一、SIFT和SURF算子实现特征点检测
概述
在OpenCV的features2d中实现了SIFT和SURF算法,可以用于图像特征点的自动检测。具体实现是采用SiftFeatureDetector/SurfFeatureDetector类的detect函数检测SIFT/SURF特征的关键点,并保存在vector容器中,最后使用drawKeypoints函数绘制出特征点。
实验所用环境是opencv2.4.9+vs2013+win7
SIFT特征点检测
实验代码如下。这里需要注意SiftFeatureDetector是包含在opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp中,所以应该include这个头文件,并且在“项目属性->链接器->输入->附加依赖项”中加入库文件:opencv_nonfree249d.lib。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp" //SurfFeatureDetector实际在该头文件中
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat src = imread("image1.jpg", 0);
if (!src.data)
{
cout << " --(!) Error reading images " << endl;
return -1;
}
//1--初始化SIFT检测算子
int minHessian = 400;
SiftFeatureDetector detector(minHessian);
//2--使用SIFT算子检测特征点
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;
detector.detect(src, keypoints);
//3--绘制特征点
Mat keypointImg;
drawKeypoints(src, keypoints, keypointImg, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT);
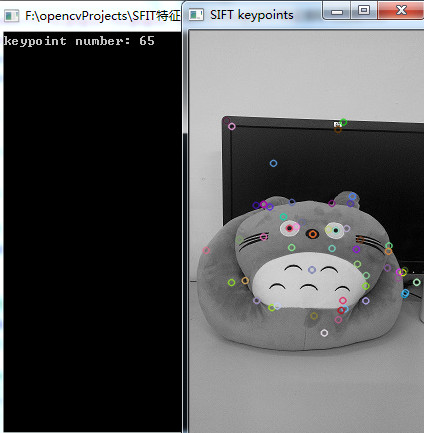
imshow("SIFT keypoints", keypointImg);
cout << "keypoint number: " << keypoints.size() << endl;
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
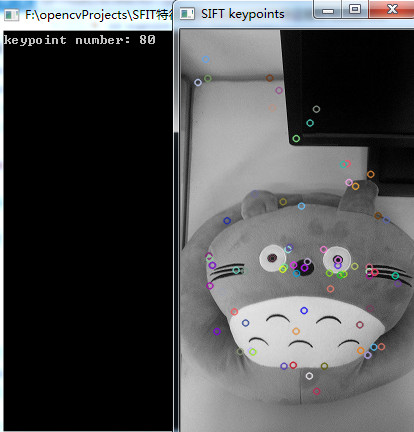
SURF特征点检测
同样的,使用SURF特征描述子进行特征点检测的过程类似,只不过换成了SurfFeatureDetector类,实验代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp" //SurfFeatureDetector实际在该头文件中
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat src = imread("image1.jpg", 0);
if (!src.data)
{
cout << " --(!) Error reading images " << endl;
return -1;
}
//1--初始化SIFT检测算子
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector(minHessian);
//2--使用SIFT算子检测特征点
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;
detector.detect(src, keypoints);
//3--绘制特征点
Mat keypointImg;
drawKeypoints(src, keypoints, keypointImg, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT);
imshow("SIFT keypoints", keypointImg);
cout << "keypoint number: " << keypoints.size() << endl;
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
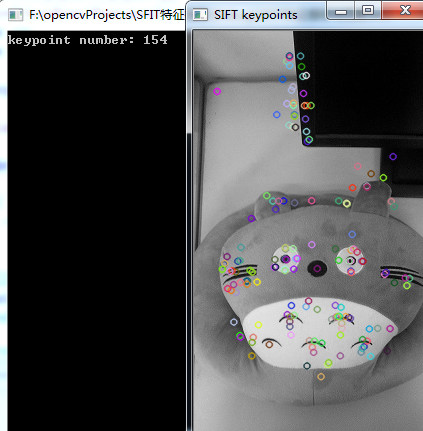
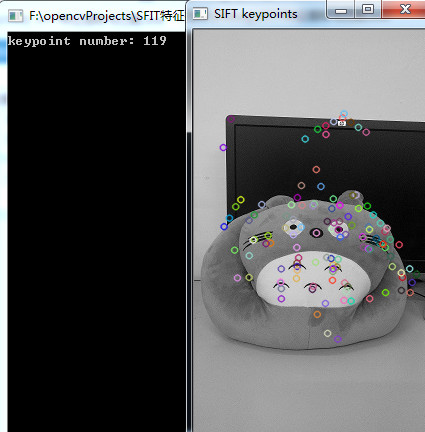
从检测结果可以看出,SURF算子检测到的特征点远远多于SIFT算子,至于检测的精确度如何,后面试试利用SIFT和SURF算子进行特征点匹配来区分。
二、SIFT和SURF算子实现特征点提取与匹配
前面SIFT和SURF算子实现特征点检测简单地讲了利用SIFT和SURF算子检测特征点,在检测的基础上可以使用SIFT和SURF算子对特征点进行特征提取并使用匹配函数进行特征点的匹配。具体实现是首先采用SurfFeatureDetector检测特征点,再使用SurfDescriptorExtractor计算特征点的特征向量,最后采用BruteForceMatcher暴力匹配法或者FlannBasedMatcher选择性匹配法(二者的不同)来进行特征点匹配。
实验所用环境是opencv2.4.9+vs2013+win7,需要注意opencv2.4.X版本中SurfFeatureDetector是包含在opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp中,BruteForceMatcher是包含在opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp中,FlannBasedMatcher是包含在opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp中。
BruteForce匹配法
首先使用BruteForceMatcher暴力匹配法,代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp" //SurfFeatureDetector实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp" //BruteForceMatcher实际在该头文件中
//#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp" //FlannBasedMatcher实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat src_1 = imread("image1.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
