前言
本篇博客是我对分别使用MLP和CNN完成姓氏分类系统进行了学习之后,使用费曼学习法通过输出反向倒逼自己"被输入"知识,从而更好的学习这方面的知识.若文中存在任何错误或不当之处,恳请各位不吝赐教.
本文主要分为使用MLP完成姓氏分类系统和使用CNN完成姓氏分类系统两部分.先对不同模型的原理进行分析和讨论,再使用代码实现.
姓氏分类系统的任务是将姓氏分类到其原籍国
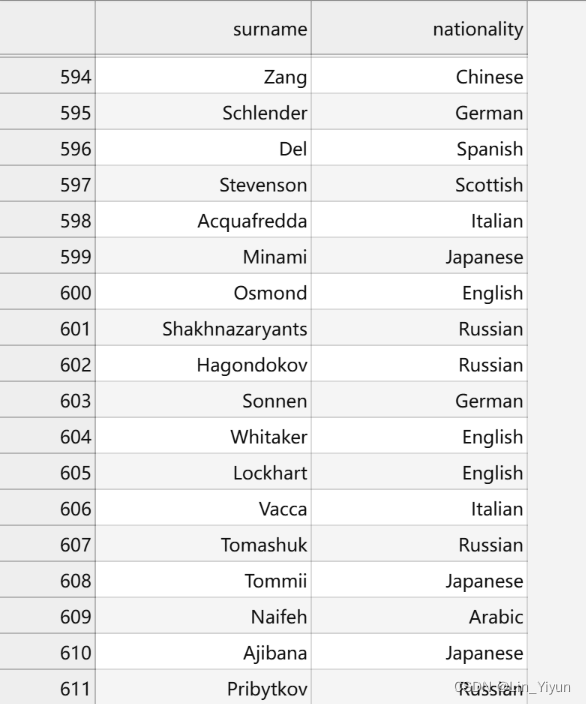
通过让模型学习这些数据,任意给一个姓氏,让模型预测是哪个国家的姓氏
看起来很简单吧,让我们开始吧!
MLP?你小子行吗?
MLP的原理分析
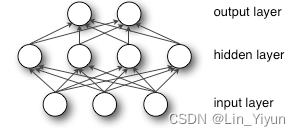
上图就是一个最简单的MLP结构示意图
除了输入层和输出层,多层感知机(MLP)还包括至少一层隐藏层,实际上,可以有多个这样的隐藏层。值得注意的是,这些层之间是全连接的,意味着前一层的每一个神经元都与下一层的所有神经元相连,这种结构确保了信息能够在整个网络中充分传播和交互。
具体来说,隐藏层的作用在于进行非线性变换
什么是线性变换 什么又是非线性变换???
线性变换
在神经网络中,每一层的神经元接收来自前一层的输入,并执行加权求和的操作,再加上一个偏置项(bias)。这个过程可以用矩阵乘法和向量加法表示,本质上是一个线性变换。如果网络只包含这些线性变换,无论有多少层,整体上它仍然只能表达一个线性函数,因为线性函数的复合仍然是线性函数。
非线性变换:激活函数的角色
为了使神经网络能够逼近复杂的非线性函数,我们需要在每一层的线性变换之后添加一个非线性元素,这就是激活函数的由来。激活函数是一个非线性的数学函数,它被应用于每个神经元的加权求和结果上,产生该神经元的最终输出。
举个例子,考虑一个二分类问题,其中两类数据在二维平面上的分布是非线性的,无法通过一条直线分开。在这种情况下,单靠输入层和输出层的线性操作是无法实现有效分类的。但通过添加隐藏层,尤其是多层隐藏层,网络就能学会构建更复杂的决策边界,有效地将这两类数据区分开来。
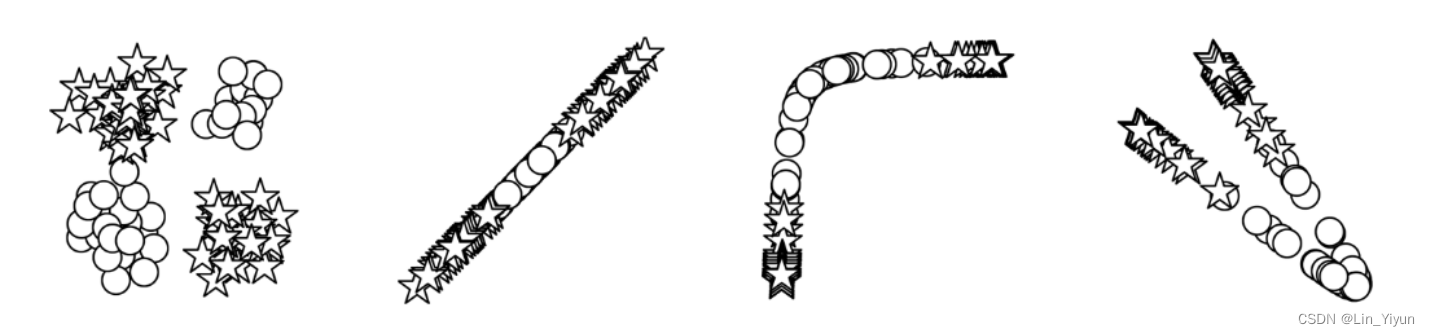
现在我们再把MLP和我们要解决的问题---姓氏分类到其原籍国 联系一下
我们在怎么做?
- 先要有一个数据集,无论是机器学习还是深度学习都遵循着"垃圾进垃圾出"的定律,进行数据清洗,特征工程
- 然后就将数据丢进MLP?不太行吧,MLP也不是什么都吃的 我们得将数据变成MLP能吃下去的形式,所以可以使用词汇表、向量化器和DataLoader将姓氏字符串转换为向量化的minibatches.
- 然后就让MLP这小伙子开始学?把这些姓氏和国籍给他"吃"(学习)一遍,然后就开始考试?显然是不对的吧?以辅导老师的角度想一想,如果让你去辅导MLP这小伙去备战高考,你会怎么做?
