✅博主简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,Matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:海神之光
🏆代码获取方式:
海神之光Matlab王者学习之路—代码获取方式
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
Matlab图像处理(进阶版)
路径规划(Matlab)
神经网络预测与分类(Matlab)
优化求解(Matlab)
语音处理(Matlab)
信号处理(Matlab)
车间调度(Matlab)
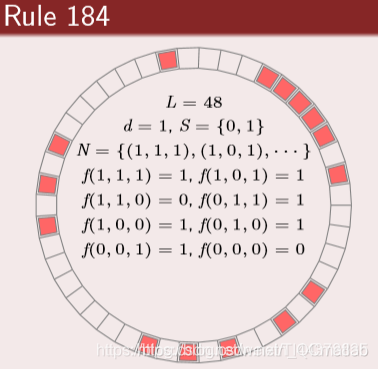
⛄一、元胞自动机简介
1 元胞自动机发展历程
最初的元胞自动机是由冯 · 诺依曼在 1950 年代为模拟生物 细胞的自我复制而提出的. 但是并未受到学术界重视.
1970 年, 剑桥大学的约翰 · 何顿 · 康威设计了一个电脑游戏 “生命游戏” 后, 元胞自动机才吸引了科学家们的注意.
1983 年 S.Wolfram 发表了一系列论文. 对初等元胞机 256 种 规则所产生的模型进行了深入研究, 并用熵来描述其演化行 为, 将细胞自动机分为平稳型, 周期型, 混沌型和复杂型.
2 对元胞自动机的初步认识
元胞自动机(CA)是一种用来仿真局部规则和局部联系的方法。典型的元胞自动机是定义在网格上的,每一个点上的网格代表一个元胞与一种有限的状态。变化规则适用于每一个元胞并且同时进行。典型的变化规则,决定于元胞的状态,以及其( 4 或 8 )邻居的状态。
3 元胞的变化规则&元胞状态
典型的变化规则,决定于元胞的状态,以及其( 4 或 8 )邻居的状态。
4 元胞自动机的应用
元胞自动机已被应用于物理模拟,生物模拟等领域。
5 元胞自动机的matlab编程
结合以上,我们可以理解元胞自动机仿真需要理解三点。一是元胞,在matlab中可以理解为矩阵中的一点或多点组成的方形块,一般我们用矩阵中的一点代表一个元胞。二是变化规则,元胞的变化规则决定元胞下一刻的状态。三是元胞的状态,元胞的状态是自定义的,通常是对立的状态,比如生物的存活状态或死亡状态,红灯或绿灯,该点有障碍物或者没有障碍物等等。
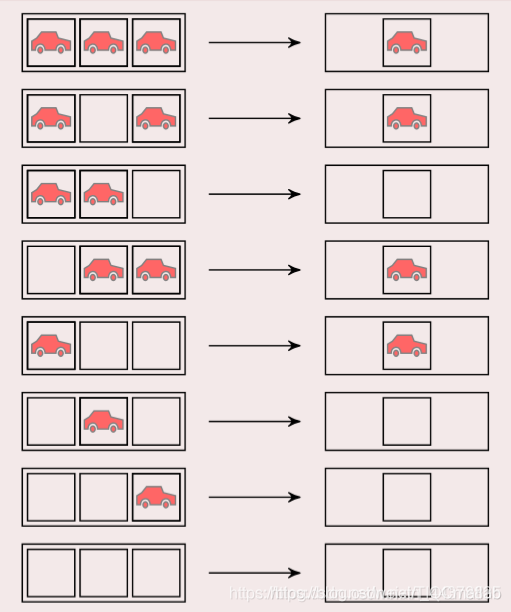
6 一维元胞自动机——交通规则
定义:
6.1 元胞分布于一维线性网格上.
6.2 元胞仅具有车和空两种状态.
7 二维元胞自动机——生命游戏
定义:
7.1 元胞分布于二维方型网格上.
7.2 元胞仅具有生和死两种状态.
