1、googleNet—Inception V1结构
googlenet的主要思想就是围绕这两个思路去做的:
(1).深度,层数更深,文章采用了22层,为了避免上述提到的梯度消失问题,googlenet巧妙的在不同深度处增加了两个loss(辅助分类器)来保证梯度回传消失的现象。
(2).宽度,增加了多种核 1x1,3x3,5x5,还有直接max pooling的 但是如果简单的将这些应用到feature map上的话,concat起来的feature map厚度将会很大,所以在googlenet中为了避免这一现象提出的inception具有如下结构,在3x3前,5x5前, max pooling后分别加上了1x1的卷积核起到了降低feature map厚度的作用。

对上图做如下说明:
( 1 ) 显然GoogLeNet采用了Inception模块化(9个)的结构,共22层,方便增添和修改;
( 2 ) 网络最后采用了 average pooling来代替全连接层 ,想法来自NIN,参数量仅为AlexNet的1/12,性能优于AlexNet,
事实证明可以将TOP1 accuracy提高0.6%。 但是, 实际在最后还是加了一个全连接层 ,主要是为了方便finetune;
( 3 ) 虽然移除了全连接,但是 网络中依然使用了Dropout ;
( 4 ) 为了 避免梯度消失,网络额外增加了2个辅助的softmax用于向前传导梯度 。
文章中说这两个辅助的分类器的loss应该加一个衰减系数,但看caffe中的model也没有加任何衰减。此外, 实际测试的时候,这两个额外的softmax会被去掉 。
2、Inception V2结构
·问题:大尺寸的卷积核可以带来更大的感受野,也意味着更多的参数,比如5x5卷积核参数是3x3卷积核的25/9=2.78倍
为此,作者提出可以用2个连续的3x3卷积层(stride=1)组成的小网络来代替单个的5x5卷积层,这便是Inception V2结构,
保持感受野范围的同时又减少了参数量,如下图:




3、Inception V3结构
大卷积核完全可以由一系列的3x3卷积核来替代,那能不能分解的更小一点呢。文章考虑了 nx1 卷积核,如下图所示的取代3x3卷积:
于是,任意nxn的卷积都可以通过1xn卷积后接nx1卷积来替代。实际上,作者发现在网络的前期使用这种分解效果并不好,还有在中度大小的feature map上使用效果才会更好,对于mxm大小的feature map,建议m在12到20之间。
用nx1卷积来代替大卷积核,这里设定n=7来应对17x17大小的feature map。该结构被正式用在GoogLeNet V2中。




4、整体架构代码实现
GoogLeNet.py文件实现Inception v3网络前向传播过程以及网络的参数:
(一)slim应用介绍
slim这个模块是在16年新推出的,其主要目的是来做所谓的“代码瘦身”。
tensorflow官方对它的描述是:此目录中的任何代码未经官方支持,可能会随时更改或删除。每个目录下都有指定的所有者。它旨在包含额外功能和贡献,最终会合并到核心TensorFlow中,但其接口可能仍然会发生变化,或者需要进行一些测试,看是否可以获得更广泛的接受。所以slim依然不属于原生tensorflow。
slim是一个使构建,训练,评估神经网络变得简单的库。它可以消除原生tensorflow里面很多重复的模板性的代码,让代码更紧凑,更具备可读性。另外slim提供了很多计算机视觉方面的著名模型(VGG, AlexNet等),我们不仅可以直接使用,甚至能以各种方式进行扩展。
1、slim的导入方法

