import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
os.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = "tensorflow"
os.environ['HF_ENDPOINT'] = 'https://hf-mirror.com'
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import ndimage
from IPython.display import Image, display
import tensorflow as tf
import keras
from keras import layers
from keras.applications import xception
img_size = (299, 299, 3)
model = xception.Xception()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_img_array(img_path, size=(299, 299)):#加载图片数据
img = keras.utils.load_img(img_path, target_size=size)
array = keras.utils.img_to_array(img)
array = np.expand_dims(array, axis=0)
return array
def get_gradients(img_input, top_pred_idx,model):#获取梯度
images = tf.cast(img_input, tf.float32)#float32
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(images)
preds = model(images)#获取模型预测
top_class = preds[:, top_pred_idx]#模型预测的类的分数
grads = tape.gradient(top_class, images)
return grads
def get_integrated_gradients(img_input, top_pred_idx, baseline=None,model=None, num_steps=50):
if baseline is None:#形状(299,299,3)
baseline = np.zeros(img_size).astype(np.float32)
else:
baseline = baseline.astype(np.float32)
img_input = img_input.astype(np.float32)
interpolated_image = [
baseline + (step / num_steps) * (img_input - baseline)
for step in range(num_steps + 1)#51次,随步数的增加,img_input - baseline的占比加大,51
]
# print(f'{len(interpolated_image)=}')
interpolated_image = np.array(interpolated_image).astype(np.float32)#(51,299,299,3)
print(interpolated_image.shape)
interpolated_image = xception.preprocess_input(interpolated_image)#转换数据到(-1,1)
# print(interpolated_image[-1].max(),interpolated_image[-1].min())
grads = []
for i, img in enumerate(interpolated_image):#51次
img = tf.expand_dims(img, axis=0)#变成4维张量
grad = get_gradients(img,top_pred_idx,model)#获取梯度
grads.append(grad[0])#添加梯度图
grads = tf.convert_to_tensor(grads, dtype=tf.float32)#(51,299,299,3)
grads = (grads[:-1] + grads[1:]) / 2.0#(50,299,299,3)
