✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,代码获取、论文复现及科研仿真合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
🔥 内容介绍
癫痫是一种神经系统疾病,其特征是反复发作的癫痫发作。癫痫发作是由大脑中神经元的异常电活动引起的。神经元动作电位是神经元电活动的基本单位,在癫痫发作的发生中起着至关重要的作用。
神经元动作电位
神经元动作电位是一种快速、全或无的电脉冲,沿着神经元的轴突传播。它是由神经元膜上的离子通道的打开和关闭引起的。
动作电位有以下几个阶段:
-
**静息电位:**在静息状态下,神经元膜内侧为负电,外侧为正电。
-
**去极化:**当神经元受到刺激时,钠离子通道打开,钠离子流入细胞,导致膜电位变得不那么负电。
-
**动作电位:**当膜电位达到阈值时,钠离子通道完全打开,钠离子大量涌入细胞,导致膜电位迅速反转。
-
**超极化:**钠离子通道关闭后,钾离子通道打开,钾离子流出细胞,导致膜电位变得比静息电位更负电。
-
**折返极化:**钾离子通道关闭后,膜电位逐渐恢复到静息电位。
癫痫神经元动作电位
在癫痫神经元中,动作电位发生异常,导致癫痫发作。这些异常包括:
-
**持续性去极化:**癫痫神经元可以持续去极化,导致反复的动作电位。
-
**爆发性放电:**癫痫神经元可以突然释放一系列动作电位。
-
**后放电:**癫痫神经元在动作电位后可以产生额外的动作电位。
癫痫发作的机制
癫痫发作是由大脑中神经元的同步异常放电引起的。这些异常放电可以导致大脑功能的暂时性中断,从而产生癫痫发作的症状,如意识丧失、抽搐和感觉异常。
治疗
癫痫的治疗旨在控制癫痫发作。治疗方法包括:
-
**药物:**抗癫痫药物可以阻断癫痫神经元的异常放电。
-
**手术:**在某些情况下,可以切除引起癫痫发作的大脑区域。
-
**神经刺激:**迷走神经刺激和深部脑刺激等神经刺激疗法可以帮助控制癫痫发作。
结论
癫痫神经元动作电位异常是癫痫发作发生的关键因素。了解这些异常对于癫痫的诊断和治疗至关重要。通过持续的研究,我们有望开发出更有效的癫痫治疗方法。的治疗重点是控制癫痫发作。治疗方案可能包括药物、手术和神经刺激疗法。抗癫痫药物可以调节离子通道功能、神经递质释放和突触可塑性,以减少神经元过度兴奋和癫痫发作。
结论
癫痫神经元动作电位异常是癫痫发作的电生理基础。这些异常可能由离子通道功能异常、神经递质释放异常和突触可塑性改变引起。了解癫痫神经元动作电位的机制对于开发新的治疗方法至关重要,这些方法可以有效控制癫痫发作并改善患者的生活质量。
📣 部分代码
axonmain();function [t,x]=axonmain()global P % parameterssetUp;[t,x]=ode15s(@Dyn,P.tD,P.Xo);plotResults(t,x); % axonend% dynamic functionfunction Dx=Dyn(t,x)% setProcess: Establish G matrix & other values for the process%Set the drive matrix as wellglobal P % param&I-stimN=length(x)/4; G=zeros(N); f=zeros(N,1); % numberOnodesV=x(1:N);m=x(N+1:2*N);h=x(2*N+1:3*N);n=x(3*N+1:4*N); % extractStatesfor i=1:N % loop eachNodega=P.xSectArea(i)/((P.Ra*P.dx(i))); % axon conductgL=P.surfArea(i)/(P.RL); % chloride/leakgNaMax=P.gMax_Na*P.surfArea(i)*P.isActive(i); % Na maxConductgKMax =P.gMax_K *P.surfArea(i)*P.isActive(i); % K maxConductC=P.C*P.surfArea(i); % capacitance-FgNa=m(i)^3*h(i)*gNaMax; % conductWgatesgK =n(i)^4*gKMax; % conductWgatesa = 0.8e-4;Rout = 24e4;gout = 1/(Rout/P.xSectArea(i));SUMgChan=gNa+gK+gL; % sum memb g'sf(i)=(gNa*P.ENa)+(gK*P.EK)+(gL*P.ECl); % sum driveif N==1G = -SUMgCHan;f = f+interp1(P.Io(:,1),P.Io(:,2),t);elseif