- 先让MLP这小伙子把考点熟悉一遍
- 做个小测试,看看他哪些学的好哪些学的不好
- 根据测试结果调整授课侧重点
- 再测试再调整
让我们回到MLP模型的训练上来,把辅导高考的流程转移到训练模型上
- 前向传播---把考点熟悉一遍
- 损失函数---做个小测试
- 梯度下降算法---调整侧重点
- 反向传播---再测试再调整
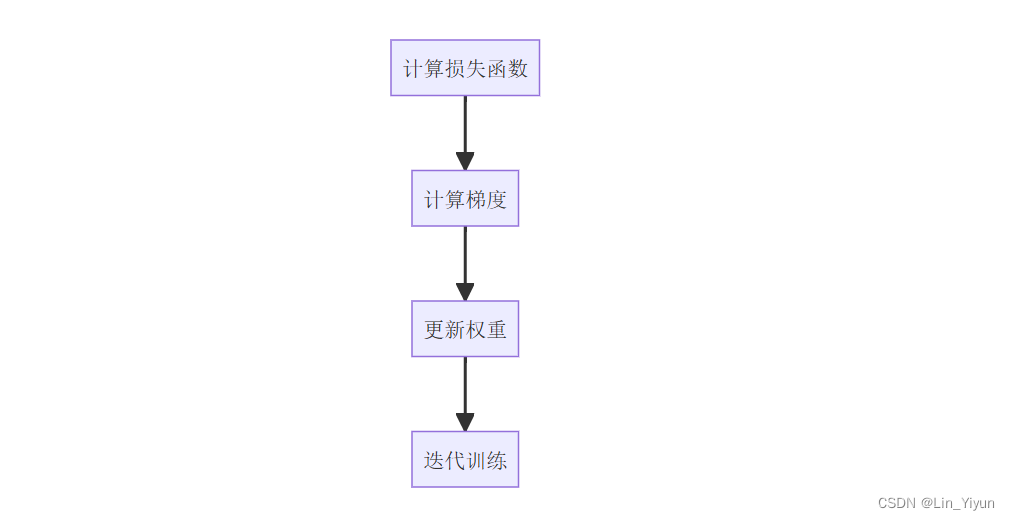
大概流程已经知道了,让我们开始编码吧
编码
向量化
使用词汇表、向量化器和DataLoader将姓氏字符串转换为向量化的minibatches,让MLP能看得懂"考点"
The Vocabulary
class Vocabulary(object):
"""Class to process text and extract vocabulary for mapping"""
def __init__(self, token_to_idx=None, add_unk=True, unk_token="<UNK>"):
"""
Args:
token_to_idx (dict): a pre-existing map of tokens to indices
add_unk (bool): a flag that indicates whether to add the UNK token
unk_token (str): the UNK token to add into the Vocabulary
"""
if token_to_idx is None:
token_to_idx = {}
self._token_to_idx = token_to_idx
self._idx_to_token = {idx: token
for token, idx in self._token_to_idx.items()}
self._add_unk = add_unk
self._unk_token = unk_token
self.unk_index = -1
if add_unk:
self.unk_index = self.add_token(unk_token)
def to_serializable(self):
""" returns a dictionary that can be serialized """
return {'token_to_idx': self._token_to_idx,
'add_unk': self._add_unk,
'unk_token': self._unk_token}
@classmethod
def from_serializable(cls, contents):
""" instantiates the Vocabulary from a serialized dictionary """
return cls(**contents)
def add_token(self, token):
"""Update mapping dicts based on the token.
Args:
token (str): the item to add into the Vocabulary
Returns:
index (int): the integer corresponding to the token
"""
try:
index = self._token_to_idx[token]
except KeyError:
index = len(self._token_to_idx)
self._token_to_idx[token] = index
self._idx_to_token[index] = token
return index
def add_many(self, tokens):
"""Add a list of tokens into the Vocabulary
Args:
tokens (list): a list of string tokens
Returns:
indices (list): a list of indices corresponding to the tokens
"""
return [self.add_token(token) for token in tokens]
def lookup_token(self, token):
"""Retrieve the index associated with the token
or the UNK index if token isn't present.
