论文全名:Multi-site fMRI analysis using privacy-preserving federated learning and domain adaptation: ABIDE results
论文代码:https://github.com/xxlya/Fed_ABIDE
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.4.1. Basic privacy-preserving federated learning setup
2.4.2. Boosting multi-site learning with domain adaptation
2.5.2. Federated training setup and hyper-parameters discussion
2.5.3. Comparisons with different strategies
2.5.4. Evaluate model from interpretation perspective
2.5.5. Limitation and discussion
1. 心得
(1)有一说一FL的对比表是真的爽...
(2)也可能是比较古早了,感觉就是MLP6105-16-2+域对抗学习2loss+交叉熵损失
(3)用FC来直接表示生物标志物认真的吗?这个哪里表示是学习出来的呢?感觉作者没有很细讲
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①They proposed 2 domain adaptation methods
2.2. Introduction
①The healthcare system is unwilling to disclose data due to concerns about customer theft and loss of patients(会咩)
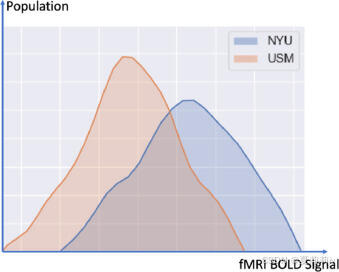
②Different data distribution on different sites:
2.3. Related work
2.3.1. Federated learning
①Two methods of FL: a) sending parameters only, b) information transfers between different communities by encryption techniques. They applied the first one
2.3.2. Domain adaptation
①Listing some domain adaptation methods by citation and pointing out that they do not use FL
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Basic privacy-preserving federated learning setup
(1)Problem definition
①Data in -th site is denoted by matrix
(是fMRI data所以是个矩阵)
② sites:
with institution owning private fMRI data
③Feature space is noted by (extracted fMRI feature), label space is
(diagnosis or phenotype needing predict) and sample ID space is represented by
④Data distribution:
⑤FL:
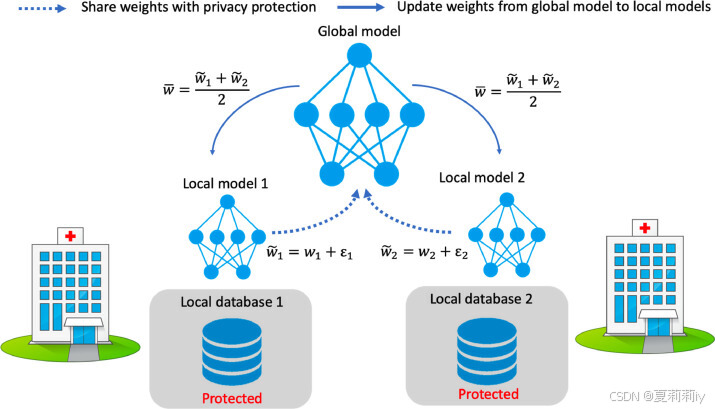
(2)Privacy-preserving decentralized training
①Cross entropy loss in this FL:
where denotes the label of the
-th subject in the
-th site,
, and
is the predicted probability
②Training process:

(3)Randomized mechanism for privacy protection
①For a deterministic real-valued function , L1 sensitivity
of
is:
if , denotes there is only one data point difference between
and
(为啥这是D和D'?而不是
和
这种?还是两个站点的数据集吗?按照普通的差分隐私来说,应该代指两个数据集间只有一个数据的差异,但是不知道这里作者是不是这个意思。我超,查了网上的差分隐私看见别人都是D和D’这种表示,不会是作者搬过来的时候没有改表达吧。)
②They define in their model is the
weight parameters
③Differential privacy:
or
(作者都没说这里在干嘛诶....S是什么?Pr又是什么?虽然不用把文章当成普通科普,但是符号的定义至少要给啊...)