i == 1G(1, 1) = - ga - SUMgChan ;G(1, 2) = ga;f(1) = f(1)+interp1(P.Io(:,1),P.Io(:,2),t);elseif i == NG(N,N) = -(SUMgChan+ga);G(N,N-1)= ga;elseG(i,i) = -(2*ga+SUMgChan);G(i,i-1) = ga;G(i,i+1) = ga;endendend % endForEachNodDV=(G*V+f)./C; % curentBalance[mA,nA,hA,mB,nB,hB]=getRates(V,P.Vrest); % alpha & betasrn = randi(3,i,1);if (rn(i)==2)nB = 0;endDm=(-(mA+mB).*m+mA);Dh=(-(hA+hB).*h+hA);Dn=(-(nA+nB).*n+nA);% gates probsDx=[DV;Dm;Dh;Dn]; % asembleStatesset(P.h,'yData',V);title(num2str(t));drawnow; % updateAnims% process varsend% setUp : intialize variablesfunction P=setUp(P)% messagesclose all; % clearfprintf('No Branching Axon'); % announce% setup variablesglobal PP.tMax=0.004; % simu time secP.tD=0:P.tMax/100:P.tMax; % desired output time stepsP.Vrest = -60e-3; % rest voltageP.C = 1e-6; % bulk capcitance F/cm^2P.RL = 15e3; % bulk Cl Resist Ohms*cm^2P.Ra = 3e3; % bulk axon resist ohms*cm -changeBak2 3e3P.gMax_K = 60e-3; % bulk K conductance S/cm^2P.gMax_Na = 120e-3; % bulk Na conduct. S/cm^2P.ENa = 55e-3; % Nernst poten. Na voltsP.EK = -75e-3; % Nernst poten. K voltsP.ECl = -40e-3; % Nernst poten. Cl volts -changeBak2 -403e-3P.N=10; % # compartments/nodes/SectP.L=.007; % overall length (cm)% VECTOR for EACH:Z=ones(P.N,1); z=zeros(P.N,1); % utility vectors 1's & 0'sP.dx=Z*(P.L/P.N); % subsection length (cm)P.a=Z*3e-5; % radii of all nodes (cm)P.surfArea=2*pi.*P.a.*P.dx; % cm^2 -VECTOR for EACHP.xSectArea=pi.*P.a.^2; % cm^2 -VECTOR for EACHP.isActive=Z; % 1 if active node, else 0% initial conditionsVo=P.Vrest*Z; mo=0.06915; ho=0.5142; no=0.3534; % initial gate probabilityP.Xo=[Vo;mo*Z;ho*Z;no*Z]; % stack initial states ->Xo% Injected current pulse (Istim = Io):I=1e-10; t1=1e-4; dur=1e-4; t2=t1+dur; miu=1e-9;% pulse start & length timeP.Io= [0 t1-miu t1 t2 t2+miu 2*P.tMax; ... % assemble time and[0 0 1 1 0 0]*I]'; % current mag (pico=E-12)setUpPlots(100,'Axon with 35 Nodes'); % Seup plots ahead of simend% setup figures & animationfunction setUpPlots(figNum,titleText)global PS=get(0,'ScreenSize'); % ask 4 screen sizeif ~exist('figNum','var'), figure, % if