@封装/方法/可空类型/数组/字符串/结构体/枚举
一、C# 封装
封装 被定义为"把一个或多个项目封闭在一个物理的或者逻辑的包中"。在面向对象程序设计方法论中,封装是为了防止对实现细节的访问。
抽象和封装是面向对象程序设计的相关特性。抽象允许相关信息可视化,封装则使开发者实现所需级别的抽象。
C# 封装根据具体的需要,设置使用者的访问权限,并通过 访问修饰符 来实现。
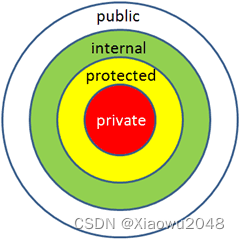
一个 访问修饰符 定义了一个类成员的范围和可见性。C# 支持的访问修饰符如下所示:
public:所有对象都可以访问;
private:对象本身在对象内部可以访问;
protected:只有该类对象及其子类对象可以访问
internal:同一个程序集的对象可以访问;
protected internal:访问限于当前程序集或派生自包含类的类型
1.1 Public 访问修饰符
Public 访问修饰符允许一个类将其成员变量和成员函数暴露给其他的函数和对象。任何公有成员可以被外部的类访问。
下面的实例说明了这点:
using System;
namespace RectangleApplication
{
class Rectangle
{
//成员变量
public double length;
public double width;
public double GetArea()
{
return length * width;
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("长度: {0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("宽度: {0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}", GetArea());
}
}// Rectangle 结束
class ExecuteRectangle
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
r.length = 4.5;
r.width = 3.5;
r.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
长度: 4.5
宽度: 3.5
面积: 15.75
在上面的实例中,成员变量 length 和 width 被声明为 public,所以它们可以被函数 Main() 使用 Rectangle 类的实例 r 访问。
成员函数 Display() 和 GetArea() 可以直接访问这些变量。
成员函数 Display() 也被声明为 public,所以它也能被 Main() 使用 Rectangle 类的实例 r 访问
1.2 Private 访问修饰符
Private 访问修饰符允许一个类将其成员变量和成员函数对其他的函数和对象进行隐藏。只有同一个类中的函数可以访问它的私有成员。即使是类的实例也不能访问它的私有成员。
下面的实例说明了这点:
using System;
namespace RectangleApplication
{
class Rectangle
{
//成员变量
private double length;
private double width;
public void Acceptdetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入长度:");
length = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("请输入宽度:");
width = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
}
public double GetArea()
{
return length * width;
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("长度: {0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("宽度: {0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}", GetArea());
}
}//end class Rectangle
class ExecuteRectangle
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
r.Acceptdetails();
r.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
请输入长度:
4.4
请输入宽度:
3.3
长度: 4.4
宽度: 3.3
面积: 14.52
在上面的实例中,成员变量 length 和 width 被声明为 private,所以它们不能被函数 Main() 访问。
成员函数 AcceptDetails() 和 Display() 可以访问这些变量。
由于成员函数 AcceptDetails() 和 Display() 被声明为 public,所以它们可以被 Main() 使用 Rectangle 类的实例 r 访问
1.3 Protected 访问修饰符
Protected 访问修饰符允许子类访问它的基类的成员变量和成员函数。这样有助于实现继承
1.4 Internal 访问修饰符
Internal 访问修饰符允许一个类将其成员变量和成员函数暴露给当前程序中的其他函数和对象。换句话说,带有 internal 访问修饰符的任何成员可以被定义在该成员所定义的应用程序内的任何类或方法访问。
下面的实例说明了这点
using System;
namespace RectangleApplication
{
class Rectangle
{
//成员变量
internal double length;
internal double width;
double GetArea()
{
return length * width;
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("长度: {0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("宽度: {0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}", GetArea());
}
}//end class Rectangle
class ExecuteRectangle
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
r.length = 4.5;
r.width = 3.5;
r.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
长度: 4.5
宽度: 3.5
面积: 15.75
在上面的实例中,请注意成员函数 GetArea() 声明的时候不带有任何访问修饰符。如果没有指定访问修饰符,则使用类成员的默认访问修饰符,即为 private
1.5 Protected Internal 访问修饰符
Protected Internal 访问修饰符允许在本类,派生类或者包含该类的程序集中访问。这也被用于实现继承
二、方法
一个方法是把一些相关的语句组织在一起,用来执行一个任务的语句块。每一个 C# 程序至少有一个带有 Main 方法的类。
要使用一个方法,您需要:
定义方法
调用方法
2.1 C# 中定义方法
当定义一个方法时,从根本上说是在声明它的结构的元素。在 C# 中,定义方法的语法如下:
<Access Specifier> <Return Type> <Method Name>(Parameter List)
{
Method Body
}
下面是方法的各个元素:
1、Access Specifier:访问修饰符,这个决定了变量或方法对于另一个类的可见性。
2、Return type:返回类型,一个方法可以返回一个值。返回类型是方法返回的值的数据类型。如果方法不返回任何值,则返回类型为 void。
3、Method name:方法名称,是一个唯一的标识符,且是大小写敏感的。它不能与类中声明的其他标识符相同。
4、Parameter list:参数列表,使用圆括号括起来,该参数是用来传递和接收方法的数据。参数列表是指方法的参数类型、顺序和数量。参数是可选的,也就是说,一个方法可能不包含参数。
5、Method body:方法主体,包含了完成任务所需的指令集
下面的代码片段显示一个函数 FindMax,它接受两个整数值,并返回两个中的较大值。它有 public 访问修饰符,所以它可以使用类的实例从类的外部进行访问
class NumberManipulator
{
public int FindMax(int num1, int num2)
{
/* 局部变量声明 */
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}
...
