基本概念
在定义一个新的类B时,如果该类与某个已有的类A的特点相似,及B拥有A的全部特点,那么久可以把A作为一个基类,而把B作为一个派生类(子 类)
派生类写法:
class A:public B{
……..
;}
class CStudent{
private:
string sName;
int nAge;
public:
bool isThreeGood(){};
void setName(const string & name){
sName=name;
}
};
class CUndergraduateStudent:public CStudent{
private:
int nDepartment;
public:
bool isThreeGood();
bool CanBaoYan();
};举例:
class CStudent{
private:
string name;string id;
char gender; int age;
public:
void PrintInfo();
void SetInfo(const string & name_, const string & id_, char gender_, int age_);
string GetName() {
return name;
}
};
void CStudent::PrintInfo() {
cout << "Name:" << name << endl;
cout << "ID:" << id << endl;
cout << "Age:" << age << endl;
cout << "Gender:" << gender << endl;
}
void CStudent::SetInfo(const string & name_, const string & id_, char gender_, int age_) {
name = name_; id = id_;
gender = gender_; age = age_;
}
class CUndergraduateStudent:public CStudent{
private:
string deparment;
public:
void QualifiedForBaoYan() {
cout << "qualified for baoyan" << endl;
}
void PrintInfo() {
CStudent::PrintInfo();
cout << "deparment:" << deparment << endl;
}
void SetInfo(const string & name_, const string & id_, char gender_, int age_, const string &deparment_) {
CStudent::SetInfo(name_, id_, gender_, age_);
deparment = deparment_;
}
};
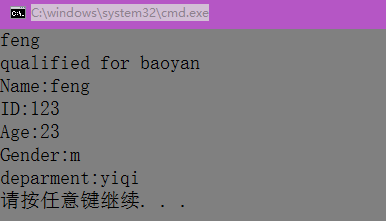
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
CUndergraduateStudent s2;
s2.SetInfo("feng", "123", 'm', 23, "yiqi");
cout << s2.GetName() << endl;
s2.QualifiedForBaoYan();
s2.PrintInfo();
return 0;
}输出:
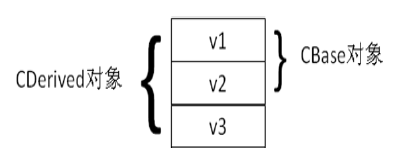
派生类对象的内存空间
派生类对象的体积,等于基类对象的体积,加上派生类对象自己成员变量的体积。
class BASE{
int v1,v2;
}
class deriverd:public BASE{
int v3;
}继承和复合关系
继承:“是”的关系
–基类A,B是基类A的派生类。
–逻辑上要求,一个B对象也是A对象。
———- *
复合:“有”的关系
–类C中有成员变量K,K是类D的对象,则C和D是复合关系
–逻辑上要求,D对象是C对象固有属性或组成部分
- 继承–一个男人同时也是人
- 点与圆
注意:
一个圆不是一个点,而圆包含点的属性(圆心)
基类/派生类同名成员 与Protected关键字
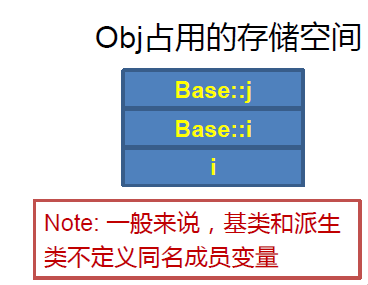
- 基类/派生类同名成员
class base{
private:
int j;
public:
int i;
void fun();
};
class derived:public base{
private:
public:
int i;
void access();
void func();
};
void derived::access(){
j = 5; //error
i = 5; //引用的是派生类的 i
base::i = 5; //引用的是基类的 i
func(); //派生类的
base::func(); //基类的
}
- Protected关键字
基类的private成员: 可以被下列函数访问
•—-基类的成员函数
•—-基类的友员函数
基类的public成员: 可以被下列函数访问
•—-基类的成员函数
•—-基类的友员函数
•—-派生类的成员函数
•—-派生类的友员函数
•—-其他的函数
基类的protected成员: 可以被下列函数访问
•—-基类的成员函数
•—-基类的友员函数
•—-派生类的成员函数可以访问当前对象的基类的保护成员
class Father {
private: int nPrivate; //私有成员
public: int nPublic; //公有成员
protected: int nProtected; // 保护成员
};
class Son : public Father {
void AccessFather() {
nPublic = 1; // ok;
nPrivate = 1; // wrong
nProtected = 1; // OK, 访问从基类继承的protected成员
Son f;
f.nProtected = 1; //wrong, f不是当前对象
}
};
int main() {
Father f;
Son s;
f.nPublic = 1; // Ok
s.nPublic = 1; // Ok
f.nProtected = 1; // error
f.nPrivate = 1; // error
s.nProtected = 1; //error
s.nPrivate = 1; // error
return 0;
}派生类的构造函数
派生类对象包含基类对象
执行派生类对象构造函数之前,先执行基类对象构造函数
class Bug {
private:
int nLegs; int nColor;
public:
int nType;
Bug(int legs, int color);
void PrintBug() { };
};
class FlyBug : public Bug { // FlyBug是Bug的派生类
int nWings;
public:
FlyBug(int legs, int color, int wings);
};
Bug::Bug(int legs, int color) {
nLegs = legs;
nColor = color;
}
//错误的FlyBug构造函数:
FlyBug::FlyBug(int legs, int color, int wings) {
nLegs = legs; // 不能访问
nColor = color; // 不能访问
nType = 1; // ok
nWings = wings;
}
//正确的FlyBug构造函数:
FlyBug::FlyBug(int legs, int color, int wings) :Bug(legs, color) {
nWings = wings;
}
int main() {
FlyBug fb(2, 3, 4);
fb.PrintBug();
fb.nType = 1;
fb.nLegs = 2; // error.nLegs is private
return 0;
}调用基类构造函数的两种方式
- 显式方式(基类构造函数提供参数)
- 隐式方式(省略基类构造函数,调用基类默认构造函数)
派生类析构函数执行时候,先执行派生类析构函数,在执行基类析构函数
class Base{
public:
int n;
Base(int i) :n(i) {
cout << "Base" << n << "constructed" << endl;
}
~Base() {
cout << "Base" << n << "deconstructed" << endl;
}
};
class Derived:public Base{
public:
Derived(int i) :Base(i) {
cout <<"derived constructed" << endl;
}
~Derived() {
cout << "derived deconstructed" << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
Derived obj(3);
return 0;
}public继承的赋值兼容规则
class base{};
class derived:public base{
base b;
}
derived d;
- 派生类对象可以赋值给基类: b=d;
- 派生类对象可以初始化基类引用:base & br=d;
- 派生类对地址可以赋值给基类地址:base *br=&d;
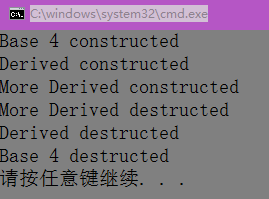
class Base {
public: int n;
Base(int i) :n(i) {
cout << "Base " << n << " constructed" << endl;
}
~Base() {
cout << "Base " << n << " destructed" << endl;
}
};
class Derived :public Base
{
public:
Derived(int i) :Base(i) {
cout << "Derived constructed" << endl;
}
~Derived() {
cout << "Derived destructed" << endl;
}
};
class MoreDerived :public Derived {
public:
MoreDerived() :Derived(4) {
cout << "More Derived constructed" << endl;
}
~MoreDerived() {
cout << "More Derived destructed" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
MoreDerived Obj;
return 0;
}























 368
368











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








