数组
- 数组(array)是一种数据格式,能够存储多个同类型的值。
- 每个值存储在独立数组元素中,在内存中连续存储各个元素
- 创建数组,使用声明语句
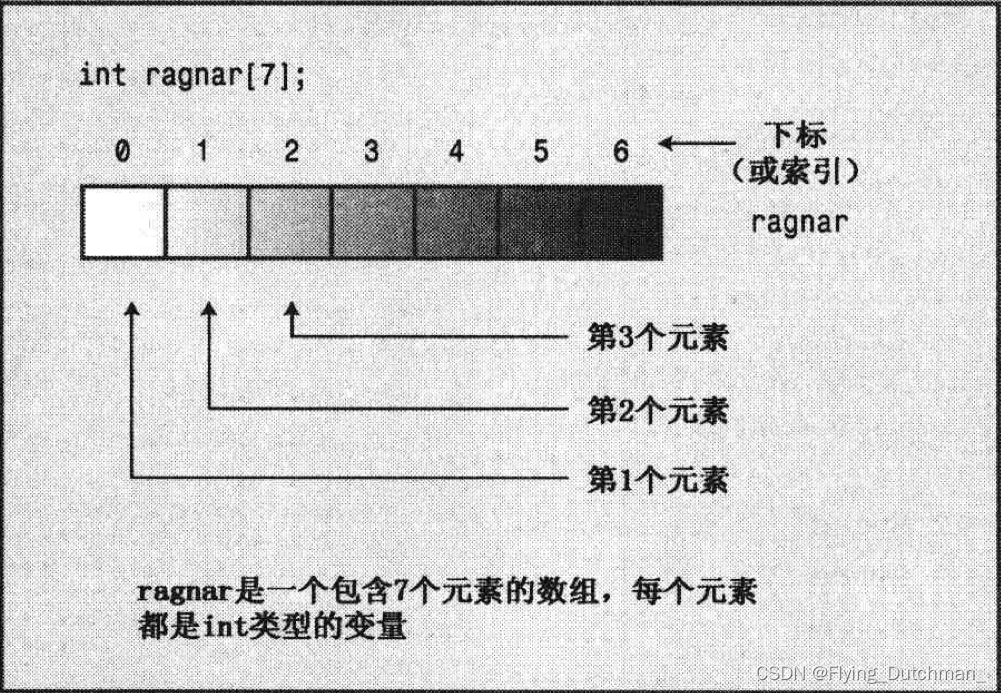
- 数组声明包括:存储在每个元素中值的类型、数组名、数组中元素数
- 通用格式:typeName arrayName [arraySize]; arrarSize必须整型常数,不能是变量
- 单独访问数组元素的方法是使用下标或索引对元素编号。
- C++数组从0开始编号,最后一个元素的索引比数组长度少1
//程序清单4.1
//整数数组
#include <iostream>
int main (void)
{
using namespace std;
int yams[3]; //创建包含三个元素的int类型数组
yam[0] = 7; //给每个元素赋值
yam[1] = 8;
yam[2] = 6;
int yamcosts[3] = {20, 30, 5]; //创建和初始化数组
cout << "Total yams = " << yams[0] + yams[1] + yams[2] << endl;
cout << "The package with " << yams[1] << " yams costs " << yamcosts[1] << " cents per yam.\n";
int total = yams[0] * yamcosts[0] + yams[1] * yamcosts[1] + yams[2] * yamcosts[2];
cout << "The total yam expense is " << total << " cents.\n";
cout << "\nSize of yams array = " << sizeof yams << " bytes.\n"; //12 bytes
cout << "Size of one element = " << sizeof yams[0] << " bytes.\n"; //4 bytes
return 0;
}
- 程序给yam赋值和给yamcost赋值采用了两种方法
- sizeof运算符返回类型或数据对象的长度(单位为字节)
数组初始化规则
- 只有定义数组时才能使用初始化,此后不能使用,也不能将一个数组赋值给另一个数组;可以使用下标分别给数组元素赋值
int cards[4] = {3, 6, 8, 10}; //可以
int hand[4]; //可以
hand[4] = {5, 6, 7, 8}; //不可以
hand = cards; //不可以
- 初始化时提供的值可以小于数组元素数目,编译器将剩余元素设置为0
- 将数组所有元素初始化为0,只需显式地将第一个元素初始化为0
- 如果初始化为{1}而不是{0},则第一个元素被设置为1,其余元素为0
- 如果初始化数组是【】为空,则C++编译器计算元素个数
- 数组初始化,可省略=
字符串
- 字符串常量(双引号,字符+ \0)——字符串地址
- 字符常量(单引号,字符)——ASCII码
//程序清单4.2
//在数组中存储字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> //为了使用strlen()函数
int main (void)
{
using namespace std;
const int Size = 15;
char name1[Size];
char name2[Size] = "C++owboy";
cout << "Howdy! I'm " << name2 << "! What's your name?\n";
cin >> name1; //Basicman
cout << "Well, " << name1 << ", your name has " << strlen(name1); //8 letters
cout << " letters and is stored in an array of " << sizeof(name1) << " bytes.\n";//15 bytes
cout << "Your initial is " << name1[0] << ".\n"; //B
name2[3] = '\0';
cout << "Here are the first 3 characters of my name: " << name2 << endl; //C++