avg_grads = tf.reduce_mean(grads, axis=0)#求interpolated_image的平均梯度
# print(f'{avg_grads.shape=},{grads.shape=}')
integrated_grads = (img_input - baseline) * avg_grads#(1,299,299,3)*(299,299,3),对应元素相乘
return integrated_grads
def random_baseline_integrated_gradients(#随机baseline
img_input, top_pred_idx,model=None,num_steps=50, num_runs=2
):
integrated_grads = []
for run in range(num_runs):#0,1
baseline = np.random.random(img_size) * 255#获取0-1之间的随机数,形状(299,299,3)
igrads = get_integrated_gradients(
img_input=img_input,
top_pred_idx=top_pred_idx,
baseline=baseline,
num_steps=num_steps,
model=model
)
integrated_grads.append(igrads)#两次
integrated_grads = tf.convert_to_tensor(integrated_grads)
return tf.reduce_mean(integrated_grads, axis=0)#(299.299.3)
def __init__(self, positive_channel=None, negative_channel=None):
if positive_channel is None:
self.positive_channel = [0, 255, 0]
else:
self.positive_channel = positive_channel
if negative_channel is None:
self.negative_channel = [255, 0, 0]
else:
self.negative_channel = negative_channel
def apply_polarity(self, attributions, polarity):
if polarity == "positive":
return np.clip(attributions, 0, 1)
else:
return np.clip(attributions, -1, 0)
def apply_linear_transformation(
self,
attributions,
clip_above_percentile=99.9,
clip_below_percentile=70.0,
lower_end=0.2,
):
m = self.get_thresholded_attributions(
attributions, percentage=100 - clip_above_percentile
)
e = self.get_thresholded_attributions(
attributions, percentage=100 - clip_below_percentile
)
transformed_attributions = (1 - lower_end) * (np.abs(attributions) - e) / (
m - e
) + lower_end
transformed_attributions *= np.sign(attributions)
transformed_attributions *= transformed_attributions >= lower_end
transformed_attributions = np.clip(transformed_attributions, 0.0, 1.0)
return transformed_attributions
def get_thresholded_attributions(self, attributions, percentage):
if percentage == 100.0:
return np.min(attributions)
flatten_attr = attributions.flatten()
total = np.sum(flatten_attr)
sorted_attributions = np.sort(np.abs(flatten_attr))[::-1]
