 5);
initializationValue();
}
下面我们具体看这4个消息
- segmented_cloud 分割好的点云。
- segmented_cloud_info 分割好的点云,和segmented_cloud的区别是,segmented_cloud_info的强度信息是距离,而segmented_cloud的是range image的行列信息。
- outlier_cloud 离群点,也就是分割失败的点。
- imuTopic 接收imu的消息。
在理解了上述4个消息之后,我们分别看下他们的回调,点云消息的回调主要是把ROS的消息转换为点云,IMU的回调主要是把IMU的消息放入buffer中。
// 1. 接收"/segmented_cloud"消息,保存到segmentedCloud
void laserCloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg){
cloudHeader = laserCloudMsg->header;
timeScanCur = cloudHeader.stamp.toSec();
timeNewSegmentedCloud = timeScanCur;
segmentedCloud->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*laserCloudMsg, *segmentedCloud);
newSegmentedCloud = true;
}
// 2. 接收"/outlier_cloud"消息,保存到outlierCloud
void outlierCloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& msgIn){
timeNewOutlierCloud = msgIn->header.stamp.toSec();
outlierCloud->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*msgIn, *outlierCloud);
newOutlierCloud = true;
}
// 3. 接收"/segmented_cloud_info"消息,并且保存到segInfo中
// 注意这里没有转换为PCL点云,而是直接保存的消息cloud_msgs::cloud_info segInfo
void laserCloudInfoHandler(const cloud_msgs::cloud_infoConstPtr& msgIn)
{
timeNewSegmentedCloudInfo = msgIn->header.stamp.toSec();
segInfo = *msgIn;
newSegmentedCloudInfo = true;
}
接下来看IMU回调函数,接收到IMU消息之后保存到数组。IMU还做了一些角度的转换,这里暂时不做深究,后面有时间再补充。
void imuHandler(const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr& imuIn)
{
double roll, pitch, yaw;
tf::Quaternion orientation;
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(imuIn->orientation, orientation);
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
float accX = imuIn->linear_acceleration.y - sin(roll) * cos(pitch) * 9.81;
float accY = imuIn->linear_acceleration.z - cos(roll) * cos(pitch) * 9.81;
float accZ = imuIn->linear_acceleration.x + sin(pitch) * 9.81;
imuPointerLast = (imuPointerLast + 1) % imuQueLength;
imuTime[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->header.stamp.toSec();
imuRoll[imuPointerLast] = roll;
imuPitch[imuPointerLast] = pitch;
imuYaw[imuPointerLast] = yaw;
imuAccX[imuPointerLast] = accX;
imuAccY[imuPointerLast] = accY;
imuAccZ[imuPointerLast] = accZ;
imuAngularVeloX[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->angular_velocity.x;
imuAngularVeloY[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->angular_velocity.y;
imuAngularVeloZ[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->angular_velocity.z;
AccumulateIMUShiftAndRotation();
}
接着分别对位置、速度和角度做积分,计算出当前的位置、速度和角度。
void AccumulateIMUShiftAndRotation()
{
float roll = imuRoll[imuPointerLast];
float pitch = imuPitch[imuPointerLast];
float yaw = imuYaw[imuPointerLast];
float accX = imuAccX[imuPointerLast];
float accY = imuAccY[imuPointerLast];
float accZ = imuAccZ[imuPointerLast];
float x1 = cos(roll) * accX - sin(roll) * accY;
