面向对象有四大基本特性:抽象、封装、继承和多态,所以我们可以用面向对象的思想对线程进行封装
1、线程相关函数介绍
1.1线程的创建
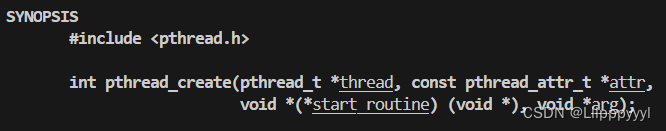
1.2 线程终止
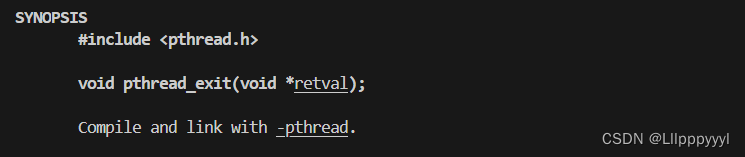
1.3线程等待

1.4 线程取消

1.5线程分离

以上是线程相关的函数,对应参数及相关文档可以man一下,毕竟“有问题找男人”!!!!!
2、面向对象的线程封装
有了抽象的概念之后,我们可以将线程封装成一个类,用类的观点去看线程。然后用线程类去创建躯体的对象。接下来就为线程类设置成员,每个线程会有线程号,可以设置为数据成员;线程是否开始运行、线程是否结束,对应会有start函数与join函数;线程入口函数可以封装为一个函数threadFunc,然后具体需要执行的任务可以封装为一个run方法,具体的业务留给Thread的派生类去实现,所以run方法可以设置为虚方法,Thread类也就成为抽象类了。为了实 现具体的任务方法,可以在用一个类去继承抽象类Thread,并实现虚方法run,所以可以设置为下面的关系图。
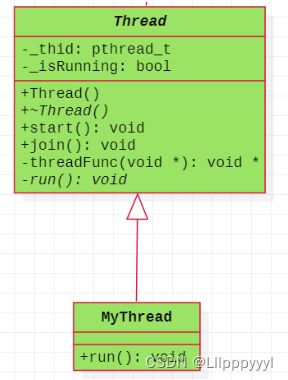
具体代码实现
2.1 Thread.h实现
#ifndef __THREAD_H
#define __THREAD_H
#include<pthread.h>
class Thread{
public:
Thread();
virtual ~Thread();
void start();
void join();
static void* threadFunc(void* args);
virtual void run() = 0;
private:
pthread_t _thid;
bool _isRunning;
};
#endif
2.2 Thread.cc
#include "Thread.h"
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
Thread::Thread()
:_thid(0)
,_isRunning(false)
{
}
Thread::~Thread()
{
}
void Thread::start()
{
int ret = pthread_create(&_thid, nullptr, threadFunc, this);
if(ret != 0)
{
printf("pthread_create error");
return;
}
_isRunning = true;
}
void Thread::join()
{
if(_isRunning)
{
int ret = pthread_join(_thid, nullptr);
if(ret != 0)
{
printf("pthread_join error");
return;
}
_isRunning = false;
}
}
//static
void* Thread::threadFunc(void* args)
{
Thread* pthread = static_cast<Thread *> (args);
if(pthread)
{
pthread->run();
}else
{
printf("hello");
}
pthread_exit(nullptr);
}2.3测试代码Threadtest.cc
#include"Thread.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
class Mythread : public Thread
{
private:
public:
Mythread(/* args */);
~Mythread();
void run() override
{
while (1)
{
printf("Mythread is running!\n");
sleep(1);
}
}
};
Mythread::Mythread(/* args */)
{
}
Mythread::~Mythread()
{
}
void test()
{
Mythread mth;
mth.start();
mth.join();
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}3、难点及问题
当Threadfunc作为成员函数的时候,在第一个参数的位置会隐含一个this指针,而pthread_create的第三个参数是固定的,为了消除this指针的影响,将Threadfunc设置为静态 static,pthread_create第四的参数不能设置为nullptr, 否则Threadfunc中args也为空。







 本文介绍了如何使用面向对象的抽象、封装、继承和多态特性,将线程功能封装到类中,包括线程的创建、终止、等待等操作,并通过示例展示了如何创建Thread类及其派生类来实现线程功能。特别提到将threadFunc设为静态解决成员函数this指针问题。
本文介绍了如何使用面向对象的抽象、封装、继承和多态特性,将线程功能封装到类中,包括线程的创建、终止、等待等操作,并通过示例展示了如何创建Thread类及其派生类来实现线程功能。特别提到将threadFunc设为静态解决成员函数this指针问题。














 1740
1740

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