④Gaussian Mechanism: adding noise to
, where the
differential privacy will become
and
⑤Laplace Mechanism: 我先随便插几张拉普拉斯分布的图,可以见得它和高斯分布有点类似只是是尖尖的,而且也是俩参数,公式还比高斯看起来简单一点:
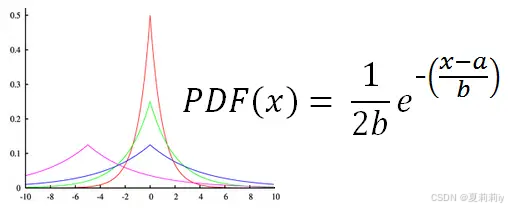

They employ Laplace Distribution with scale :
and , the
noise will be add to
, the difference privacy is
(作者只用了一个参数咩~)。然后他们为了简化讨论假定灵敏度
为1???这能假定吗?这不是两个数据集间的差异吗。我猜测作者是在说两个站点间参数的差异为1?
2.4.2. Boosting multi-site learning with domain adaptation
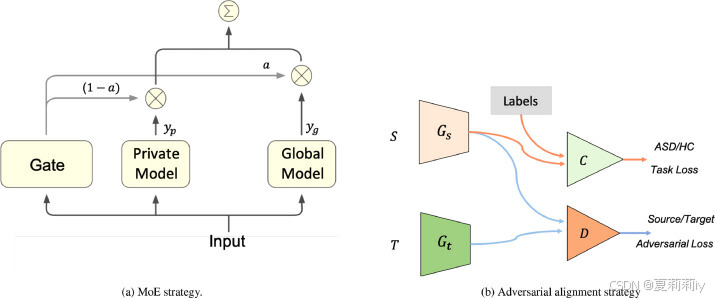
(1)Mixture of experts (MoE) domain adaptation
①Experts: mean deep learning models
②MoE: trainable gating network used in feed-forward neural network
③Domain adaptation strategies with FL:
④The final output of their network:
where the is the gating function in MoE and they use an non-linear layer
to represent it,
is Sigmoid,
and
are learnable weights
(2)Adversarial domain alignment
①They trained a local feature extractor for the source site
②They also trained a local feature generator for the target site
③They align distribution of and
by training a adversarial domain discriminator
④ and
aim to confuse
by adding noise (generate
and
,
denotes noise generator) and
aims to identify the domain
⑤To discriminate domain:
⑥第二步中的损失??第二步是什么?不变但
更新?以前也没这个东西啊怎么能叫更新?
⑦Algorithm(在这个第八行感觉出⑤和⑥俩损失就是直接都用上就行,但是作者也没有特别的解释,不知道从哪扒来的):

(3)Evaluate model by interpreting biomarkers
①Gradient based method:
where denotes the input ground class,
is the score of the
lass befor softmax,
is the
-th feature in the input,
denotes the imprtance of classifying
of feature
2.5. Experiments and results
2.5.1. Data
(1)Participants
①Sites chosen: the largest four, UM1、NYU、USM、UCLA1 with 106, 175, 72, 71. Eliminating incomplete data samples, left 88, 167, 52, 63 each
②Atlas: HO with 111 ROIs
③Slicing window: 32 size with 1 stride to crop the original time series
④Sample statistics:

⑤Demographic data:

(2)Data preprocessing
①FC: average ROI series by Pearson Correlation
②FC is applied to Fisher transformation
③Only remain the upper triangular matrix and flatten them to vector, fed them to MLP later (111*(111-1)/2=6105 dimension)
2.5.2. Federated training setup and hyper-parameters discussion
①MLP: 6105-16-2(哥们儿跳水呢?)
②Cross validation: 5 fold
③They define instances for each subject, if more than
instances are 'ASD' tag, then the subject is classified to ASD(哪里来的实例??MLP输出不是2吗不就是一个概率吗怎么还有多头了呢)
④Learning rate: 1e-5 with 1/2 decline each 20 epoch and stop at the 50-th epoch
⑤Optimizer: Adam
⑥Steps of each epoch: 60(这是什么玩意儿?)
⑦Batch size: 60
⑧Local uptating on each epoch: rely on communication pace (这又是什么玩意儿?是训练每
次就去服务器更新一下吗?然后这个玩意儿是60的因数是吗?)
