本专栏用于记录关于深度学习的笔记,不光方便自己复习与查阅,同时也希望能给您解决一些关于深度学习的相关问题,并提供一些微不足道的人工神经网络模型设计思路。
专栏地址:「深度学习一遍过」必修篇
目录
项目 GitHub 地址
项目心得
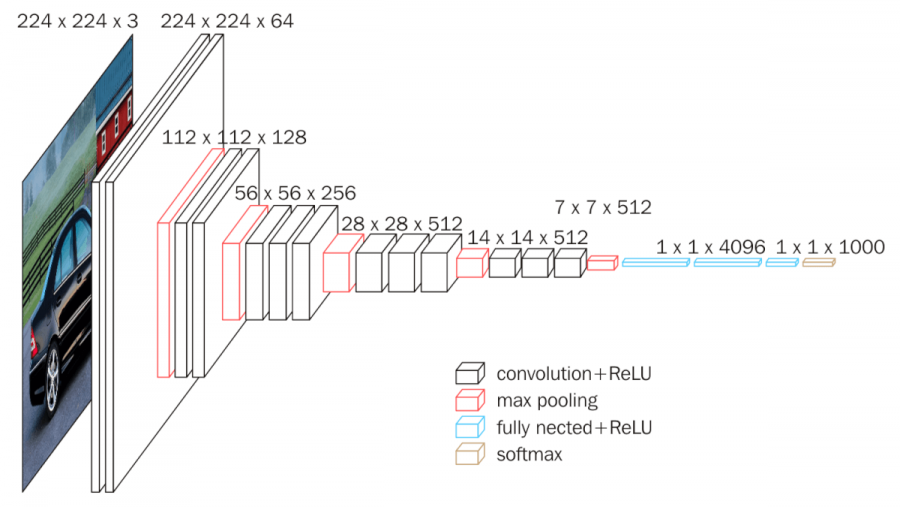
- 2014 年——VGGNet:这是 2014 年牛津大学计算机视觉组和 Google DeepMind 公司研究员一起研发的深度网络模型。该网络结构被分为 11,13,16,19 层;该项目自己搭建了 VGGNet 网络并在 MNIST 手写数字识别项目中得到了应用。(注:该项目主要修改了 AlexNet 应用实例中的 net.py 代码,由于输入图片通道数依然为 3 通道,所以延续了 AlexNet 应用实例中的 train.py 与 test.py ,仅调小了其中的 banch_size (由 16 变为了 8),以避免因 CUDA 内存不足而引起的报错)
项目代码
net.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# 作者:赵泽荣
# 时间:2021年9月9日(农历八月初三)
# 个人站点:1.https://zhao302014.github.io/
# 2.https://blog.csdn.net/IT_charge/
# 个人GitHub地址:https://github.com/zhao302014
# ------------------------------------------------- #
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
# 自己搭建一个 Vgg16 模型结构
# · 提出时间:2014 年
# · VGGNet 的网络结构被分为 11,13,16,19 层,该实例实现 16 层的 VGGNet
# · VGGNet 网络深,卷积层多
# · 卷积核都是 3* 3 的或 1* 1 的,且同一层中 channel 的数量都是相同的。最大池化层全是 2*2。
# · 每经过一个 pooling 层,channel 的数量会乘上2(即每次池化之后,Feature Map宽高降低一半,通道数量增加一倍)
# · 意义:1.证明了更深的网络,能更好的提取特征;2.成为了后续很多网络的 backbone。
# · 基准 Vgg16 截止到下述代码的 f16 层;由于本实例是手写数字识别(10分类问题),故再后续了一层全连接层 f_output
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
class MyVgg16Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyVgg16Net, self).__init__()
self.ReLU = nn.ReLU() # 论文中的表格,每一大行对应是一个隐藏层,每个隐藏层计算完后的结果都需要经过 ReLU 激活函数进行激活
# 第一段卷积神经网络:共 3 层,由 2 个卷积层和 1 个最大池化层构成
self.c1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (224 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 224
self.c2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (224 - 3 + 2*2) / 1 + 1 = 224
self.s1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# 第二段卷积神经网络:共 3 层,由 2 个卷积层和 1 个最大池化层构成
self.c3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (112 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 112
self.c4 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (112 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 112
self.s2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# 第三段卷积神经网络:共 4 层,由 3 个卷积层和 1 个最大池化层构成
self.c5 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (56 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 56
self.c6 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (56 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 56
self.c7 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (56 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 56
self.s3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# 第四段卷积神经网络:共 4 层,由 3 个卷积层和 1 个最大池化层构成