float y1 = sin(roll) * accX + cos(roll) * accY;
float z1 = accZ;
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(pitch) * y1 - sin(pitch) * z1;
float z2 = sin(pitch) * y1 + cos(pitch) * z1;
accX = cos(yaw) * x2 + sin(yaw) * z2;
accY = y2;
accZ = -sin(yaw) * x2 + cos(yaw) * z2;
int imuPointerBack = (imuPointerLast + imuQueLength - 1) % imuQueLength;
double timeDiff = imuTime[imuPointerLast] - imuTime[imuPointerBack];
if (timeDiff < scanPeriod) {
// 1. 位置积分
imuShiftX[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftX[imuPointerBack] + imuVeloX[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff + accX * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuShiftY[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftY[imuPointerBack] + imuVeloY[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff + accY * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuShiftZ[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftZ[imuPointerBack] + imuVeloZ[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff + accZ * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
// 2. 速度积分
imuVeloX[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloX[imuPointerBack] + accX * timeDiff;
imuVeloY[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloY[imuPointerBack] + accY * timeDiff;
imuVeloZ[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloZ[imuPointerBack] + accZ * timeDiff;
// 3. 角度积分
imuAngularRotationX[imuPointerLast] = imuAngularRotationX[imuPointerBack] + imuAngularVeloX[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff;
imuAngularRotationY[imuPointerLast] = imuAngularRotationY[imuPointerBack] + imuAngularVeloY[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff;
imuAngularRotationZ[imuPointerLast] = imuAngularRotationZ[imuPointerBack] + imuAngularVeloZ[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff;
}
}
以上就是消息接收过程,接下来我们看主流程runFeatureAssociation。
主流程(runFeatureAssociation)
主函数的流程非常清晰,总共分为2个大的步骤
- 特征提取,提取线特征和面特征
- 特征匹配,利用最小二乘法,获取当前最优的位姿
void runFeatureAssociation()
{
// 0. 判断是否接收到消息,并且消息延迟小于0.05s
if (newSegmentedCloud && newSegmentedCloudInfo && newOutlierCloud &&
std::abs(timeNewSegmentedCloudInfo - timeNewSegmentedCloud) < 0.05 &&
std::abs(timeNewOutlierCloud - timeNewSegmentedCloud) < 0.05){
newSegmentedCloud = false;
newSegmentedCloudInfo = false;
newOutlierCloud = false;
}else{
return;
}
// 1. Feature Extraction(特征提取)
// 1.1 点云运动补偿
adjustDistortion();
// 1.2 计算平滑度
calculateSmoothness();
// 1.3 标记遮挡点
markOccludedPoints();
// 1.4 提取特征
extractFeatures();
// 1.5 发布点云
publishCloud(); // cloud for visualization
// 2. Feature Association(特征匹配)
if (!systemInitedLM) {
// 2.1 检查系统初始化
checkSystemInitialization();
return;
}
// 2.2 更新初始猜测位置
updateInitialGuess();
// 2.3 特征匹配,输出Transformation
updateTransformation();
// 2.4 变换坐标Transformation