Args:
token (str): the token to look up
Returns:
index (int): the index corresponding to the token
Notes:
`unk_index` needs to be >=0 (having been added into the Vocabulary)
for the UNK functionality
"""
if self.unk_index >= 0:
return self._token_to_idx.get(token, self.unk_index)
else:
return self._token_to_idx[token]
def lookup_index(self, index):
"""Return the token associated with the index
Args:
index (int): the index to look up
Returns:
token (str): the token corresponding to the index
Raises:
KeyError: if the index is not in the Vocabulary
"""
if index not in self._idx_to_token:
raise KeyError("the index (%d) is not in the Vocabulary" % index)
return self._idx_to_token[index]
def __str__(self):
return "<Vocabulary(size=%d)>" % len(self)
def __len__(self):
return len(self._token_to_idx)The Vectorizer
class SurnameVectorizer(object):
""" The Vectorizer which coordinates the Vocabularies and puts them to use"""
def __init__(self, surname_vocab, nationality_vocab):
"""
Args:
surname_vocab (Vocabulary): maps characters to integers
nationality_vocab (Vocabulary): maps nationalities to integers
"""
self.surname_vocab = surname_vocab
self.nationality_vocab = nationality_vocab
def vectorize(self, surname):
"""
Args:
surname (str): the surname
Returns:
one_hot (np.ndarray): a collapsed one-hot encoding
"""
vocab = self.surname_vocab
one_hot = np.zeros(len(vocab), dtype=np.float32)
for token in surname:
one_hot[vocab.lookup_token(token)] = 1
return one_hot
@classmethod
def from_dataframe(cls, surname_df):
"""Instantiate the vectorizer from the dataset dataframe
Args:
surname_df (pandas.DataFrame): the surnames dataset
Returns:
an instance of the SurnameVectorizer
"""
surname_vocab = Vocabulary(unk_token="@")
nationality_vocab = Vocabulary(add_unk=False)
for index, row in surname_df.iterrows():
for letter in row.surname:
surname_vocab.add_token(letter)
nationality_vocab.add_token(row.nationality)
return cls(surname_vocab, nationality_vocab)
@classmethod
def from_serializable(cls, contents):
surname_vocab = Vocabulary.from_serializable(contents['surname_vocab'])
nationality_vocab = Vocabulary.from_serializable(contents['nationality_vocab'])
return cls(surname_vocab=surname_vocab, nationality_vocab=nationality_vocab)
def to_serializable(self):
return {'surname_vocab': self.surname_vocab.to_serializable(),
'nationality_vocab': self.nationality_vocab.to_serializable()}The Dataset
# 姓氏数据集
class SurnameDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, surname_df, vectorizer):
"""
Args:
surname_df (pandas.DataFrame): the dataset
vectorizer (SurnameVectorizer): vectorizer instatiated from dataset
"""
self.surname_df = surname_df
self._vectorizer = vectorizer
self.train_df = self.surname_df[self.surname_df.split=='train']
self.train_size = len(self.train_df)
self.val_df = self.surname_df[self.surname_df.split=='val']
self.validation_size = len(self.val_df)
self.test_df = self.surname_df[self.surname_df.split=='test']
self.test_size = len(self.test_df)
self._lookup_dict = {'train': (self.train_df, self.train_size),
'val': (self.val_df, self.validation_size),
'test': (self.test_df, self.test_size)}
self.set_split('train')
# Class weights
class_counts = surname_df.nationality.value_counts().to_dict()
def sort_key(item):
return self._vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_token(item[0])
sorted_counts = sorted(class_counts.items(), key=sort_key)
frequencies = [count for _, count in sorted_counts]
self.class_weights = 1.0 / torch.tensor(frequencies, dtype=torch.float32)
@classmethod
def load_dataset_and_make_vectorizer(cls, surname_csv):
"""Load dataset and make a new vectorizer from scratch
Args:
surname_csv (str): location of the dataset
Returns:
an instance of SurnameDataset
"""
surname_df = pd.read_csv(surname_csv)
train_surname_df = surname_df[surname_df.split =='train']
return cls(surname_df, SurnameVectorizer.from_dataframe(train_surname_df))
@classmethod
def load_dataset_and_load_vectorizer(cls, surname_csv, vectorizer_filepath):
"""Load dataset and the corresponding vectorizer.
Used in the case in the vectorizer has been cached for re-use
Args:
surname_csv (str): location of the dataset
vectorizer_filepath (str): location of the saved vectorizer
Returns:
an instance of SurnameDataset
"""
surname_df = pd.read_csv(surname_csv)
vectorizer = cls.load_vectorizer_only(vectorizer_filepath)
return cls(surname_df, vectorizer)
@staticmethod
def load_vectorizer_only(vectorizer_filepath):
"""a static method for loading the vectorizer from file
Args:
vectorizer_filepath (str): the location of the serialized vectorizer
Returns:
an instance of SurnameVectorizer
"""
with open(vectorizer_filepath) as fp:
return SurnameVectorizer.from_serializable(json.load(fp))
def save_vectorizer(self, vectorizer_filepath):
"""saves the vectorizer to disk using json
Args:
vectorizer_filepath (str): the location to save the vectorizer
"""
with open(vectorizer_filepath, "w") as fp:
json.dump(self._vectorizer.to_serializable(), fp)
def get_vectorizer(self):
""" returns the vectorizer """
return self._vectorizer
def set_split(self, split="train"):
""" selects the splits in the dataset using a column in the dataframe """
self._target_split = split
self._target_df, self._target_size = self._lookup_dict[split]
def __len__(self):
return self._target_size
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""the primary entry point method for PyTorch datasets
Args:
index (int): the index to the data point
Returns:
a dictionary holding the data point's:
features (x_surname)
label (y_nationality)
"""
row = self._target_df.iloc[index]
surname_vector = \
self._vectorizer.vectorize(row.surname)
nationality_index = \
self._vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_token(row.nationality)
return {'x_surname': surname_vector,
'y_nationality': nationality_index}
def get_num_batches(self, batch_size):
"""Given a batch size, return the number of batches in the dataset
Args:
batch_size (int)
Returns:
number of batches in the dataset
"""
return len(self) // batch_size
def generate_batches(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=True,
drop_last=True, device="cpu"):
"""
A generator function which wraps the PyTorch DataLoader. It will
ensure each tensor is on the write device location.
"""
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=dataset, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=shuffle, drop_last=drop_last)
for data_dict in dataloader:
out_data_dict = {}
for name, tensor in data_dict.items():
out_data_dict[name] = data_dict[name].to(device)
yield out_data_dict定义模型
先把MLP模型定义出来才能训练啦
class SurnameClassifier(nn.Module):
# 第一个线性层将输入向量映射到中间向量,并对该向量应用非线性。第二线性层将中间向量映射到预测向量。
""" A 2-layer Multilayer Perceptron for classifying surnames """
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
"""
Args:
input_dim (int): the size of the input vectors
hidden_dim (int): the output size of the first Linear layer
output_dim (int): the output size of the second Linear layer
"""
super(SurnameClassifier, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x_in, apply_softmax=False):
"""The forward pass of the classifier
Args:
x_in (torch.Tensor): an input data tensor.
x_in.shape should be (batch, input_dim)
apply_softmax (bool): a flag for the softmax activation
should be false if used with the Cross Entropy losses
Returns:
the resulting tensor. tensor.shape should be (batch, output_dim)
"""
intermediate_vector = F.relu(self.fc1(x_in))
prediction_vector = self.fc2(intermediate_vector)
if apply_softmax:
prediction_vector = F.softmax(prediction_vector, dim=1)
return prediction_vector训练过程
先别急 虽说差生文具多 但是学习最基本的工具还是该有的吧
先定义一下辅助函数和做一些准备工作
什么准备工作?
