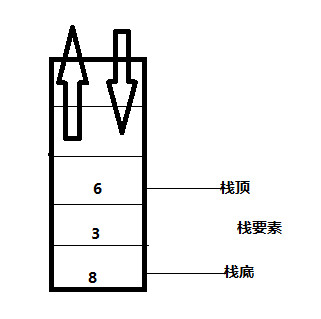
在计算机中栈是一种机制,栈机制是指后进先出LIFO(last in first out),比如我们使用电梯的时候就是后进入电梯的人先出去,栈的基本机制如下图所示:
一、栈的基本机制及实现
下面我们简单实现一下栈的机制,包括入栈,出栈,栈的遍历等,定义一个MyStack.h如下:
#ifndef MYSTACK_H
#define MYSTACK_H
class MyStack{
public:
MyStack(int size); //分配内存初始化栈空间,设定栈容量,栈顶
~MyStack(); //回收空间内存
bool stackEmpty(); //判定栈是否为空,为空返回true,非空返回false
bool stackFull(); //判定栈是否已满,为满返回true,不满返回false
void clearStack(); //清空栈
int stackLength(); //已有元素的个数
bool push(char elem); //元素入栈,栈顶上升
bool pop(char &elem); //元素出栈,栈顶下降
void stackTraverse(bool isFromButton); //遍历栈中所有元素
private:
char *m_pBuffer; //栈空间指针
int m_iSize; //栈容量
int m_iTop; //栈顶,栈中元素个数
};
#endif#include "MyStack.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
MyStack::MyStack(int size){
m_iSize = size;
m_pBuffer = new char[size];
m_iTop = 0;
}
MyStack::~MyStack(){
delete[]m_pBuffer;
}
bool MyStack::stackEmpty(){
if (0==m_iTop)//if (m_iTop==0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyStack::stackFull(){
if (m_iTop==m_iSize)//>=
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void MyStack::clearStack(){
m_iTop = 0;
}
int MyStack::stackLength(){
return m_iTop;
}
bool MyStack::push(char elem){
if (stackFull())
{
return false;
}
m_pBuffer[m_iTop] = elem;
m_iTop++;
return true;
}
bool MyStack::pop(char &elem){
if (stackEmpty())
{
return false;
}
m_iTop--;
elem = m_pBuffer[m_iTop];
return true;
}
void MyStack::stackTraverse(bool isFromButton){
if (isFromButton == true)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_iTop; i++)
{
cout << m_pBuffer[i] << ",";
}
cout << endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = m_iTop - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
cout << m_pBuffer[i] << ",";
}
cout << endl;
}
}#include "MyStack.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/************************************************************************/
/* 掌握栈的实现原理和运行机制 */
/************************************************************************/
int main(void){
MyStack *pStack = new MyStack(5);
pStack->push('h');//底
pStack->push('e');
pStack->push('l');
pStack->push('l');
pStack->push('o');//顶
pStack->stackTraverse(true);
char elem = 0;
pStack->pop(elem);
cout << elem << endl;
pStack->stackTraverse(false);
//pStack->clearStack();
if (pStack->stackEmpty())
{
cout << "栈为空" << endl;
}
if (pStack->stackFull())
{
cout << "栈为满" << endl;
}
delete pStack;
pStack = NULL;
system("pause");
}
二、栈的改造适用于坐标类Coordinate(int x, int y)
接下来我们对栈的进行扩展改变,使其可以适用于坐标类Coordinate(int x, int y),MyStack.h修改为
#ifndef MYSTACK_H
#define MYSTACK_H
#include "Coordinate.h"
class MyStack{
public:
MyStack(int size); //分配内存初始化栈空间,设定栈容量,栈顶
~MyStack(); //回收空间内存
bool stackEmpty(); //判定栈是否为空,为空返回true,非空返回false
bool stackFull(); //判定栈是否已满,为满返回true,不满返回false
void clearStack(); //清空栈
int stackLength(); //已有元素的个数
bool push(Coordinate elem); //元素入栈,栈顶上升 传值有值的复制
bool pop(Coordinate &elem); //元素出栈,栈顶下降
void stackTraverse(bool isFromButton); //遍历栈中所有元素
private:
Coordinate *m_pBuffer; //栈空间指针
int m_iSize; //栈容量
int m_iTop; //栈顶,栈中元素个数
};
#endif#include "MyStack.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
MyStack::MyStack(int size){
m_iSize = size;
m_pBuffer = new Coordinate[size];
m_iTop = 0;
}
MyStack::~MyStack(){
delete[]m_pBuffer;
}
bool MyStack::stackEmpty(){
if (0==m_iTop)//if (m_iTop==0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyStack::stackFull(){
if (m_iTop==m_iSize)//>=
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void MyStack::clearStack(){
m_iTop = 0;
}
int MyStack::stackLength(){
return m_iTop;
}
bool MyStack::push(Coordinate elem){
if (stackFull())
{
return false;
}
m_pBuffer[m_iTop] = elem; //Coordinate类只是普通的值 只需要简单的复制即可
m_iTop++;
return true;
}
bool MyStack::pop(Coordinate &elem){
if (stackEmpty())
{
return false;
}
m_iTop--;