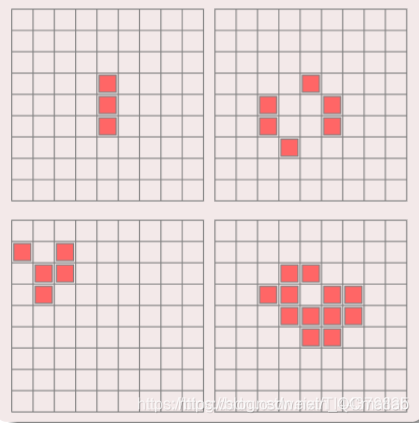
元胞状态由周围八邻居决定.
规则:
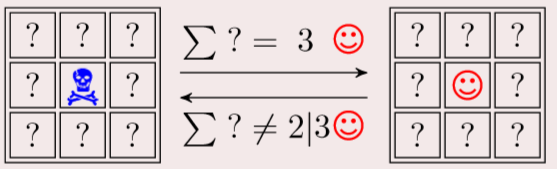
骷髅:死亡;笑脸:生存
周围有三个笑脸,则中间变为笑脸
少于两个笑脸或者多于三个,中间则变死亡。
8 什么是元胞自动机
离散的系统: 元胞是定义在有限的时间和空间上的, 并且元 胞的状态是有限.
动力学系统: 元胞自动机的举止行为具有动力学特征.
简单与复杂: 元胞自动机用简单规则控制相互作用的元胞 模拟复杂世界.
9 构成要素
(1)元胞 (Cell)
元胞是元胞自动机基本单元:
状态: 每一个元胞都有记忆贮存状态的功能.
离散: 简单情况下, 元胞只有两种可能状态; 较复杂情况下, 元胞具有多种状态.
更新: 元胞的状态都安照动力规则不断更新.
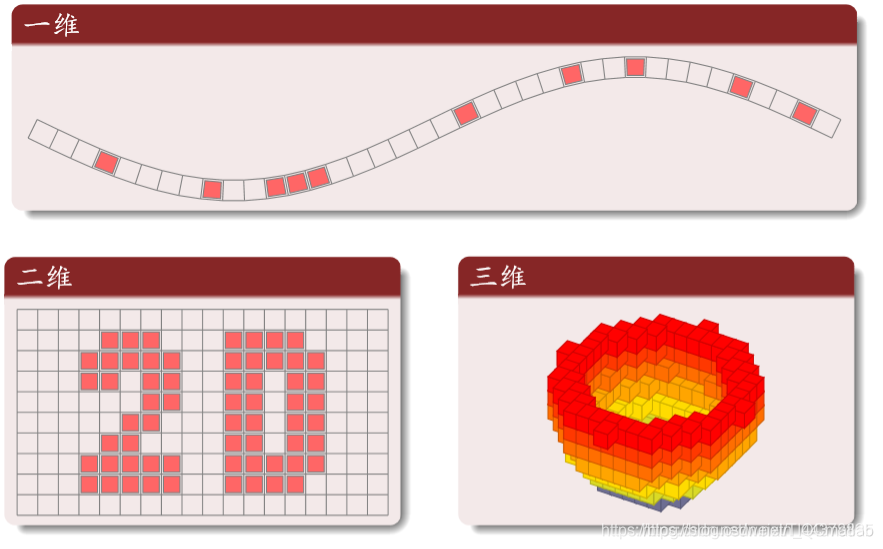