return 0;
}
- sizeof运算符指出整个数组的长度:15字节;strlen()函数返回存储在数组中字符串的长度,不算空字符在内
- 此程序有个缺陷:cin使用空白(空格、制表符、换行符)确定字符串结束位置。如果输入输入的是pin duoduo,程序只是读取pin到name1中,将duoduo 保留在输入队列。此时要用面向行的输入:getline()和get()
//程序清单4.4 4.5
//getline() 和get()
#include <iostream>
int main (void)
{
using namespace std;
const int ArSize = 20;
char name[ArSize];
char dessert[ArSize];
cout << "面向行的输入:getline()" << endl;
cout << "Enter your name:\n";
cin.getline(name, ArSize);
cout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";
cin.getline(dessert, ArSize);
cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert << " for you, " << name << ".\n";
cout << "面向行的输入:get()" << endl;
cout << "Enter your name:\n";
cin.get(name, ArSize).get();
cout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";
cin.get(dessert, ArSize).get();
cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert << " for you, " << name << ".\n";
return 0;
}
- getline()函数读取整行,通过换行符确定行尾,但不保存换行符,在存储字符串时,用空字符替换换行符
- get()函数读取整行,但保存换行符在队列中,用不带任何参数的get()处理换行符
cin.get(name, ArSize);
cin.get();
//或
cin.get(name, ArSize).get();
- 该函数们有两个参数。第一个参数用来存储数组名称,第二个参数读取字符数。如果第二个参数为20,则最多读取19个字符,余下留给空字符\0。但cin.get()有多种参数形式,也可以没有参数get(),后面再说
//程序清单4.6
//以下数字输入与行输入
#include <iostream>
int main (void)
{
using namespace std;
cout << "What year was your house built?\n";









 数组数组(array)是一种数据格式,能够存储多个同类型的值。 每个值存储在独立数组元素中,在内存中连续存储各个元素 创建数组,使用声明语句 数组声明包括:存储在每个元素中值的类型、数组名、数组中元素数 通用格式:typeName arrayName [arraySize]; arrarSize必须整型常数,不能是变量 单独访问数组元素的方法是使用下标或索引对元素编号。 C++数组从0开始编号,最后一个元素的索引比数组长度少1//程序清单4.1//整数数组#include &l
数组数组(array)是一种数据格式,能够存储多个同类型的值。 每个值存储在独立数组元素中,在内存中连续存储各个元素 创建数组,使用声明语句 数组声明包括:存储在每个元素中值的类型、数组名、数组中元素数 通用格式:typeName arrayName [arraySize]; arrarSize必须整型常数,不能是变量 单独访问数组元素的方法是使用下标或索引对元素编号。 C++数组从0开始编号,最后一个元素的索引比数组长度少1//程序清单4.1//整数数组#include &l
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 465
465











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