2、slim子模块及功能介绍
(1)arg_scope:
除了基本的namescope,variabelscope外,又加了arg_scope,它是用来控制每一层的默认超参数的。如果你的网络有大量相同的参数,如下所示:
net = slim.conv2d(inputs, 64, [11, 11], 4, padding='SAME',
weights_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01),
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(0.0005), scope='conv1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [11, 11], padding='VALID',
weights_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01),
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(0.0005), scope='conv2')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [11, 11], padding='SAME',
weights_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01),
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(0.0005), scope='conv3')
用arg_scope处理一下:(有点像公共域的使用)
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], padding='SAME',
weights_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01)
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(0.0005)):
net = slim.conv2d(inputs, 64, [11, 11], scope='conv1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [11, 11], padding='VALID', scope='conv2')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [11, 11], scope='conv3')
arg_scope作用范围内:是定义了 指定层的默认参数 ,若想 特别指定某些层的参数,可以重新赋值 (相当于重写)
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected],
activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
weights_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01),
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(0.0005)):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], stride=1, padding='SAME'):
net = slim.conv2d(inputs, 64, [11, 11], 4, padding='VALID', scope='conv1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [5, 5],
weights_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.03),
scope='conv2')
net = slim.fully_connected(net, 1000, activation_fn=None, scope='fc')
(2)layers:
这个比较重要,slim的核心和精髓,一些复杂层的定义。
对比分别用tensorflow和slim实现一个卷积层的案例:
#tensorflow实现卷积层
with tf.name_scope('conv1_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 64, 128], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
#slim实现卷积层
net = slim.conv2d(input, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv1_1')
比较吸引人的是slim中的repeat和stack操作,假设定义三个相同的卷积层,在slim中的repeat操作可减少代码量:
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_2')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_3')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2')
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2')
stack是处理卷积核或者输出不一样的情况 :假设定义三层FC:
# Verbose way:
x = slim.fully_connected(x, 32, scope='fc/fc_1')
x = slim.fully_connected(x, 64, scope='fc/fc_2')
x = slim.fully_connected(x, 128, scope='fc/fc_3')
使用stack操作:
slim.stack(x, slim.fully_connected, [32, 64, 128], scope='fc')
卷积层使用stack的方法:
# 普通方法:
x = slim.conv2d(x, 32, [3, 3], scope='core/core_1')
x = slim.conv2d(x, 32, [1, 1], scope='core/core_2')
x = slim.conv2d(x, 64, [3, 3], scope='core/core_3')
x = slim.conv2d(x, 64, [1, 1], scope='core/core_4')
# 简便方法:
slim.stack(x, slim.conv2d, [(32, [3, 3]), (32, [1, 1]), (64, [3, 3]), (64, [1, 1])], scope='core')
(3)nets:
包含一些经典网络,VGG等,用的也比较多.
(4)variables:
这个比较有用,slim管理变量的机制.
变量分为两类:模型变量和局部变量。局部变量是不作为模型参数保存的,而模型变量会再save的时候保存下来。诸如global_step之类的就是局部变量。slim中可以写明变量存放的设备,正则和初始化规则。还有获取变量的函数也需要注意一下,get_variables是返回所有的变量。
slim中定义一个变量的实例:
# Model Variables
weights = slim.model_variable('weights',
shape=[10, 10, 3 , 3],
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1),
regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(0.05),
device='/CPU:0')
model_variables = slim.get_model_variables()
# Regular variables
my_var = slim.variable('my_var',
shape=[20, 1],
initializer=tf.zeros_initializer())
regular_variables_and_model_variables = slim.get_variables()
(5)regularizers:
包含一些正则规则.
(6)metrics:
评估模型的度量标准.
(7)queues:
文本队列管理,比较有用。
(8)learning、losses
(二)inception_v3的网络结构

(三)inception_v3用slim实现的具体步骤及代码
1、定义函数 inception_v3_arg_scope 用来生成网络中经常用到的函数的默认参数


import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim
#定义简单的函数产生截断的正态分布
trunc_normal = lambda stddev:tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.0,stddev)
#定义函数 inception_v3_arg_scope 用来生成网络中经常用到的函数的默认参数
def inception_v3_arg_scope(weight_decay=0.00004,stddev=0.1,
batch_norm_var_collection="moving_vars"):
batch_norm_params = {
"decay":0.9997,"epsilon":0.001,"updates_collections":tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
"variables_collections":{
"beta":None,"gamma":None,"moving_mean":[batch_norm_var_collection],
"moving_variance":[batch_norm_var_collection]
}
}
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d,slim.fully_connected],
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay)):
#对卷积层生成函数的几个参数赋予默认值
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d],
weights_regularizer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=stddev),
activation_fc = tf.nn.relu,
normalizer_fc = slim.batch_norm,
normalizer_params = batch_norm_params) as scope:
return scope
2、定义Inception V3的卷积部分