}
2.2 C# 中调用方法
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public int FindMax(int num1, int num2)
{
/* 局部变量声明 */
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
int ret;
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
//调用 FindMax 方法
ret = n.FindMax(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("最大值是: {0}", ret );
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
最大值是: 200
也可以使用类的实例从另一个类中调用其他类的公有方法。例如,方法 FindMax 属于 NumberManipulator 类,可以从另一个类 Test 中调用它。
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public int FindMax(int num1, int num2)
{
/* 局部变量声明 */
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}
}
class Test
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
int ret;
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
//调用 FindMax 方法
ret = n.FindMax(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("最大值是: {0}", ret );
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
2.3 递归方法调用
一个方法可以自我调用。这就是所谓的 递归。下面的实例使用递归函数计算一个数的阶乘:
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public int factorial(int num)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int result;
if (num == 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
result = factorial(num - 1) * num;
return result;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
//调用 factorial 方法
Console.WriteLine("6 的阶乘是: {0}", n.factorial(6));
Console.WriteLine("7 的阶乘是: {0}", n.factorial(7));
Console.WriteLine("8 的阶乘是: {0}", n.factorial(8));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
6 的阶乘是: 720
7 的阶乘是: 5040
8 的阶乘是: 40320
2.4 参数传递
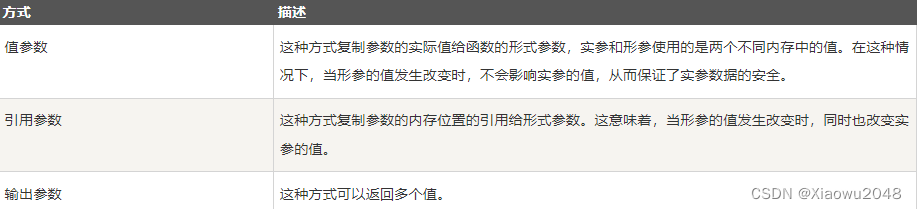
当调用带有参数的方法时,您需要向方法传递参数。在 C# 中,有三种向方法传递参数的方式:
2.5 按值传递参数
这是参数传递的默认方式。在这种方式下,当调用一个方法时,会为每个值参数创建一个新的存储位置。
实际参数的值会复制给形参,实参和形参使用的是两个不同内存中的值。所以,当形参的值发生改变时,不会影响实参的值,从而保证了实参数据的安全。下面的实例演示了这个概念:
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public void swap(int x, int y)
{
int temp;
temp = x; /* 保存 x 的值 */
x = y; /* 把 y 赋值给 x */
y = temp; /* 把 temp 赋值给 y */
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,b 的值: {0}", b);
/* 调用函数来交换值 */
n.swap(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,b 的值: {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
在交换之前,a 的值:100
在交换之前,b 的值:200
在交换之后,a 的值:100
在交换之后,b 的值:200
2.6 按引用传递参数
引用参数是一个对变量的内存位置的引用。当按引用传递参数时,与值参数不同的是,它不会为这些参数创建一个新的存储位置。引用参数表示与提供给方法的实际参数具有相同的内存位置。
在 C# 中,使用 ref 关键字声明引用参数。下面的实例演示了这点:
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public void swap(ref int x, ref int y)
{
int temp;
temp = x; /* 保存 x 的值 */
x = y; /* 把 y 赋值给 x */
y = temp; /* 把 temp 赋值给 y */
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,b 的值: {0}", b);
/* 调用函数来交换值 */
n.swap(ref a, ref b);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,b 的值: {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
在交换之前,a 的值:100
在交换之前,b 的值:200
在交换之后,a 的值:200
在交换之后,b 的值:100
结果表明,swap 函数内的值改变了,且这个改变可以在 Main 函数中反映出来
2.7 按输出传递参数
return 语句可用于只从函数中返回一个值。但是,可以使用 输出参数 来从函数中返回两个值。输出参数会把方法输出的数据赋给自己,其他方面与引用参数相似。
下面的实例演示了这点:
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public void getValue(out int x )
{
int temp = 5;
x = temp;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之前,a 的值: {0}", a);
/* 调用函数来获取值 */
n.getValue(out a);
Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之后,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
在方法调用之前,a 的值: 100
在方法调用之后,a 的值: 5
提供给输出参数的变量不需要赋值。当需要从一个参数没有指定初始值的方法中返回值时,输出参数特别有用。请看下面的实例,来理解这一点:
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public void getValues(out int x, out int y )
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入第一个值: ");
x = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("请输入第二个值: ");
y = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a , b;
/* 调用函数来获取值 */
n.getValues(out a, out b);
Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之后,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之后,b 的值: {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
请输入第一个值:
7
请输入第二个值:
8
在方法调用之后,a 的值: 7
在方法调用之后,b 的值: 8
三、可空类型
3.1 C# 单问号 ? 与 双问号 ??
? 单问号用于对 int、double、bool 等无法直接赋值为 null 的数据类型进行 null 的赋值,意思是这个数据类型是 Nullable 类型的
int? i = 3;
等同于:
Nullable<int> i = new Nullable<int>(3);
int i; //默认值0
int? ii; //默认值null
?? 双问号用于判断一个变量在为 null 的时候返回一个指定的值
3.2 C# 可空类型(Nullable)
C# 提供了一个特殊的数据类型,nullable 类型(可空类型),可空类型可以表示其基础值类型正常范围内的值,再加上一个 null 值。
例如,Nullable< Int32 >,读作"可空的 Int32",可以被赋值为 -2,147,483,648 到 2,147,483,647 之间的任意值,也可以被赋值为 null 值。类似的,Nullable< bool > 变量可以被赋值为 true 或 false 或 null。
在处理数据库和其他包含可能未赋值的元素的数据类型时,将 null 赋值给数值类型或布尔型的功能特别有用。例如,数据库中的布尔型字段可以存储值 true 或 false,或者,该字段也可以未定义。
声明一个 nullable 类型(可空类型)的语法如下:
< data_type> ? <variable_name> = null;
下面的实例演示了可空数据类型的用法:
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NullablesAtShow
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int? num1 = null;
int? num2 = 45;
double? num3 = new double?();
double? num4 = 3.14157;
bool? boolval = new bool?();
// 显示值
Console.WriteLine("显示可空类型的值: {0}, {1}, {2}, {3}",
num1, num2, num3, num4);
Console.WriteLine("一个可空的布尔值: {0}", boolval);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
显示可空类型的值: , 45, , 3.14157
一个可空的布尔值:
3.3 Null 合并运算符( ?? )
Null 合并运算符用于定义可空类型和引用类型的默认值。Null 合并运算符为类型转换定义了一个预设值,以防可空类型的值为 Null。Null 合并运算符把操作数类型隐式转换为另一个可空(或不可空)的值类型的操作数的类型。
如果第一个操作数的值为 null,则运算符返回第二个操作数的值,否则返回第一个操作数的值。下面的实例演示了这点:
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NullablesAtShow
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double? num1 = null;
double? num2 = 3.14157;
double num3;
num3 = num1 ?? 5.34; // num1 如果为空值则返回 5.34
Console.WriteLine("num3 的值: {0}", num3);
num3 = num2 ?? 5.34;
Console.WriteLine("num3 的值: {0}", num3);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
num3 的值: 5.34
num3 的值: 3.14157
四、C# 数组(Array)
数组是一个存储相同类型元素的固定大小的顺序集合。数组是用来存储数据的集合,通常认为数组是一个同一类型变量的集合。
声明数组变量并不是声明 number0、number1、…、number99 一个个单独的变量,而是声明一个就像 numbers 这样的变量,然后使用 numbers[0]、numbers[1]、…、numbers[99] 来表示一个个单独的变量。数组中某个指定的元素是通过索引来访问的。
所有的数组都是由连续的内存位置组成的。最低的地址对应第一个元素,最高的地址对应最后一个元素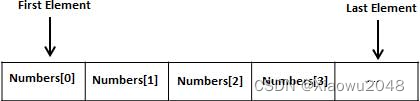
4.1声明数组