你总不能教一个幼儿园的小豆丁三个月内精通高考数学吧
我们的准备工作主要是将我们刚刚定义好的MLP小豆丁迅速变成一个高中生
也就是加载预训练模型 加速训练
# Helper functions
def make_train_state(args):
return {'stop_early': False,
'early_stopping_step': 0,
'early_stopping_best_val': 1e8,
'learning_rate': args.learning_rate,
'epoch_index': 0,
'train_loss': [],
'train_acc': [],
'val_loss': [],
'val_acc': [],
'test_loss': -1,
'test_acc': -1,
'model_filename': args.model_state_file}
def update_train_state(args, model, train_state):
"""Handle the training state updates.
Components:
- Early Stopping: Prevent overfitting.
- Model Checkpoint: Model is saved if the model is better
:param args: main arguments
:param model: model to train
:param train_state: a dictionary representing the training state values
:returns:
a new train_state
"""
# Save one model at least
if train_state['epoch_index'] == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), train_state['model_filename'])
train_state['stop_early'] = False
# Save model if performance improved
elif train_state['epoch_index'] >= 1:
loss_tm1, loss_t = train_state['val_loss'][-2:]
# If loss worsened
if loss_t >= train_state['early_stopping_best_val']:
# Update step
train_state['early_stopping_step'] += 1
# Loss decreased
else:
# Save the best model
if loss_t < train_state['early_stopping_best_val']:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), train_state['model_filename'])
# Reset early stopping step
train_state['early_stopping_step'] = 0
# Stop early ?
train_state['stop_early'] = \
train_state['early_stopping_step'] >= args.early_stopping_criteria
return train_state
def compute_accuracy(y_pred, y_target):
_, y_pred_indices = y_pred.max(dim=1)
n_correct = torch.eq(y_pred_indices, y_target).sum().item()
return n_correct / len(y_pred_indices) * 100
general utilities
def set_seed_everywhere(seed, cuda):
np.random.seed(seed)
torch.manual_seed(seed)
if cuda:
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
def handle_dirs(dirpath):
if not os.path.exists(dirpath):
os.makedirs(dirpath)
# Settings and some prep work
args = Namespace(
# Data and path information
surname_csv="data/surnames/surnames_with_splits.csv",
vectorizer_file="vectorizer.json",
model_state_file="model.pth",
save_dir="model_storage/ch4/surname_mlp",
# Model hyper parameters
hidden_dim=300,
# Training hyper parameters
seed=1337,
num_epochs=100,
early_stopping_criteria=5,
learning_rate=0.001,
batch_size=64,
# Runtime options
cuda=False,
reload_from_files=False,
expand_filepaths_to_save_dir=True,
)
if args.expand_filepaths_to_save_dir:
args.vectorizer_file = os.path.join(args.save_dir,
args.vectorizer_file)
args.model_state_file = os.path.join(args.save_dir,
args.model_state_file)
print("Expanded filepaths: ")
print("\t{}".format(args.vectorizer_file))
print("\t{}".format(args.model_state_file))
# Check CUDA
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
args.cuda = False
args.device = torch.device("cuda" if args.cuda else "cpu")
print("Using CUDA: {}".format(args.cuda))
# Set seed for reproducibility
set_seed_everywhere(args.seed, args.cuda)
# handle dirs
handle_dirs(args.save_dir)还是不能着急 先进行初始化 马上就能训练了
if args.reload_from_files:
# training from a checkpoint
print("Reloading!")
dataset = SurnameDataset.load_dataset_and_load_vectorizer(args.surname_csv,
args.vectorizer_file)
else:
# create dataset and vectorizer
print("Creating fresh!")
dataset = SurnameDataset.load_dataset_and_make_vectorizer(args.surname_csv)
dataset.save_vectorizer(args.vectorizer_file)
vectorizer = dataset.get_vectorizer()
classifier = SurnameClassifier(input_dim=len(vectorizer.surname_vocab),
hidden_dim=args.hidden_dim,
output_dim=len(vectorizer.nationality_vocab))ok!一切准备就绪 开始"辅导"你的MLP吧
classifier = classifier.to(args.device)
dataset.class_weights = dataset.class_weights.to(args.device)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(dataset.class_weights)
optimizer = optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate)
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer=optimizer,
mode='min', factor=0.5,
patience=1)
train_state = make_train_state(args)
epoch_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='training routine',
total=args.num_epochs,
position=0)
dataset.set_split('train')
train_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='split=train',
total=dataset.get_num_batches(args.batch_size),
position=1,
leave=True)
dataset.set_split('val')
val_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='split=val',
total=dataset.get_num_batches(args.batch_size),
position=1,
leave=True)
try:
for epoch_index in range(args.num_epochs):
train_state['epoch_index'] = epoch_index
# Iterate over training dataset
# setup: batch generator, set loss and acc to 0, set train mode on
dataset.set_split('train')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.0
running_acc = 0.0
classifier.train()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# the training routine is these 5 steps:
# --------------------------------------
# step 1. zero the gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# step 2. compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# step 3. compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# step 4. use loss to produce gradients
loss.backward()
# step 5. use optimizer to take gradient step
optimizer.step()
# -----------------------------------------
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
# update bar
train_bar.set_postfix(loss=running_loss, acc=running_acc,
epoch=epoch_index)
train_bar.update()
train_state['train_loss'].append(running_loss)
train_state['train_acc'].append(running_acc)
# Iterate over val dataset
# setup: batch generator, set loss and acc to 0; set eval mode on
dataset.set_split('val')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.
running_acc = 0.
