vibe算法是一种像素级的前景检测算法,实时性高,内存占有率低,前景检测准确率高。但是会出现“鬼影”,当然基于对鬼影的处理,也会有相应的对vibe算法的改进。
把下面三篇文章看明白,基本就会掌握vibe算法的过程:
《 ViBe: a powerful random technique to estimate the background in video sequences》
《Background Subtraction: Experiments and Improvements for ViBe 》
《ViBe: A universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences》
该算法的原文链接地址,作者已经给出了C代码。
以下用opencv复现一遍。
原理:
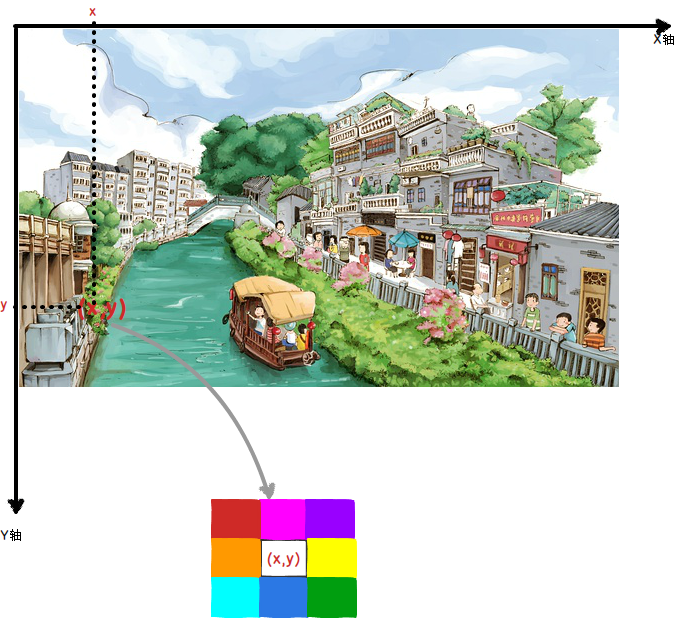
论文中以(x,y)为中心,取3x3的区域,即(x,y)处的8-领域。也可以选择5x5区域,即24-领域
对(x,y)处的8-领域,按平均分布 随机抽样numberSamples次,论文中给出的是numberSamples=20,假设以下为随机取样的结果:
做为下一帧(x,y)处的背景模型。
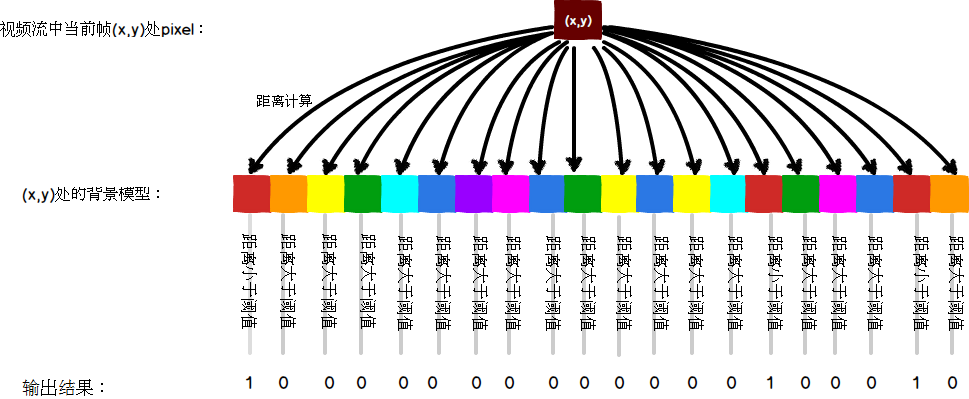
问题1:怎么判断视频流中的下一帧坐标(x,y)处是背景点还是前景点?