在 C# 中声明一个数组,您可以使用下面的语法:
datatype[] arrayName;
其中,
1、datatype 用于指定被存储在数组中的元素的类型。
2、[ ] 指定数组的秩(维度)。秩指定数组的大小。
3、arrayName 指定数组的名称。
例如:
double[] balance;
4.2 初始化数组
声明一个数组不会在内存中初始化数组。当初始化数组变量时,您可以赋值给数组。
数组是一个引用类型,所以您需要使用 new 关键字来创建数组的实例。
例如:
double[] balance = new double[10];
4.3 赋值给数组
可以通过使用索引号赋值给一个单独的数组元素,比如:
double[] balance = new double[10];
balance[0] = 4500.0;
可以在声明数组的同时给数组赋值,比如:
double[] balance = { 2340.0, 4523.69, 3421.0};
也可以创建并初始化一个数组,比如:
int [] marks = new int[5] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};
在上述情况下,也可以省略数组的大小,比如:
int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};
也可以赋值一个数组变量到另一个目标数组变量中。在这种情况下,目标和源会指向相同的内存位置:
int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};
int[] score = marks;
当创建一个数组时,C# 编译器会根据数组类型隐式初始化每个数组元素为一个默认值。例如,int 数组的所有元素都会被初始化为 0。
4.4 访问数组元素
元素是通过带索引的数组名称来访问的。这是通过把元素的索引放置在数组名称后的方括号中来实现的。例如:
double salary = balance[9];
下面是一个实例,使用上面提到的三个概念,即声明、赋值、访问数组:
实例
using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int [] n = new int[10]; /* n 是一个带有 10 个整数的数组 */
int i,j;
/* 初始化数组 n 中的元素 */
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
{
n[ i ] = i + 100;
}
/* 输出每个数组元素的值 */
for (j = 0; j < 10; j++ )
{
Console.WriteLine("Element[{0}] = {1}", j, n[j]);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Element[0] = 100
Element[1] = 101
Element[2] = 102
Element[3] = 103
Element[4] = 104
Element[5] = 105
Element[6] = 106
Element[7] = 107
Element[8] = 108
Element[9] = 109
使用 foreach 循环
在前面的实例中,我们使用一个 for 循环来访问每个数组元素。也可以使用一个 foreach 语句来遍历数组。
实例
using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int [] n = new int[10]; /* n 是一个带有 10 个整数的数组 */
/* 初始化数组 n 中的元素 */
for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
{
n[i] = i + 100;
}
/* 输出每个数组元素的值 */
foreach (int j in n )
{
int i = j-100;
Console.WriteLine("Element[{0}] = {1}", i, j);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Element[0] = 100
Element[1] = 101
Element[2] = 102
Element[3] = 103
Element[4] = 104
Element[5] = 105
Element[6] = 106
Element[7] = 107
Element[8] = 108
Element[9] = 109
4.5 数组细节
4.5.1 多维数组