#定义Inception V3的卷积部分
def inception_v3_base(inputs,scope=None):
end_points = {}
with tf.variable_scope(scope,"InceptionV3",[inputs]):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d,slim.max_pool2d,slim.avg_pool2d],
stride = 1,padding = "VALID"):
net = slim.conv2d(inputs,num_outputs=32,kernel_size=[3,3],stride=2,scope="Conv2d_1a_3x3")
net = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=32,kernel_size=[3,3],scope="Conv2d_2a_3x3")
net = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=64,kernel_size=[3,3],padding="SAME",scope="Conv2d_2b_3x3")
net = slim.max_pool2d(net,kernel_size=[3,3],stride=2,scope="MaxPool_3a_3x3")
net = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=80,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_3b_1x1")
net = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=192,kernel_size=[3,3],scope="Conv2d_4a_3x3")
net = slim.max_pool2d(net,kernel_size=[3,3],stride=2,scope="MaxPool_5a_3x3")
3.1、定义第一个Inception模块组

#定义第一个Inception模块组
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d,slim.max_pool2d,slim.avg_pool2d],
stride = 1,padding = "SAME"):
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_5b"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=64,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=48,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1,num_outputs=64,kernel_size=[5,5],scope="Conv2d_0b_5x5")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=64,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2,num_outputs=96,kernel_size=[3,3],scope="Conv2d_0b_3x3")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2,num_outputs=96,kernel_size=[3,3],scope="Conv2d_0c_3x3")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_3"):
batch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net,kernel_size=[3,3],scope="AvgPool_0a_3x3")
batch_3 = slim.conv2d(batch_3,num_outputs=32,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
net = tf.concat([batch_0,batch_1,batch_2,batch_3],3)