classifier.eval()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# step 3. compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.to("cpu").item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
val_bar.set_postfix(loss=running_loss, acc=running_acc,
epoch=epoch_index)
val_bar.update()
train_state['val_loss'].append(running_loss)
train_state['val_acc'].append(running_acc)
train_state = update_train_state(args=args, model=classifier,
train_state=train_state)
scheduler.step(train_state['val_loss'][-1])
if train_state['stop_early']:
break
train_bar.n = 0
val_bar.n = 0
epoch_bar.update()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Exiting loop")训练评测与结果展示
训练完就开始检测MLP这个模型能达到什么样的准确率和Loss
# compute the loss & accuracy on the test set using the best available model
classifier.load_state_dict(torch.load(train_state['model_filename']))
classifier = classifier.to(args.device)
dataset.class_weights = dataset.class_weights.to(args.device)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(dataset.class_weights)
dataset.set_split('test')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.
running_acc = 0.
classifier.eval()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
train_state['test_loss'] = running_loss
train_state['test_acc'] = running_acc
print("Test loss: {};".format(train_state['test_loss']))
print("Test Accuracy: {}".format(train_state['test_acc']))最后做几个函数让我们的模型可以做一定的预测
def predict_nationality(surname, classifier, vectorizer):
"""Predict the nationality from a new surname
Args:
surname (str): the surname to classifier
classifier (SurnameClassifer): an instance of the classifier
vectorizer (SurnameVectorizer): the corresponding vectorizer
Returns:
a dictionary with the most likely nationality and its probability
"""
vectorized_surname = vectorizer.vectorize(surname)
vectorized_surname = torch.tensor(vectorized_surname).view(1, -1)
result = classifier(vectorized_surname, apply_softmax=True)
probability_values, indices = result.max(dim=1)
index = indices.item()
predicted_nationality = vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_index(index)
probability_value = probability_values.item()
return {'nationality': predicted_nationality, 'probability': probability_value}
new_surname = input("Enter a surname to classify: ")
classifier = classifier.to("cpu")
prediction = predict_nationality(new_surname, classifier, vectorizer)
print("{} -> {} (p={:0.2f})".format(new_surname,
prediction['nationality'],
prediction['probability']))
vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_index(8)
'Irish'
def predict_topk_nationality(name, classifier, vectorizer, k=5):
vectorized_name = vectorizer.vectorize(name)
vectorized_name = torch.tensor(vectorized_name).view(1, -1)
prediction_vector = classifier(vectorized_name, apply_softmax=True)
probability_values, indices = torch.topk(prediction_vector, k=k)
# returned size is 1,k
probability_values = probability_values.detach().numpy()[0]
indices = indices.detach().numpy()[0]
results = []
for prob_value, index in zip(probability_values, indices):
nationality = vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_index(index)
results.append({'nationality': nationality,
'probability': prob_value})
return results
new_surname = input("Enter a surname to classify: ")
classifier = classifier.to("cpu")
k = int(input("How many of the top predictions to see? "))
if k > len(vectorizer.nationality_vocab):
print("Sorry! That's more than the # of nationalities we have.. defaulting you to max size :)")
k = len(vectorizer.nationality_vocab)
predictions = predict_topk_nationality(new_surname, classifier, vectorizer, k=k)
print("Top {} predictions:".format(k))
print("===================")
for prediction in predictions:
print("{} -> {} (p={:0.2f})".format(new_surname,
prediction['nationality'],
prediction['probability']))最后让我们看看MLP能达到什么样子的效果吧

这个acc效果有点差 可能需要进一步调参和优化
![]()
Liu(刘,柳)被识别成了越南姓?
展示预测概率前十
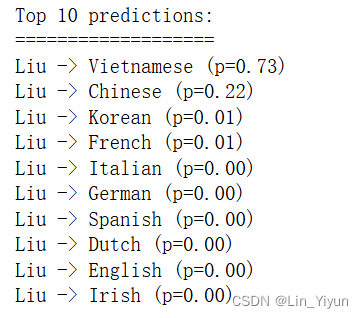
CNN!这孩子打小就聪明!
我们有辅导MLP这个小孩的经验了
现在我们要辅导这个天赋异禀的CNN
先让我们了解一下CNN
CNN的原理分析
下面是一张典型的CNN结构图
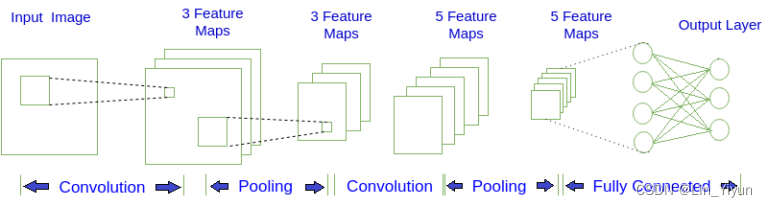
- 卷积层:使用一组可学习的滤波器来扫描输入数据,每个滤波器负责提取一种特定的特征。
- 激活函数:引入非线性,使网络能够学习复杂的模式,常用的激活函数有ReLU。
- 池化层:降低特征图的空间维度,减少计算量和参数数量,防止过拟合。
- 全连接层:将前面卷积层和池化层提取到的特征图转换为一维特征向量,进行最终的分类或回归分析。
输入矩阵经过不断的卷积和池化 使模型逐步学习到了重要特征
换言之CNN这小孩会抓住重点 学习考点能学到知识的本质
根据之前辅导MLP的经验,我们可以大体一样的用在CNN身上
开始编码吧!
