- 一个类可以定义自己类型的对象吗?
类中定义静态变量
class base {
static base base1;
};
int main() {
return 0;
}定义静态类没有问题,因为他们是共享的
类中定义指针
class base {
base *base1;
};
int main() {
return 0;
}这个是没问题的啊,可以想到做的leetcode里面怎么定义treeNode的。这里面不知道是不是有一个默认构造函数,base1指向null的。()
int main() {
class base {
public:
base *base1;
};
base w;
if (w.base1 == NULL)
cout << "yes" << endl;
return 0;
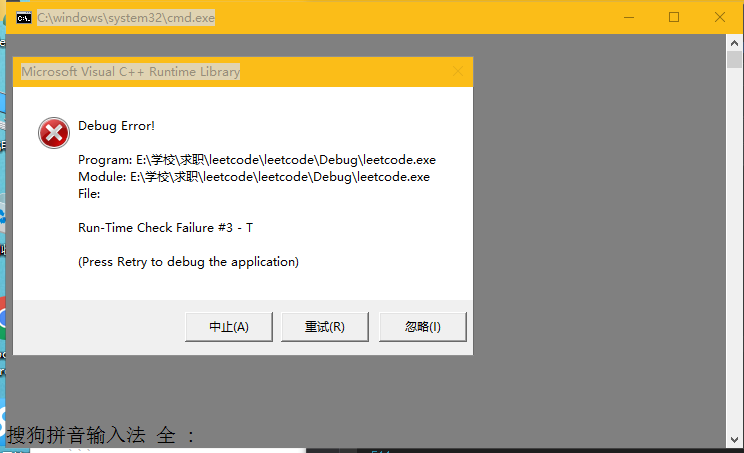
}能够编译成功,但运行出错
int main() {
class base {
public:
base *base1;
base():base1(NULL){}
};
base w;
if (w.base1 == NULL)
cout << "yes" << endl;
return 0;
}类中再定义类
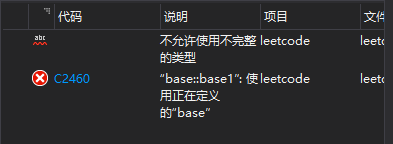
class base {
base base1;
};
int main() {
return 0;
}解释:类里面再定义一个本类,然后本类再定义另外一个类,无穷无尽啊。
- 为什么空类大小不为0
#
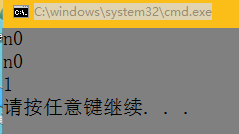
空类不为0,是为了生成不同类的时候,他们所在地址不相同。
class base {
};
int main() {
base *a =new base(), *b = new base();
if (a == b)
cout << "yes" << endl;
else
cout << "n0" << endl;
base c, d;
if (&c==&d)
cout << "yes" << endl;
else
cout << "n0" << endl;
return 0;
}题目1
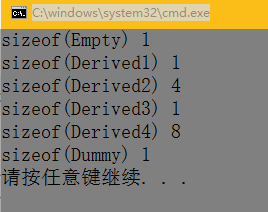
class Empty{ };
class Derived1 : public Empty{};
class Derived2 : virtual public Empty{};
class Derived3 : public Empty{
char c;
};
class Derived4 : virtual public Empty{
char c;
};
class Dummy{
char c;
};
int main() {
cout << "sizeof(Empty) " << sizeof(Empty) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived1) " << sizeof(Derived1) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived2) " << sizeof(Derived2) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived3) " << sizeof(Derived3) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived4) " << sizeof(Derived4) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Dummy) " << sizeof(Dummy) << endl;
return 0;
}#
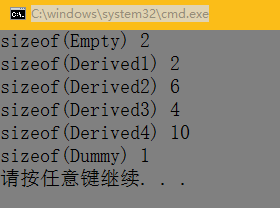
class Empty{ short int i; };
class Derived1 : public Empty{};
class Derived2 : virtual public Empty{};
class Derived3 : public Empty{
char c;
};
class Derived4 : virtual public Empty{
char c;
};
class Dummy{
char c;
};
int main() {
cout << "sizeof(Empty) " << sizeof(Empty) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived1) " << sizeof(Derived1) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived2) " << sizeof(Derived2) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived3) " << sizeof(Derived3) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived4) " << sizeof(Derived4) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Dummy) " << sizeof(Dummy) << endl;
return 0;
}#
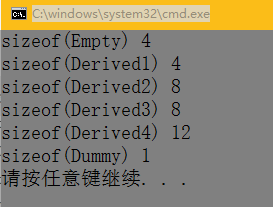
class Empty{ int i; };
class Derived1 : public Empty{};
class Derived2 : virtual public Empty{};
class Derived3 : public Empty{
char c;
};
class Derived4 : virtual public Empty{
char c;
};
class Dummy{
char c;
};
int main() {
cout << "sizeof(Empty) " << sizeof(Empty) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived1) " << sizeof(Derived1) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived2) " << sizeof(Derived2) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived3) " << sizeof(Derived3) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Derived4) " << sizeof(Derived4) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(Dummy) " << sizeof(Dummy) << endl;
return 0;
}总结,继承一个空类,不会在原有大小为1 的基础上增加对应的大小。
如果有虚函数,那就先加4,因为里面有虚指针。
第一个里面,一开始为空,到了虚函数,先加4,然后char c本身占据1个字节,但是不能小于之前的字节量,所以也加4;
第二个里面,short int 占据2个字节,在public那边,已经占据2个,char c本身占据1个字节,但再加的内存不能再小于2,所以加2,得4;到了虚函数,先加4,然后char c本身占据1个字节,但是不能小于之前的字节量,所以也加4,得10;
最后一个同理了,int首先是4字节,后面增加的不能小于4,所以出现一个12





















 598
598

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