cum_sum = 100.0 * np.cumsum(sorted_attributions) / total
indices_to_consider = np.where(cum_sum >= percentage)[0][0]
attributions = sorted_attributions[indices_to_consider]
return attributions
def binarize(self, attributions, threshold=0.001):
return attributions > threshold
def morphological_cleanup_fn(self, attributions, structure=np.ones((4, 4))):
closed = ndimage.grey_closing(attributions, structure=structure)
opened = ndimage.grey_opening(closed, structure=structure)
return opened
def draw_outlines(
self,
attributions,
percentage=90,
connected_component_structure=np.ones((3, 3)),
):
attributions = self.binarize(attributions)
attributions = ndimage.binary_fill_holes(attributions)
connected_components, num_comp = ndimage.label(
attributions, structure=connected_component_structure
)
total = np.sum(attributions[connected_components > 0])
component_sums = []
for comp in range(1, num_comp + 1):
mask = connected_components == comp
component_sum = np.sum(attributions[mask])
component_sums.append((component_sum, mask))
sorted_sums_and_masks = sorted(component_sums, key=lambda x: x[0], reverse=True)
sorted_sums = list(zip(*sorted_sums_and_masks))[0]
cumulative_sorted_sums = np.cumsum(sorted_sums)
cutoff_threshold = percentage * total / 100
cutoff_idx = np.where(cumulative_sorted_sums >= cutoff_threshold)[0][0]
if cutoff_idx > 2:
cutoff_idx = 2
border_mask = np.zeros_like(attributions)
for i in range(cutoff_idx + 1):
border_mask[sorted_sums_and_masks[i][1]] = 1
eroded_mask = ndimage.binary_erosion(border_mask, iterations=1)
border_mask[eroded_mask] = 0
return border_mask
def process_grads(
self,
image,
attributions,
polarity="positive",
clip_above_percentile=99.9,
clip_below_percentile=0,
morphological_cleanup=False,
structure=np.ones((3, 3)),
outlines=False,
outlines_component_percentage=90,
overlay=True,
):
if polarity not in ["positive", "negative"]:
raise ValueError(
f""" Allowed polarity values: 'positive' or 'negative'
but provided {polarity}"""
)
