简介
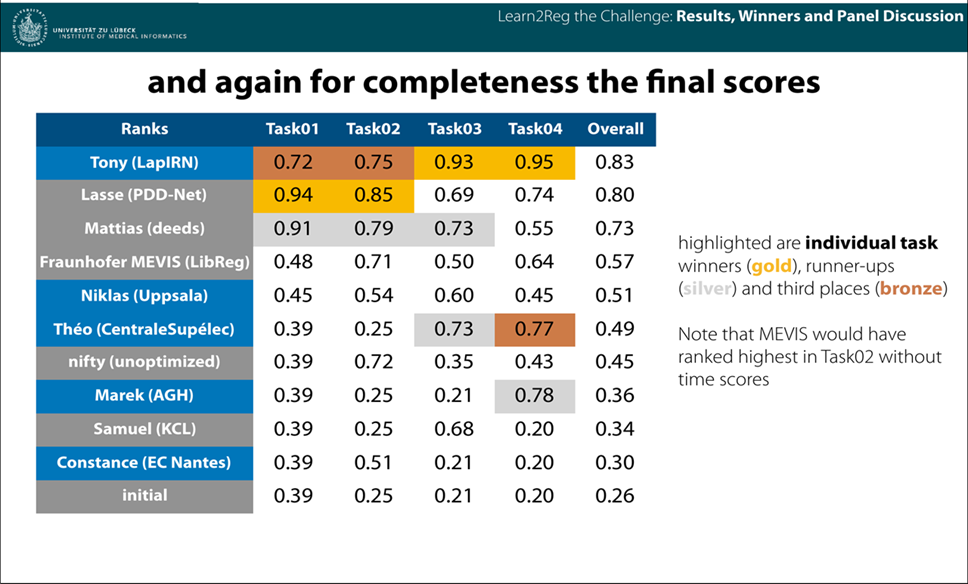
PDD-net 是德国吕贝克大学的 Mattias P. Heinrich 和 Lasse Hansen 在深度神经网络应用于医学图像配准(MICCAI 2020 - Learn2Reg chanllenge)竞赛中的 SOTA 成果。其中,他们的 PDD-net 在所有挑战选手中排名前三,四个子任务分别获得两个第一名和三个第二名。以下是最近他们在 MICCAI 赛后发表的解释性文章。
我主要是关注他们在 Task 1 3D 多模态医学图像配准上的 SOTA 成绩。
Discrete Unsupervised 3D Registration Methods for the Learn2Reg Challenge 👉
- Mattias P. Heinrich and Lasse Hansen
- MICCAI 2020 - Learn2Reg chanllenge
- pdd-net 2.5、deeds
- unsupervised
- Discrete optimisation、Constrast-independent features
1. Abstract:
In this short paper, we describe our choices for two state-of-the-art discrete 3D registration methods that enable fast and accurate estimation of large deformations without expert supervision during training. Both approaches primarily focus on the use of contrast-invariant features with dense displacement evaluation
- Question: 目的和难度不尽相同的 4 个 3D 医学图像配准任务。
- Method: two state-of-the-art discrete 3D registration methods, focus on the use of contrast-invariant features with dense displacement evaluation。
- Answer: enable fast and accurate estimation of large deformations without expert supervision during training。
2. Introduction:
-
为什么研究这个课题?
传统的配准方法要么依赖于多重扭曲和从粗到细的分辨率方案(由于内存限制,在基于学习的框架内很难模拟传统配准),要么依赖离散优化以避免局部极小值。
-
目前这个课题的研究进行到了哪一阶段?
-
作者使用了什么模型和算法?(看不明白也没关系,先抄下来)
deeds:
- instead of directly solving the deformation estimation with a single quantised warp, several levels of decreasingly coarse control point grids are employed
- patch-based similarity metrics are approximated using a quantised range of values (and the efficient Hamming distance) and a subsampling of voxels
- a simplified graph-model, namely a minimum-spanning-tree is employed (that only requires a single forward and backward path of messages for optimisation) in combination with a symmetric inverse consistency approach
- 通过使用健壮而准确的 hand-crafted MIND self-similarity context (SSC) descriptors,该方法适用于多模态任务以及具有挑战性的图像外观(大变形)。
PDD-net:
- The PDD-net aims to mimic the successful discrete components of deeds.
