前言
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目
前提条件
- 熟悉Python
相关介绍
- Python是一种跨平台的计算机程序设计语言。是一个高层次的结合了解释性、编译性、互动性和面向对象的脚本语言。最初被设计用于编写自动化脚本(shell),随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,越多被用于独立的、大型项目的开发。
实验环境
- Python 3.x (面向对象的高级语言)
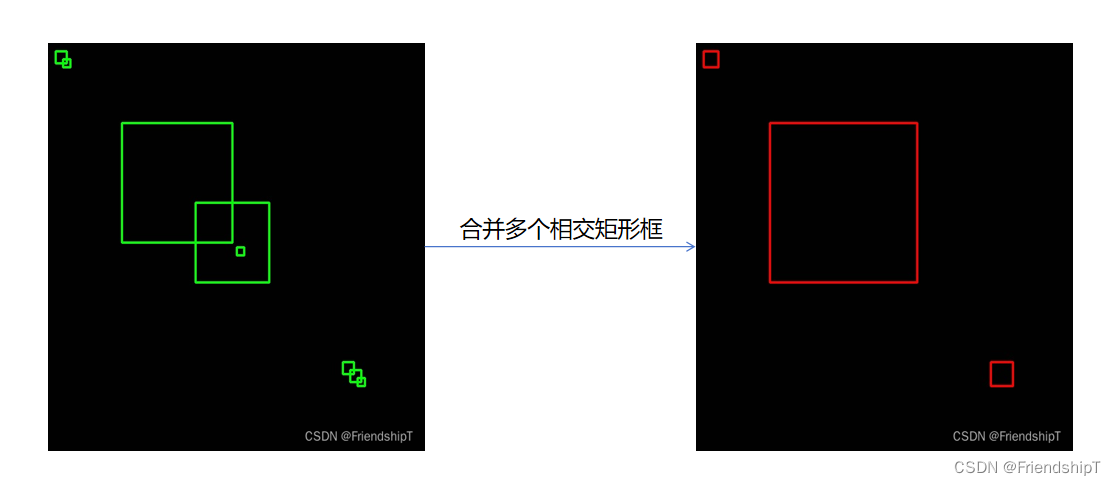
Python合并多个相交矩形框