(2)网格 (Lattice)
不同维网格
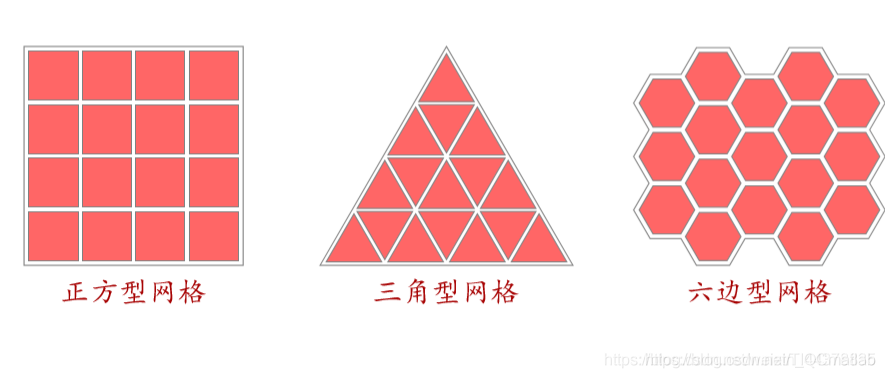
常用二维网格
(3)邻居 (Neighborhood)
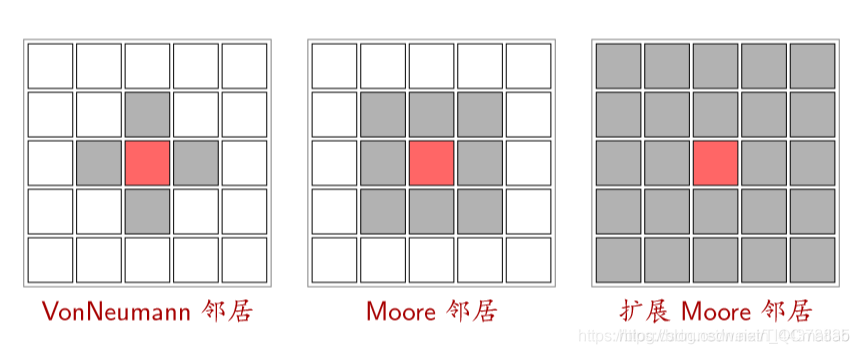
(4)边界 (Boundary)
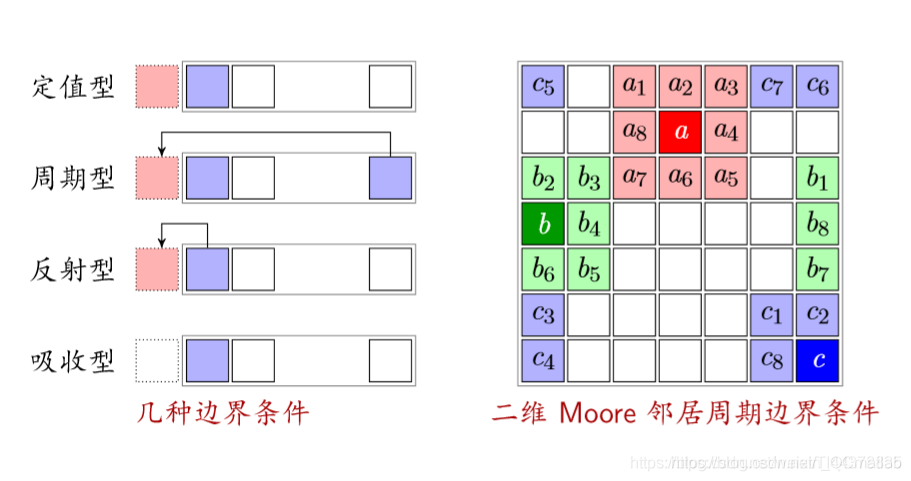
反射型:以自己作为边界的状态
吸收型:不管边界(车开到边界就消失)
(5)规则(状态转移函数)
定义:根据元胞当前状态及其邻居状况确定下一时刻该元胞状态的动力学函数, 简单讲, 就是一个状态转移函数.
分类 :
总和型: 某元胞下时刻的状态取决于且仅取决于它所有邻居 的当前状态以及自身的当前状态.
合法型: 总和型规则属于合法型规则. 但如果把元胞自动机 的规则限制为总和型, 会使元胞自动机具有局限性.