对于上述的结果,如果“1”的数量大于某一阈值minMatch(文章中设为2),则视为背景点,并更新背景模型,否则,为前景点。
问题2:更新背景模型的策略
文中给出了伪码,主要基于均匀随机抽样的方法。把背景点,按照一定的概率更新到背景模型中。
代码:(opencv实现)
class OriginalVibe{
public:
//构造函数
OriginalVibe(int _numberSamples, int _minMatch,int _distanceThreshold,int _updateFactor,int _neighborWidth,int _neighborHeight):numberSamples(_numberSamples),minMatch(_minMatch),distanceThreshold(_distanceThreshold),updateFactor(_updateFactor),neighborWidth(_neighborWidth),neighborHeight(_neighborHeight){};
~OriginalVibe(){};
//操作成员变量
void setUpdateFactor(int _updateFactor);
//灰度图像
void originalVibe_Init_GRAY(const Mat &firstFrame);
void originalVibe_ClassifyAndUpdate_GRAY(const Mat &frame,OutputArray &_segmentation);
//RGB三通道
void originalVibe_Init_BGR(const Mat & firstFrame);
void originalVibe_ClassifyAndUpdate_BGR(const Mat &frame,OutputArray &_segmentation);
private:
//背景模型
const int numberSamples;
std::vector<Mat> backgroundModel;
//像素点的分类判断的参数
const int minMatch;
int distanceThreshold;
//背景模型更新概率
int updateFactor;
//8-领域(3 x 3)
const int neighborWidth;
const int neighborHeight;
//前景和背景分割
const static unsigned char BACK_GROUND;
const static unsigned char FORE_GROUND;
//BGR的距离计算
int distanceL1(const Vec3b &src1,const Vec3b &src2);
float distanceL2(const Vec3b &src1,const Vec3b &src2);
};
#include"originalVibe.h"
#include<iostream>
const unsigned char OriginalVibe::BACK_GROUND = 0;
const unsigned char OriginalVibe::FORE_GROUND = 255;
//操作成员变量
void OriginalVibe::setUpdateFactor(int _updateFactor)
{
this->updateFactor = _updateFactor;
}
//第一种方法:最原始的vibe灰度通道
void OriginalVibe::originalVibe_Init_GRAY(const Mat &firstFrame)
{
int height = firstFrame.rows;
int width = firstFrame.cols;
//背景模型分配内存
backgroundModel.clear();
for(int index = 0;index < this->numberSamples;index++)
{
backgroundModel.push_back(Mat::zeros(height,width,CV_8UC1));
}
//随机数
RNG rng;
int cshift;
int rshift;
for(int r = 0;r < height ;r++)
{
for(int c = 0;c < width ; c++)
{
if( c < neighborWidth/2 || c > width - neighborWidth/2 -1|| r < neighborHeight/2 || r > height - neighborHeight/2 -1)
{
/*随机数的生成方式有很多种*/
/*
cshift = randu<int>()%neighborWidth - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = randu<int>()%neighborHeight - neighborHeight/2;
*/
cshift = rand()%neighborWidth - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = rand()%neighborHeight - neighborHeight/2;
for(std::vector<Mat>::iterator it = backgroundModel.begin();it != backgroundModel.end();it++)
{
for(;;)
{
/*
cshift = rng.uniform(-neighborWidth/2,neighborWidth/2 + 1);