integrateTransformation();
// 2.5 发布雷达里程计
publishOdometry();
// 2.6 发布点云用于建图
publishCloudsLast(); // cloud to mapOptimization
}
特征提取的过程:先对点云进行畸变校正(运动补偿),接着计算点的平滑程度,然后按照平滑度排序,如果是不平滑的点,则选为线特征(柱子或者墙壁的棱角),如果是平滑的点,则选为面特征(地面,墙面等平面)。同时为了避免选择的特征过于集中在同一个地方,会把360°方向切分为6个区域,每个区域平均选择2个线特征和4个面特征。
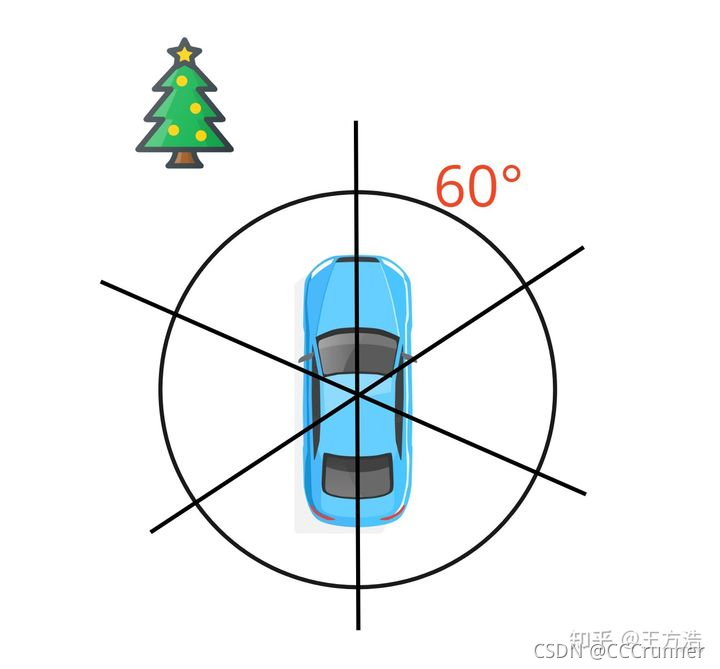
运动补偿
由于Lidar扫描过程中,小车在运动,这样对于同一个物体可能会导致出现畸变的情况,需要根据小车的位移对点云进行校正。
计算平滑度
平滑度的计算是取当前点的左边5个点和右边5个点和当前点的深度差值,然后求平方。而论文中的计算方法和代码中的不一样,论文中是取深度差的平均值,然后除以自身的模,也就是说论文中的曲率和尺度无关,不管当前点离lidar近还是远,只要曲率超过一定的值就可以,同时在仿真环境也可以解决尺度的问题,而代码中直接取得是绝对大小。

论文中S为点集, r j r_j rj 表示S中不等于i的点的深度, r i r_i ri则表示自身的深度。
void calculateSmoothness()
{
int cloudSize = segmentedCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 5; i < cloudSize - 5; i++) {
// 1. 计算相邻10个点深度差的和
float diffRange = segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-5] + segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-4]
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-3] + segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-2]
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-1] - segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i] * 10
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+1] + segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+2]
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+3] + segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+4]
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+5];
// 2. 取平方
cloudCurvature[i] = diffRange*diffRange;
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 0;
cloudLabel[i] = 0;
// 3. 保存曲率,保存索引
cloudSmoothness[i].value = cloudCurvature[i];
cloudSmoothness[i].ind = i;
}
}
为什么cloudSmoothness也要保存索引,是因为后面会对cloudSmoothness数组排序,排序之后数组原来的索引就乱了,保存索引之后就知道点在原始点云中的索引(index)是多少。
标记遮挡点
计算完平滑度之后,我们首先标记一下效果不是非常理想的点,方便后续处理。那么什么是效果不好的点呢?在LOAM论文中有以下2种情况。

- 图(a) 中有2个特征点A和B,但B的方向和激光雷达的光束几乎平行,因此移动的过程中很可能丢失,所以尽量不要选择B。
- 图(b)中有2个特征点A和B,但A后续可能会被B遮挡了,橙色线标识的部分。所以A也尽量要排除。
实际上图(a)中所说的情况在LOAM中存在,而在LeGO-LOAM中可能不存在,因为LOAM没有做分割,而LeGO-LOAM做过分割,已经去除掉斜率比较大的点了,所以代码中我没有找到图(a)的情况。
void markOccludedPoints()
{
int cloudSize = segmentedCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 5; i < cloudSize - 6; ++i){
float depth1 = segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i];
float depth2 = segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+1];
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[i+1] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[i]));
// 1. 标记有遮挡的点
if (columnDiff < 10){
if (depth1 - depth2 > 0.3){
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 5] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 4] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 3] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 2] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 1] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 1;