self.c8 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c9 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c10 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.s4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# 第五段卷积神经网络:共 4 层,由 3 个卷积层和 1 个最大池化层构成
self.c11 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c12 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c13 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.s5 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# 3 个全连接层置于 5 段卷积层之后
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.f14 = nn.Linear(7*7*512, 4096)
self.f15 = nn.Linear(4096, 4096)
self.f16 = nn.Linear(4096, 1000)
# 为满足该实例另加 ↓
self.f_output = nn.Linear(1000, 10)
def forward(self, x): # 输入shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
x = self.c1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 224, 224])
x = self.c2(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 224, 224])
x = self.s1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
x = self.ReLU(x)
x = self.c3(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 112, 112])
x = self.c4(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 112, 112])
x = self.s2(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 56, 56])
x = self.ReLU(x)
x = self.c5(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 56, 56])
x = self.c6(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 56, 56])
x = self.c7(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 56, 56])
x = self.s3(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 28, 28])
x = self.ReLU(x)
x = self.c8(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 28, 28])
x = self.c9(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 28, 28])
x = self.c10(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 28, 28])
x = self.s4(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x = self.ReLU(x)
x = self.c11(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x = self.c12(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x = self.c13(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x = self.s5(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 7, 7])
x = self.ReLU(x)
x = self.flatten(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 25088])
x = self.f14(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
x = self.f15(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
x = self.f16(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 1000])
# 为满足该实例另加 ↓
x = self.f_output(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
# 全连接层之后使用了 softmax
x = F.softmax(x, dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = torch.rand([1, 3, 224, 224])
model = MyVgg16Net()