rshift = rng.uniform(-neighborHeight/2,neighborHeight/2 +1 );
*/
cshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborWidth) - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborHeight) - neighborHeight/2;
if(!(cshift == 0 && rshift==0))
break;
}
if(c + cshift < 0 || c + cshift >=width)
cshift *= -1;
if(r + rshift < 0 || r + rshift >= height)
rshift *= -1;
(*it).at<uchar>(r,c) = firstFrame.at<uchar>(r+rshift,c+cshift);
}
}
else
{
for(std::vector<Mat>::iterator it = backgroundModel.begin();it != backgroundModel.end();it++)
{
for(;;)
{
/*
cshift = rng.uniform(-neighborWidth/2,neighborWidth/2 + 1);
rshift = rng.uniform(-neighborHeight/2,neighborHeight/2 +1 );
*/
cshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborWidth) - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborHeight) - neighborHeight/2;
if(!(cshift == 0 && rshift == 0))
break;
}
(*it).at<uchar>(r,c) = firstFrame.at<uchar>(r+rshift,c+cshift);
}
}
}
}
}
void OriginalVibe::originalVibe_ClassifyAndUpdate_GRAY(const Mat &frame,OutputArray &_segmentation)
{
int width = frame.cols;
int height = frame.rows;
int rshift;
int cshift;
_segmentation.create(frame.size(),CV_8UC1);
Mat segmentation = _segmentation.getMat();
RNG rng;
for(int r = 0; r < height;r++)
{
for(int c = 0;c < width ;c++)
{
int count = 0;
unsigned char pixel = frame.at<uchar>(r,c);
//让pixel和背景模板中backgroundModel进行比较
for(std::vector<Mat>::iterator it = backgroundModel.begin();it != backgroundModel.end();it++)
{
if( abs( int(pixel) - int( (*it).at<uchar>(r,c)) ) < (this->distanceThreshold) )
{
count++;
//循环到一定阶段,判断count的值是否大于 minMatch,更新背景模型
if( count >= this->minMatch)
{
int random = rng.uniform(0,this->updateFactor);
if(random == 0)
{
int updateIndex = rng.uniform(0,this->numberSamples);
backgroundModel[updateIndex].at<uchar>(r,c) = pixel;
}
random = rng.uniform(0,this->updateFactor);
if(random == 0)
{
if(c < neighborWidth/2 || c > width - neighborWidth/2-1 || r < neighborHeight/2 || r > height - neighborHeight/2-1)
{
for(;;)
{
/*
cshift = rng.uniform(-neighborWidth/2,neighborWidth/2 + 1);
rshift = rng.uniform(-neighborHeight/2,neighborHeight/2 +1 );
*/
cshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborWidth) - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborHeight) - neighborHeight/2;
if(!(cshift == 0 && rshift ==0))
break;
}
if(c + cshift < 0 || c + cshift >=width)
cshift *= -1;
if(r + rshift < 0 || r + rshift >= height)
rshift *= -1;
int updateIndex = rng.uniform(0,this->numberSamples);