Mat src_2 = imread("image2.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
if (!src_1.data || !src_2.data)
{
cout << " --(!) Error reading images " << endl;
return -1;
}
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF算子检测特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector(minHessian);
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect(src_1, keypoints_1);
detector.detect(src_2, keypoints_2);
cout << "img1--number of keypoints: " << keypoints_1.size() << endl;
cout << "img2--number of keypoints: " << keypoints_2.size() << endl;
//-- Step 2: 使用SURF算子提取特征(计算特征向量)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute(src_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
extractor.compute(src_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
//-- Step 3: 使用BruteForce法进行暴力匹配
BruteForceMatcher< L2<float> > matcher;
vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches);
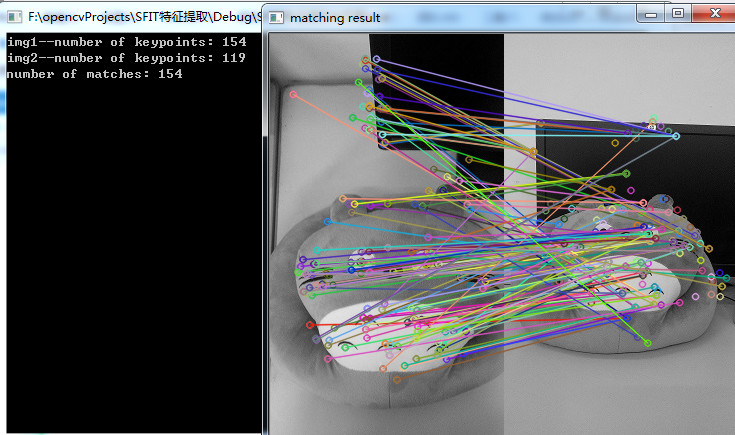
cout << "number of matches: " << matches.size() << endl;
//-- 显示匹配结果
Mat matchImg;
drawMatches(src_1, keypoints_1, src_2, keypoints_2, matches, matchImg);
imshow("matching result", matchImg);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}实验结果:
FLANN匹配法
使用暴力匹配的结果不怎么好,下面使用FlannBasedMatcher进行特征匹配,只保留好的特征匹配点,代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp" //SurfFeatureDetector实际在该头文件中
//#include "opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp" //BruteForceMatcher实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp" //FlannBasedMatcher实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat src_1 = imread("image1.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
Mat src_2 = imread("image2.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
if (!src_1.data || !src_2.data)
{
cout << " --(!) Error reading images " << endl;
return -1;
}
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF算子检测特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector(minHessian);
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect(src_1, keypoints_1);
detector.detect(src_2, keypoints_2);
cout << "img1--number of keypoints: " << keypoints_1.size() << endl;
cout << "img2--number of keypoints: " << keypoints_2.size() << endl;
//-- Step 2: 使用SURF算子提取特征(计算特征向量)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute(src_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
extractor.compute(src_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
//-- Step 3: 使用FLANN法进行匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector< DMatch > allMatches;
matcher.match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, allMatches);
cout << "number of matches before filtering: " << allMatches.size() << endl;
//-- 计算关键点间的最大最小距离
double maxDist = 0;
double minDist = 100;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++)
{
double dist = allMatches[i].distance;
if (dist < minDist)
minDist = dist;
if (dist > maxDist)