C# 支持多维数组。多维数组又称为矩形数组。
可以声明一个 string 变量的二维数组,如下:
string [,] names;
或者,您可以声明一个 int 变量的三维数组,如下:
int [ , , ] m;
二维数组
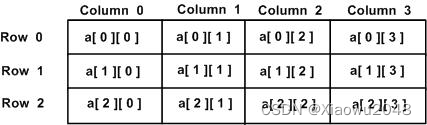
多维数组最简单的形式是二维数组。一个二维数组,在本质上,是一个一维数组的列表。
一个二维数组可以被认为是一个带有 x 行和 y 列的表格。下面是一个二维数组,包含 3 行和 4 列:
C# 中的二维数组
因此,数组中的每个元素是使用形式为 a[ i , j ] 的元素名称来标识的,其中 a 是数组名称,i 和 j 是唯一标识 a 中每个元素的下标。
初始化二维数组
多维数组可以通过在括号内为每行指定值来进行初始化。下面是一个带有 3 行 4 列的数组。
int [,] a = new int [3,4] {
{0, 1, 2, 3} , /* 初始化索引号为 0 的行 /
{4, 5, 6, 7} , / 初始化索引号为 1 的行 /
{8, 9, 10, 11} / 初始化索引号为 2 的行 */
};
访问二维数组元素
二维数组中的元素是通过使用下标(即数组的行索引和列索引)来访问的。例如:
int val = a[2,3];
上面的语句将获取数组中第 3 行第 4 个元素。您可以通过上面的示意图来进行验证。让我们来看看下面的程序,我们将使用嵌套循环来处理二维数组:
实例
using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 一个带有 5 行 2 列的数组 */
int[,] a = new int[5, 2] {{0,0}, {1,2}, {2,4}, {3,6}, {4,8} };
int i, j;
/* 输出数组中每个元素的值 */
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i,j]);
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
a[0,0]: 0
a[0,1]: 0
a[1,0]: 1
a[1,1]: 2
a[2,0]: 2
a[2,1]: 4
a[3,0]: 3
a[3,1]: 6
a[4,0]: 4
a[4,1]: 8
4.5.2 交错数组
交错数组是数组的数组。
交错数组是一维数组。
可以声明一个带有 int 值的交错数组 scores,如下所示:
int [][] scores;
声明一个数组不会在内存中创建数组。创建上面的数组:
int[][] scores = new int[5][];
for (int i = 0; i < scores.Length; i++)
{
scores[i] = new int[4];
}
可以初始化一个交错数组,如下所示:
int[][] scores = new int[2][]{new int[]{92,93,94},new int[]{85,66,87,88}};
其中,scores 是一个由两个整型数组组成的数组 – scores[0] 是一个带有 3 个整数的数组,scores[1] 是一个带有 4 个整数的数组。
实例
下面的实例演示了如何使用交错数组:
实例
using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 一个由 5 个整型数组组成的交错数组 */
int[][] a = new int[][]{new int[]{0,0},new int[]{1,2},
new int[]{2,4},new int[]{ 3, 6 }, new int[]{ 4, 8 } };
int i, j;
/* 输出数组中每个元素的值 */
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0}][{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i][j]);
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
a[0][0] = 0
a[0][1] = 0
a[1][0] = 1
a[1][1] = 2
a[2][0] = 2
a[2][1] = 4
a[3][0] = 3
a[3][1] = 6
a[4][0] = 4
a[4][1] = 8
4.5.3 传递数组给函数
using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
double getAverage(int[] arr, int size)