elem = m_pBuffer[m_iTop];
return true;
}
void MyStack::stackTraverse(bool isFromButton){
if (isFromButton == true)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_iTop; i++)
{
//cout << m_pBuffer[i] << ",";
m_pBuffer[i].printCoordinate();
}
cout << endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = m_iTop - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
//cout << m_pBuffer[i] << ",";
m_pBuffer[i].printCoordinate();
}
cout << endl;
}
}#ifndef CORRDINATE_H
#define CORRDINATE_H
class Coordinate{
public:
Coordinate(int x = 0, int y = 0);
void printCoordinate();
private:
int m_iX;
int m_iY;
};
#endif#include "Coordinate.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Coordinate::Coordinate(int x, int y){
m_iX = x;
m_iY = y;
}
void Coordinate::printCoordinate(){
cout << "(" << m_iX << "," << m_iY << ")" << endl;
}#include "MyStack.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "Coordinate.h"
/************************************************************************/
/*
栈
要求:
1.定义Coordinate坐标类
2.改造栈类,使其可以适用于坐标类
目的:灵活掌握栈机制,理解抽象数据类型在栈中的应用
*/
/************************************************************************/
int main(void){
MyStack *pStack = new MyStack(5);
pStack->push(Coordinate(1, 2)); //底
pStack->push(Coordinate(3, 4));
pStack->stackTraverse(true);
pStack->stackTraverse(false);
//pStack->clearStack();
cout << pStack->stackLength() << endl;
if (pStack->stackEmpty())
{
cout << "栈为空" << endl;
}
if (pStack->stackFull())
{
cout << "栈为满" << endl;
}
delete pStack;
pStack = NULL;
system("pause");
}
注意:
1.
bool push(Coordinate elem); //元素入栈,栈顶上升 传值有值的复制
bool pop(Coordinate &elem); //元素出栈,栈顶下降这里我们push和pop进去的是对象,如果放进去的是一个对象的话就意味着将来传的是值,传值就意味着会发生值的复制,所以如果我们的Coordinate 对象很复杂(在它的数据成员中不是基本的数据类型而是指针,指针又在构造函数中分配了一块内存),这时候我们就需要写拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符。当数据类型比较简单的时候它进行值复制就可以了,所以我们使用默认的拷贝构造函数和默认的赋值运算符重载就可以了。
2.如果我们想要别的数据类型怎么办呢?我们可以使用类模板
三、template <typename T>实现栈的类模板
对于很多编译器并不支持.h和.cpp分开编译对于栈模板我们将MyStack.h和MyStack.cpp进行合并为MyStack.h
#ifndef MYSTACK_H
#define MYSTACK_H
template <typename T>
class MyStack{
public:
MyStack(int size); //分配内存初始化栈空间,设定栈容量,栈顶
~MyStack(); //回收空间内存
bool stackEmpty(); //判定栈是否为空,为空返回true,非空返回false
bool stackFull(); //判定栈是否已满,为满返回true,不满返回false
void clearStack(); //清空栈
int stackLength(); //已有元素的个数
bool push(T elem); //元素入栈,栈顶上升 传值有值的复制
bool pop(T &elem); //元素出栈,栈顶下降
void stackTraverse(bool isFromButton); //遍历栈中所有元素
private:
T *m_pBuffer; //栈空间指针
int m_iSize; //栈容量
int m_iTop; //栈顶,栈中元素个数
};
template<typename T>
MyStack<T>::MyStack(int size){
m_iSize = size;
m_pBuffer = new T[size];
m_iTop = 0;
}
template<typename T>
MyStack<T>::~MyStack(){
delete[]m_pBuffer;
}
template<typename T>
bool MyStack<T>::stackEmpty(){
if (0 == m_iTop)//if (m_iTop==0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
template<typename T>
bool MyStack<T>::stackFull(){
if (m_iTop == m_iSize)//>=
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
template<typename T>
void MyStack<T>::clearStack(){
m_iTop = 0;
}
template<typename T>
int MyStack<T>::stackLength(){
return m_iTop;
}
template<typename T>
bool MyStack<T>::push(T elem){
if (stackFull())
{
return false;
}
m_pBuffer[m_iTop] = elem; //Coordinate类只是普通的值 只需要简单的复制即可
m_iTop++;
return true;
}
template<typename T>
bool MyStack<T>::pop(T &elem){
if (stackEmpty())
{
return false;
}
m_iTop--;
elem = m_pBuffer[m_iTop];
return true;
}
template<typename T>
void MyStack<T>::stackTraverse(bool isFromButton){
if (isFromButton == true)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_iTop; i++)
{
cout << m_pBuffer[i];
//m_pBuffer[i].printCoordinate();
}
cout << endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = m_iTop - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
cout << m_pBuffer[i];