maxDist = dist;
}
printf(" max dist : %f \n", maxDist);
printf(" min dist : %f \n", minDist);
//-- 过滤匹配点,保留好的匹配点(这里采用的标准:distance<2*minDist)
vector< DMatch > goodMatches;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++)
{
if (allMatches[i].distance < 2 * minDist)
goodMatches.push_back(allMatches[i]);
}
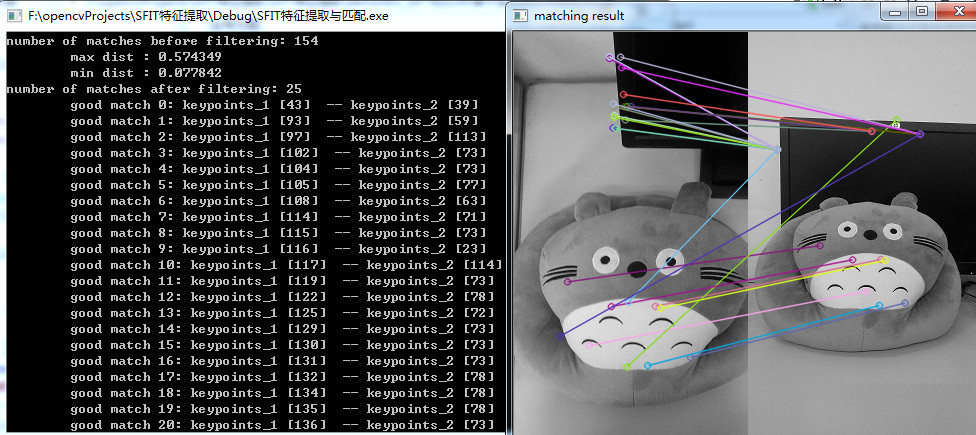
cout << "number of matches after filtering: " << goodMatches.size() << endl;
//-- 显示匹配结果
Mat matchImg;
drawMatches(src_1, keypoints_1, src_2, keypoints_2,
goodMatches, matchImg, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(),
DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS //不显示未匹配的点
);
imshow("matching result", matchImg);
//-- 输出匹配点的对应关系
for (int i = 0; i < goodMatches.size(); i++)
printf(" good match %d: keypoints_1 [%d] -- keypoints_2 [%d]\n", i,
goodMatches[i].queryIdx, goodMatches[i].trainIdx);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
从第二个实验结果可以看出,经过过滤之后特征点数目从154减少到25,匹配的准确度有所上升。当然也可以使用SIFT算子进行上述两种匹配实验,只需要将SurfFeatureDetector换成SiftFeatureDetector,将SurfDescriptorExtractor换成SiftDescriptorExtractor即可。
区别
二者的区别在于BFMatcher总是尝试所有可能的匹配,从而使得它总能够找到最佳匹配,这也是Brute Force(暴力法)的原始含义。而FlannBasedMatcher中FLANN的含义是Fast Library forApproximate Nearest Neighbors,从字面意思可知它是一种近似法,算法更快但是找到的是最近邻近似匹配,所以当我们需要找到一个相对好的匹配但是不需要最佳匹配的时候往往使用FlannBasedMatcher。当然也可以通过调整FlannBasedMatcher的参数来提高匹配的精度或者提高算法速度,但是相应地算法速度或者算法精度会受到影响。
此外,使用特征提取过程得到的特征描述符(descriptor)数据类型有的是float类型的,比如说SurfDescriptorExtractor,SiftDescriptorExtractor,有的是uchar类型的,比如说有ORB,BriefDescriptorExtractor。对应float类型的匹配方式有:FlannBasedMatcher,BruteForce<L2<float>>,BruteForce<SL2<float>>,BruteForce<L1<float>>。对应uchar类型的匹配方式有:BruteForce<Hammin>,BruteForce<HammingLUT>。所以ORB和BRIEF特征描述子只能使用BruteForce匹配法。
三、SIFT和SURF算法实现目标检测
概述
之前SIFT和SURF算子实现特征点检测和SURF算子实现特征点提取与匹配简单地讲了利用SIFT和SURF算子检测特征点,并且对特征点进行特征提取得到特征描述符(descriptors),在此基础上还可以进一步利用透视变换和空间映射找出已知物体(目标检测)。这里具体的实现是首先采用SURF/SIFT特征点检测与特征提取,然后采用FLANN匹配法保留好的匹配点,再利用findHomography找出相应的透视变换,最后采用perspectiveTransform函数映射点群,在场景中获取目标的位置。
实验所用环境是opencv2.4.9+vs2013+win7,需要注意opencv2.4.X版本中SurfFeatureDetector/SiftFeatureDetector是包含在opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp中,FlannBasedMatcher是包含在opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp中。
SURF算子
首先使用SURF算子进行目标检测,代码如下:
/**
* @概述: 采用SURF算子在场景中进行已知目标检测
* @类和函数: SurfFeatureDetector + SurfDescriptorExtractor + FlannBasedMatcher + findHomography + perspectiveTransform
* @实现步骤:
* Step 1: 在图像中使用SURF算法SurfFeatureDetector检测关键点
* Step 2: 对检测到的每一个关键点使用SurfDescriptorExtractor计算其特征向量(也称描述子)
* Step 3: 使用FlannBasedMatcher通过特征向量对关键点进行匹配,使用阈值剔除不好的匹配
* Step 4: 利用findHomography基于匹配的关键点找出相应的透视变换
* Step 5: 利用perspectiveTransform函数映射点群,在场景中获取目标的位置
*/
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp" //SurfFeatureDetector实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp" //FlannBasedMatcher实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp" //findHomography所需头文件
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat imgObject = imread("image1.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