}else if (depth2 - depth1 > 0.3){
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 1] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 2] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 3] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 4] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 5] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 6] = 1;
}
}
float diff1 = std::abs(float(segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-1] - segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i]));
float diff2 = std::abs(float(segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+1] - segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i]));
// 2. 这里我理解是标记离群点,也就是和周围点相差比较大的点。
if (diff1 > 0.02 * segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i] && diff2 > 0.02 * segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i])
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 1;
}
}
提取特征
接下来就进行提取特征的操作了,提取的特征分为2类,一类是曲率比较大的线特征,一类是曲率比较小的面特征。
提取的方法是把平面划分为6等分,也就是6个方向(LOAM中为前、后、左、右4个方向),根据上述计算好的曲率进行排序,然后每个方向最多选择2个线特征和4个面特征,如果超过则跳过,在下一个方向上继续选择。如果一个点已经被选择为特征点,那么它的相邻点会被标记,不允许被选为特征了。
void extractFeatures()
{
cornerPointsSharp->clear();
cornerPointsLessSharp->clear();
surfPointsFlat->clear();
surfPointsLessFlat->clear();
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCAN; i++) {
surfPointsLessFlatScan->clear();
// 1. 分为6个方向,每个方向分别选择线特征和面特征
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
int sp = (segInfo.startRingIndex[i] * (6 - j) + segInfo.endRingIndex[i] * j) / 6;
int ep = (segInfo.startRingIndex[i] * (5 - j) + segInfo.endRingIndex[i] * (j + 1)) / 6 - 1;
if (sp >= ep)
continue;
// 2. 根据曲率排序
std::sort(cloudSmoothness.begin()+sp, cloudSmoothness.begin()+ep, by_value());
int largestPickedNum = 0;
// 3. 选择线特征,不为地面,segInfo.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[ind] == false
for (int k = ep; k >= sp; k--) {
int ind = cloudSmoothness[k].ind;
if (cloudNeighborPicked[ind] == 0 &&
cloudCurvature[ind] > edgeThreshold &&
segInfo.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[ind] == false) {
largestPickedNum++;
// 3.1 选择最多2个线特征
if (largestPickedNum <= 2) {
cloudLabel[ind] = 2;
cornerPointsSharp->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[ind]);
cornerPointsLessSharp->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[ind]);
// 3.2 平滑一些的线特征20个,用于mapping
} else if (largestPickedNum <= 20) {
cloudLabel[ind] = 1;
cornerPointsLessSharp->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[ind]);
} else {
// 3.3 超过则退出
break;
}
// 3.4 标记相邻点,防止特征点过于集中
cloudNeighborPicked[ind] = 1;
for (int l = 1; l <= 5; l++) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l - 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
