
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.3. Neuropsychiatric disease datasets and model performance metrics
2.3.2. Quality evaluation metrics of artificial intelligence models
2.4. Capturing key information through image preprocessing
2.4.1. rs-fMRI image processing tools and pre-processing steps
2.4.2. Repositioning ROIs by brain atlases
2.6. Graph convolutional methods and milestone progress in neuropsychiatric disorders diagnosis
2.6.1. Convolutional network backbone of the whole framework
2.6.2. Downsampling pooling strategies
2.6.3. Milestones and representative models
2.7. Diagnostic methods for brain diseases
2.7.1. Characterizing individual hallmark features by graph level representation readout
2.7.2. Implementing probability prediction through the final classifier
2.8.1. Existing issues at the data level
2.8.2. Limitations and improvement directions of current GNN modules
2.8.3. Future prospects of CAD in neuropsychiatric disorders
1. 心得
(1)这是关于指导初学者怎么去写一篇属于自己的GNN神经精神疾病诊断的论文,数据源于fMRI
(2)总感觉对于综述来说,整合的意义其实大于解释某一个经典论文,毕竟论文大家都会去看,但是归纳总结归类可能是综述更需要的
(3)我用英文也是想,如果初学者读的话其实很需要在意专有名词的英文写法,不然自己写的时候被误翻译成其他的也比较尴尬,如果英语阅读困难也可以edge浏览器自带翻译,一样当中文看
(4)希望大家都能设计出自己的模型
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①They aim to analyse GNN in neuropsychiatric disorders through fMRI
2.2. Introduction
①Introducing the neuropsychiatric disorders → how fMRI reflects them → how AI (especially GNN) applied in it
②PRISMA:

③⭐They aim to explain the process of diagnosis by GNN
④Overall pipeline of diagnosis/classification:

2.3. Neuropsychiatric disease datasets and model performance metrics
2.3.1. Large rs-fMRI datasets
①OpenNeuro: OpenNeuro
②OpenfMRI: OpenfMRI
③SchizConnect: https://schizconnect.org/
④NITRC: https://www.nitrc.org/
⑤HCP: Connectome - Homepage
(1)ASD datasets
①ABIDE I: ABIDE
②ABIDE II: ABIDE
(2)ADHD dataset
①ADHD-200: ADHD200
(3)AD dataset
①ADNI: ADNI | Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
②OASIS-3: OASIS Brains
(4)MDD dataset
①Rest-meta-mdd: Data Sharing of the REST-meta-MDD Project from the DIRECT Consortium | The R-fMRI Network
2.3.2. Quality evaluation metrics of artificial intelligence models
①Evaluation metrics for classification:

②ACC may fluctuate when the classes are imbalance, F1 undulates when there is trade in ACC and recall
③⭐SPE denotes the identify of "negative/healthy", but SEN cares the accurate of identifying "positive/diseased"(宁愿健康人被误诊成患病,也不能患者被诊断为健康,从而错过了最佳诊疗时间)(不过现在大家其实就爱看ACC)
2.4. Capturing key information through image preprocessing
2.4.1. rs-fMRI image processing tools and pre-processing steps
①Rreprocessing steps: SPM, AFNI, DPARSF, FreeSurfer, SFL, RESTplus, fMRIPrep, FuNP
②⭐但是不同的处理软件和处理方式导致了复现代码上极大的困难,也没有一个给所有人公平比较模型性能的数据。虽然可能医学这边本来ACC就不是最重要的,感觉就算拉到百分百,没有医学的支撑还是难搞
③Preprocessing steps:
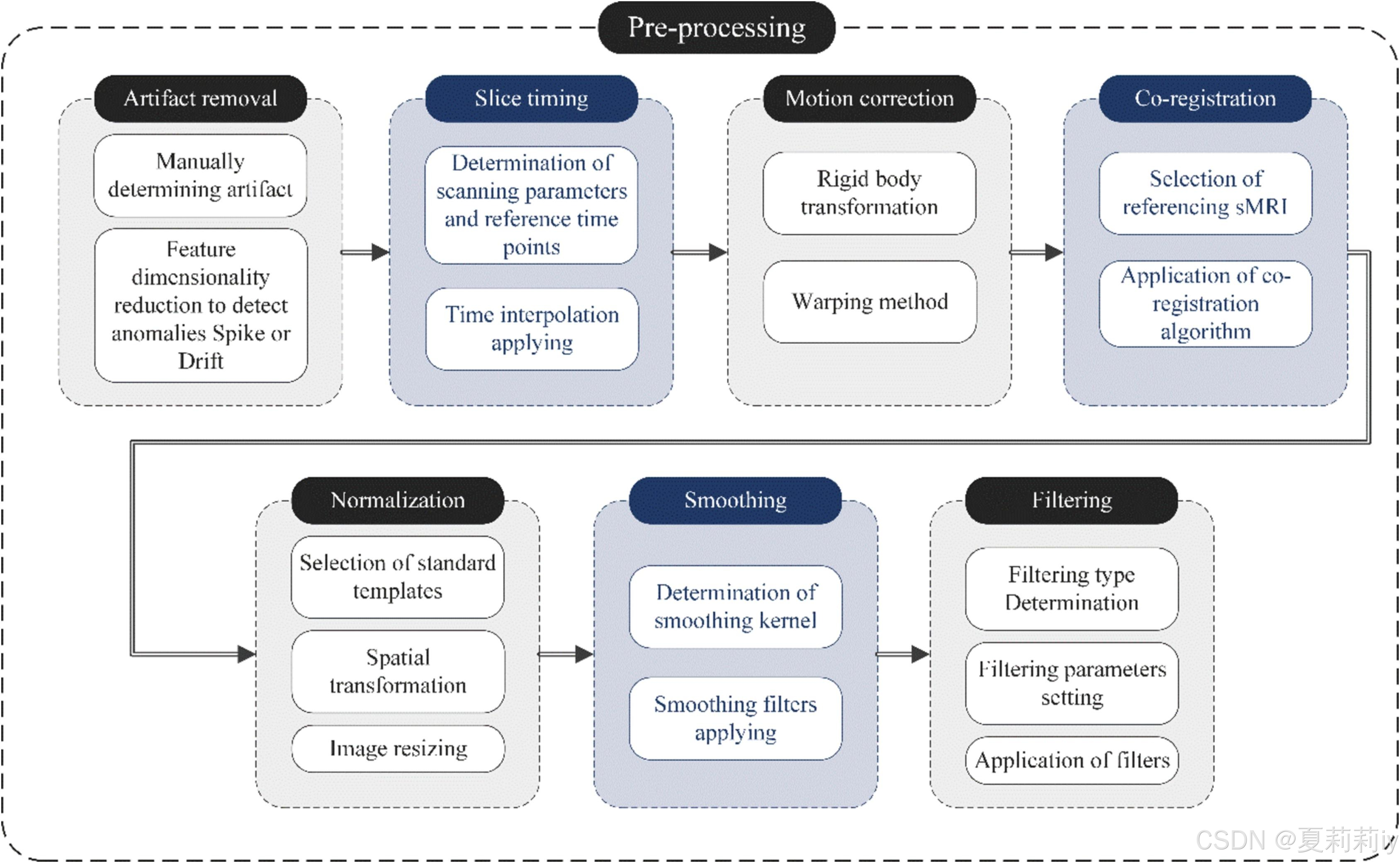
2.4.2. Repositioning ROIs by brain atlases
①Introducing common/famous atlases: Schaefer, HO, AAL, CC200
②⭐和上面一样,这个也导致了复现的难度以及大家非常不统一,而且一般也不会专门去解释“我为什么要用这个脑图谱~”,其实潜台词差不多是“我用这个脑图谱效果好~”“好懒得处理我就只尝试一个脑图谱好了~”
2.5. Brain graph construction
①Introduce graph classification (local graph) and node classification (global graph):
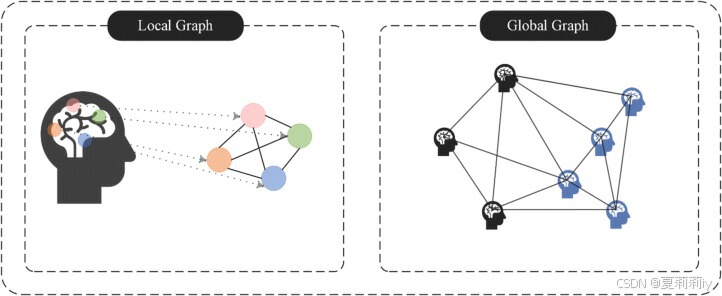
2.5.1. Node feature defining
①⭐节点特征一直是脑图里面比较睿智的一个东西,大家都爱拿皮尔逊相关的一行来作为节点特征,不过节点特征其实有很多选择,比如BOLD信号本身,或者处理出来的ALFF,ReHO和DC,独热编码也不是不行
2.5.2. Edge feature defining
①Common edge feature: the full/pooled original/binarized value in Pearson correlation matrix/Partial correlation matrix
②⭐关于连接取不取负值一直非常有争议,有的做法把负值保留,觉得正相关是同激活/抑制,负相关是相反激活抑制;另外的做法把负值全变为0,认为负值是除去全脑信号带来的虚假相关或大脑竞争资源的分配
2.5.3. Graph pruning
①脑图是全连接的~~就像计算皮尔逊和偏相关~这样的图太密集了,比如CC200的相关矩阵就是200*200的密集矩阵,大概率需要Prune一下,比如设置
| 1 | 负值全为0 |
| 2 | 只取top 20%值 |
| 3 | 只取值高于0.2的 |
| 4 | 每个节点只留一条边 |
2.6. Graph convolutional methods and milestone progress in neuropsychiatric disorders diagnosis
2.6.1. Convolutional network backbone of the whole framework
①Common backbones:
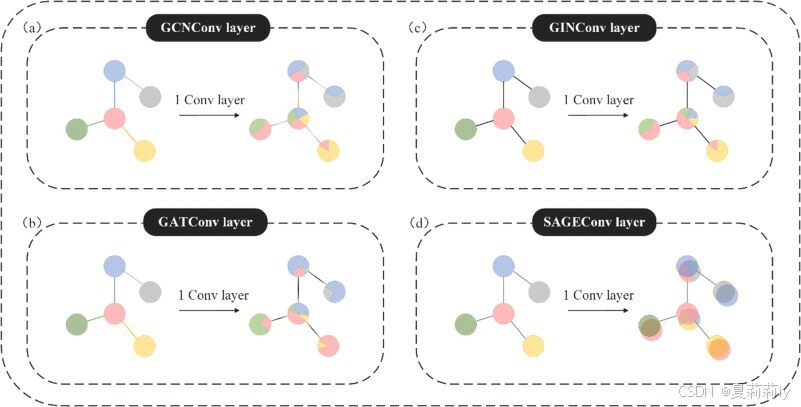
2.6.2. Downsampling pooling strategies
①Only remian the ROIs which actually affect the disease, there are some famous node pooling strategies:

(最后一列应该编辑排版错了,mapping(M)指的是一群节点映射成一个超节点,dropping(D)指的是把没用的节点丢弃了,这个看自己喜欢吧)
②Limitations of pooling:
| Weak transferability | Common pooling strategies may not suitable for brain |
| The balance between data and knowledge | Medical images often contain strong prior information |
| Inherent problems | Weak interpretability, fixed patterns and incompatible loss function |
| Out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization | Subtypes and races can affect brain signals |
2.6.3. Milestones and representative models
①Milestones:
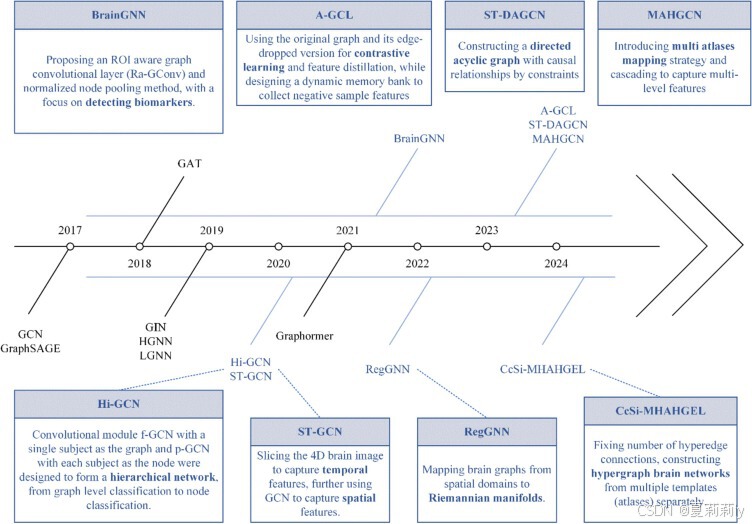
②⭐一些比较典的图分类模型以及其使用的节点特征,边缘特征,backbone,池化,读出和分类方法:

③节点分类(通常是先图再节点因此称为双阶段):

④Performance on ABIDE(⭐大家用的被试个数几乎是完全不一样的!!精度看个乐就好了,被试就是sample那一列):

⑤Performance on ADHD-200:

⑥Performance on ADNI(是fMRI噢做MRI的小伙伴不要混淆了):

2.7. Diagnostic methods for brain diseases
2.7.1. Characterizing individual hallmark features by graph level representation readout
①一般来说节点分类不需要读出(READOUT),但是脑分类一般是图分类,需要读出。读出函数的意思差不多就是把整个脑所有ROI的特征结合起来代表一个人,当然这个结合是全相加还是取平均还是取最高完全取决于自己,以下是一些常见的方法:

2.7.2. Implementing probability prediction through the final classifier
①深度学习分类器一般都是MLP,只是激活函数可能不一样吧。想用其他的也不是不行
2.8. Challenges and prospects
2.8.1. Existing issues at the data level
①Qualities of image: 硬件的进化必然带来软件的进化,不然软件就纯在自嗨。fine,还有就是不当的数据处理可能对结果造成不好的影响
②Collection of control samples: 潜在共病可能影响脑区域
③Class imbalance: 导致测试和泛化性能不好
2.8.2. Limitations and improvement directions of current GNN modules
①Sample size sensitivity: existing datasets are small on sample size
②Module dispersion
③Inappropriate pooling
④Dynamicity and real-time properties: light weight and fast needed
⑤Fusion learning
2.8.3. Future prospects of CAD in neuropsychiatric disorders
①Multimodal intelligent diagnosis: MRI, DTI, PET, EEG, MEG etc.
②Personalized medicine:
③Interdisciplinary research: wearable devices and remote monitoring technologies
④Privacy protection
⑤Hyperparameter optimization (HPO)
2.9. Conclusion
~
3. Reference
Gu, J. et al. (2025) Assisted diagnosis of neuropsychiatric disorders based on functional connectivity: A survey on application and performance evaluation of graph neural network. Expert Systems with Applications, 265. doi: Redirecting

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