//m_pBuffer[i].printCoordinate();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
#endif#ifndef CORRDINATE_H
#define CORRDINATE_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Coordinate{
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, Coordinate &coor);
public:
Coordinate(int x = 0, int y = 0);
void printCoordinate();
private:
int m_iX;
int m_iY;
};
#endif#include "Coordinate.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Coordinate::Coordinate(int x, int y){
m_iX = x;
m_iY = y;
}
void Coordinate::printCoordinate(){
cout << "(" << m_iX << "," << m_iY << ")" << endl;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, Coordinate &coor){
out << "(" << coor.m_iX << " , " << coor.m_iY << ")" << endl;
return out;
}
#include "MyStack.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "Coordinate.h"
/************************************************************************/
/*
栈
要求:
1.定义Coordinate坐标类
2.改造栈类,使其可以适用于坐标类
目的:灵活掌握栈机制,理解抽象数据类型在栈中的应用
*/
/************************************************************************/
int main(void){
MyStack<Coordinate> *pStack = new MyStack<Coordinate>(5);
pStack->push(Coordinate(1, 2)); //底
pStack->push(Coordinate(3, 4));
pStack->stackTraverse(true);
pStack->stackTraverse(false);
//pStack->clearStack();
cout << pStack->stackLength() << endl;
if (pStack->stackEmpty())
{
cout << "栈为空" << endl;
}
if (pStack->stackFull())
{
cout << "栈为满" << endl;
}
delete pStack;
pStack = NULL;
system("pause");
}四、栈的应用
4.1 栈应用1--数制转换
#include "MyStack.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "Coordinate.h"
/************************************************************************/
/*
栈应用--数制转换
描述:输入任意的十进制正整数N,分别输出该整数N的二进制、八进制、十六进制的数
公式:N = (N div d)* d + N mod d(div表示整除,mod表示求余)
(1348)(十进制) = (2504)(八进制) = (544)(十六进制) = (10101000100)(二进制)
短除法
N N div 8 N mod 8
1348 168 4
168 21 0
21 2 5
2 0 2
N N div 16 N mod 16
1348 84 4
84 5 4
5 0 5
目的:通过实例灵活掌握栈机制的使用技巧
*/
/************************************************************************/
#define BINARY 2
#define OCTONARY 8
#define HEXADECIMAL 16
int main(void){
char num[] = "0123456789ABCDEF";
MyStack<int> *pStack = new MyStack<int>(30);
int N = 2016;
int mod = 0;
while (N != 0)
{
mod = N % HEXADECIMAL;
pStack->push(mod);
N = N / HEXADECIMAL;
}
//pStack->stackTraverse(false);
int elem = 0;
while (!pStack->stackEmpty())
{
pStack->pop(elem);
cout << num[elem];
}
delete pStack;
pStack = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}4.2 栈应用2--括号匹配
#include "MyStack.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "Coordinate.h"
using namespace std;
/************************************************************************/
/*
栈应用--括号匹配
描述:任意输入一组括号,可以判断括号是否匹配
字符窜示例:[()] [()()] [()[)]] [[()]
目的:通过实例灵活掌握栈机制的使用技巧
*/
/************************************************************************/
int main(void){
MyStack<char> *pStack = new MyStack<char>(30);
MyStack<char> *pNeedStack = new MyStack<char>(30);
char str[] = "[()]]";
char currentNeed = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(str);i++)
{
if (str[i] != currentNeed)
{
pStack->push(str[i]);
switch (str[i])
{
case'[':
if (currentNeed != 0)
{
pNeedStack->push(currentNeed);
}
currentNeed = ']';
break;
case'(':
if (currentNeed != 0)
{
pNeedStack->push(currentNeed);
}
currentNeed = ')';
break;
default:
cout << "字符串括号不匹配" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
}
else
{
char elem;
pStack->pop(elem);
if (!pNeedStack->pop(currentNeed))
{
currentNeed = 0;
}
}
}
if (pStack->stackEmpty())
{
cout << "字符窜括号匹配" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "字符串括号不匹配" << endl;
}
delete pStack;
pStack = NULL;
delete pNeedStack;
pNeedStack = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}


























 79
79

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