if clip_above_percentile < 0 or clip_above_percentile > 100:
raise ValueError("clip_above_percentile must be in [0, 100]")
if clip_below_percentile < 0 or clip_below_percentile > 100:
raise ValueError("clip_below_percentile must be in [0, 100]")
if polarity == "positive":
attributions = self.apply_polarity(attributions, polarity=polarity)
channel = self.positive_channel
else:
attributions = self.apply_polarity(attributions, polarity=polarity)
attributions = np.abs(attributions)
channel = self.negative_channel
attributions = np.average(attributions, axis=2)
attributions = self.apply_linear_transformation(
attributions,
clip_above_percentile=clip_above_percentile,
clip_below_percentile=clip_below_percentile,
lower_end=0.0,
)
if morphological_cleanup:
attributions = self.morphological_cleanup_fn(
attributions, structure=structure
)
if outlines:
attributions = self.draw_outlines(
attributions, percentage=outlines_component_percentage
)
attributions = np.expand_dims(attributions, 2) * channel
if overlay:
attributions = np.clip((attributions * 0.8 + image), 0, 255)
return attributions
def visualize(
self,
image,
gradients,
integrated_gradients,
polarity="positive",
clip_above_percentile=99.9,
clip_below_percentile=0,
morphological_cleanup=False,
structure=np.ones((3, 3)),
outlines=False,
outlines_component_percentage=90,
overlay=True,
figsize=(15, 8),
):
img1 = np.copy(image)
img2 = np.copy(image)
grads_attr = self.process_grads(
image=img1,
attributions=gradients,
polarity=polarity,
clip_above_percentile=clip_above_percentile,
clip_below_percentile=clip_below_percentile,
morphological_cleanup=morphological_cleanup,
structure=structure,
outlines=outlines,
outlines_component_percentage=outlines_component_percentage,
overlay=overlay,
)
igrads_attr = self.process_grads(
image=img2,
attributions=integrated_gradients,
polarity=polarity,
clip_above_percentile=clip_above_percentile,
clip_below_percentile=clip_below_percentile,
morphological_cleanup=morphological_cleanup,
structure=structure,
outlines=outlines,