编码
向量化
还是先把知识变成考点教给CNN
与MLP不同的是
Vectorizer的vectorize()方法已经更改,以适应CNN模型的需要
# 定义Vocabulary类实现了一个基本的词语到索引的映射结构
class Vocabulary(object):
"""Class to process text and extract vocabulary for mapping"""
def __init__(self, token_to_idx=None, add_unk=True, unk_token="<UNK>"):
"""
Args:
token_to_idx (dict): a pre-existing map of tokens to indices
add_unk (bool): a flag that indicates whether to add the UNK token
unk_token (str): the UNK token to add into the Vocabulary
"""
if token_to_idx is None:
token_to_idx = {}
self._token_to_idx = token_to_idx
self._idx_to_token = {idx: token
for token, idx in self._token_to_idx.items()}
self._add_unk = add_unk
self._unk_token = unk_token
self.unk_index = -1
if add_unk:
self.unk_index = self.add_token(unk_token)
def to_serializable(self):
""" returns a dictionary that can be serialized """
return {'token_to_idx': self._token_to_idx,
'add_unk': self._add_unk,
'unk_token': self._unk_token}
@classmethod
def from_serializable(cls, contents):
""" instantiates the Vocabulary from a serialized dictionary """
return cls(**contents)
def add_token(self, token):
"""Update mapping dicts based on the token.
Args:
token (str): the item to add into the Vocabulary
Returns:
index (int): the integer corresponding to the token
"""
try:
index = self._token_to_idx[token]
except KeyError:
index = len(self._token_to_idx)
self._token_to_idx[token] = index
self._idx_to_token[index] = token
return index
def add_many(self, tokens):
"""Add a list of tokens into the Vocabulary
Args:
tokens (list): a list of string tokens
Returns:
indices (list): a list of indices corresponding to the tokens
"""
return [self.add_token(token) for token in tokens]
def lookup_token(self, token):
"""Retrieve the index associated with the token
or the UNK index if token isn't present.
Args:
token (str): the token to look up
Returns:
index (int): the index corresponding to the token
Notes:
`unk_index` needs to be >=0 (having been added into the Vocabulary)
for the UNK functionality
"""
if self.unk_index >= 0:
return self._token_to_idx.get(token, self.unk_index)
else:
return self._token_to_idx[token]
def lookup_index(self, index):
"""Return the token associated with the index
Args:
index (int): the index to look up
Returns:
token (str): the token corresponding to the index
Raises:
KeyError: if the index is not in the Vocabulary
"""
if index not in self._idx_to_token:
raise KeyError("the index (%d) is not in the Vocabulary" % index)
return self._idx_to_token[index]
def __str__(self):
return "<Vocabulary(size=%d)>" % len(self)
def __len__(self):
return len(self._token_to_idx)
class SurnameVectorizer(object):
""" The Vectorizer which coordinates the Vocabularies and puts them to use"""
def __init__(self, surname_vocab, nationality_vocab, max_surname_length):
"""
Args:
surname_vocab (Vocabulary): maps characters to integers
nationality_vocab (Vocabulary): maps nationalities to integers
max_surname_length (int): the length of the longest surname
"""
self.surname_vocab = surname_vocab
self.nationality_vocab = nationality_vocab
self._max_surname_length = max_surname_length
def vectorize(self, surname):
"""
Args:
surname (str): the surname
Returns:
one_hot_matrix (np.ndarray): a matrix of one-hot vectors
"""
one_hot_matrix_size = (len(self.surname_vocab), self._max_surname_length)
one_hot_matrix = np.zeros(one_hot_matrix_size, dtype=np.float32)
for position_index, character in enumerate(surname):
character_index = self.surname_vocab.lookup_token(character)
one_hot_matrix[character_index][position_index] = 1
return one_hot_matrix
@classmethod
def from_dataframe(cls, surname_df):
"""Instantiate the vectorizer from the dataset dataframe
Args:
surname_df (pandas.DataFrame): the surnames dataset
Returns:
an instance of the SurnameVectorizer
"""
surname_vocab = Vocabulary(unk_token="@")
nationality_vocab = Vocabulary(add_unk=False)
max_surname_length = 0
for index, row in surname_df.iterrows():
max_surname_length = max(max_surname_length, len(row.surname))
for letter in row.surname:
surname_vocab.add_token(letter)
nationality_vocab.add_token(row.nationality)
return cls(surname_vocab, nationality_vocab, max_surname_length)
@classmethod
def from_serializable(cls, contents):
surname_vocab = Vocabulary.from_serializable(contents['surname_vocab'])
nationality_vocab = Vocabulary.from_serializable(contents['nationality_vocab'])
return cls(surname_vocab=surname_vocab, nationality_vocab=nationality_vocab,
max_surname_length=contents['max_surname_length'])
def to_serializable(self):
return {'surname_vocab': self.surname_vocab.to_serializable(),
'nationality_vocab': self.nationality_vocab.to_serializable(),
'max_surname_length': self._max_surname_length}
# 定义 `SurnameVectorizer`类作为协调器,通过使用两个 `Vocabulary` 实例,将姓氏及其关联国籍编码为数值格式。
# 它将原始姓氏字符串转换为独热编码表示,并将国籍作为分类数据处理,使得处理后的数据能被机器学习模型所使用。
class SurnameDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, surname_df, vectorizer):
"""
Args:
name_df (pandas.DataFrame): the dataset
vectorizer (SurnameVectorizer): vectorizer instatiated from dataset
"""
self.surname_df = surname_df
self._vectorizer = vectorizer
self.train_df = self.surname_df[self.surname_df.split=='train']
self.train_size = len(self.train_df)
self.val_df = self.surname_df[self.surname_df.split=='val']
self.validation_size = len(self.val_df)
self.test_df = self.surname_df[self.surname_df.split=='test']
self.test_size = len(self.test_df)
self._lookup_dict = {'train': (self.train_df, self.train_size),
'val': (self.val_df, self.validation_size),
'test': (self.test_df, self.test_size)}
self.set_split('train')
# Class weights
class_counts = surname_df.nationality.value_counts().to_dict()
def sort_key(item):
return self._vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_token(item[0])
sorted_counts = sorted(class_counts.items(), key=sort_key)
frequencies = [count for _, count in sorted_counts]
self.class_weights = 1.0 / torch.tensor(frequencies, dtype=torch.float32)
@classmethod
def load_dataset_and_make_vectorizer(cls, surname_csv):
"""Load dataset and make a new vectorizer from scratch
Args:
surname_csv (str): location of the dataset
Returns:
an instance of SurnameDataset
"""
surname_df = pd.read_csv(surname_csv)
train_surname_df = surname_df[surname_df.split=='train']
return cls(surname_df, SurnameVectorizer.from_dataframe(train_surname_df))
@classmethod
def load_dataset_and_load_vectorizer(cls, surname_csv, vectorizer_filepath):
"""Load dataset and the corresponding vectorizer.