Mat imgScene = imread("image2.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
if (!imgObject.data || !imgScene.data)
{
cout << " --(!) Error reading images " << endl;
return -1;
}
double begin = clock();
///-- Step 1: 使用SURF算子检测特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector(minHessian);
vector<KeyPoint> keypointsObject, keypointsScene;
detector.detect(imgObject, keypointsObject);
detector.detect(imgScene, keypointsScene);
cout << "object--number of keypoints: " << keypointsObject.size() << endl;
cout << "scene--number of keypoints: " << keypointsScene.size() << endl;
///-- Step 2: 使用SURF算子提取特征(计算特征向量)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptorsObject, descriptorsScene;
extractor.compute(imgObject, keypointsObject, descriptorsObject);
extractor.compute(imgScene, keypointsScene, descriptorsScene);
///-- Step 3: 使用FLANN法进行匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector< DMatch > allMatches;
matcher.match(descriptorsObject, descriptorsScene, allMatches);
cout << "number of matches before filtering: " << allMatches.size() << endl;
//-- 计算关键点间的最大最小距离
double maxDist = 0;
double minDist = 100;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptorsObject.rows; i++)
{
double dist = allMatches[i].distance;
if (dist < minDist)
minDist = dist;
if (dist > maxDist)
maxDist = dist;
}
printf(" max dist : %f \n", maxDist);
printf(" min dist : %f \n", minDist);
//-- 过滤匹配点,保留好的匹配点(这里采用的标准:distance<3*minDist)
vector< DMatch > goodMatches;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptorsObject.rows; i++)
{
if (allMatches[i].distance < 2 * minDist)
goodMatches.push_back(allMatches[i]);
}
cout << "number of matches after filtering: " << goodMatches.size() << endl;
//-- 显示匹配结果
Mat resultImg;
drawMatches(imgObject, keypointsObject, imgScene, keypointsScene,
goodMatches, resultImg, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1), vector<char>(),
DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS //不显示未匹配的点
);
//-- 输出匹配点的对应关系
for (int i = 0; i < goodMatches.size(); i++)
printf(" good match %d: keypointsObject [%d] -- keypointsScene [%d]\n", i,
goodMatches[i].queryIdx, goodMatches[i].trainIdx);
///-- Step 4: 使用findHomography找出相应的透视变换
vector<Point2f> object;
vector<Point2f> scene;
for (size_t i = 0; i < goodMatches.size(); i++)
{
//-- 从好的匹配中获取关键点: 匹配关系是关键点间具有的一 一对应关系,可以从匹配关系获得关键点的索引
//-- e.g. 这里的goodMatches[i].queryIdx和goodMatches[i].trainIdx是匹配中一对关键点的索引
object.push_back(keypointsObject[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt);
scene.push_back(keypointsScene[goodMatches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
Mat H = findHomography(object, scene, CV_RANSAC);
///-- Step 5: 使用perspectiveTransform映射点群,在场景中获取目标位置
std::vector<Point2f> objCorners(4);
objCorners[0] = cvPoint(0, 0);
objCorners[1] = cvPoint(imgObject.cols, 0);
objCorners[2] = cvPoint(imgObject.cols, imgObject.rows);
objCorners[3] = cvPoint(0, imgObject.rows);
std::vector<Point2f> sceneCorners(4);