# 第二个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_5c"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=48, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[5, 5], scope="Conv2d_0c_5x5")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=96, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="Conv2d_0b_3x3")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=96, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="Conv2d_0c_3x3")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_3"):
batch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="AvgPool_0a_3x3")
batch_3 = slim.conv2d(batch_3, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2, batch_3], 3)
# 第三个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_5d"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=48, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[5, 5], scope="Conv2d_0c_5x5")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=96, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="Conv2d_0b_3x3")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=96, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="Conv2d_0c_3x3")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_3"):
batch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="AvgPool_0a_3x3")
batch_3 = slim.conv2d(batch_3, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2, batch_3], 3)```
###### 3.2、定义第二个Inception模块组
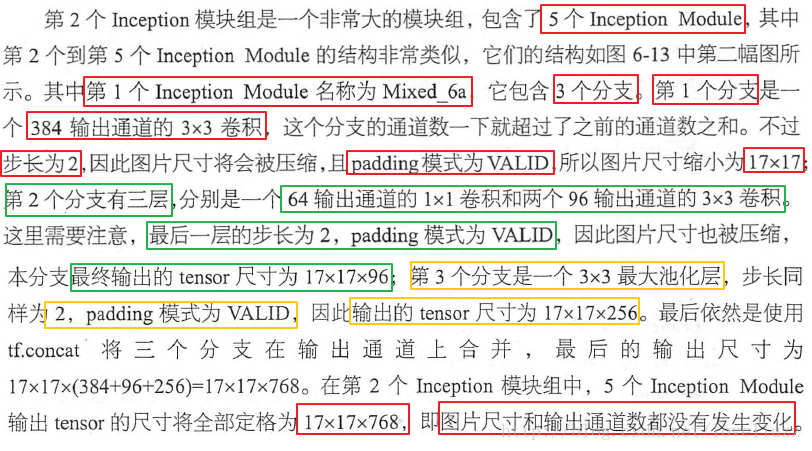
```python
# 定义第二个Inception模块组,第一个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_6a"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=384, kernel_size=[3,3],
stride=2, padding="VALID",scope="Conv2d_1a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=96, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="Conv2d_0b_3x3")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=96, kernel_size=[3, 3],
stride=2, padding="VALID",scope="Conv2d_1a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.max_pool2d(net,kernel_size=[3,3],stride=2,padding="VALID",
scope="MaxPool_1a_3x3")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2], 3)

# 定义第二个Inception模块组,第一个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_6b"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=192,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=128, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=128, kernel_size=[1,7], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x7")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[7, 1],scope="Conv2d_0c_7x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=128, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=128, kernel_size=[7, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_7x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=128, kernel_size=[1, 7], scope="Conv2d_0c_1x7")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=128, kernel_size=[7, 1], scope="Conv2d_0d_7x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 7], scope="Conv2d_0e_1x7")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_3"):
batch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="AvgPool_0a_3x3")
batch_3 = slim.conv2d(batch_3, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2,batch_3], 3)

# 定义第二个Inception模块组,第三个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_6c"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=192,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1,7], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x7")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[7, 1],scope="Conv2d_0c_7x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[7, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_7x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1, 7], scope="Conv2d_0c_1x7")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[7, 1], scope="Conv2d_0d_7x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 7], scope="Conv2d_0e_1x7")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_3"):
batch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="AvgPool_0a_3x3")
batch_3 = slim.conv2d(batch_3, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2,batch_3], 3)
# 定义第二个Inception模块组,第四个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_6d"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=192,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1,7], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x7")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[7, 1],scope="Conv2d_0c_7x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[7, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_7x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1, 7], scope="Conv2d_0c_1x7")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[7, 1], scope="Conv2d_0d_7x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 7], scope="Conv2d_0e_1x7")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_3"):
batch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="AvgPool_0a_3x3")
batch_3 = slim.conv2d(batch_3, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2,batch_3], 3)
# 定义第二个Inception模块组,第五个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_6e"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=192,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1,7], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x7")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[7, 1],scope="Conv2d_0c_7x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[7, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_7x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[1, 7], scope="Conv2d_0c_1x7")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=160, kernel_size=[7, 1], scope="Conv2d_0d_7x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 7], scope="Conv2d_0e_1x7")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_3"):
batch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, kernel_size=[3, 3], scope="AvgPool_0a_3x3")
