文章目录
1. this指针的引出
我们先定义一个日期类:
class Date
{
public:
void Init(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
private:
int _year; // 年
int _month; // 月
int _day; // 日
};
int main()
{
Date d1, d2;
d1.Init(2022, 1, 11);
d2.Init(2022, 1, 12);
d1.Print();
d2.Print();
return 0;
}对于上述类,有这样的一个问题:
Date类中有 Init 与 Print 两个成员函数,函数体中没有关于不同对象的区分,那当d1调用 Init 函
数时,该函数是如何知道应该设置d1对象,而不是设置d2对象呢?
C++中通过引入this指针解决该问题,即:C++编译器给每个“非静态的成员函数“增加了一个隐藏
的指针参数,让该指针指向当前对象(函数运行时调用该函数的对象),在函数体中所有“成员变量”
的操作,都是通过该指针去访问。只不过所有的操作对用户是透明的,即用户不需要来传递,编
译器自动完成。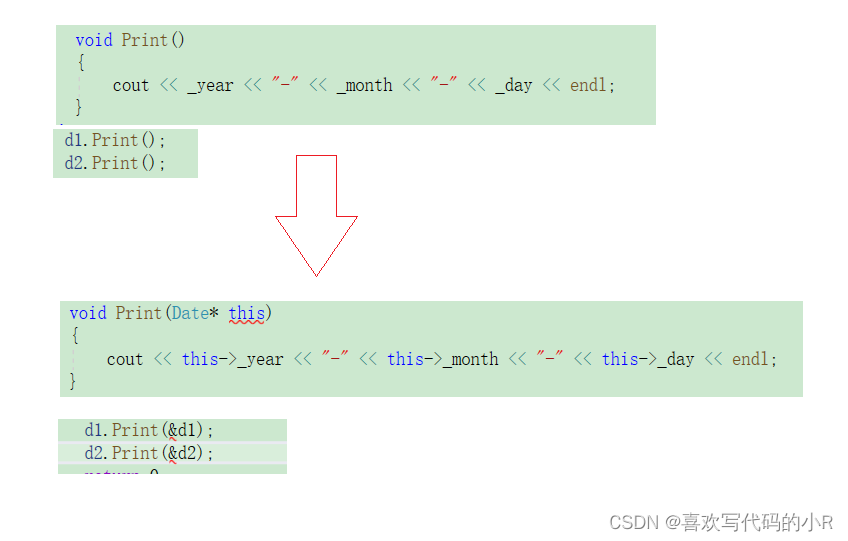
2. this指针的特性
- this指针的类型:类类型* const,即成员函数中,不能给this指针赋值。
- 只能在“成员函数”的内部使用。
- this指针本质上是“成员函数”的形参,当对象调用成员函数时,将对象地址作为实参传递给this形参,所以对象中不储存this指针。
- this指针式“成员函数”第一个隐含的指针形参,一般情况由编译器通过ecx寄存器自动传递,不需要用户传递。
接下来有两道经典的面试题:
- this指针存在哪里?
- this指针可以为空吗?
首先,针对第一题this指针存在哪里?
通过前面的了解我们得知了this指针本质上是“成员函数”的形参,所以this指针和普通参数一样存在函数调用的栈帧里面。
第二题,this指针可以为空吗?
由这个问题我们就要引出接下来的两道程序题了:
// 1.下面程序编译运行结果是? A、编译报错 B、运行崩溃 C、正常运行
class A
{
public:
void Print()
{
cout << "Print()" << endl;
}
private:
int _a;
};
int main()
{
A* p = nullptr;
p->Print();
return 0;
}
// 2.下面程序编译运行结果是? A、编译报错 B、运行崩溃 C、正常运行
class A
{
public:
void PrintA()
{
cout<<_a<<endl;
}
private:
int _a;
};
int main()
{
A* p = nullptr;
p->PrintA();
return 0;
}先来公布一下结果:第一题C,第二题B
为什么呢?
首先来看第一题:

再来看第二题:

综上所述:this指针不可以为空,如若为空,那么在运行时一旦访问了对应的对象那么就会发生野指针的情况。
3. C语言和C++实现Stack的对比
1. C语言实现
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
DataType* array;
int capacity;
int size;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType) * 3);
if (NULL == ps->array)
{
assert(0);
return;
}
ps->capacity = 3;
ps->size = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->array)
{
free(ps->array);
ps->array = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->size = 0;
}
}
void CheckCapacity(Stack* ps)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity * 2;
DataType* temp = (DataType*)realloc(ps->array,
newcapacity * sizeof(DataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc申请空间失败!!!");
return;
}
ps->array = temp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, DataType data)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps);
ps->array[ps->size] = data;
ps->size++;
}
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return 0 == ps->size;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
if (StackEmpty(ps))
return;
ps->size--;
}
DataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->array[ps->size - 1];
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->size;
}
int main()
{
Stack s;
StackInit(&s);
StackPush(&s, 1);
StackPush(&s, 2);
StackPush(&s, 3);
StackPush(&s, 4);
printf("%d\n", StackTop(&s));
printf("%d\n", StackSize(&s));
StackPop(&s);
StackPop(&s);
printf("%d\n", StackTop(&s));
printf("%d\n", StackSize(&s));
StackDestroy(&s);
return 0;
}
可以看到,在用C语言实现时,Stack相关操作函数有以下共性:
- 每个函数的第一个参数都是Stack*
- 函数中必须要对第一个参数检测,因为该参数可能会为NULL
- 函数中都是通过Stack*参数操作栈的
- 调用时必须传递Stack结构体变量的地址
结构体中只能定义存放数据的结构,操作数据的方法不能放在结构体中,即数据和操作数据的方式是分离开的,而且是线上相对复杂一点,涉及到大量指针操作,稍不注意就可能会出现错误。
2. C++实现
typedef int DataType;
class Stack
{
public:
void Init()
{
_array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType) * 3);
if (NULL == _array)
{
perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");
return;
}
_capacity = 3;
_size = 0;
}
void Push(DataType data)
{
CheckCapacity();
_array[_size] = data;
_size++;
}
void Pop()
{
if (Empty())
return;
_size--;
}
DataType Top() { return _array[_size - 1]; }
int Empty() { return 0 == _size; }
int Size() { return _size; }
void Destroy()
{
if (_array)
{
free(_array);
_array = NULL;
_capacity = 0;
_size = 0;
}
}
private:
void CheckCapacity()
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;
DataType* temp = (DataType*)realloc(_array, newcapacity *
sizeof(DataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc申请空间失败!!!");
return;
}
_array = temp;
_capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
private:
DataType* _array;
int _capacity;
int _size;
};
int main()
{
Stack s;
s.Init();
s.Push(1);
s.Push(2);
s.Push(3);
s.Push(4);
printf("%d\n", s.Top());
printf("%d\n", s.Size());
s.Pop();
s.Pop();
printf("%d\n", s.Top());
printf("%d\n", s.Size());
s.Destroy();
return 0;
}C++中通过类可以将数据以及操作数据的方法进行完美结合,通过访问权限可以控制那些方法在类外可以被调用,即封装,在使用时就像使用自己的成员一样,更符合人类对一件事物的认知。而且每个方法不需要传递Stack*参数了,编译器编译之后该参数会自动还原,即C++中Stack*参数是编译器维护的,C语言中需要用户自己维护。
以上就是C++中this指针的全部内容,如有遗漏或是其他问题,还请各位大佬同行斧正,感谢各位支持!























 479
479











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