fig# not inputelse figure(figNum); endVo=P.Xo(1:P.N);mo=P.Xo(P.N+1:2*P.N); % extractInitStatesho=P.Xo(2*P.N+1:3*P.N);no=P.Xo(3*P.N+1:4*P.N); % extractInitStates% place summary figure on screen:set(gcf,'name',titleText) % window titleset(gcf,'Position',[.68*S(3) 0 .3*S(3) .9*S(4)]); % put figure% setup Stim (Io) windowsubplot(4,1,1);plot(P.Io(:,1),P.Io(:,2),'.-','linewidth',2); % plot Iohold on; xlim([0 P.tMax]);xlabel('Sec'); ylabel('Amp'); title('Io');% setup volt vs node windowsubplot(4,1,2);P.h=plot(1:P.N,P.Xo(1:P.N),'.-','markersize',12); % P.h points 2 plothold on; xlabel('Node #'); ylabel('Volts'); %set(gca,'ytick',[-.3 -.2 -.1 P.Vrest -.025 0 .1 ]); %ylim(.15*[-1 1]); %% setup gates vs time windowsubplot(4,1,3);plot(0,mo,'b.-',0,ho,'g.-',0,no,'r.-'); hold on; % all gatesxlabel('sec');ylabel('Prob.');ylim([0 1]);xlim([0 P.tMax])%text(0,.96,' m','fontsize',6,'fontweight','bold','color','b')text(0,.90,' h','fontsize',6,'fontweight','bold','color','g')text(0,.84,' n','fontsize',6,'fontweight','bold','color','r')% setup 3d figure windowsubplot(4,1,4);plot3(zeros(P.N,1),1:P.N,Vo,'.-','markersize',7); %ylabel('Node #'); xlabel('time(s)'); zlabel('Volts'); %set(gca,'ztick',[-.3 -.2 -.1 P.Vrest -.025 0 .1 ]); % displaygrid on; xlim([0 P.tMax]); zlim(.15*[-1 1]); hold on; %% shrink fonts and turn off box on all:for i=1:4,subplot(4,1,i);set(gca,'box','off','fontsize',5);endsubplot(4,1,2);fprintf('...Plots & variables set up...Simulating...');drawnow;endfunction [alpha_m,alpha_n,alpha_h,beta_m,beta_n,beta_h]=getRates(Vm,Vm_rest,plotIt)V = Vm-Vm_rest; V=V*1e3; % convert2 millivolts%% rates:%Input Rate Equation Functions Herealpha_n = 0.01*((-V+10)./(exp((-V+10)/10)-1))*1000;beta_n = 0.125*exp(-V/80)*1000;alpha_m = 0.1*((-V+25)./(exp((-V+25)/10)-1))*1000;beta_m = 4*exp(-V/18)*1000;alpha_h = 0.07*exp(-V/20)*1000;beta_h = 1./(exp((-V+30)/10)+1)*1000;%% fix near singularities:if(abs(V-25)<1e-2), alpha_m=1*1e3; end; % @ v=25if(abs(V-10)<1e-2), alpha_n=0.1*1e3; end; % @ v=10%% plot if asked:if exist('plotIt','var') % PLOT if variable inplot(Vm,alpha_m,'b.:',Vm,beta_m,'b.