- 首先使用一个紧凑的可变形卷积网络(OBELISK-net)4来提取特征,并计算一个密集的 6D 相异张量(3 个空间 + 3 个位移维度)。
- 选择了一个更简单的 graphical model,即条件随机场的平均场推断(不同于马尔可夫随机场,无需计算定向信息),这使得信息能够在三个空间维度上通过(高斯)滤波操作传递。
- 在大多数情况下,PDD-net 的一个扭曲在不到一秒钟的时间内能产生非常精确的结果,而且还可以使用连续实例优化或第二次扭曲进一步微调。
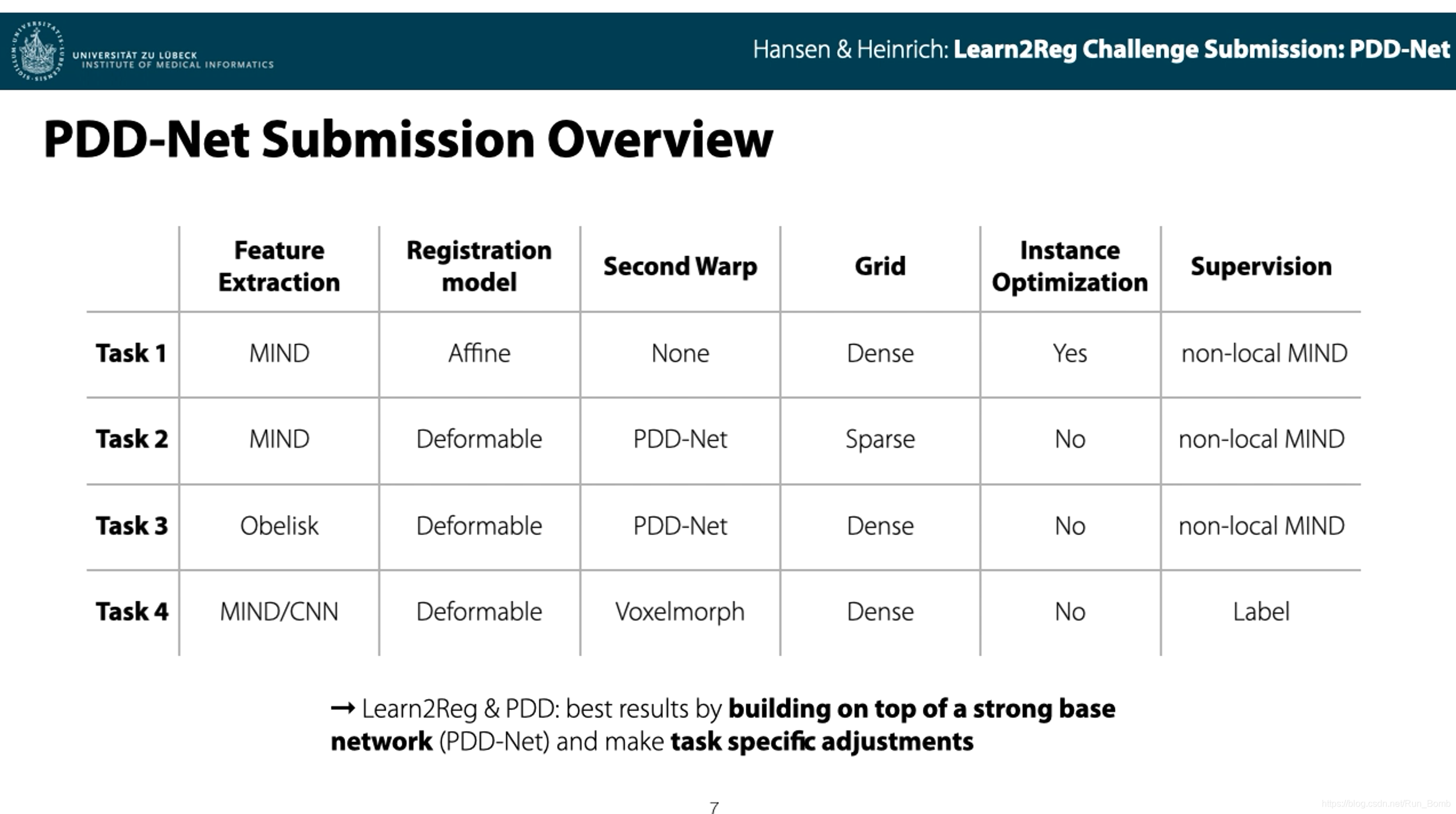
3. Experiments and Result:(PDD-net)
-
Task 1 CuRIOUS US / MRI
- We chose to use handcrafted MIND features,在多模态配准上表现强劲。(此处没有说明这个 handcrafted MIND features 和原版的 MIND 有何分别)
- 使用修剪最小二乘法从预测的位移场估计仿射矩阵。
- 为了达到鲁棒性的配准,还需要对超声图像做 mask。
- 配准精度的测量使用了人工标注的 landmark,并计算 TRE
-
Task 2 Lung CT
- use fixed MIND features for the PDD-Net
- 为了使用肺部的血管来辅助配准,他们使用 Foerstner5 算子来提取稀疏关键点,并且将固定网格(fixed grid)上的高斯滤波替换为 kNN 图(k = 10)上的拉普拉斯平滑。
- 经过二次扭曲后(在 moving img 已经扭曲后再输入网络扭曲一次?),精度很高;第一次扭曲用了 1024 个关键点,第二次用了 1536 个关键点。
- 配准精度的测量使用了人工标注的 landmark,并计算 TRE
-
Task 3 Abdominal CT(inter-patient)
- using an unsupervised non-local MIND loss
- We employed a second warp after the first transformation of the moving image (using the same feature extraction network).