Used in the case in the vectorizer has been cached for re-use
Args:
surname_csv (str): location of the dataset
vectorizer_filepath (str): location of the saved vectorizer
Returns:
an instance of SurnameDataset
"""
surname_df = pd.read_csv(surname_csv)
vectorizer = cls.load_vectorizer_only(vectorizer_filepath)
return cls(surname_df, vectorizer)
@staticmethod
def load_vectorizer_only(vectorizer_filepath):
"""a static method for loading the vectorizer from file
Args:
vectorizer_filepath (str): the location of the serialized vectorizer
Returns:
an instance of SurnameDataset
"""
with open(vectorizer_filepath) as fp:
return SurnameVectorizer.from_serializable(json.load(fp))
def save_vectorizer(self, vectorizer_filepath):
"""saves the vectorizer to disk using json
Args:
vectorizer_filepath (str): the location to save the vectorizer
"""
with open(vectorizer_filepath, "w") as fp:
json.dump(self._vectorizer.to_serializable(), fp)
def get_vectorizer(self):
""" returns the vectorizer """
return self._vectorizer
def set_split(self, split="train"):
""" selects the splits in the dataset using a column in the dataframe """
self._target_split = split
self._target_df, self._target_size = self._lookup_dict[split]
def __len__(self):
return self._target_size
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""the primary entry point method for PyTorch datasets
Args:
index (int): the index to the data point
Returns:
a dictionary holding the data point's features (x_data) and label (y_target)
"""
row = self._target_df.iloc[index]
surname_matrix = \
self._vectorizer.vectorize(row.surname)
nationality_index = \
self._vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_token(row.nationality)
return {'x_surname': surname_matrix,
'y_nationality': nationality_index}
def get_num_batches(self, batch_size):
"""Given a batch size, return the number of batches in the dataset
Args:
batch_size (int)
Returns:
number of batches in the dataset
"""
return len(self) // batch_size
def generate_batches(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=True,
drop_last=True, device="cpu"):
"""
A generator function which wraps the PyTorch DataLoader. It will
ensure each tensor is on the write device location.
"""
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=dataset, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=shuffle, drop_last=drop_last)
for data_dict in dataloader:
out_data_dict = {}
for name, tensor in data_dict.items():
out_data_dict[name] = data_dict[name].to(device)
yield out_data_dict定义模型
class SurnameClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, initial_num_channels, num_classes, num_channels):
"""
Args:
initial_num_channels (int): size of the incoming feature vector
num_classes (int): size of the output prediction vector
num_channels (int): constant channel size to use throughout network
"""
super(SurnameClassifier, self).__init__()
# 定义一个卷积神经网络序列,用于特征提取
self.convnet = nn.Sequential(
# 第一层1D卷积,用于捕捉局部特征
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=initial_num_channels, out_channels=num_channels, kernel_size=3),
nn.ELU(), # 使用ELU激活函数增加非线性
# 第二层1D卷积,步长为2,开始减少空间维度
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=num_channels, out_channels=num_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.ELU(),
# 第三层1D卷积,进一步减少空间维度
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=num_channels, out_channels=num_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.ELU(),
# 第四层1D卷积,无步长变化
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=num_channels, out_channels=num_channels, kernel_size=3),
nn.ELU()
)
# 全连接层,用于将卷积层的输出转换为类别预测
self.fc = nn.Linear(num_channels, num_classes)
def forward(self, x_surname, apply_softmax=False):
"""The forward pass of the classifier
Args:
x_surname (torch.Tensor): an input data tensor.
x_surname.shape should be (batch, initial_num_channels, max_surname_length)
apply_softmax (bool): a flag for the softmax activation
should be false if used with the Cross Entropy losses
Returns:
the resulting tensor. tensor.shape should be (batch, num_classes)
"""
# 通过卷积网络处理输入序列数据,然后挤压维度以准备全连接层的输入
features = self.convnet(x_surname).squeeze(dim=2)
# 全连接层生成预测向量
prediction_vector = self.fc(features)
# 如果要求,则对预测向量应用softmax激活,通常在输出层需要概率分布时使用
if apply_softmax:
prediction_vector = F.softmax(prediction_vector, dim=1)
# 返回预测向量
return prediction_vector训练过程
def make_train_state(args):
return {'stop_early': False,
'early_stopping_step': 0,
'early_stopping_best_val': 1e8,
'learning_rate': args.learning_rate,
'epoch_index': 0,
'train_loss': [],
'train_acc': [],
'val_loss': [],
'val_acc': [],
'test_loss': -1,
'test_acc': -1,
'model_filename': args.model_state_file}
# 负责处理训练过程中的状态更新,主要涉及两个关键环节:
#- 早停(Early Stopping):用来防止过拟合,当验证集上的损失不再显著减少时停止训练。
#- 模型检查点(Model Checkpoint):在模型性能提升时保存模型。
def update_train_state(args, model, train_state):
"""Handle the training state updates.
Components:
- Early Stopping: Prevent overfitting.