perspectiveTransform(objCorners, sceneCorners, H);
//-- 在被检测到的目标四个角之间划线
line(resultImg, sceneCorners[0] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), sceneCorners[1] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4);
line(resultImg, sceneCorners[1] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), sceneCorners[2] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4);
line(resultImg, sceneCorners[2] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), sceneCorners[3] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4);
line(resultImg, sceneCorners[3] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), sceneCorners[0] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4);
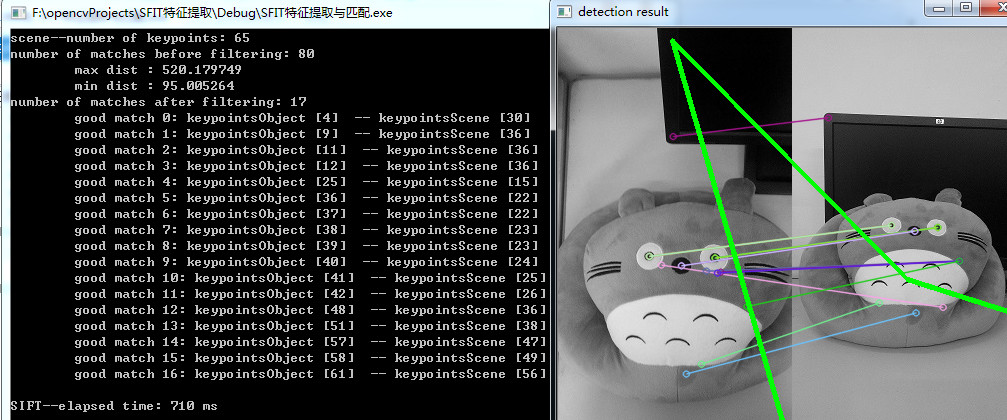
//-- 显示检测结果
imshow("detection result", resultImg);
double end = clock();
cout << "\nSURF--elapsed time: " << (end - begin) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000 << " ms\n";
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
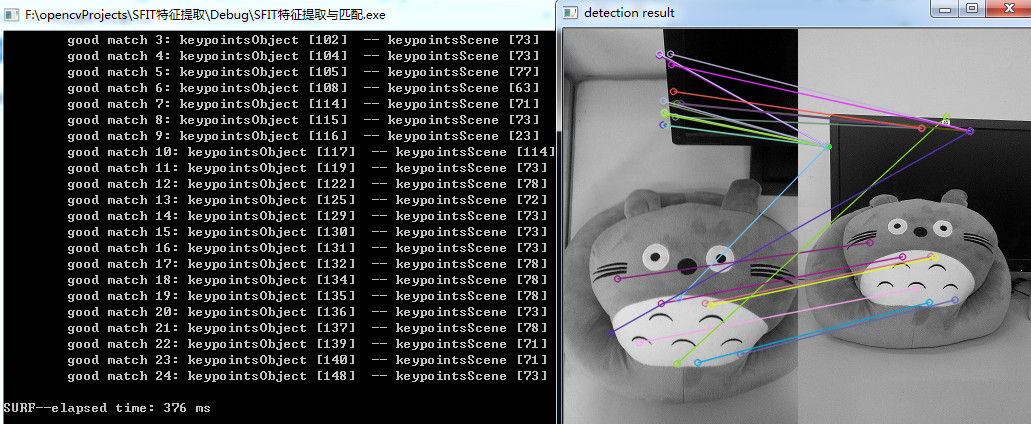
SIFT算子
作为对比,再使用SIFT算子进行目标检测,只需要将SurfFeatureDetector换成SiftFeatureDetector,将SurfDescriptorExtractor换成SiftDescriptorExtractor即可。代码如下:
/**
* @概述: 采用SIFT算子在场景中进行已知目标检测
* @类和函数: SiftFeatureDetector + SiftDescriptorExtractor + FlannBasedMatcher + findHomography + perspectiveTransform
* @实现步骤:
* Step 1: 在图像中使用SIFT算法SiftFeatureDetector检测关键点
* Step 2: 对检测到的每一个关键点使用SiftDescriptorExtractor计算其特征向量(也称描述子)
* Step 3: 使用FlannBasedMatcher通过特征向量对关键点进行匹配,使用阈值剔除不好的匹配
* Step 4: 利用findHomography基于匹配的关键点找出相应的透视变换
* Step 5: 利用perspectiveTransform函数映射点群,在场景中获取目标的位置
*/
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp" //SiftFeatureDetector实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp" //FlannBasedMatcher实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp" //findHomography所需头文件
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat imgObject = imread("image1.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
Mat imgScene = imread("image2.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
if (!imgObject.data || !imgScene.data)
{
cout << " --(!) Error reading images " << endl;
return -1;
}
double begin = clock();
///-- Step 1: 使用SIFT算子检测特征点
//int minHessian = 400;
SiftFeatureDetector detector;//( minHessian );
vector<KeyPoint> keypointsObject, keypointsScene;
detector.detect(imgObject, keypointsObject);
detector.detect(imgScene, keypointsScene);
cout << "object--number of keypoints: " << keypointsObject.size() << endl;
cout << "scene--number of keypoints: " << keypointsScene.size() << endl;
///-- Step 2: 使用SIFT算子提取特征(计算特征向量)
SiftDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptorsObject, descriptorsScene;
extractor.compute(imgObject, keypointsObject, descriptorsObject);
extractor.compute(imgScene, keypointsScene, descriptorsScene);
///-- Step 3: 使用FLANN法进行匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector< DMatch > allMatches;
matcher.match(descriptorsObject, descriptorsScene, allMatches);