for (int l = -1; l >= -5; l--) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l + 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
}
}
int smallestPickedNum = 0;
// 4. 选择面特征,为地面,segInfo.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[ind] == true
for (int k = sp; k <= ep; k++) {
int ind = cloudSmoothness[k].ind;
if (cloudNeighborPicked[ind] == 0 &&
cloudCurvature[ind] < surfThreshold &&
segInfo.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[ind] == true) {
cloudLabel[ind] = -1;
surfPointsFlat->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[ind]);
// 4.1 选择最多4个面特征
smallestPickedNum++;
if (smallestPickedNum >= 4) {
break;
}
// 4.2 标记相邻点
cloudNeighborPicked[ind] = 1;
for (int l = 1; l <= 5; l++) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l - 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
for (int l = -1; l >= -5; l--) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l + 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
}
}
// 5. 选择是地面的面特征,和其它没被选择的点(除了地面的点,并且不是线特征)
for (int k = sp; k <= ep; k++) {
if (cloudLabel[k] <= 0) {
surfPointsLessFlatScan->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[k]);
}
}
}
// 5.1 下采样平滑一些的面特征
surfPointsLessFlatScanDS->clear();
downSizeFilter.setInputCloud(surfPointsLessFlatScan);
downSizeFilter.filter(*surfPointsLessFlatScanDS);
*surfPointsLessFlat += *surfPointsLessFlatScanDS;
}
}
最后总结一下,特征点的选择满足以下3个条件。
- 选择的边缘点或平面点的数量不能超过每个方向上的最大值,一共有6个方向,每个方向上最多2个线特征,4个面特征。
- 线特征和面特征周围相邻的点不能被选中。
- 不能是平行于激光雷达光束的点或者被遮挡的点。
然后接着总结下代码中的输出
- cornerPointsSharp 线特征(不为地面),每个方向上最多2个
- cornerPointsLessSharp 比cornerPointsSharp平滑的线特征(不为地面),每个方向上20个
- surfPointsFlat 面特征(为地面),每个方向上最多4个
- surfPointsLessFlat 面特征(地面或者分割点云中不为线特征的点)
至此,特征提取就介绍完毕了,接着介绍特征匹配。
特征匹配
特征匹配主要是根据上述提取出的面特征和线特征进行匹配,然后根据最小二乘法,得出前后2帧的坐标转换。LeGO-LOAM相对LOAM的不同之处在于,LeGO-LOAM分别对线和面进行匹配,根据线特征匹配得到 t x , t y , θ y a w t_x,t_y,\theta_{yaw} tx,ty,θyaw,根据面特征匹配得到 t z , θ r o l l , θ p i t c h t_z,\theta_{roll},\theta_{pitch} tz,θroll,θpitch 。而LOAM是合并了2个匹配,一次得出 t x , t y , t z , θ y a w , θ r o l l , θ p i t c h t_x,t_y,t_z,\theta_{yaw},\theta_{roll},\theta_{pitch} tx,ty,tz,θyaw,θroll,θpitch。
为什么LeGO-LOAM这么做呢,我们先看面特征匹配。
由于LeGO-LOAM做了地面分割,而且面特征是地面上的点,因此2个地面的点进行匹配之后,我们实际上只能保证
t
z
,
θ
r
o
l
l
,
θ
p
i
t
c
h
t_z,\theta_{roll},\theta_{pitch}
tz,θroll,θpitch 是准确的。因为2个平面重叠时候
t
z
,
θ
r
o
l
l
,
θ
p
i
t
c
h
t_z,\theta_{roll},\theta_{pitch}
tz,θroll,θpitch 必定是确定的。

如下图所示,虽然2个平面重叠了,它还可以在水平面上移动和旋转(yaw),也就是说
t
x
,
t
y
θ
y
a
w
t_x,t_y\theta_{yaw}
tx,tyθyaw还可以变换,这是建立在只有水平地面的情况下,如果有多个平面,那么
t
x
,
t
y
θ
y
a
w
t_x,t_y\theta_{yaw}
tx,tyθyaw 也可以是确定的。
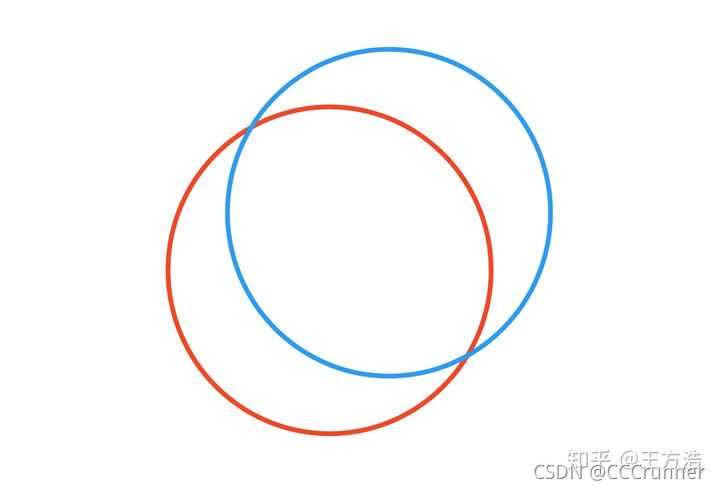
在通过面特征确定好 t z , θ r o l l , θ p i t c h t_z,\theta_{roll},\theta_{pitch} tz,θroll,θpitch 之后,接着再根据线特征确认 t x , t y , θ y a w t_x,t_y,\theta_{yaw} tx,ty,θyaw。线特征的匹配也是通过计算点到线的距离最短,通过线特征主要是确定 t x , t y , θ y a w t_x,t_y,\theta_{yaw} tx,ty,θyaw。至此整个匹配的过程就完成了。通过上述方法LeGO-LOAM达到同样的精度,比LOAM节省了35%的时间。