代码实现
import cv2
import numpy as np
def xyxy2xywh(rect):
'''
(x1,y1,x2,y2) -> (x,y,w,h)
'''
return [rect[0],rect[1],rect[2]-rect[0],rect[3]-rect[1]]
def xywh2xyxy(rect):
'''
(x,y,w,h) -> (x1,y1,x2,y2)
'''
return [rect[0],rect[1],rect[0]+rect[2],rect[1]+rect[3]]
def is_RecA_RecB_interSect(RecA, RecB): # Rec = [xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax]
# 获取交集区域的[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax]
x_A_and_B_min = max(RecA[0], RecB[0])
y_A_and_B_min = max(RecA[1], RecB[1])
x_A_and_B_max = min(RecA[2], RecB[2])
y_A_and_B_max = min(RecA[3], RecB[3])
# 计算交集部分面积, 当(xmax - xmin)为负时,说明A与B框无交集,直接置为0。 (ymax - ymin)同理。
interArea = max(0, x_A_and_B_max - x_A_and_B_min) * max(0, y_A_and_B_max - y_A_and_B_min)
return interArea > 0
def merge_RecA_RecB(RecA, RecB): # Rec = [xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax]
# 获取合并区域的[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax]
xmin = min(RecA[0], RecB[0])
ymin = min(RecA[1], RecB[1])
xmax = max(RecA[2], RecB[2])
ymax = max(RecA[3], RecB[3])
return [xmin,ymin, xmax,ymax]
# def merge_rect(box,box_len):
# if box_len== 1:
# return box
# for i in range(box_len):
# RecA_xywh = box[i]
# RecA_xyxy = xywh2xyxy(RecA_xywh)
# for j in range(i+1,box_len):
# RecB_xywh = box[j]
# RecB_xyxy = xywh2xyxy(RecB_xywh)
# print(is_RecA_RecB_interSect(RecA_xyxy, RecB_xyxy))
# if is_RecA_RecB_interSect(RecA_xyxy, RecB_xyxy):
# rect_xyxy = merge_RecA_RecB(RecA_xyxy, RecB_xyxy)
# rect_xywh = xyxy2xywh(rect_xyxy)
# box.remove(RecA_xywh)
# box.remove(RecB_xywh)
# box.append(rect_xywh)
# box_len = len(box)
# merge_rect(box,box_len)
# # 此处少了return box会报错
# return box
# def merge_rect(box, box_len):
# if box_len == 1:
# return box
# for i in range(box_len):
# RecA_xywh = box[i]
# RecA_xyxy = xywh2xyxy(RecA_xywh)
# for j in range(i+1, box_len):
# RecB_xywh = box[j]
# RecB_xyxy = xywh2xyxy(RecB_xywh)
# if is_RecA_RecB_interSect(RecA_xyxy, RecB_xyxy):
# rect_xyxy = merge_RecA_RecB(RecA_xyxy, RecB_xyxy)
# rect_xywh = xyxy2xywh(rect_xyxy)
# # 使用remove(elem)来移除元素
# box.remove(RecA_xywh)
# box.remove(RecB_xywh)
# box.append(rect_xywh)
# box_len = len(box)
# merge_rect(box, box_len)
# # 返回上一级循环,避免重复处理已合并的矩形
# return box
# return box
'''
递归是一个过程或函数在其定义或说明中有直接或间接调用自身的一种方法,
它通常把一个大型复杂的问题层层转化为一个与原问题相似的规模较小的问题来求解。
因此递归过程,最重要的就是查看能不能讲原本的问题分解为更小的子问题,这是使用递归的关键。
终止条件:矩形框数为1或者为空。
返回值: 新合并的矩形框
本级任务: 每一级需要做的就是遍历从它开始的后续矩形框,寻找可以和他合并的矩形
'''
def merge_rect(box):
'''
合并重叠框
输入参数: box :[[x,y,w,h],...]
返回:
合并后的box:[[x,y,w,h],...]
'''
if len(box) == 1 or len(box) == 0 : # 矩形框数为1或者为空
return box
for i in range(len(box)):
RecA_xywh = box[i]
RecA_xyxy = xywh2xyxy(RecA_xywh)
for j in range(i+1, len(box)):
RecB_xywh = box[j]
RecB_xyxy = xywh2xyxy(RecB_xywh)
if is_RecA_RecB_interSect(RecA_xyxy, RecB_xyxy):
rect_xyxy = merge_RecA_RecB(RecA_xyxy, RecB_xyxy)
rect_xywh = xyxy2xywh(rect_xyxy)
# 使用remove(elem)来移除元素
box.remove(RecA_xywh)
box.remove(RecB_xywh)
box.append(rect_xywh)
merge_rect(box)
# 返回上一级循环,避免重复处理已合并的矩形
return box
return box
if __name__=="__main__":
# 原始
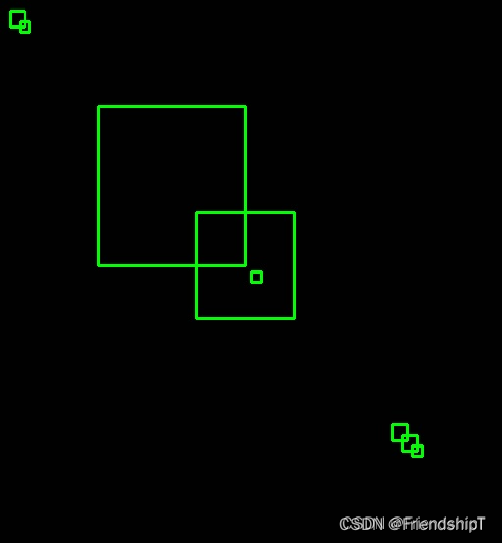
box = [[256,256,10,10],[10,10,15,15],[20,20,10,10],[100,100,150,150],
[200,200,100,100],[400,400,15,15],[410,410,15,15],[420,420,10,10]] # (x,y,w,h)
print("原始的矩形框:",box)
img = np.ones([512, 512, 3], np.uint8)
for x,y,w,h in box:
img = cv2.rectangle(img, (x,y), (x+w,y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('origin', img)
# 合并后
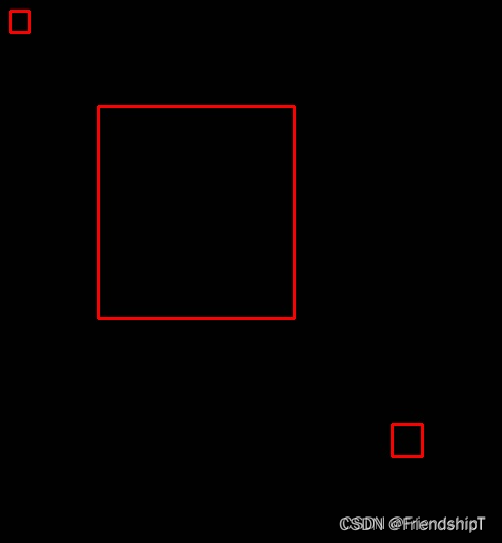
merged_box = merge_rect(box)
print("合并的矩形框:",merged_box)
img = np.ones([512, 512, 3], np.uint8)
for x,y,w,h in merged_box:
img = cv2.rectangle(img, (x,y), (x+w,y+h), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow('merged', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目
























 521
521











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