cout << "number of matches before filtering: " << allMatches.size() << endl;
//-- 计算关键点间的最大最小距离
double maxDist = 0;
double minDist = 100;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptorsObject.rows; i++)
{
double dist = allMatches[i].distance;
if (dist < minDist)
minDist = dist;
if (dist > maxDist)
maxDist = dist;
}
printf(" max dist : %f \n", maxDist);
printf(" min dist : %f \n", minDist);
//-- 过滤匹配点,保留好的匹配点(这里采用的标准:distance<3*minDist)
vector< DMatch > goodMatches;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptorsObject.rows; i++)
{
if (allMatches[i].distance < 2 * minDist)
goodMatches.push_back(allMatches[i]);
}
cout << "number of matches after filtering: " << goodMatches.size() << endl;
//-- 显示匹配结果
Mat resultImg;
drawMatches(imgObject, keypointsObject, imgScene, keypointsScene,
goodMatches, resultImg, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1), vector<char>(),
DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS //不显示未匹配的点
);
//-- 输出匹配点的对应关系
for (int i = 0; i < goodMatches.size(); i++)
printf(" good match %d: keypointsObject [%d] -- keypointsScene [%d]\n", i,
goodMatches[i].queryIdx, goodMatches[i].trainIdx);
///-- Step 4: 使用findHomography找出相应的透视变换
vector<Point2f> object;
vector<Point2f> scene;
for (size_t i = 0; i < goodMatches.size(); i++)
{
//-- 从好的匹配中获取关键点: 匹配关系是关键点间具有的一 一对应关系,可以从匹配关系获得关键点的索引
//-- e.g. 这里的goodMatches[i].queryIdx和goodMatches[i].trainIdx是匹配中一对关键点的索引
object.push_back(keypointsObject[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt);
scene.push_back(keypointsScene[goodMatches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
Mat H = findHomography(object, scene, CV_RANSAC);
///-- Step 5: 使用perspectiveTransform映射点群,在场景中获取目标位置
std::vector<Point2f> objCorners(4);
objCorners[0] = cvPoint(0, 0);
objCorners[1] = cvPoint(imgObject.cols, 0);
objCorners[2] = cvPoint(imgObject.cols, imgObject.rows);
objCorners[3] = cvPoint(0, imgObject.rows);
std::vector<Point2f> sceneCorners(4);
perspectiveTransform(objCorners, sceneCorners, H);
//-- 在被检测到的目标四个角之间划线
line(resultImg, sceneCorners[0] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), sceneCorners[1] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4);
line(resultImg, sceneCorners[1] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), sceneCorners[2] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4);
line(resultImg, sceneCorners[2] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), sceneCorners[3] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4);
line(resultImg, sceneCorners[3] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), sceneCorners[0] + Point2f(imgObject.cols, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4);
//-- 显示检测结果
imshow("detection result", resultImg);
double end = clock();
cout << "\nSIFT--elapsed time: " << (end - begin) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000 << " ms\n";
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
























 2875
2875

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