下面我们详细介绍下特征匹配的过程,首先是线特征匹配。
线特征匹配
空间中一个点的坐标可以通过旋转和平移来转换到另一个坐标。
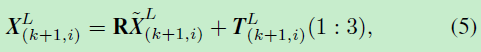
那么前1帧中的点通过公式(5)可以转换到当前帧,假设我们以空间中点的欧式距离来表示匹配的好坏,那么我们可以把问题转换为以下公式。

找到 T ( k + 1 , i ) L T_{(k+1,i)}^L T(k+1,i)L(可以理解为公式5中的R和T)使得前一帧中所有的点通过 T ( k + 1 , i ) L T_{(k+1,i)}^L T(k+1,i)L 转换后,和当前帧的点的欧式距离最小,这样的R和T就是前一帧和当前帧的最优坐标转换。
最小二乘法
上述的问题是不是有点类似以下经典的最小二乘法的问题。

我们希望找到一条直线 Y = a X + b Y = aX + b Y=aX+b ,并且使得它和这4个点最匹配。回到坐标转换的例子,X代表前一帧的点,Y代表当前帧的点,而a代表旋转矩阵R,b代表平移矩阵b。通过计算每个点的平方差最小,来求解a和b的最优值。
代价函数
实际上LeGO-LOAM中线特征匹配不是计算2个点之间的平方差最小,而是先根据当前点i,查找它在前一帧的最小近邻点j,并且找到离j最近的l,j和l不是同一个扫描线但都属于前一帧的点云。然后再求点i到线
(
j
,
l
)
(j,l)
(j,l)的距离,实际上就是求点到线的距离。然后遍历当前帧所有的线特征,重复执行上述过程直到收敛。

可以看到上述最小二乘法中的代价函数没有采用点和点的匹配,而是采用线和线的匹配,而求解线和线的距离用到的是点到线的距离。也就说最小二乘法的代价函数可以定义任意的类型,而不仅仅限定于欧氏距离,你定义了什么样的代价函数,就会得到什么样的拟合结果。

点和线的距离
面特征匹配
面特征的匹配也是类似线特征匹配,不过是计算点到面的距离,因此根据当前帧的点i,查找上一帧中最小近邻点j,然后在当前扫描线中找到l,在相邻的扫描线中找到m,构成一个平面,然后计算点i到平面
(
j
,
l
,
m
)
(j,l,m)
(j,l,m) 的距离。

点到面的距离计算公式。

面特征的匹配就是找到一个转换
T
(
k
+
1
,
i
)
L
T_{(k+1,i)}^L
T(k+1,i)L,使得当前帧所有点到前一帧面的距离平方差最小。
下面我们开始分析特征匹配的代码。
void updateTransformation(){
if (laserCloudCornerLastNum < 10 || laserCloudSurfLastNum < 100)
return;
// 1. 面特征匹配
for (int iterCount1 = 0; iterCount1 < 25; iterCount1++) {
laserCloudOri->clear();
coeffSel->clear();
// 1.1 查找匹配的特征
findCorrespondingSurfFeatures(iterCount1);
if (laserCloudOri->points.size() < 10)
continue;
// 1.2 计算Transformation
if (calculateTransformationSurf(iterCount1) == false)
break;
}
// 2. 线特征匹配
for (int iterCount2 = 0; iterCount2 < 25; iterCount2++) {
laserCloudOri->clear();
coeffSel->clear();
// 2.1 查找匹配的特征
findCorrespondingCornerFeatures(iterCount2);
if (laserCloudOri->points.size() < 10)
continue;
// 2.2 计算Transformation
if (calculateTransformationCorner(iterCount2) == false)
break;
}
}
calculateTransformationSurf
查找面特征和计算回归系数,点离线越远回归系数越低,离线越近的点系数越高。
void findCorrespondingSurfFeatures(int iterCount){
int surfPointsFlatNum = surfPointsFlat->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < surfPointsFlatNum; i++) {
// 1. 转换到起始点
TransformToStart(&surfPointsFlat->points[i], &pointSel);
if (iterCount % 5 == 0) {
// 2.1 通过i查找j
kdtreeSurfLast->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 1, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
int closestPointInd = -1, minPointInd2 = -1, minPointInd3 = -1;
if (pointSearchSqDis[0] < nearestFeatureSearchSqDist) {
closestPointInd = pointSearchInd[0];
int closestPointScan = int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].intensity);
float pointSqDis, minPointSqDis2 = nearestFeatureSearchSqDist, minPointSqDis3 = nearestFeatureSearchSqDist;
for (int j = closestPointInd + 1; j < surfPointsFlatNum; j++) {
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) > closestPointScan + 2.5) {
break;
}
pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) <= closestPointScan) {
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2) {
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
} else {
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3) {
minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd3 = j;
}
}
}
for (int j = closestPointInd - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) < closestPointScan - 2.5) {
break;
}
pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) >= closestPointScan) {
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2) {
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
} else {
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3) {
minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd3 = j;
}
}
}
}
// 2.2 查找l和m
pointSearchSurfInd1[i] = closestPointInd;
pointSearchSurfInd2[i] = minPointInd2;
pointSearchSurfInd3[i] = minPointInd3;
}
if (pointSearchSurfInd2[i] >= 0 && pointSearchSurfInd3[i] >= 0) {
tripod1 = laserCloudSurfLast->points[pointSearchSurfInd1[i]];
tripod2 = laserCloudSurfLast->points[pointSearchSurfInd2[i]];
tripod3 = laserCloudSurfLast->points[pointSearchSurfInd3[i]];
float pa = (tripod2.y - tripod1.y) * (tripod3.z - tripod1.z)
- (tripod3.y - tripod1.y) * (tripod2.z - tripod1.z);
float pb = (tripod2.z - tripod1.z) * (tripod3.x - tripod1.x)
- (tripod3.z - tripod1.z) * (tripod2.x - tripod1.x);
float pc = (tripod2.x - tripod1.x) * (tripod3.y - tripod1.y)
- (tripod3.x - tripod1.x) * (tripod2.y - tripod1.y);
float pd = -(pa * tripod1.x + pb * tripod1.y + pc * tripod1.z);
float ps = sqrt(pa * pa + pb * pb + pc * pc);
pa /= ps;
pb /= ps;
pc /= ps;
pd /= ps;
float pd2 = pa * pointSel.x + pb * pointSel.y + pc * pointSel.z + pd;
float s = 1;
if (iterCount >= 5) {
s = 1 - 1.8 * fabs(pd2) / sqrt(sqrt(pointSel.x * pointSel.x
+ pointSel.y * pointSel.y + pointSel.z * pointSel.z));
}
// 3. 计算回归系数
if (s > 0.1 && pd2 != 0) {
coeff.x = s * pa;
coeff.y = s * pb;
coeff.z = s * pc;
coeff.intensity = s * pd2;
laserCloudOri->push_back(surfPointsFlat->points[i]);
coeffSel->push_back(coeff);
}
}
}
}
最小二乘法求解
通过回归系数求解坐标转换Transformation[4]
bool calculateTransformationSurf(int iterCount){
int pointSelNum = laserCloudOri->points.size();
cv::Mat matA(pointSelNum, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAt(3, pointSelNum, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtA(3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matB(pointSelNum, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtB(3, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matX(3, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
float srx = sin(transformCur[0]);
float crx = cos(transformCur[0]);
float sry = sin(transformCur[1]);
float cry = cos(transformCur[1]);
float srz = sin(transformCur[2]);
float crz = cos(transformCur[2]);