y = model(x)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
# 已知:在 VGG16 中,使用 2 个 3*3 卷积核来代替 5*5 卷积核;这样做的主要目的是在保证具有相同感受野的条件下,提升了网络的深度,在一定程度上提升了神经网络的效果。
# 问:为什么 1 个 5*5 的卷积核可以由 2 个 3*3 的卷积核替代?
# 答:我们假设图片是 28*28 的
# 我们使用 5*5 的卷积核对其卷积,步长为 1,得到的结果是:(28-5)/1+1=24
# 然后我们使用 2 个卷积核为 3*3 的,这里的 2 个是指 2 层:
# 第一层 3*3:得到的结果是:(28-3)/1+1=26
# 第二层 3*3:得到的结果是:(26-3)/1+1=24
# 所以我们的最终结果和 5*5 的卷积核是一样的!!!
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #train.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# 作者:赵泽荣
# 时间:2021年9月9日(农历八月初三)
# 个人站点:1.https://zhao302014.github.io/
# 2.https://blog.csdn.net/IT_charge/
# 个人GitHub地址:https://github.com/zhao302014
# ------------------------------------------------- #
import torch
from torch import nn
from net import MyVgg16Net
import numpy as np
from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Scale(224), # 缩放图像大小为 224*224
transforms.ToTensor() # 仅对数据做转换为 tensor 格式操作
])
# 加载训练数据集
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, transform=data_transform, download=True)
# 给训练集创建一个数据集加载器
train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 加载测试数据集
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, transform=data_transform, download=True)
# 给测试集创建一个数据集加载器
test_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 如果显卡可用,则用显卡进行训练
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# 调用 net 里定义的模型,如果 GPU 可用则将模型转到 GPU
model = MyVgg16Net().to(device)
# 定义损失函数(交叉熵损失)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义优化器(SGD:随机梯度下降)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9)
# 学习率每隔 10 个 epoch 变为原来的 0.1
lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=10, gamma=0.1)
# 定义训练函数
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
loss, current, n = 0.0, 0.0, 0
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
# 单通道转为三通道
X = np.array(X)
X = X.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置
image = np.concatenate((X, X, X), axis=0)
image = image.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置回来
image = torch.tensor(image) # 将 numpy 数据格式转为 tensor
# 前向传播
image, y = image.to(device), y.to(device)
output = model(image)
cur_loss = loss_fn(output, y)
_, pred = torch.max(output, axis=1)
cur_acc = torch.sum(y == pred) / output.shape[0]
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad()
cur_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss += cur_loss.item()
current += cur_acc.item()
n = n + 1
print('train_loss:' + str(loss / n))
print('train_acc:' + str(current / n))
# 定义测试函数
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
# 将模型转换为验证模式
model.eval()
loss, current, n = 0.0, 0.0, 0
# 非训练,推理期用到(测试时模型参数不用更新,所以 no_grad)
with torch.no_grad():
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
# 单通道转为三通道
X = np.array(X)
X = X.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置
image = np.concatenate((X, X, X), axis=0)
image = image.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置回来
image = torch.tensor(image) # 将 numpy 数据格式转为 tensor
image, y = image.to(device), y.to(device)
output = model(image)
cur_loss = loss_fn(output, y)
_, pred = torch.max(output, axis=1)
cur_acc = torch.sum(y == pred) / output.shape[0]
loss += cur_loss.item()
current += cur_acc.item()
n = n + 1
print('test_loss:' + str(loss / n))
print('test_acc:' + str(current / n))
# 开始训练
epoch = 100
for t in range(epoch):
lr_scheduler.step()
print(f"Epoch {t + 1}\n----------------------")
train(train_dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
test(test_dataloader, model, loss_fn)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "save_model/{}model.pth".format(t)) # 模型保存
print("Done!")test.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# 作者:赵泽荣
# 时间:2021年9月9日(农历八月初三)
# 个人站点:1.https://zhao302014.github.io/
# 2.https://blog.csdn.net/IT_charge/
# 个人GitHub地址:https://github.com/zhao302014
# ------------------------------------------------- #
import torch
from net import MyVgg16Net
import numpy as np
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torchvision.transforms import ToPILImage
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Scale(224), # 缩放图像大小为 224*224
transforms.ToTensor() # 仅对数据做转换为 tensor 格式操作
])
# 加载训练数据集
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, transform=data_transform, download=True)
# 给训练集创建一个数据集加载器
train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 加载测试数据集
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, transform=data_transform, download=True)
# 给测试集创建一个数据集加载器
test_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 如果显卡可用,则用显卡进行训练
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# 调用 net 里定义的模型,如果 GPU 可用则将模型转到 GPU
model = MyVgg16Net().to(device)
# 加载 train.py 里训练好的模型
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("./save_model/99model.pth"))
# 获取预测结果
classes = [
"0",
"1",
"2",
"3",
"4",
"5",
"6",
"7",
"8",
"9",
]
# 把 tensor 转成 Image,方便可视化
show = ToPILImage()
# 进入验证阶段
model.eval()
# 对 test_dataset 里 10000 张手写数字图片进行推理
for i in range(len(test_dataset)):
x, y = test_dataset[i][0], test_dataset[i][1]
# tensor格式数据可视化
show(x).show()
# 扩展张量维度为 4 维
x = Variable(torch.unsqueeze(x, dim=0).float(), requires_grad=False).to(device)
# 单通道转为三通道
x = x.cpu()
x = np.array(x)
x = x.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置
x = np.concatenate((x, x, x), axis=0)
x = x.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置回来
x = torch.tensor(x).to(device) # 将 numpy 数据格式转为 tensor,并转回 cuda 格式
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model(x)
# 得到预测类别中最高的那一类,再把最高的这一类对应classes中的哪一个标签
predicted, actual = classes[torch.argmax(pred[0])], classes[y]
# 最终输出预测值与真实值
print(f'Predicted: "{predicted}", Actual: "{actual}"')
© 2021 GitHub, Inc.






















 1011
1011











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