{
int i;
double avg;
int sum = 0;
for (i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
sum += arr[i];
}
avg = (double)sum / size;
return avg;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyArray app = new MyArray();
/* 一个带有 5 个元素的 int 数组 */
int [] balance = new int[]{1000, 2, 3, 17, 50};
double avg;
/* 传递数组的指针作为参数 */
avg = app.getAverage(balance, 5 ) ;
/* 输出返回值 */
Console.WriteLine( "平均值是: {0} ", avg );
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
平均值是: 214.4
4.5.4 参数数组
params 关键字
在使用数组作为形参时,C# 提供了 params 关键字,使调用数组为形参的方法时,既可以传递数组实参,也可以传递一组数组元素。params 的使用格式为:
public 返回类型 方法名称( params 类型名称[] 数组名称 )
实例
下面的实例演示了如何使用参数数组:
实例
using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class ParamArray
{
public int AddElements(params int[] arr)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (int i in arr)
{
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
}
class TestClass
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ParamArray app = new ParamArray();
int sum = app.AddElements(512, 720, 250, 567, 889);
Console.WriteLine("总和是: {0}", sum);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
总和是: 2938
4.5.5 Array 类
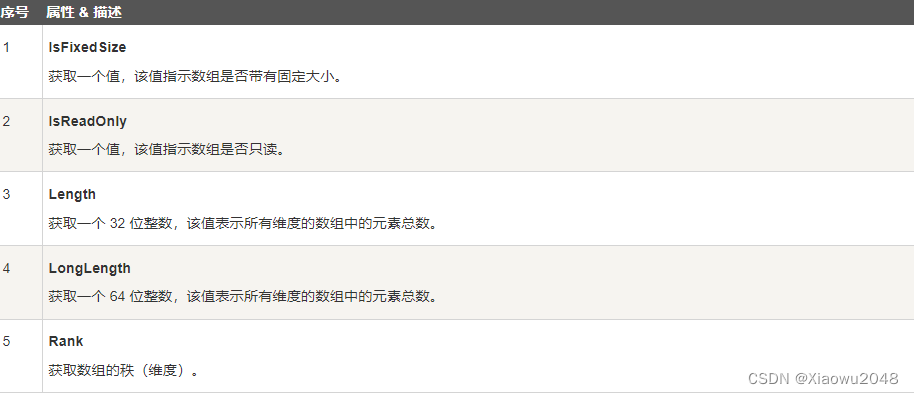
Array 类的属性
下表列出了 Array 类中一些最常用的属性:
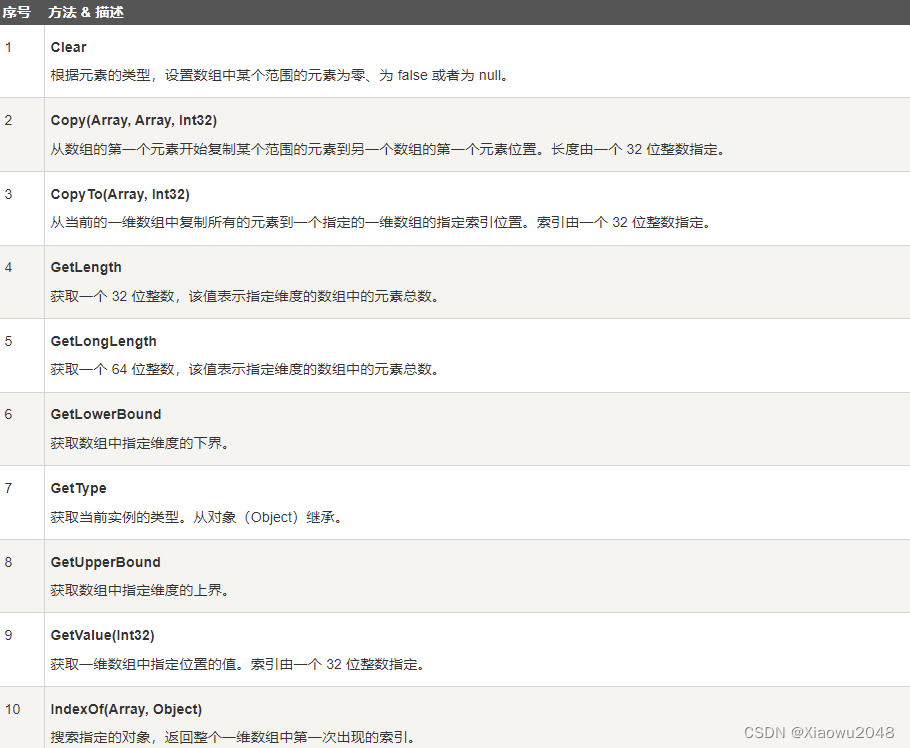
Array 类的方法
下表列出了 Array 类中一些最常用的方法:

using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] list = { 34, 72, 13, 44, 25, 30, 10 };
Console.Write("原始数组: ");
foreach (int i in list)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 逆转数组
Array.Reverse(list);
Console.Write("逆转数组: ");
foreach (int i in list)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 排序数组
Array.Sort(list);
Console.Write("排序数组: ");
foreach (int i in list)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
原始数组: 34 72 13 44 25 30 10
逆转数组: 10 30 25 44 13 72 34
排序数组: 10 13 25 30 34 44 72
五、C# 字符串(String)
在 C# 中,您可以使用字符数组来表示字符串,但是,更常见的做法是使用 string 关键字来声明一个字符串变量。string 关键字是 System.String 类的别名
5.1 创建 String 对象
可以使用以下方法之一来创建 string 对象:
通过给 String 变量指定一个字符串
通过使用 String 类构造函数
通过使用字符串串联运算符( + )
通过检索属性或调用一个返回字符串的方法