-', ...Vm,alpha_n,'g.:',Vm,beta_n,'g.-', ...Vm,alpha_h,'r.:',Vm,beta_h,'r.-')text(0,800,'m','fontsize',8,'fontweight','bold','color','b')text(0,800,' h','fontsize',8,'fontweight','bold','color','r')text(0,800,' n','fontsize',8,'fontweight','bold','color','g')title('Hodgekin and Huxley Gate Kinetic Rates');ylabel('(1/sec)'); xlabel('Volts')endend% plotResults function: wrap up by ploting final resultsfunction plotResults(t,x);global P;% get variablesN=size(x,2)/4; nt=size(x,1); v1=ones(nt,1); % #S time,nodesV=x(:,1:N);m=x(:,N+1:2*N);h=x(:,2*N+1:3*N);n=x(:,3*N+1:4*N);% extractStates% V,m,h,n% make plotssubplot(4,1,2); ; % volt VS nodeplot(1:N,V); % prob VS timesubplot(4,1,3); % 3D plot t,N,Vplot(t,m,'-b',t,h,'-g',t,n,'-r')subplot(4,1,4);for i= 1:Nplot3(t,i*v1,x(:,i))endaxis autosound(sin(1:1000),1e4); % annouyingBeepend
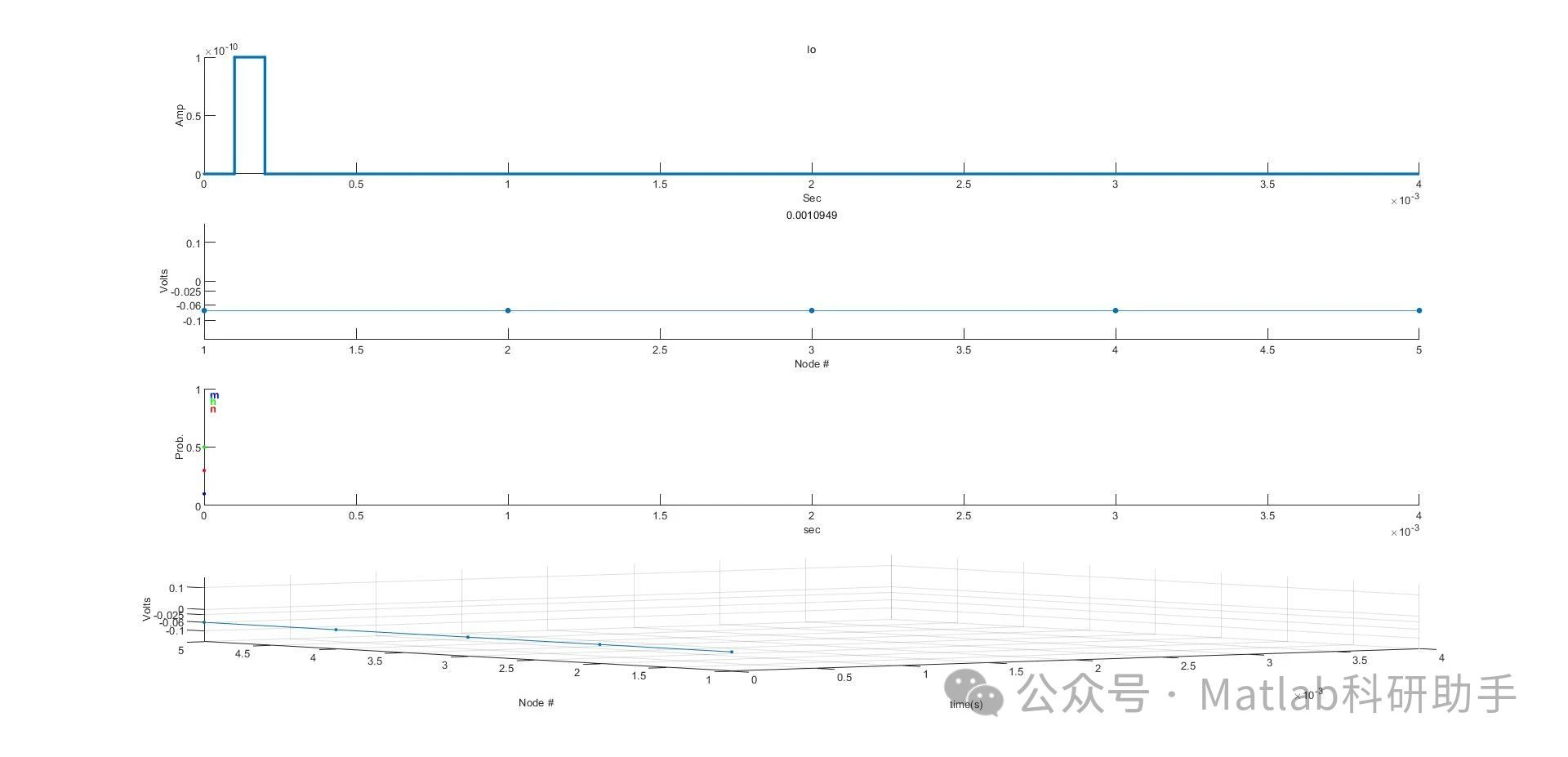
⛳️ 运行结果
🔗 参考文献
[1]师黎,牛晓可,万红.基于动作电位脑电信号的预处理技术研究[J]. 2012.
🎈 部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
1 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化、背包问题、 风电场布局、时隙分配优化、 最佳分布式发电单元分配、多阶段管道维修、 工厂-中心-需求点三级选址问题、 应急生活物质配送中心选址、 基站选址、 道路灯柱布置、 枢纽节点部署、 输电线路台风监测装置、 集装箱船配载优化、 机组优化、 投资优化组合、云服务器组合优化、 天线线性阵列分布优化
2 机器学习和深度学习方面
2.1 bp时序、回归预测和分类
2.2 ENS声神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.3 SVM/CNN-SVM/LSSVM/RVM支持向量机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.4 CNN/TCN卷积神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.5 ELM/KELM/RELM/DELM极限学习机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.6 GRU/Bi-GRU/CNN-GRU/CNN-BiGRU门控神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.7 ELMAN递归神经网络时序、回归\预测和分类
2.8 LSTM/BiLSTM/CNN-LSTM/CNN-BiLSTM/长短记忆神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.9 RBF径向基神经网络时序、回归预测和分类








 本文介绍了Matlab在科研中的应用,特别是针对癫痫神经元动作电位的分析,探讨了其在癫痫发作中的关键作用以及异常情况,如持续性去极化和爆发性放电。文章还讨论了癫痫的治疗方法,包括药物、手术和神经刺激疗法。通过理解这些电生理机制,有望开发出更有效的癫痫管理方法。
本文介绍了Matlab在科研中的应用,特别是针对癫痫神经元动作电位的分析,探讨了其在癫痫发作中的关键作用以及异常情况,如持续性去极化和爆发性放电。文章还讨论了癫痫的治疗方法,包括药物、手术和神经刺激疗法。通过理解这些电生理机制,有望开发出更有效的癫痫管理方法。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