⑨ ablation:
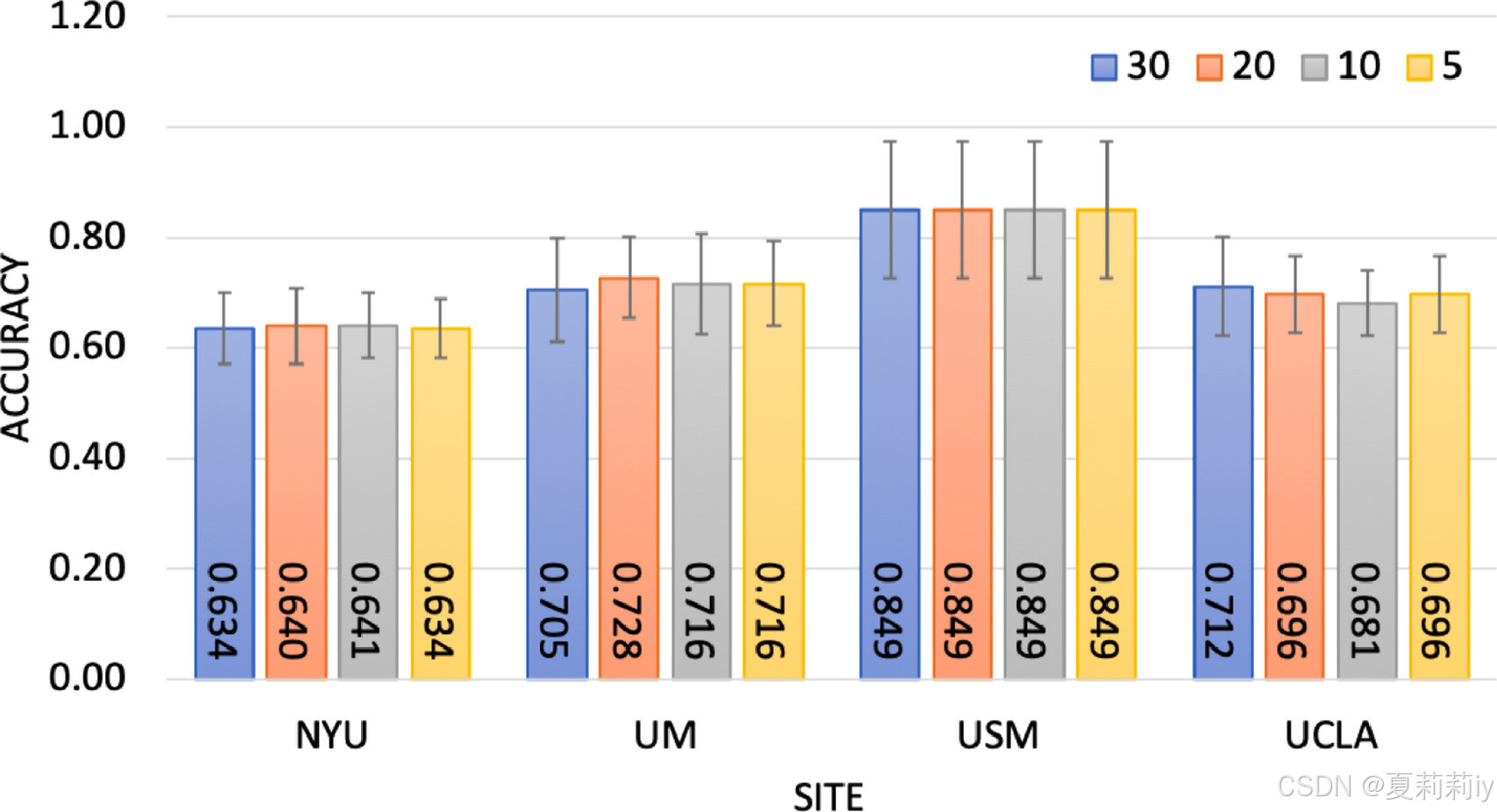
no significant difference
⑩Accuracy when adding different noise in Gauss mechanism (L2 norm and ):
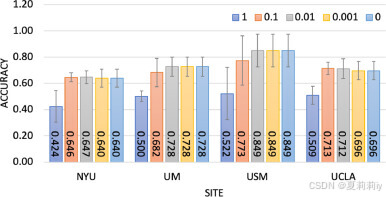
the variable is
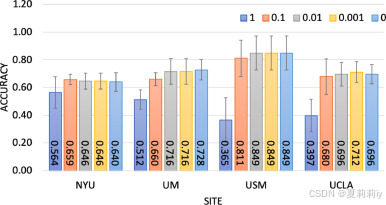
⑪Adding Laplace noise to local weight and varying
:
2.5.3. Comparisons with different strategies
①Evaluation methods:
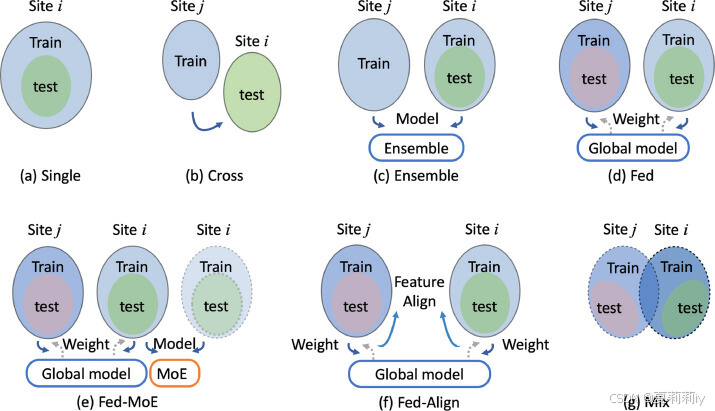
②Comparison result:

2.5.4. Evaluate model from interpretation perspective
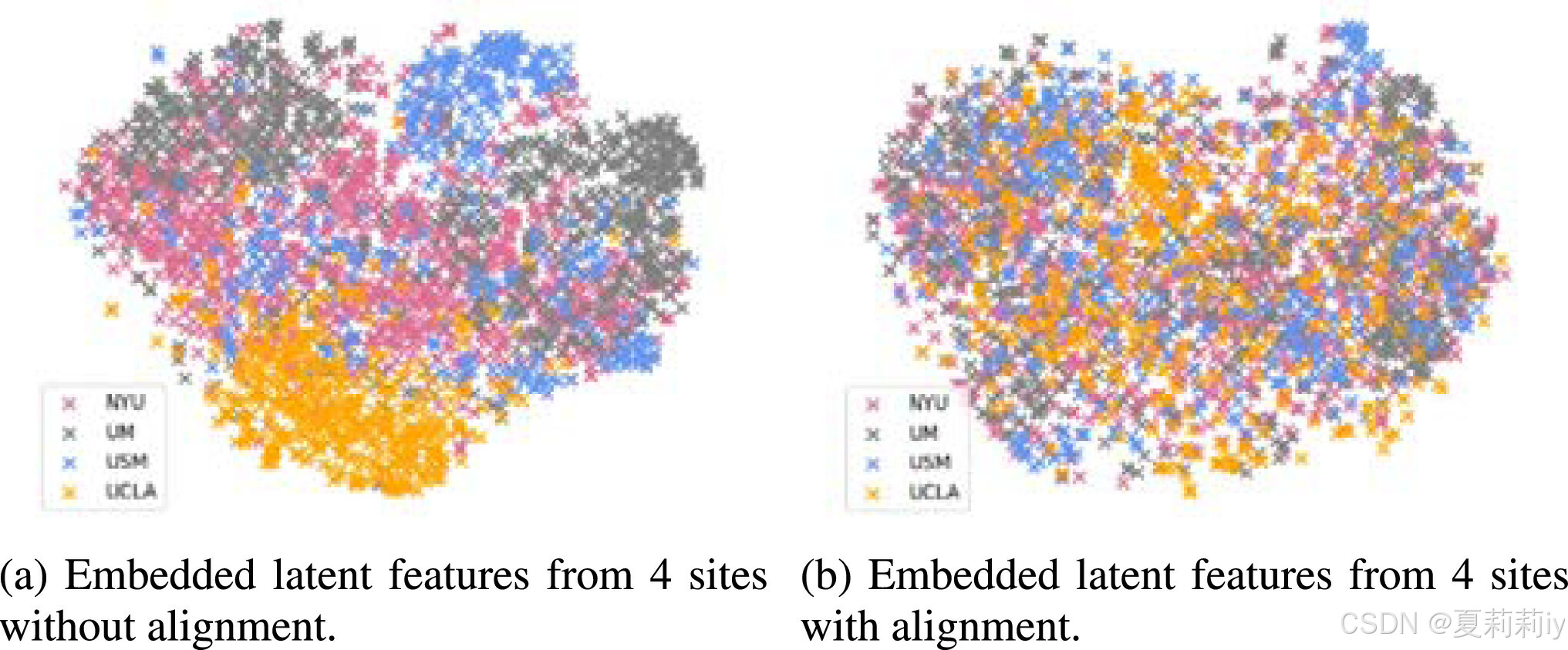
(1)Aligned feature embedding
①Visualizing fully connected layer embedding:
(2)MoE Gating value
①Gate value in different sites:
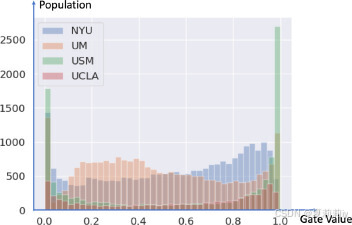