outlines_component_percentage=outlines_component_percentage,
overlay=overlay,
)
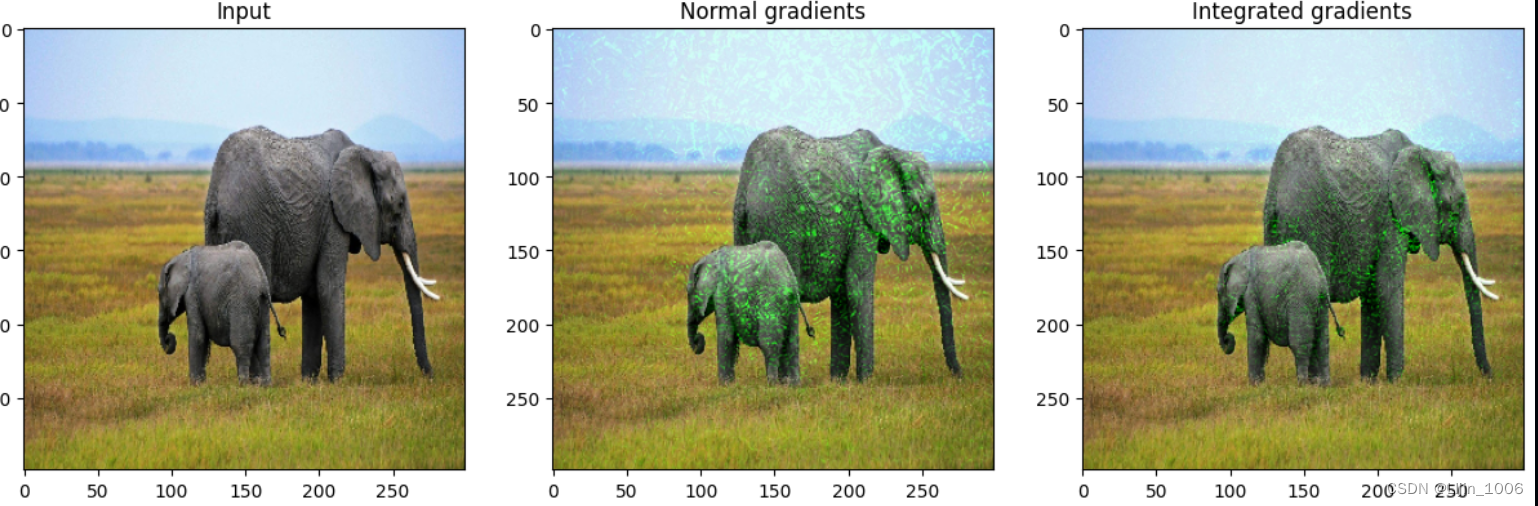
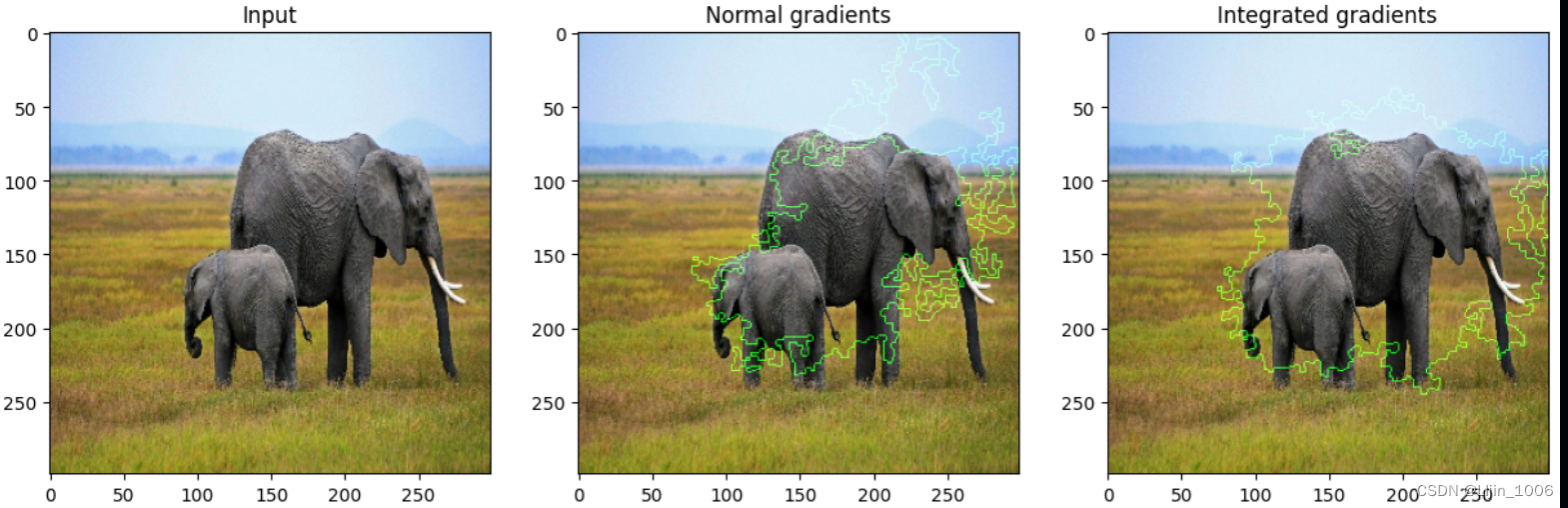
_, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=figsize)
ax[0].imshow(image)
ax[1].imshow(grads_attr.astype(np.uint8))
ax[2].imshow(igrads_attr.astype(np.uint8))
ax[0].set_title("Input")
ax[1].set_title("Normal gradients")
ax[2].set_title("Integrated gradients")
plt.show()
img = get_img_array(img_path)
print(img.shape,img.max(),img.min())#(1, 299, 299, 3) 255.0 0.0
orig_img = np.copy(img[0]).astype(np.uint8)# (299, 299, 3),原图
print(orig_img.shape,orig_img.max(),orig_img.min())
plt.imshow(orig_img.astype('uint8'))
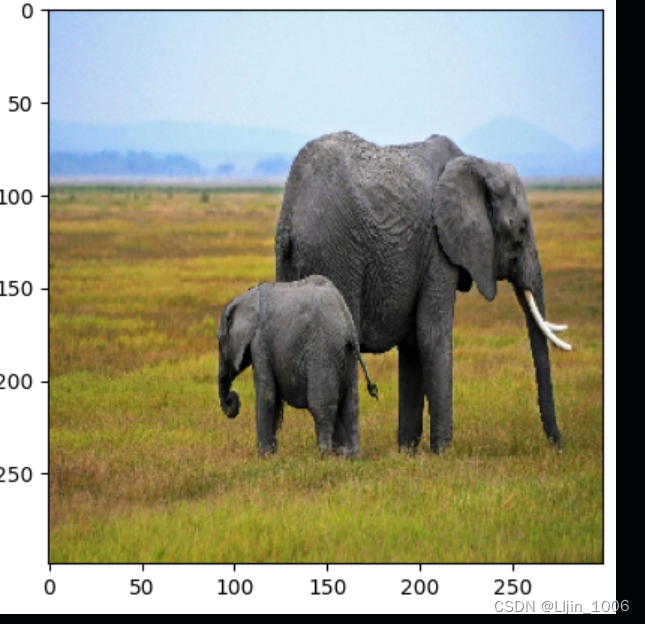
img_processed = tf.cast(xception.preprocess_input(img), dtype=tf.float32)#(1, 299, 299, 3)
preds = model.predict(img_processed)#获取xception对图片的预测
#(1,1000) 0.7279243 0 float32 386,模型预测是对图片所属类别的置信程度
#最大值对应的索引就是模型预测的类别
print(preds.shape,preds.max(),preds.min(),preds.dtype,preds.argmax())
top_pred_idx = tf.argmax(preds[0])#预测的类别
print("Predicted:", top_pred_idx, xception.decode_predictions(preds, top=1)[0])
plt.imshow((img_processed[0]*0.5+0.5))
grads = get_gradients(img_processed,top_pred_idx,model)
aa=grads*10+0.5
plt.imshow(aa[0])
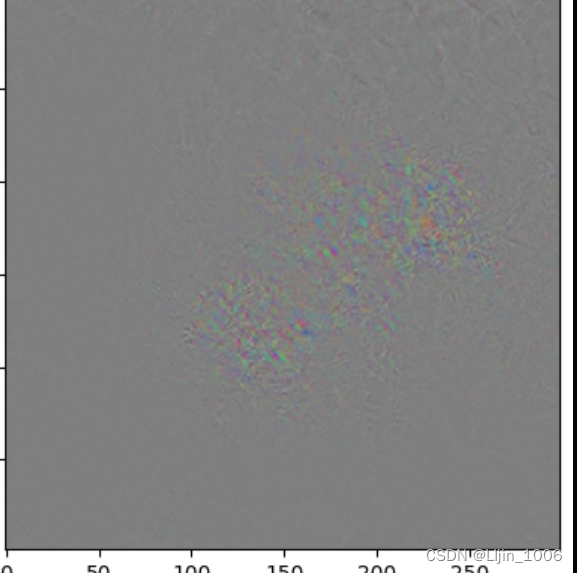
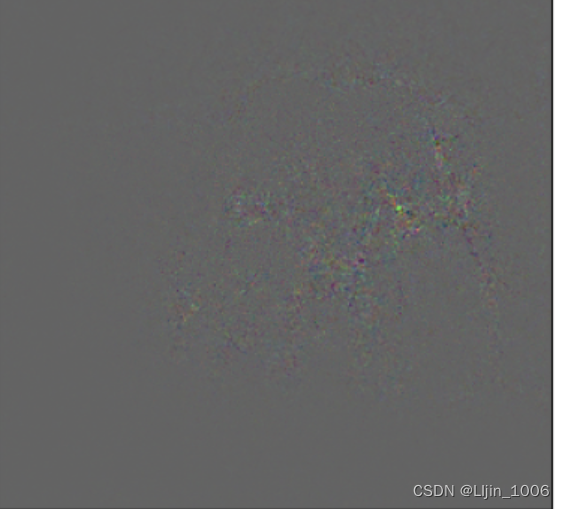
igrads = random_baseline_integrated_gradients(
np.copy(orig_img), top_pred_idx=top_pred_idx,model=model,num_steps=50, num_runs=2
)
bb=(igrads-tf.reduce_min(igrads))/(tf.reduce_max(igrads)-tf.reduce_min(igrads))
plt.imshow(bb)
vis = GradVisualizer()
vis.visualize(
image=orig_img,
gradients=grads[0].numpy(),
integrated_gradients=igrads.numpy(),
clip_above_percentile=99,
clip_below_percentile=0,
)
vis.visualize(
image=orig_img,
gradients=grads[0].numpy(),
integrated_gradients=igrads.numpy(),
clip_above_percentile=95,
clip_below_percentile=28,
morphological_cleanup=True,
outlines=True,
)





















 871
871

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