(6)森林火灾
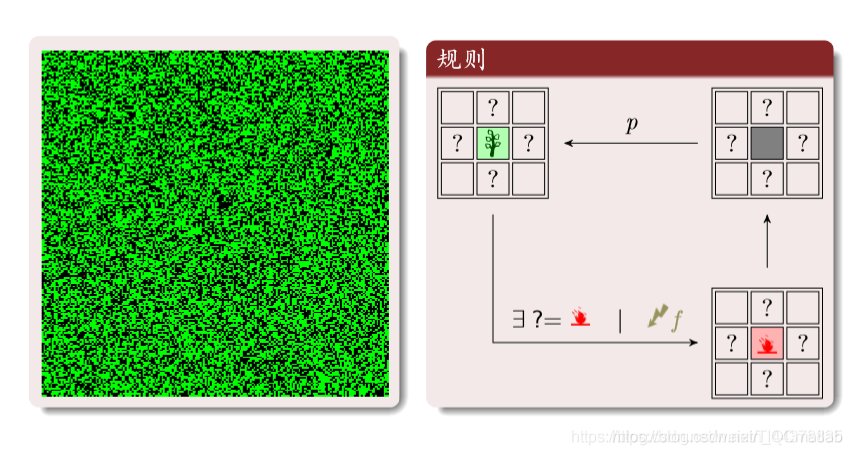
绿色:树木;红色:火;黑色:空地。
三种状态循环转化:
树:周围有火或者被闪电击中就变成火。
空地:以概率p变为树木
理性分析:红为火;灰为空地;绿是树
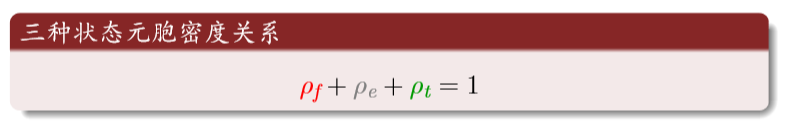
元胞三种状态的密度和为1
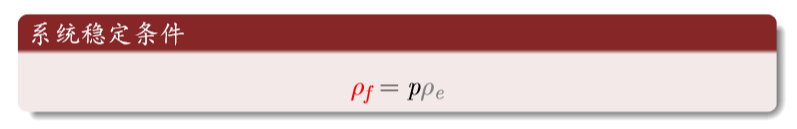
火转化为空地的密度等于空地转换为树的密度(新长出来的树等于烧没的树)

f是闪电的概率:远远小于树生成的概率;T s m a x T_{smax}T smax
是一大群树被火烧的时间尺度
程序实现
周期性边界条件
购进啊
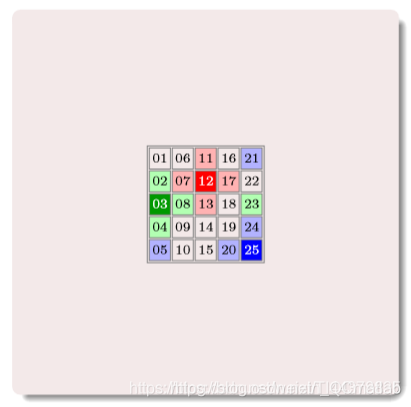
其中的数字为编号
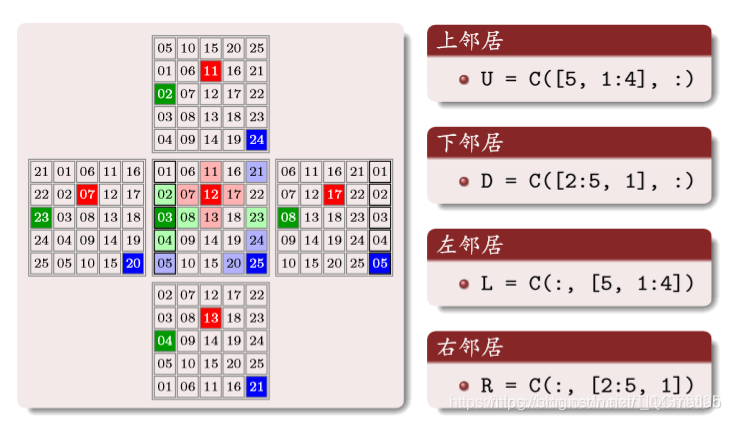
构建邻居矩阵

上面矩阵中的数字编号,对应原矩阵相同位置编号的上邻居编号,一 一对应
同样道理:
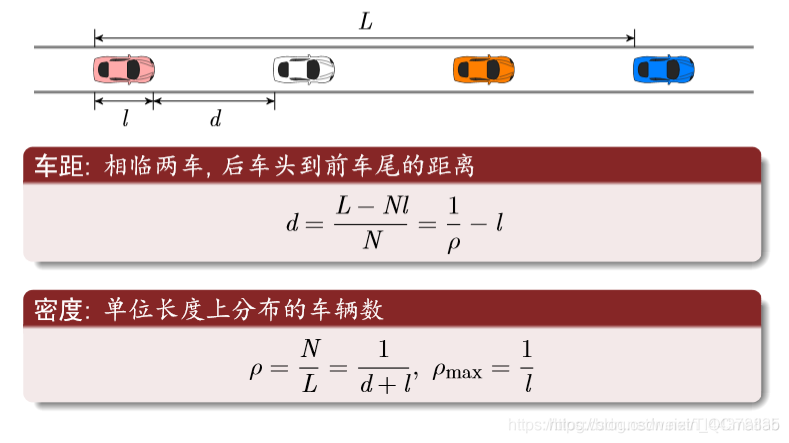
(7)交通概念
车距和密度
流量方程

守恒方程

