学习内容:
Attention机制的本质思想理解
有关空间注意力机制和通道注意力机制的内容可以参考一下文章《空间注意力机制和通道注意力机制详解》
注意力机制的原理从本质上可以怎么理解呢!?
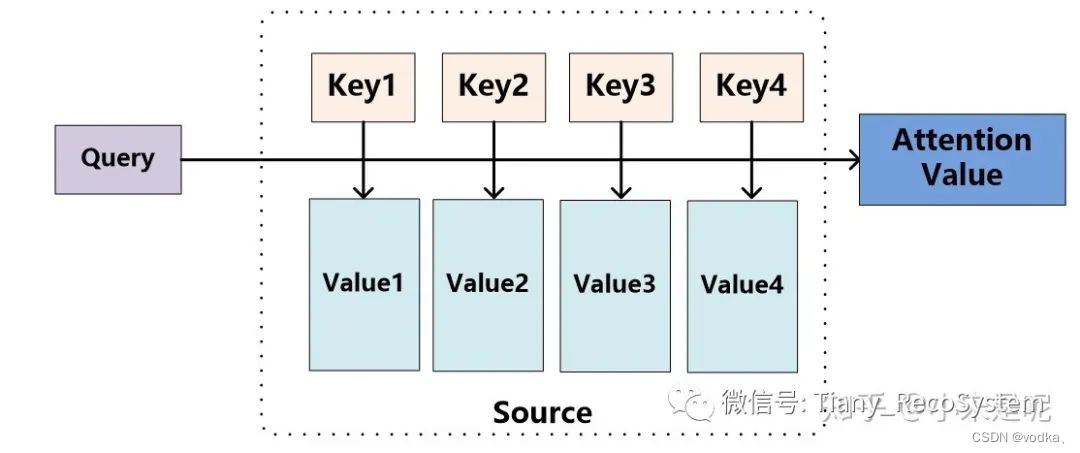
如上图所示,可以将Source中的元素看成是一系列由<key,value>数据对构成的特殊结构。这时对于某个元素Query来说,可以计算每个key与Query之间的相似性,或者说是相关性。接着将相关性进行归一化,就可以得到每个Key对应Value的权重系数,最后用Value和权重系数进行加权求和,得到最终结果。可以预见的是,权重越大,该处的Value的重要性就越高。因此在长串序列压缩时就可以通过重要程度,对原始数据信息进行取舍。(以下贴一段学习代码)
#coding=utf-8
'''
Single model may achieve LB scores at around 0.043
Don't need to be an expert of feature engineering
All you need is a GPU!!!!!!!
The code is tested on Keras 2.0.0 using Theano backend, and Python 3.5
referrence Code:https://www.kaggle.com/lystdo/lstm-with-word2vec-embeddings
'''
########################################
## import packages
########################################
import os
import re
import csv
import codecs
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
########################################
## set directories and parameters
########################################
from keras import backend as K
from keras.engine.topology import Layer
# from keras import initializations
from keras import initializers, regularizers, constraints
np.random.seed(2018)
class Attention(Layer):
def __init__(self,
W_regularizer=None, b_regularizer=None,
W_constraint=None, b_constraint=None,
bias=True, **kwargs):
"""
Keras Layer that implements an Attention mechanism for temporal data.
Supports Masking.
Follows the work of Raffel et al. [https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.08756]
# Input shape
3D tensor with shape: `(samples, steps, features)`.
# Output shape
2D tensor with shape: `(samples, features)`.
:param kwargs:
"""
self.supports_masking = True
# self.init = initializations.get('glorot_uniform')
self.init = initializers.get('glorot_uniform')
self.W_regularizer = regularizers.get(W_regularizer)
self.b_regularizer = regularizers.get(b_regularizer)
self.W_constraint = constraints.get(W_constraint)
self.b_constraint = constraints.get(b_constraint)
self.bias = bias
self.features_dim = 0
super(Attention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self, input_shape):
self.step_dim = input_shape[1]
assert len(input_shape) == 3 # batch ,timestep , num_features
print(input_shape)
self.W = self.add_weight((input_shape[-1],), #num_features
initializer=self.init,
name='{}_W'.format(self.name),
regularizer=self.W_regularizer,
constraint=self.W_constraint)
self.features_dim = input_shape[-1]
if self.bias:
self.b = self.add_weight((input_shape[1],),#timesteps
initializer='zero',
name='{}_b'.format(self.name),
regularizer=self.b_regularizer,
constraint=self.b_constraint)
else:
self.b = None
self.built = True
def compute_mask(self, input, input_mask=None):
# do not pass the mask to the next layers
return None
def call(self, x, mask=None):
features_dim = self.features_dim
step_dim = self.step_dim
print(K.reshape(x, (-1, features_dim)))# n, d
print(K.reshape(self.W, (features_dim, 1)))# w= dx1
print(K.dot(K.reshape(x, (-1, features_dim)), K.reshape(self.W, (features_dim, 1))))#nx1
eij = K.reshape(K.dot(K.reshape(x, (-1, features_dim)), K.reshape(self.W, (features_dim, 1))), (-1, step_dim))#batch,step
print(eij)
if self.bias:
eij += self.b
eij = K.tanh(eij)
a = K.exp(eij)
# apply mask after the exp. will be re-normalized next
if mask is not None:
# Cast the mask to floatX to avoid float64 upcasting in theano
a *= K.cast(mask, K.floatx())
a /= K.cast(K.sum(a, axis=1, keepdims=True) + K.epsilon(), K.floatx())
print(a)
a = K.expand_dims(a)
print("expand_dims:")
print(a)
print("x:")
print(x)
weighted_input = x * a
print(weighted_input.shape)
return K.sum(weighted_input, axis=1)
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
# return input_shape[0], input_shape[-1]
return input_shape[0], self.features_dim





















 824
824











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