通过格式化方法来转换一个值或对象为它的字符串表示形式
using System;
namespace StringApplication
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//字符串,字符串连接
string fname, lname;
fname = "Rowan";
lname = "Atkinson";
string fullname = fname + lname;
Console.WriteLine("Full Name: {0}", fullname);
//通过使用 string 构造函数
char[] letters = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l','o' };
string greetings = new string(letters);
Console.WriteLine("Greetings: {0}", greetings);
//方法返回字符串
string[] sarray = { "Hello", "From", "Tutorials", "Point" };
string message = String.Join(" ", sarray);
Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", message);
//用于转化值的格式化方法
DateTime waiting = new DateTime(2012, 10, 10, 17, 58, 1);
string chat = String.Format("Message sent at {0:t} on {0:D}",
waiting);
Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", chat);
Console.ReadKey() ;
}
}
}
Full Name: RowanAtkinson
Greetings: Hello
Message: Hello From Tutorials Point
Message: Message sent at 17:58 on Wednesday, 10 October 2012
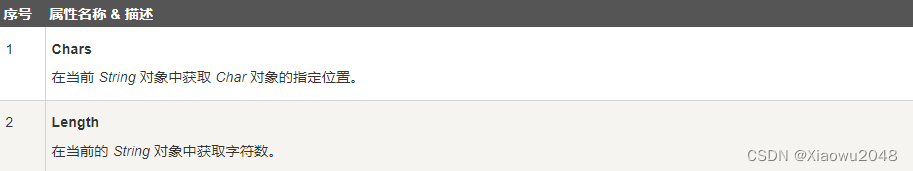
5.2 String 类的属性
String 类有以下两个属性:
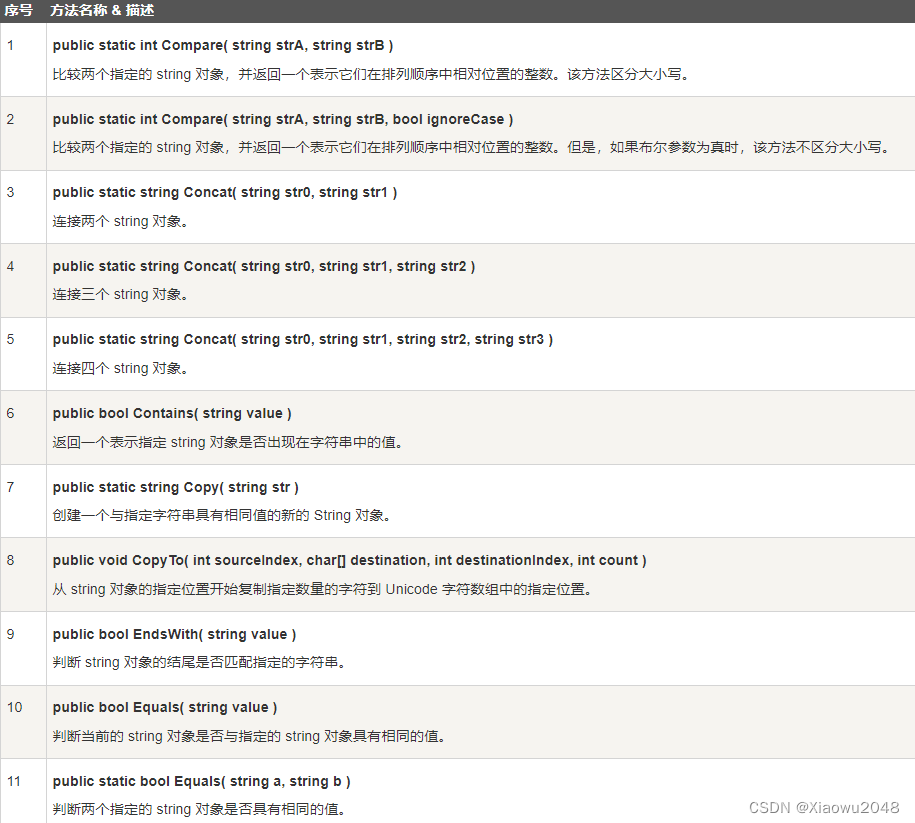
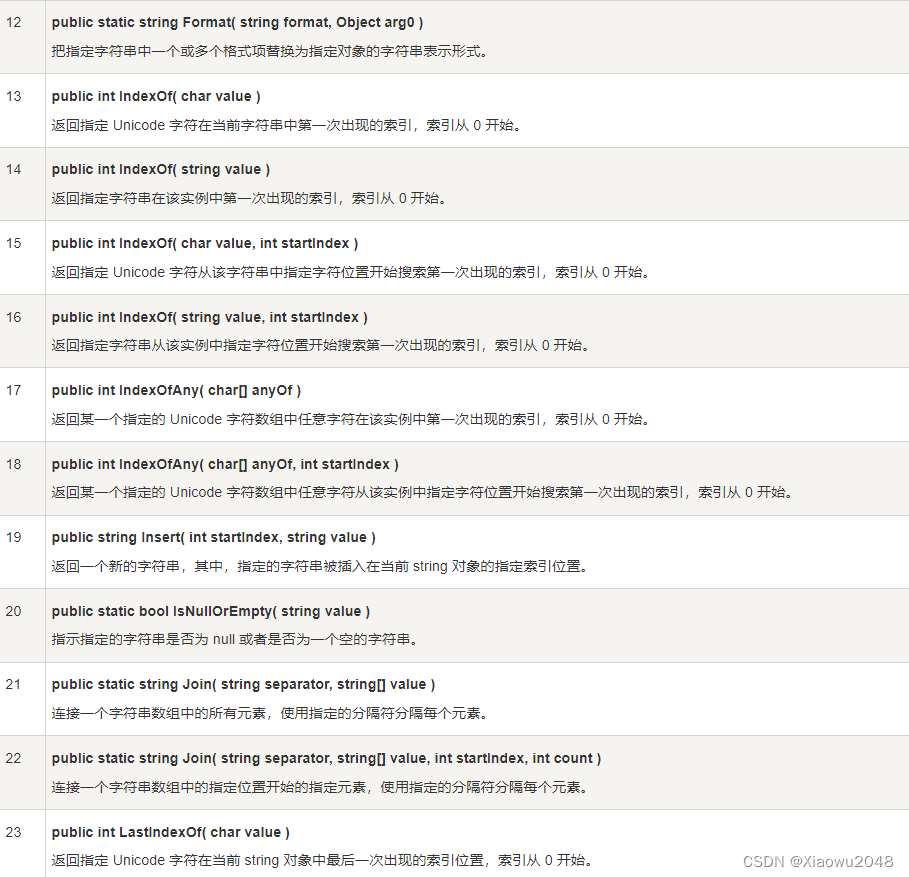
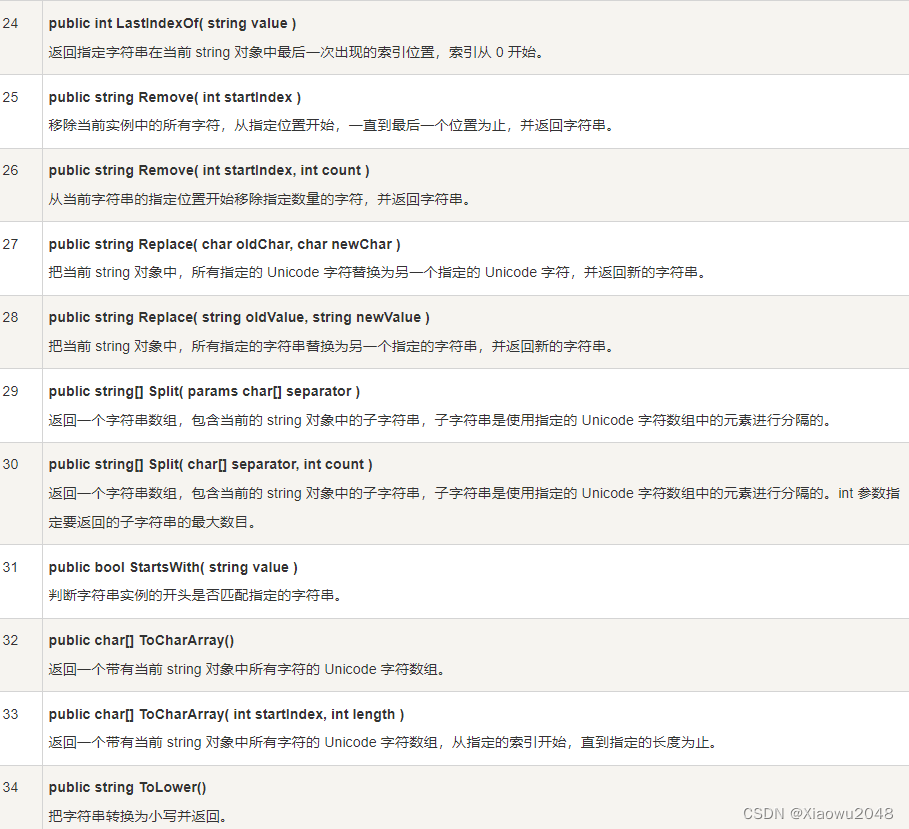
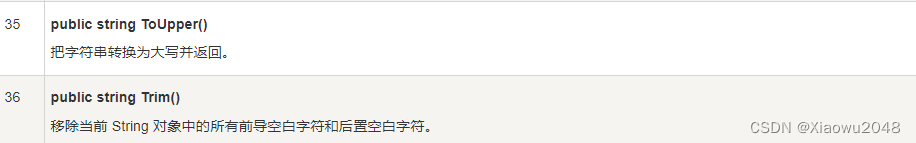
5.3 String 类的方法
String 类有许多方法用于 string 对象的操作。下面的表格提供了一些最常用的方法:
using System;
namespace StringApplication
{
class StringProg
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str1 = "This is test";
string str2 = "This is text";
if (String.Compare(str1, str2) == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine(str1 + " and " + str2 + " are equal.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(str1 + " and " + str2 + " are not equal.");
}
Console.ReadKey() ;
}
}
}
This is test and This is text are not equal.
字符串包含字符串:
using System;
namespace StringApplication
{
class StringProg
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "This is test";
if (str.Contains("test"))
{
Console.WriteLine("The sequence 'test' was found.");
}
Console.ReadKey() ;
}
}
}
The sequence ‘test’ was found.