时空轨迹(横轴是空间纵轴为时间)

红线横线与蓝色交点表示每个时间车的位置。
如果是竖线则表示车子在该位置对应的时间
宏观连续模型:
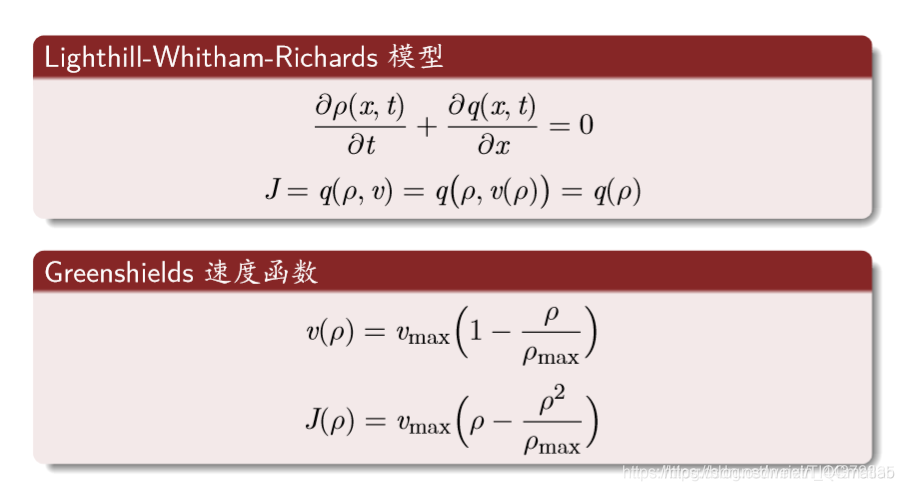
最常用的规则:
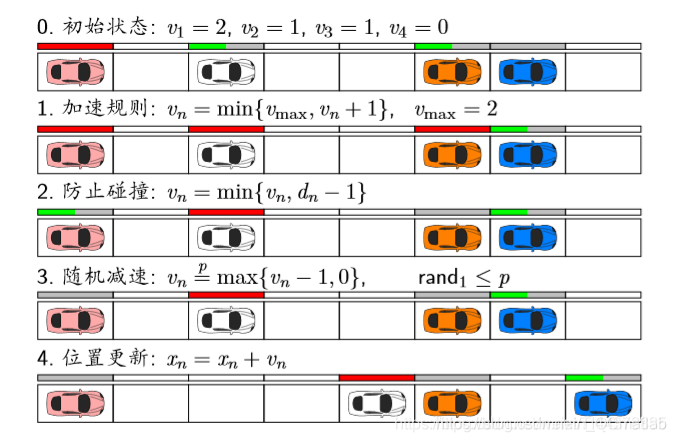
红色条表示速度是满的。
1 加速规则:不能超过v m a x ( 2 格 / s ) v_{max}(2格/s)v
max(2格/s)
2 防止碰撞:不能超过车距
理论分析:
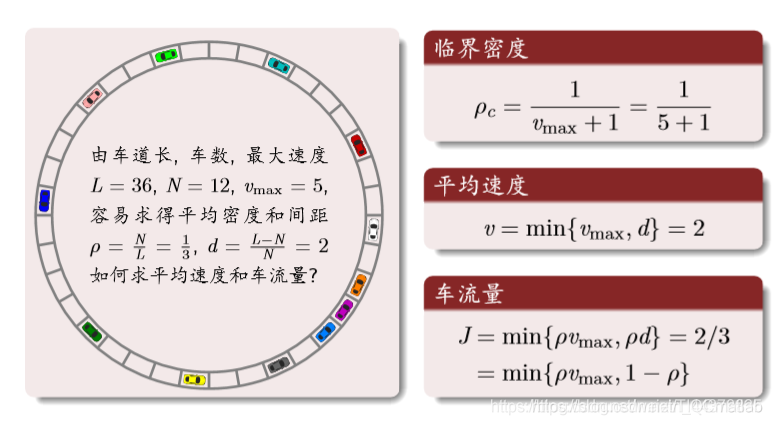
结果分析: 密度与流量
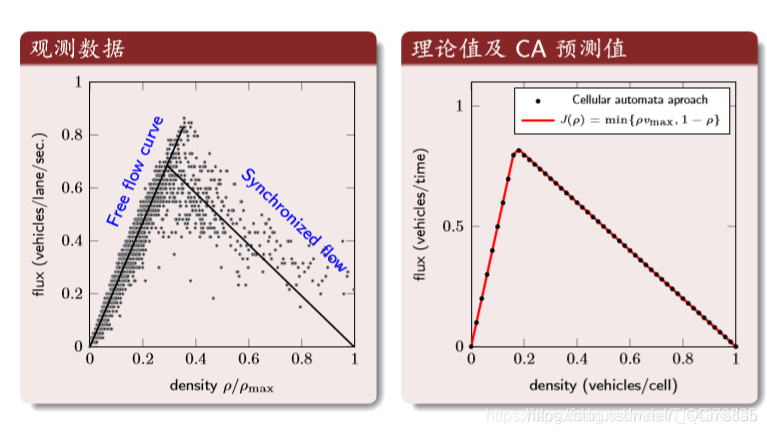
第一个图:横坐标是归一化后的密度,纵坐标是车流量。第二个图:理论值与CA的结果
结果分析: 时空轨迹
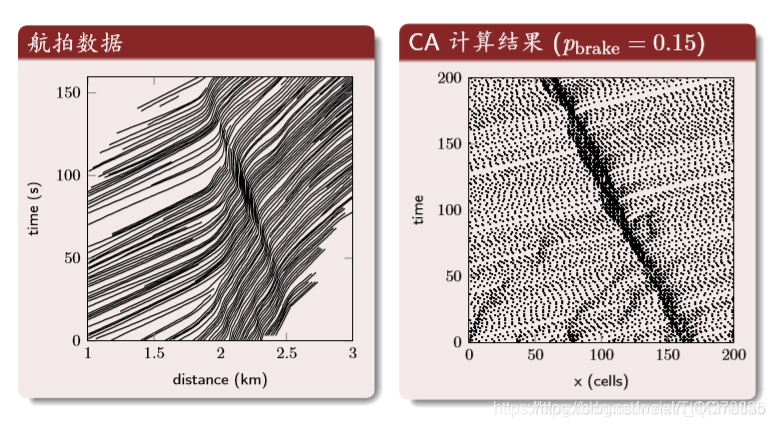
中间的深色区域是交通堵塞的区域。
⛄二、案例及部分源代码
1 案例
基于元胞自动机的人员疏散模型研究,可以根据未疏散人员位置信息、为环境信息、为未疏散人数、未疏散人员个体特性、为场所区域宽、为区域长、元胞边长、出口信息;同时可以改变人数、出口大小,出口位置分布,火灾扩散速度等参数,人员移动速度,4邻域或8邻域模式。并有GUI界面和动图展示,美观形象。
2 部分源代码
function varargout = renyuanshusan(varargin)
% RENYUANSHUSAN M-file for renyuanshusan.fig
% RENYUANSHUSAN, by itself, creates a new RENYUANSHUSAN or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = RENYUANSHUSAN returns the handle to a new RENYUANSHUSAN or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% RENYUANSHUSAN(‘CALLBACK’,hObject,eventData,handles,…) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in RENYUANSHUSAN.M with the given input arguments.