(gate value是learnable的参数)(哥们儿怎么在画图啊不能化成三维吗后面的都被挡住了)
(3)Neural patterns: Connectivity in the autistic brain
①They define "informativity" as functional representation difference between ASD and HC groups and "robustness" as the biomarker consistency of 4 sites
②They applied guided back-propagation method to detect the robust biomarkers of HC in Fed:
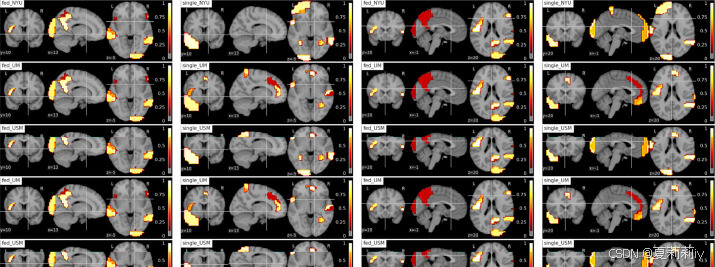
③ASD biomarker:
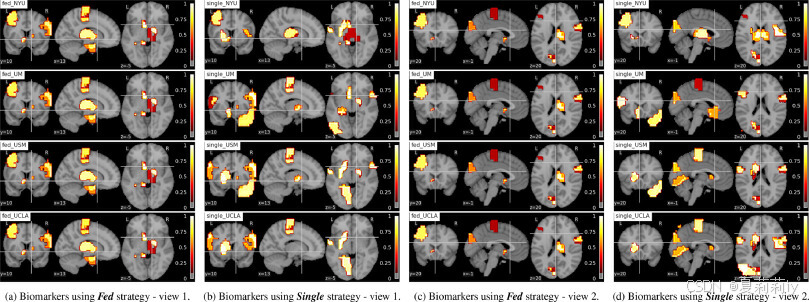
④Function correlation:

2.5.5. Limitation and discussion
①“尽管根据我们的实证调查,控制局部和全局模型更新权重信息频率的通信速度不会影响分类性能,但我们不能得出速度参数无关紧要的结论”
②Sensitivity of deep learning is hard to define
2.6. Conclusion
~
3. 知识补充
3.1. Differential privacy