backgroundModel[updateIndex].at<uchar>(r+rshift,c+cshift) = pixel;
}
else
{
for(;;)
{
/*
cshift = rng.uniform(-neighborWidth/2,neighborWidth/2 + 1);
rshift = rng.uniform(-neighborHeight/2,neighborHeight/2 +1 );
*/
cshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborWidth) - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborHeight) - neighborHeight/2;
if(!(cshift == 0 && rshift==0))
break;
}
int updateIndex = rng.uniform(0,this->numberSamples);
backgroundModel[updateIndex].at<uchar>(r+rshift,c+cshift) = pixel;
}
}
segmentation.at<uchar>(r,c) = this ->BACK_GROUND;
break;
}
}
}
if( count < this->minMatch)
segmentation.at<uchar>(r,c) = this->FORE_GROUND;
}
}
}
//第三种方法:BGR通道
void OriginalVibe::originalVibe_Init_BGR(const Mat & fristFrame)
{
int height = fristFrame.rows;
int width = fristFrame.cols;
//背景模型分配内存
backgroundModel.clear();
for(int index = 0;index < this->numberSamples;index++)
{
backgroundModel.push_back( Mat::zeros(height,width,CV_8UC3) );
}
//随机数
RNG rng;
int cshift;
int rshift;
for(int r =0 ; r < height; r++)
{
for(int c = 0;c < width ;c++)
{
if( c < neighborWidth/2 || c > width - neighborWidth/2 -1|| r < neighborHeight/2 || r > height - neighborHeight/2 -1 )
{
/*
初始化背景模型:开始
*/
for(vector<Mat>::iterator iter = backgroundModel.begin(); iter != backgroundModel.end();iter++)
{
for(;;)
{
cshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborWidth) - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborHeight) - neighborHeight/2;
if(!(cshift == 0 && rshift==0))
break;
}
if(c + cshift < 0 || c + cshift >=width)
cshift *= -1;
if(r + rshift < 0 || r + rshift >= height)
rshift *=-1;
(*iter).at<Vec3b>(r,c) = fristFrame.at<Vec3b>(r+rshift,c+cshift);
}
}
/*初始化背景模型:结束*/
else
{
/*******初始化背景模型:开始******/
for(vector<Mat>::iterator iter = backgroundModel.begin(); iter != backgroundModel.end();iter++)
{
for(;;)
{
cshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborWidth) - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborHeight) - neighborHeight/2;
if( !(cshift == 0 && rshift==0) )
break;
}
(*iter).at<Vec3b>(r,c) = fristFrame.at<Vec3b>(r+rshift,c+cshift);
}
/*****初始化背景模型:结束 ******/
}
}
}
}
float OriginalVibe::distanceL2(const Vec3b & src1,const Vec3b& src2)
{
return pow( pow(src1[0]-src2[0],2.0) +pow(src1[1]-src2[1],2.0) + pow(src1[2] - src2[2],2.0),0.5);
}
int OriginalVibe::distanceL1(const Vec3b & src1,const Vec3b& src2)
{
return abs(src1[0]-src2[0])+abs(src1[1] - src2[1])+abs(src1[2]-src2[2]) ;
}
