Andrew Ng coursera上的《机器学习》ex2
按照课程所给的ex2的文档要求,ex2要求完成以下几个计算过程的代码编写:
| exerciseName | description |
|---|---|
| plotData.m | function to plot 2D classification data |
| sigmoid.m | 是逻辑回归的定义函数 |
| costFunction.m | logistics regression cost function |
| predict.m | logistics regression prediction function |
| costFuntionReg.m | regularized logistic regression |
这一周的练习主要是考察对于逻辑回归函数的掌握,先是逻辑回归函数的定义sigmod函数,接着是它相对应的代价函数,接着是预测函数,最后是正则化的逻辑回归函数。
1. plotData.m
function plotData(X, y)
%PLOTDATA Plots the data points X and y into a new figure
% PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points with + for the positive examples
% and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be a Mx2 matrix.
% Create New Figure
figure; hold on;
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Plot the positive and negative examples on a
% 2D plot, using the option 'k+' for the positive
% examples and 'ko' for the negative examples.
%
pos = find(y == 1);
neg = find(y == 0);
plot(X(pos,1),X(pos,2),'k+','LineWidth',2, ...
'MarkerSize',7);
plot(X(neg,1),X(neg,2),'ko','MarkerFaceColor','y', ...
'MarkerSize',7);
% =========================================================================
hold off;
end2.sigmod.m
这个函数是逻辑回归函数的定义。定义如下:
g(z)= 1/(1+e^(-z))
h(x)=g(theta' * x)
Octave代码如下:
function g = sigmoid(z)
%SIGMOID Compute sigmoid functoon
% J = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z.
% You need to return the following variables correctly
g = zeros(size(z));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix,
% vector or scalar).
x = -z;
g = 1./(ones(size(z))+exp(x));
% =============================================================
end需要注意的是这里的z可能是矩阵,向量等多个元素的集合。所以需要在除的时候逐个儿计算。(加了.)
3. costFunction.m
如下是逻辑回归函数的代价函数的定义。
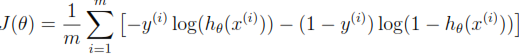
Octave代码如下:
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y)
%COSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression
% J = COSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y) computes the cost of using theta as the
% parameter for logistic regression and the gradient of the cost
% w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta
%
J = ((-y' * log(sigmoid(X*theta))) - (1-y)' * log(1-sigmoid(X*theta)))/m;
grad = (X' * (sigmoid(X*theta) - y)) ./ m;
% =============================================================
end4.predict.m
Octave代码如下:
function p = predict(theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic
%regression parameters theta
% p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a
% threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1)
m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(m, 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters.
% You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's
%
p = floor(sigmoid(X*theta) .* 2);
% =========================================================================
end其中的预测条件是概率大于0.5的时候是为1,小于0.5的时候为0。所以可以采用下取整函数floor.同时将sigmod(theta*x) . * 2,乘以2之后的值 大于0.5的将会大于1,下取整 就可以取1,小于0.5的下取整就是0就可以预测为0。
5.costFuntionReg.m
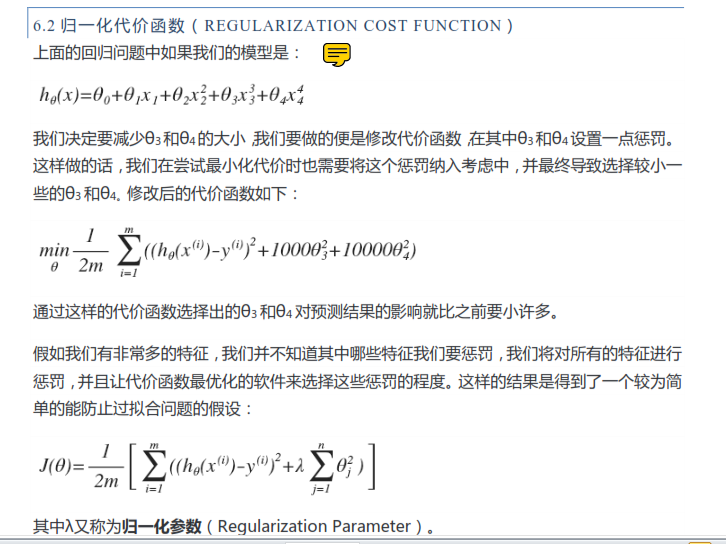
参数的归一化的相关内容见下图:
逻辑回归函数的归一化定义如下:
function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda)
%COSTFUNCTIONREG Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with regularization
% J = COSTFUNCTIONREG(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
J = ((-y' * log(sigmoid(X*theta))) ...
- (1-y)' * log(1-sigmoid(X*theta)))/m ...
+ (sum(theta .^2) - theta(1)^2)*lambda / (2 * m);
grad(1) = (X(:,1)' * (sigmoid(X*theta) -y)) ./ m;
for i = 2:size(theta)
grad(i) = (X(:,i)' * (sigmoid(X*theta) -y)) ./ m ...
+ lambda*theta(i)/m
% =============================================================
end由于该逻辑回归函数是关于参数theta的,所以后面的lambda是参数theta的归一化。























 307
307

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