- Model Checkpoint: Model is saved if the model is better
:param args: main arguments
:param model: model to train
:param train_state: a dictionary representing the training state values
:returns:
a new train_state
"""
# Save one model at least
if train_state['epoch_index'] == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), train_state['model_filename'])
train_state['stop_early'] = False
# Save model if performance improved
elif train_state['epoch_index'] >= 1:
loss_tm1, loss_t = train_state['val_loss'][-2:]
# If loss worsened
if loss_t >= train_state['early_stopping_best_val']:
# Update step
train_state['early_stopping_step'] += 1
# Loss decreased
else:
# Save the best model
if loss_t < train_state['early_stopping_best_val']:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), train_state['model_filename'])
# Reset early stopping step
train_state['early_stopping_step'] = 0
# Stop early ?
train_state['stop_early'] = \
train_state['early_stopping_step'] >= args.early_stopping_criteria
return train_state
def compute_accuracy(y_pred, y_target):
y_pred_indices = y_pred.max(dim=1)[1]
n_correct = torch.eq(y_pred_indices, y_target).sum().item()
return n_correct / len(y_pred_indices) * 100
args = Namespace(
# Data and Path information
surname_csv="data/surnames/surnames_with_splits.csv",
vectorizer_file="vectorizer.json",
model_state_file="model.pth",
save_dir="model_storage/ch4/cnn",
# Model hyper parameters
hidden_dim=100,
num_channels=256,
# Training hyper parameters
seed=1337,
learning_rate=0.001,
batch_size=128,
num_epochs=100,
early_stopping_criteria=5,
dropout_p=0.1,
# Runtime options
cuda=False,
reload_from_files=False,
expand_filepaths_to_save_dir=True,
catch_keyboard_interrupt=True
)
if args.expand_filepaths_to_save_dir:
args.vectorizer_file = os.path.join(args.save_dir,
args.vectorizer_file)
args.model_state_file = os.path.join(args.save_dir,
args.model_state_file)
print("Expanded filepaths: ")
print("\t{}".format(args.vectorizer_file))
print("\t{}".format(args.model_state_file))
# Check CUDA
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
args.cuda = False
args.device = torch.device("cuda" if args.cuda else "cpu")
print("Using CUDA: {}".format(args.cuda))
def set_seed_everywhere(seed, cuda):
np.random.seed(seed)
torch.manual_seed(seed)
if cuda:
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
def handle_dirs(dirpath):
if not os.path.exists(dirpath):
os.makedirs(dirpath)
# Set seed for reproducibility
set_seed_everywhere(args.seed, args.cuda)
# handle dirs
handle_dirs(args.save_dir)
Expanded filepaths:
model_storage/ch4/cnn/vectorizer.json
model_storage/ch4/cnn/model.pth
Using CUDA: False
if args.reload_from_files:
# training from a checkpoint
dataset = SurnameDataset.load_dataset_and_load_vectorizer(args.surname_csv,
args.vectorizer_file)
else:
# create dataset and vectorizer
dataset = SurnameDataset.load_dataset_and_make_vectorizer(args.surname_csv)
dataset.save_vectorizer(args.vectorizer_file)
vectorizer = dataset.get_vectorizer()
classifier = SurnameClassifier(initial_num_channels=len(vectorizer.surname_vocab),
num_classes=len(vectorizer.nationality_vocab),
num_channels=args.num_channels)
classifer = classifier.to(args.device)
dataset.class_weights = dataset.class_weights.to(args.device)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=dataset.class_weights)
optimizer = optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate)
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer=optimizer,
mode='min', factor=0.5,
patience=1)
train_state = make_train_state(args)
epoch_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='training routine',
total=args.num_epochs,
position=0)
dataset.set_split('train')
train_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='split=train',
total=dataset.get_num_batches(args.batch_size),
position=1,
leave=True)
dataset.set_split('val')
val_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='split=val',
total=dataset.get_num_batches(args.batch_size),
position=1,
leave=True)
try:
for epoch_index in range(args.num_epochs):
train_state['epoch_index'] = epoch_index
# Iterate over training dataset
# setup: batch generator, set loss and acc to 0, set train mode on
dataset.set_split('train')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.0
running_acc = 0.0
classifier.train()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# the training routine is these 5 steps:
# --------------------------------------
# step 1. zero the gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# step 2. compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# step 3. compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# step 4. use loss to produce gradients
loss.backward()
# step 5. use optimizer to take gradient step
optimizer.step()
# -----------------------------------------
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
# update bar
train_bar.set_postfix(loss=running_loss, acc=running_acc,
epoch=epoch_index)
train_bar.update()
train_state['train_loss'].append(running_loss)
train_state['train_acc'].append(running_acc)
# Iterate over val dataset
# setup: batch generator, set loss and acc to 0; set eval mode on
dataset.set_split('val')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.
running_acc = 0.
classifier.eval()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# step 3. compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
val_bar.set_postfix(loss=running_loss, acc=running_acc,
epoch=epoch_index)
val_bar.update()
train_state['val_loss'].append(running_loss)
train_state['val_acc'].append(running_acc)
train_state = update_train_state(args=args, model=classifier,
train_state=train_state)
scheduler.step(train_state['val_loss'][-1])
if train_state['stop_early']:
break
train_bar.n = 0
val_bar.n = 0
epoch_bar.update()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Exiting loop")训练评测与结果展示
classifier.load_state_dict(torch.load(train_state['model_filename']))
classifier = classifier.to(args.device)
dataset.class_weights = dataset.class_weights.to(args.device)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(dataset.class_weights)
dataset.set_split('test')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.
running_acc = 0.
classifier.eval()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
train_state['test_loss'] = running_loss
train_state['test_acc'] = running_acc
print("Test loss: {};".format(train_state['test_loss']))
print("Test Accuracy: {}".format(train_state['test_acc']))
相较于MLP 测试指标高了很多
结语
本文算是我人生中的第一篇博客 很早之前就有写博客的想法 不过因为种种原因都没有真正去写
感谢董老师的悉心指导与鼓励 以作业的形式强制使我迈出这一步
本文更多是以一个工科生的角度出发 形而下的讨论MLP和CNN的应用性原理
我也深知 要全面剖析这些复杂模型背后的数学理论 非一朝一夕之功 也非我当前学识所能及
奈何本人才疏学浅 文中多有疏漏不严谨之处 恳请各位不吝赐教





















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