void OriginalVibe::originalVibe_ClassifyAndUpdate_BGR(const Mat &frame,OutputArray &_segmentation)
{//*编号1
int height = frame.rows;
int width = frame.cols;
int cshift;
int rshift;
_segmentation.create(frame.size(),CV_8UC1);
Mat segmentation = _segmentation.getMat();
RNG rng;
for(int r =0 ;r < height; r++)
{//编号1-1
for(int c = 0;c < width ;c++)
{//编号1-1-1
int count = 0;
Vec3b pixel = frame.at<Vec3b>(r,c);
for( vector<Mat>::iterator iter = backgroundModel.begin() ;iter != backgroundModel.end(); iter++)
{//编号1-1-1-1
//
//
if( distanceL1(pixel,(*iter).at<Vec3b>(r,c)) < 4.5*this->distanceThreshold )
{
count++;
if(count >= this->minMatch)
{
//第一步:更新模型update
/**********开始更新模型*************/
int random = rng.uniform(0,this->updateFactor);
if(random == 0)
{
int updateIndex = rng.uniform(0,this->numberSamples);
backgroundModel[updateIndex].at<Vec3b>(r,c) = pixel;
}
random = rng.uniform(0,this->updateFactor);
if(random == 0)
{
/****************************************/
if( c < neighborWidth/2 || c > width - neighborWidth/2-1 || r < neighborHeight/2 || r > height - neighborHeight/2-1 )
{
for(;;)
{
cshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborWidth) - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = abs(randu<int>()%neighborHeight) - neighborHeight/2;
if(!(cshift == 0 && rshift==0))
break;
}
if(c + cshift < 0 || c + cshift >=width)
cshift*=-1;
if(r + rshift < 0 || r + rshift >= height)
rshift*=-1;
int updateIndex = rng.uniform(0,this->numberSamples);
backgroundModel[updateIndex].at<Vec3b>(r+rshift,c+cshift) = pixel;
}
else
{
for(;;)
{
cshift = abs(rand()%neighborWidth) - neighborWidth/2;
rshift = abs(rand()%neighborHeight) - neighborHeight/2;
if(!(cshift == 0 && rshift==0))
break;
}
int updateIndex = rng.uniform(0,this->numberSamples);
backgroundModel[updateIndex].at<Vec3b>(r+rshift,c+cshift) = pixel;
}
/****************************************/
}
/*
*********结束更新模型************
*/
//第二步:分类classify
segmentation.at<uchar>(r,c) = this->BACK_GROUND;
break;
}
}
}//编号1-1-1-1
if(count < this->minMatch)//classify
segmentation.at<uchar>(r,c) = this->FORE_GROUND;
}//编号1-1-1
}//编号1-1
}//*编号1
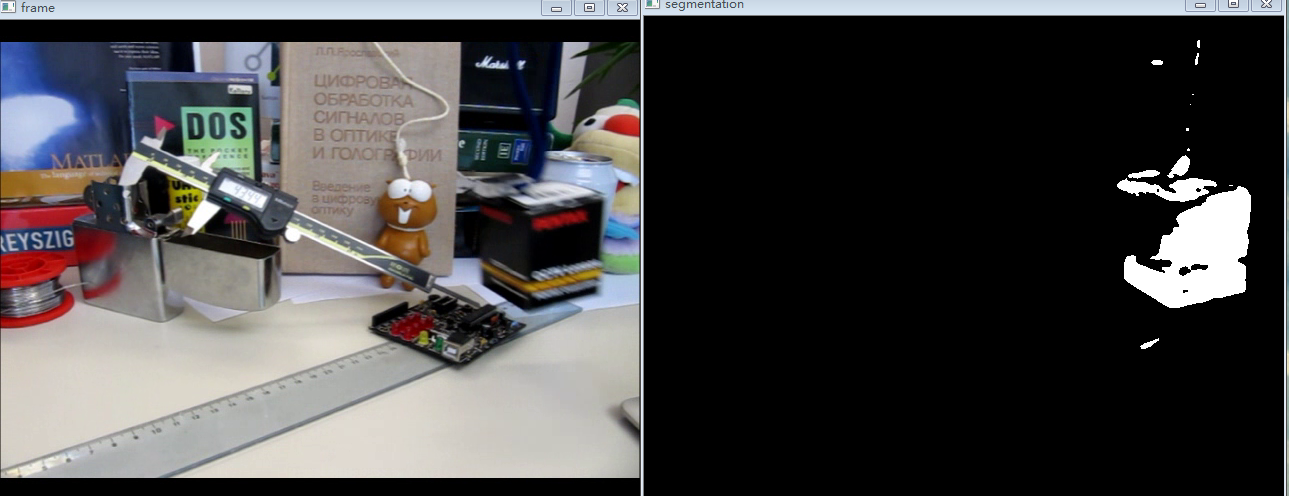
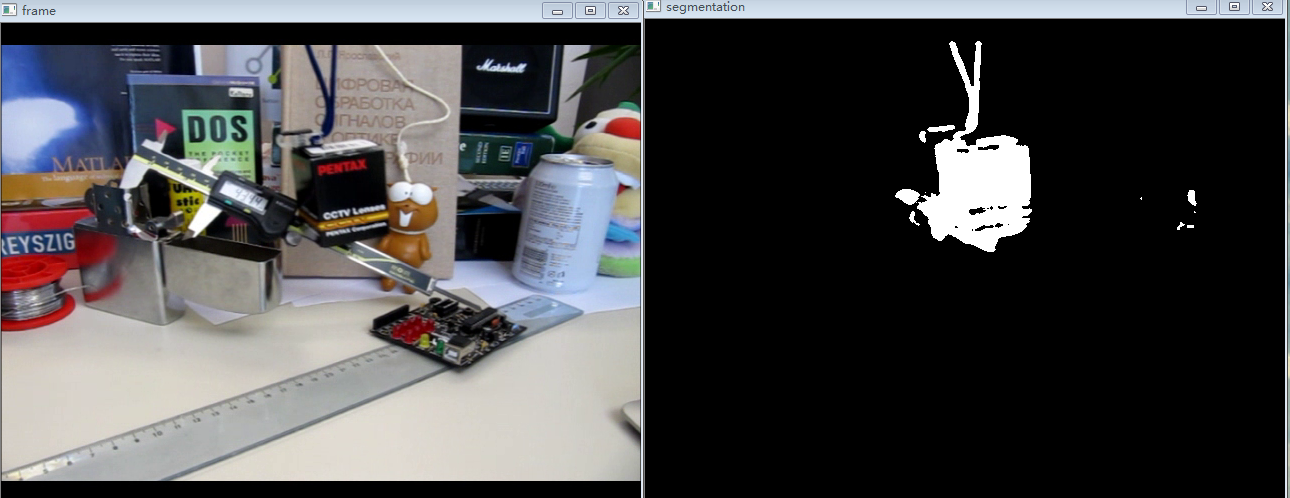
vibe前景检测算法的结果:(可以和帧差法做一比较)
【结论】
可以看到vibe算法,并没有像帧差法那样,产生大的空洞,但是会有鬼影出现
《Background Subtraction: Experiments and Improvements for ViBe》对上述原始的vibe算法,做了很多改进:
1、把固定的距离阈值,变为自适应的阈值
2、距离的计算方法改为codebook算法中距离计算公式
3、针对闪光点的判断
等等。下面还得接着研究对vide算法的改进



























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