(1)定义:差分隐私是一种数学框架,用于量化在数据发布或算法处理过程中保护个人隐私的程度。它通过在数据中引入随机性来确保即使数据被公开或分析,也无法识别出任何特定个体的信息。具体来说,差分隐私要求对于两个仅相差一个数据点的数据集(即邻接数据集),其查询结果应当具有相近的概率分布,从而无法通过观察查询结果来推断出单个数据点的存在与否。
(2)感觉就是添加噪声,使得单个数据难以被辨识。不过我感觉传神经网络参数为什么能计算出单个人的信息呢?
(3)参考学习:全局敏感度,局部敏感度和平滑敏感度到底有什么区别?【差分隐私】_全局影响度-CSDN博客
3.2. L1 sensitivity
(1)定义:L1灵敏度通常指的是在L1范数(也称为曼哈顿距离或绝对值和)意义下,某个参数或系统对输入变化的敏感度。它衡量的是当输入发生微小变化时,输出在L1范数下的变化量。
(2)计算:对于单个向量来说,L1范数(L1 norm)是指向量中各个元素绝对值之和;对于两个向量来说,是每个对应元素相减的加总:
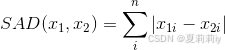
4. Reference
Li, X. et al. (2020) 'Multi-site fMRI analysis using privacy-preserving federated learning and domain adaptation: ABIDE results', Medical Image Analysis, 65. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101765

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