%
% RENYUANSHUSAN(‘Property’,‘Value’,…) creates a new RENYUANSHUSAN or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before renyuanshusan_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to renyuanshusan_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE’s Tools menu. Choose “GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)”.
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help renyuanshusan
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 08-Mar-2014 16:52:27
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct(‘gui_Name’, mfilename, …
‘gui_Singleton’, gui_Singleton, …
‘gui_OpeningFcn’, @renyuanshusan_OpeningFcn, …
‘gui_OutputFcn’, @renyuanshusan_OutputFcn, …
‘gui_LayoutFcn’, [] , …
‘gui_Callback’, []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% — Executes just before renyuanshusan is made visible.
function renyuanshusan_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to renyuanshusan (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for renyuanshusan
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes renyuanshusan wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% — Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = renyuanshusan_OutputFcn(~, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function edit1_Callback(~, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit1 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit2 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit3 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit4 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit4 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit4_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit5 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit5 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit5_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit6 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit6 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit6_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
% — Executes on slider movement.
function slider1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘Value’) returns position of slider
% get(hObject,‘Min’) and get(hObject,‘Max’) to determine range of slider
x=get(hObject,‘value’);
set(handles.text16,‘string’,num2str(x));
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function slider1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: slider controls usually have a light gray background.
if isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,[.9 .9 .9]);
end
⛄三、运行结果
⛄四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]党珊,蒋太刚,巫承军.基于元胞自动机方法的消防疏散仿真研究[J].现代电子技术. 2022,45(21)
[2]帅斌,秦梦瑶,许旻昊.基于元胞自动机的高速铁路列车运行仿真研究[J].计算机仿真. 2022,39(08)
[3]张睿洋.元胞自动机在两类传染病模型中的应用[J].现代信息科技. 2022,6(10)
3 备注
简介此部分摘自互联网,仅供参考,若侵权,请联系删除
🍅 仿真咨询
1 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化
2 机器学习和深度学习方面
卷积神经网络(CNN)、LSTM、支持向量机(SVM)、最小二乘支持向量机(LSSVM)、极限学习机(ELM)、核极限学习机(KELM)、BP、RBF、宽度学习、DBN、RF、RBF、DELM、XGBOOST、TCN实现风电预测、光伏预测、电池寿命预测、辐射源识别、交通流预测、负荷预测、股价预测、PM2.5浓度预测、电池健康状态预测、水体光学参数反演、NLOS信号识别、地铁停车精准预测、变压器故障诊断
3 图像处理方面
图像识别、图像分割、图像检测、图像隐藏、图像配准、图像拼接、图像融合、图像增强、图像压缩感知
4 路径规划方面
旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP、MVRP、CVRP、VRPTW等)、无人机三维路径规划、无人机协同、无人机编队、机器人路径规划、栅格地图路径规划、多式联运运输问题、车辆协同无人机路径规划、天线线性阵列分布优化、车间布局优化
5 无人机应用方面
无人机路径规划、无人机控制、无人机编队、无人机协同、无人机任务分配
6 无线传感器定位及布局方面
传感器部署优化、通信协议优化、路由优化、目标定位优化、Dv-Hop定位优化、Leach协议优化、WSN覆盖优化、组播优化、RSSI定位优化
7 信号处理方面
信号识别、信号加密、信号去噪、信号增强、雷达信号处理、信号水印嵌入提取、肌电信号、脑电信号、信号配时优化
8 电力系统方面
微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置
9 元胞自动机方面
交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长
10 雷达方面
卡尔曼滤波跟踪、航迹关联、航迹融合
























 1355
1355











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