float tx = transformCur[3];
float ty = transformCur[4];
float tz = transformCur[5];
float a1 = crx*sry*srz; float a2 = crx*crz*sry; float a3 = srx*sry; float a4 = tx*a1 - ty*a2 - tz*a3;
float a5 = srx*srz; float a6 = crz*srx; float a7 = ty*a6 - tz*crx - tx*a5;
float a8 = crx*cry*srz; float a9 = crx*cry*crz; float a10 = cry*srx; float a11 = tz*a10 + ty*a9 - tx*a8;
float b1 = -crz*sry - cry*srx*srz; float b2 = cry*crz*srx - sry*srz;
float b5 = cry*crz - srx*sry*srz; float b6 = cry*srz + crz*srx*sry;
float c1 = -b6; float c2 = b5; float c3 = tx*b6 - ty*b5; float c4 = -crx*crz; float c5 = crx*srz; float c6 = ty*c5 + tx*-c4;
float c7 = b2; float c8 = -b1; float c9 = tx*-b2 - ty*-b1;
for (int i = 0; i < pointSelNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudOri->points[i];
coeff = coeffSel->points[i];
float arx = (-a1*pointOri.x + a2*pointOri.y + a3*pointOri.z + a4) * coeff.x
+ (a5*pointOri.x - a6*pointOri.y + crx*pointOri.z + a7) * coeff.y
+ (a8*pointOri.x - a9*pointOri.y - a10*pointOri.z + a11) * coeff.z;
float arz = (c1*pointOri.x + c2*pointOri.y + c3) * coeff.x
+ (c4*pointOri.x - c5*pointOri.y + c6) * coeff.y
+ (c7*pointOri.x + c8*pointOri.y + c9) * coeff.z;
float aty = -b6 * coeff.x + c4 * coeff.y + b2 * coeff.z;
float d2 = coeff.intensity;
matA.at<float>(i, 0) = arx;
matA.at<float>(i, 1) = arz;
matA.at<float>(i, 2) = aty;
matB.at<float>(i, 0) = -0.05 * d2;
}
cv::transpose(matA, matAt);
matAtA = matAt * matA;
matAtB = matAt * matB;
// 1. 最小二乘法求解
cv::solve(matAtA, matAtB, matX, cv::DECOMP_QR);
if (iterCount == 0) {
cv::Mat matE(1, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV(3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV2(3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::eigen(matAtA, matE, matV);
matV.copyTo(matV2);
isDegenerate = false;
float eignThre[3] = {10, 10, 10};
for (int i = 2; i >= 0; i--) {
if (matE.at<float>(0, i) < eignThre[i]) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
matV2.at<float>(i, j) = 0;
}
isDegenerate = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
matP = matV.inv() * matV2;
}
if (isDegenerate) {
cv::Mat matX2(3, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
matX.copyTo(matX2);
matX = matP * matX2;
}
transformCur[0] += matX.at<float>(0, 0);
transformCur[2] += matX.at<float>(1, 0);
transformCur[4] += matX.at<float>(2, 0);
float deltaR = sqrt(
pow(rad2deg(matX.at<float>(0, 0)), 2) +
pow(rad2deg(matX.at<float>(1, 0)), 2));
float deltaT = sqrt(
pow(matX.at<float>(2, 0) * 100, 2));
// 2. 结果收敛则返回
if (deltaR < 0.1 && deltaT < 0.1) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
总结
LeGO-LOAM的特征提取实际上是提取面特征和线特征,然后利用最小二乘法做特征匹配,得到当前最优的坐标转换关系。当然上述过程涉及大量公式推导,有些地方也没有完全看懂,后续会继续补充。
























 1452
1452

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








