在知识图谱中如何建模规则,原文地址:https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/D16-1019.pdf
本文讲述了如何将规则和三元组建模到一个统一的空间,三元组和规则同时建模,对文章的主体内容总结如下:
方法概述:
为了联合嵌入,方法的关键是通过一阶逻辑将三元组和规则统一起来。一个三元组可看作一个基本原子,给定一个逻辑规则,首先用实体集中的实体对其进行实例化,例如对于规则![]()
![]() ,可以用实体 Pairs 和France实例化为具体规则
,可以用实体 Pairs 和France实例化为具体规则![]()
![]() ,这样具体规则可看作复杂的公式,由基本原子和逻辑连接符构成。
,这样具体规则可看作复杂的公式,由基本原子和逻辑连接符构成。
令![]() 表示可训练的公式集合(包含原子公式,即三元组,和复杂公式,即具体规则),用真值函数
表示可训练的公式集合(包含原子公式,即三元组,和复杂公式,即具体规则),用真值函数![]() 为每个公式设置一个真值,表示一个三元组成立的概率,或一个具体规则满足的概率,三元组的真值由实体和关系的嵌入确定,具体规则的真值由构成它的三元组的真值决定。这样就能将三元组和规则嵌入到一个统一框架中。最后,最小化
为每个公式设置一个真值,表示一个三元组成立的概率,或一个具体规则满足的概率,三元组的真值由实体和关系的嵌入确定,具体规则的真值由构成它的三元组的真值决定。这样就能将三元组和规则嵌入到一个统一框架中。最后,最小化![]() 上的一个全局损失以学习与三元组和规则都相容的嵌入。下面介绍三个部分:三元组建模,规则建模,和联合学习。
上的一个全局损失以学习与三元组和规则都相容的嵌入。下面介绍三个部分:三元组建模,规则建模,和联合学习。
三元组建模:
用TRansE建模三运组,三元组的真值定义为:
![]()
其中d是嵌入维度,三元组成立时,其值大,反之,希望其值很小。
规则建模:
用模糊逻辑的方法建模规则的真值。复杂公式的真值建模为它的组成成分的真值的结合:
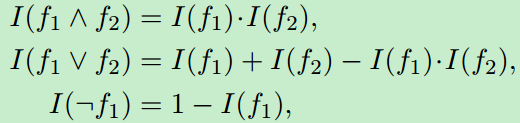
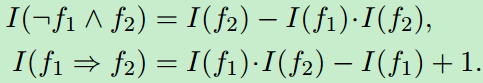
本文目前只考虑两种类型的规则,第一种是![]() ,它可以记作
,它可以记作![]() ,其真值的计算方法为:
,其真值的计算方法为:
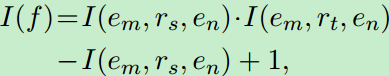
第二种是![]()
![]() ,它可以记作
,它可以记作![]() ,其真值计算方法为:
,其真值计算方法为:
![]()
真值越大,说明这一规则被满足的概率越大。
联合学习:把三元组和规则建模为原子公式和复杂公式后,最小化这一表示上的全局损失以学习同时满足三元组和规则的实体和关系的嵌入。首先构建包含正公式的训练集,包括1)已有的三元组,2)至少包含一个正三元组的具体规则。然后最小化基于间隔的损失:
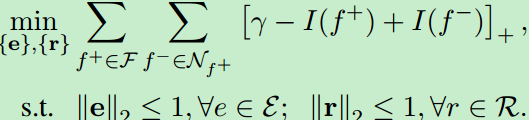
如果![]() 是三元组,则随机替换头或尾实体来生成负三元组,如果
是三元组,则随机替换头或尾实体来生成负三元组,如果![]()
![]() 是具体规则,则随机替换结论中的r来构建负样本。
是具体规则,则随机替换结论中的r来构建负样本。






















 7879
7879











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