获取子字符串:
using System;
namespace StringApplication
{
class StringProg
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "Last night I dreamt of San Pedro";
Console.WriteLine(str);
string substr = str.Substring(23);
Console.WriteLine(substr);
Console.ReadKey() ;
}
}
}
Last night I dreamt of San Pedro
San Pedro
连接字符串:
using System;
namespace StringApplication
{
class StringProg
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] starray = new string[]{"Down the way nights are dark",
"And the sun shines daily on the mountain top",
"I took a trip on a sailing ship",
"And when I reached Jamaica",
"I made a stop"};
string str = String.Join("\n", starray);
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.ReadKey() ;
}
}
}
Down the way nights are dark
And the sun shines daily on the mountain top
I took a trip on a sailing ship
And when I reached Jamaica
I made a stop
六、C# 结构体(Struct)
在 C# 中,结构体是值类型数据结构。它使得一个单一变量可以存储各种数据类型的相关数据。struct 关键字用于创建结构体。
结构体是用来代表一个记录。假设您想跟踪图书馆中书的动态。您可能想跟踪每本书的以下属性:
Title
Author
Subject
Book ID
6.1 定义结构体
为了定义一个结构体,您必须使用 struct 语句。struct 语句为程序定义了一个带有多个成员的新的数据类型。
例如,可以按照如下的方式声明 Book 结构:
struct Books
{
public string title;
public string author;
public string subject;
public int book_id;
};
using System;
using System.Text;
struct Books
{
public string title;
public string author;
public string subject;
public int book_id;
};
public class testStructure
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Books Book1; /* 声明 Book1,类型为 Books */
Books Book2; /* 声明 Book2,类型为 Books */
/* book 1 详述 */
Book1.title = "C Programming";
Book1.author = "Nuha Ali";
Book1.subject = "C Programming Tutorial";
Book1.book_id = 6495407;
/* book 2 详述 */
Book2.title = "Telecom Billing";
Book2.author = "Zara Ali";
Book2.subject = "Telecom Billing Tutorial";
Book2.book_id = 6495700;
/* 打印 Book1 信息 */
Console.WriteLine( "Book 1 title : {0}", Book1.title);
Console.WriteLine("Book 1 author : {0}", Book1.author);
Console.WriteLine("Book 1 subject : {0}", Book1.subject);
Console.WriteLine("Book 1 book_id :{0}", Book1.book_id);
/* 打印 Book2 信息 */
Console.WriteLine("Book 2 title : {0}", Book2.title);
Console.WriteLine("Book 2 author : {0}", Book2.author);
Console.WriteLine("Book 2 subject : {0}", Book2.subject);
Console.WriteLine("Book 2 book_id : {0}", Book2.book_id);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
Book 1 title : C Programming
Book 1 author : Nuha Ali
Book 1 subject : C Programming Tutorial
Book 1 book_id : 6495407
Book 2 title : Telecom Billing
Book 2 author : Zara Ali
Book 2 subject : Telecom Billing Tutorial
Book 2 book_id : 6495700
6.2 C# 结构的特点
已经用了一个简单的名为 Books 的结构。在 C# 中的结构与传统的 C 或 C++ 中的结构不同。C# 中的结构有以下特点:
结构可带有方法、字段、索引、属性、运算符方法和事件。
结构可定义构造函数,但不能定义析构函数。但是,您不能为结构定义无参构造函数。无参构造函数(默认)是自动定义的,且不能被改变。
与类不同,结构不能继承其他的结构或类。
结构不能作为其他结构或类的基础结构。
结构可实现一个或多个接口。
结构成员不能指定为 abstract、virtual 或 protected。
当您使用 New 操作符创建一个结构对象时,会调用适当的构造函数来创建结构。与类不同,结构可以不使用 New 操作符即可被实例化。
如果不使用 New 操作符,只有在所有的字段都被初始化之后,字段才被赋值,对象才被使用
6.3 类 vs 结构
类和结构有以下几个基本的不同点:
类是引用类型,结构是值类型。
结构不支持继承。
结构不能声明默认的构造函数
using System;
using System.Text;
struct Books
{
private string title;
private string author;
private string subject;
private int book_id;
public void setValues(string t, string a, string s, int id)
{
title = t;
author = a;
subject = s;
book_id =id;
}
public void display()
{
Console.WriteLine("Title : {0}", title);
Console.WriteLine("Author : {0}", author);
Console.WriteLine("Subject : {0}", subject);
Console.WriteLine("Book_id :{0}", book_id);
}
};
public class testStructure
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Books Book1 = new Books(); /* 声明 Book1,类型为 Books */
Books Book2 = new Books(); /* 声明 Book2,类型为 Books */
/* book 1 详述 */
Book1.setValues("C Programming",
"Nuha Ali", "C Programming Tutorial",6495407);
/* book 2 详述 */
Book2.setValues("Telecom Billing",
"Zara Ali", "Telecom Billing Tutorial", 6495700);
/* 打印 Book1 信息 */
Book1.display();
/* 打印 Book2 信息 */
Book2.display();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
Title : C Programming
Author : Nuha Ali
Subject : C Programming Tutorial
Book_id : 6495407
Title : Telecom Billing
Author : Zara Ali
Subject : Telecom Billing Tutorial
Book_id : 6495700
七、C# 枚举(Enum)
枚举是一组命名整型常量。枚举类型是使用 enum 关键字声明的。
C# 枚举是值类型。换句话说,枚举包含自己的值,且不能继承或传递继承
7.1 声明 enum 变量
声明枚举的一般语法:
enum <enum_name>
{
enumeration list
};
其中,
enum_name 指定枚举的类型名称。
enumeration list 是一个用逗号分隔的标识符列表。
枚举列表中的每个符号代表一个整数值,一个比它前面的符号大的整数值。默认情况下,第一个枚举符号的值是 0.例如:
enum Days { Sun, Mon, tue, Wed, thu, Fri, Sat };
using System;
public class EnumTest
{
enum Day { Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat };
static void Main()
{
int x = (int)Day.Sun;
int y = (int)Day.Fri;
Console.WriteLine("Sun = {0}", x);
Console.WriteLine("Fri = {0}", y);
}
}
Sun = 0
Fri = 5
菜鸟教程,学习记录






















 407
407











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