batch_3 = slim.conv2d(batch_3, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2,batch_3], 3)
end_points["Mixed_6e"] = net #第二个模块组的最后一个Inception模块,将Mixed_6e存储于end_points中
3.3、定义第三个Inception模块组

# 定义第三个Inception模块组,第一个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_7a"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=320, kernel_size=[3, 3],stride=2,
padding="VALID",scope="Conv2d_1a_3x3")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[1,7], scope="Conv2d_0b_1x7")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[7, 1],scope="Conv2d_0c_7x1")
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(batch_1, num_outputs=192, kernel_size=[3, 3], stride=2,
padding="VALID",scope="Conv2d_1a_3x3")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.max_pool2d(net, kernel_size=[3, 3], stride=2, padding="VALID",
scope="MaxPool_1a_3x3")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2], 3)

# 定义第三个Inception模块组,第二个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_7b"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=320, kernel_size=[1, 1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=384, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_1 = tf.concat([
slim.conv2d(batch_1,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[1,3],scope="Conv2d_0b_1x3"),
slim.conv2d(batch_1,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[3,1],scope="Conv2d_0b_3x1")],axis=3)
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=448,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[3,3],scope="Conv2d_0b_3x3")
batch_2 = tf.concat([
slim.conv2d(batch_2,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[1,3],scope="Conv2d_0c_1x3"),
slim.conv2d(batch_2,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[3,1],scope="Conv2d_0d_3x1")],axis=3)
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_3"):
batch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net,kernel_size=[3,3],scope="AvgPool_0a_3x3")
batch_3 = slim.conv2d(batch_3,num_outputs=192,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2,batch_3], 3)
# 定义第三个Inception模块组,第三个Inception模块
with tf.variable_scope("Mixed_7c"):
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_0"):
batch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=320, kernel_size=[1, 1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_1"):
batch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, num_outputs=384, kernel_size=[1, 1], scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_1 = tf.concat([
slim.conv2d(batch_1,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[1,3],scope="Conv2d_0b_1x3"),
slim.conv2d(batch_1,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[3,1],scope="Conv2d_0b_3x1")],axis=3)
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_2"):
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=448,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0a_1x1")
batch_2 = slim.conv2d(batch_2,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[3,3],scope="Conv2d_0b_3x3")
batch_2 = tf.concat([
slim.conv2d(batch_2,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[1,3],scope="Conv2d_0c_1x3"),
slim.conv2d(batch_2,num_outputs=384,kernel_size=[3,1],scope="Conv2d_0d_3x1")],axis=3)
with tf.variable_scope("Branch_3"):
batch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net,kernel_size=[3,3],scope="AvgPool_0a_3x3")
batch_3 = slim.conv2d(batch_3,num_outputs=192,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_0b_1x1")
net = tf.concat([batch_0, batch_1, batch_2,batch_3], 3)
return net,end_points
4、Inception网络最后一部分——全局平均池化、softmax和Auxiliary Logits(辅助分类的节点)



def inception_v3(inputs,num_classes=1000,is_training=True,droupot_keep_prob = 0.8,
prediction_fn = slim.softmax,spatial_squeeze = True,reuse = None,scope="InceptionV3"):
"""
InceptionV3整个网络的构建
param :
inputs -- 输入tensor
num_classes -- 最后分类数目
is_training -- 是否是训练过程
droupot_keep_prob -- dropout保留节点比例
prediction_fn -- 最后分类函数,默认为softmax
patial_squeeze -- 是否对输出去除维度为1的维度
reuse -- 是否对网络和Variable重复使用
scope -- 函数默认参数环境
return:
logits -- 最后输出结果
end_points -- 包含辅助节点的重要节点字典表
"""
with tf.variable_scope(scope,"InceptionV3",[inputs,num_classes],
reuse=reuse) as scope:
with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm,slim.dropout],
is_training = is_training):
net,end_points = inception_v3_base(inputs,scope=scope) #前面定义的整个卷积网络部分
#辅助分类节点部分
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d,slim.max_pool2d,slim.avg_pool2d],
stride = 1,padding = "SAME"):
#通过end_points取到Mixed_6e
aux_logits = end_points["Mixed_6e"]
with tf.variable_scope("AuxLogits"):
aux_logits = slim.avg_pool2d(aux_logits,kernel_size=[5,5],stride=3,
padding="VALID",scope="Avgpool_1a_5x5")
aux_logits = slim.conv2d(aux_logits,num_outputs=128,kernel_size=[1,1],scope="Conv2d_1b_1x1")
aux_logits = slim.conv2d(aux_logits,num_outputs=768,kernel_size=[5,5],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.01),padding="VALID",
scope="Conv2d_2a_5x5")
aux_logits = slim.conv2d(aux_logits,num_outputs=num_classes,kernel_size=[1,1],
activation_fn=None,normalizer_fn=None,
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.001),scope="Conv2d_1b_1x1")
#消除tensor中前两个维度为1的维度
if spatial_squeeze:
aux_logits = tf.squeeze(aux_logits,axis=[1,2],name="SpatialSqueeze")
end_points["AuxLogits"] = aux_logits #将辅助节点分类的输出aux_logits存到end_points中
#正常分类预测
with tf.variable_scope("Logits"):
net = slim.avg_pool2d(net,kernel_size=[8,8],padding="VALID",
scope="Avgpool_1a_8x8")
net = slim.dropout(net,keep_prob=droupot_keep_prob,scope="Dropout_1b")
end_points["Logits"] = net
logits = slim.conv2d(net,num_outputs=num_classes,kernel_size=[1,1],activation_fn=None,
normalizer_fn=None,scope="Conv2d_1c_1x1")
if spatial_squeeze:
logits = tf.squeeze(logits,axis=[1,2],name="SpatialSqueeze")
end_points["Logits"] = logits
end_points["Predictions"] = prediction_fn(logits,scope="Predictions")
return logits,end_points






















 6684
6684

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