- instance optimisation using Adam optimizer
- The registration accuracy is assessed by the Dice similarity of organ segmentation labels.
这里使用了分割标签来计算 dice 相似度,值得本人借鉴。
-
Task 4 Hippocampus MRI(inter-patient)
- the hippocampus MRI images are relatively small (64 × 64 × 64)
- For this task the PDD-net is extended by a Voxelmorph framework6
- For the first warp, the PDD-net with fixed MIND features is used to predict larger deformations.
- Then, to cope with remaining small scale transformations, a Voxelmorph network is trained using an unsupervised MIND loss
- the registration accuracy is evaluated using Dice similarity of segmentation labels
这里神奇地使用了两个配准网络,第一次使用自家的 PDD-net 来配准大变形(看家本领),第二次使用经过 MIND-loss 训练的 Voxelmorph 来配准小变形。
-
作者关于这个课题的构思有哪几点?
our contributions to the Learn2Reg challenge we analysed the use of two discrete registration methods (deeds, PDD-net) with several experimental design choices (MIND features, Obelisk features, instance optimisation, etc.) for the four distinctive challenge tasks.
作者针对四个不同的 task,在他们提出的离散配准网络 PDD-net 上分别对 loss 和优化器选用上做功夫,使得基于同一个特征提取网络(Obelisk-net)的配准网络能适应 4 个差异巨大的 task,并且都取得了非常好的成绩,特别是在多模和无监督的配准任务上,这值得学习和借鉴。
The PDD-net stands out with fast runtimes and winning task 1 and 2 of the challenge
4. 研究方法:
- 研究的数据从哪里来?
- 研究中用到的重要指标有哪些?
- Dice
计算的是 label 的 dice(DSC)系数,而不是用于原图像计算,因为没有 label 就没有区域(一个分割 label 的灰度值是一样的,比如 22,原图的一个区域的灰度值大概率不一样)可言,自然无法找到可以计算重叠度的方式。
- target registration error(TRE)
对于大多数配准任务,最重要的误差度量是目标配准误差(TRE),它是计算在配准变换时不使用的对应点之间配准后的距离。
- smoothness of the transformation(standard deviation of log Jacobian)
- infer time
- Dice
参考文献(都是他们的工作):
Mind: Modality independent neighbourhood descriptor for multi-modal deformable registration. ↩︎
Towards realtime multimodal fusion for image-guided interventions using self-similarities ↩︎
MRF-based deformable registration and ventilation estimation of lung CT. ↩︎
OBELISK one binary extremely large and inflecting sparse kernel ↩︎
F¨orstner, W., G¨ulch, E.: A fast operator for detection and precise location of distinct points, corners and centres of circular features. In: Intercommission Conference on Fast Processing of Photogrammetric Data, pp. 281–305 (1987) ↩︎
Balakrishnan, G., Zhao, A., Sabuncu, M.R., Guttag, J., Dalca, A.V.: Voxelmorph: a learning framework for deformable medical image registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(8), 1788–1800 (2019) ↩︎























 1120
1120











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










