类(Class)是一种数据类型,即符合该类型的数据都可以归到你定义的类中。所以要定义一个类,就必须弄清楚其特点及其作用。计算机软件各种功能不再是简单的四则运算能实现的了,因此,需要创建区别与int、char、bool等数据类型的新数据类型——类,来实现更复杂的运算。
当然,不使用类也能完成复杂的运算,面向对象的概念出现之前就是靠工程师们强大的逻辑思维来实现的。但是当面向对象的编程思想出现后,类出现后,内核的技术人员将各个相同属性的数据封装成类,形成一个个对象,令上层的开发人员能直接通过对各对象进行调度来开发软件。
这就好比集成电路,大量门电路集成(封装)为加法器,触发器等逻辑电路。而各种逻辑电路又集成(封装)为放大器,比较器等单元电路。而大量单元电路集成(封装)为CPU,RAM,ROM。上层的设计师不了解内部构造,也不能修改封装好的对象,但不影响其使用。反而加快了开发效率。这就是面向对象的编程思想,这就是类的作用。
本次实验使用Visual Studio 2012,创建一个货币类,并且使用它。
例子来源:《数据结构、算法与应用 C++语言描述》机械工业出版社
创建项目及相应的头文件,源程序文件
TheClass.h
/****************************************************************
*Name: TheClass.h
*Content: The definition of currency and illegalParameterValue
*Instructions: Used to define some classes
*Version: V1.0
*Author: Caddress
*Data: 20160226
***************************************************************/
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//Define an enumerated type
enum signType{plus, minus};
/**********************************************************
*Class: currency
*Members: amount
*Instructions: Class about currency
*Data Version Author Content
*----------------------------------------------------------
*20160226 V1.0 Caddress Declaration
***********************************************************/
class currency
{
public:
//The constructor definition
currency(signType theSign = plus,
unsigned long theDollars = 0,
unsigned int theCent = 0);
//The destructor
~currency() {}
//Two member function for assignment
void setValue(signType, unsigned long, unsigned int);
void setValue(double);
//Get the currency symbol
signType getSign() const
{if (amount < 0) return minus;
else return plus;}
//Get the dollar value
unsigned long getDollars() const
{if (amount < 0) return (-amount)/100;
else return amount / 100;}
//Get the cent value
unsigned int getCents() const
{if (amount < 0) return -amount - getDollars() * 100;
else return amount - getDollars() * 100;}
//Reloading the "+" operator
currency operator+(const currency&) const;
//Reloading the "+=" operator
currency operator+=(const currency& x)
{amount += x.amount; return *this;}
//For the output in the specified format
void output(ostream&) const;
private:
long amount;
};
/**********************************************************
*Class: illegalParameterValue
*Members: message
*Instructions: Class about Anomaly detection
*Data Version Author Content
*----------------------------------------------------------
*20160226 V1.0 Caddress Declaration
***********************************************************/
class illegalParameterValue
{
public:
illegalParameterValue():
message("Illegal parameter value"){}
illegalParameterValue(char* theMessage)
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
//The constructor definition
currency::currency(signType theSign, unsigned long theDollars, unsigned int theCents)
{
setValue( theSign, theDollars, theCents);
}
//Three parameters initialization
void currency::setValue(signType theSign, unsigned long theDollars, unsigned int theCents)
{
if(theCents > 99)
throw illegalParameterValue("Cents should be < 100");
amount = theDollars * 100 + theCents;
if(theSign == minus) amount = -amount;
}
//Single parameter initialization
void currency::setValue(double theAmount)
{
if (theAmount < 0)
amount = (long) ((theAmount - 0.001) * 100);
else
amount = (long) ((theAmount + 0.001) * 100);
}
//Reloading the "+" operator.The definition.
currency currency::operator+(const currency& x) const
{
currency result;
result.amount = amount + x.amount;
return result;
}
//The definition of output function.
void currency::output(ostream& out) const
{
long theAmount = amount;
if (theAmount < 0) {out << '-'; theAmount = -theAmount;}
long dollars = theAmount / 100;
out << '$' << dollars << '.';
int cents = theAmount -dollars * 100;
if(cents < 10) out << '0';
out << cents;
}
//Reloading the "<<" operator.The definition.
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const currency& x)
{ x.output(out); return out;}
TheClass.cpp
/********************************************************************
*Name: TheClass.cpp
*Content: main function
*Instructions: Testing can be used currency class normally
*Version: V1.0
*Author: Caddress
*Data: 20160226
*********************************************************************/
#include "TheClass.h"
/**********************************************************
*Function: main
*Input: void
*Output: string of results
*Return: 0
*Data Version Author Content
*----------------------------------------------------------
*20160226 V1.0 Caddress create
***********************************************************/
int main()
{
currency g, h(plus, 3, 50), i, j;
g.setValue(minus, 2, 25);
i.setValue(-6.45);
j = h + g;
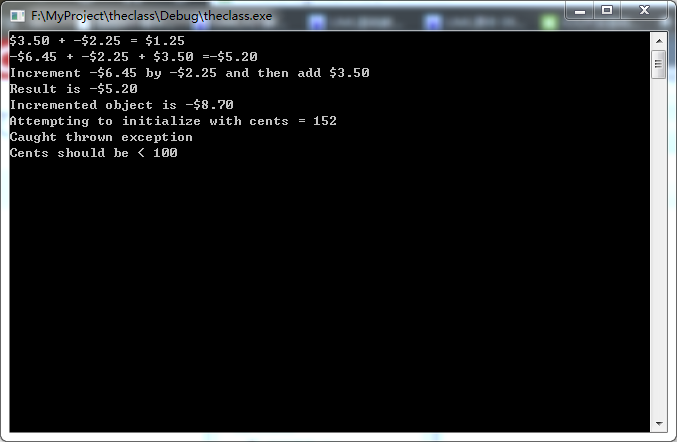
cout << h << " + " << g << " = " << j << endl;
j = i + g + h;
cout << i << " + " << g << " + " << h << " =" << j << endl;
cout << "Increment " << i << " by " << g << " and then add " << h << endl;
j = (i += g) + h;
cout << "Result is " << j << endl;
cout << "Incremented object is " << i << endl;
cout << "Attempting to initialize with cents = 152" << endl;
try {i.setValue(plus, 3, 152);}
catch (illegalParameterValue e)
{
cout << "Caught thrown exception" << endl;
e.outputMessage();
}
getchar();
return 0;
}运行结果






















 1307
1307

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








