场景:
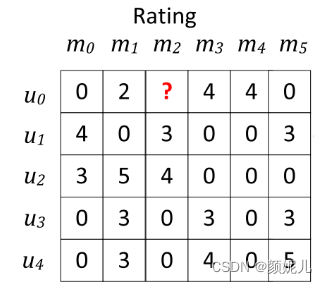
让我们根据当前的评分表预测
?
\color{Red}?
?的值。
数据描述:
U
=
{
u
0
,
u
1
,
u
2
,
u
3
,
u
4
}
U=\{u_0,u_1,u_2,u_3,u_4\}
U={u0,u1,u2,u3,u4}表示参与评分的用户数据集;
M
=
{
m
0
,
m
1
,
m
2
,
m
3
,
m
4
,
m
5
}
M=\{m_0,m_1,m_2,m_3,m_4,m_5\}
M={m0,m1,m2,m3,m4,m5}表示被评阅的电影数据集;
矩阵
R
R
R表示评分矩阵:
R
=
(
r
i
,
j
)
n
×
m
,
0
≤
i
≤
n
−
1
a
n
d
0
≤
j
≤
m
−
1
R=(r_{i,j})_{n\times m},0\le i\le n-1\ and\ 0\le j\le m-1
R=(ri,j)n×m,0≤i≤n−1 and 0≤j≤m−1
预测过程(基于item-based recommendation):
1:设置阈值
δ
\delta
δ用以确认待测值得邻近实例,用
B
(
u
i
,
m
j
)
B(u_i,m_j)
B(ui,mj)表示邻近的
m
m
m,其中
B
(
u
i
,
m
j
)
=
{
k
∣
0
≤
k
≤
m
−
1
,
j
≠
j
,
∣
r
‾
j
−
r
‾
k
∣
≤
δ
,
r
i
,
k
≠
0
}
B(u_i,m_j)=\{k|0\le k \le m-1,j\ne j,|\overline{r}_j-\overline{r}_k|\le \delta,r_{i,k}\ne 0\}
B(ui,mj)={k∣0≤k≤m−1,j=j,∣rj−rk∣≤δ,ri,k=0};
2: 预测值
p
i
,
j
=
{
∑
k
∈
B
(
u
i
,
m
j
)
r
i
,
k
∣
B
(
u
i
,
m
j
)
∣
,
∣
B
(
u
i
,
m
j
)
∣
>
0
r
‾
j
,
o
t
h
e
r
w
i
s
e
p_{i,j}= \left\{\begin{matrix} &\frac{\sum\limits_{k\in{B(u_i,m_j)}}r_{i,k}}{|B(u_i,m_j)|},\quad|B(u_i,m_j)| > 0\\ \\ &\overline{r}_j,\quad otherwise \end{matrix}\right.
pi,j=⎩⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎧∣B(ui,mj)∣k∈B(ui,mj)∑ri,k,∣B(ui,mj)∣>0rj,otherwise
其中
r
‾
j
\overline{r}_j
rj表示默认值。
数据声明:
/**
* Default rating for 1-5 points.
*/
public static final double DEFAULT_RATING = 3.0;
/**
* The total number of users.
*/
private int numUsers;
/**
* The total number of items.
*/
private int numItems;
/**
* The total number of ratings (non-zero values)
*/
private int numRatings;
/**
* The predictions.
*/
private double[] predictions;
/**
* Compressed rating matrix. User-item-rating triples.
*/
public int[][] compressedRatingMatrix;
/**
* The degree of users (how many item he has rated).
*/
private int[] userDegrees;
/**
* The average rating of the current user.
*/
private double[] userAverageRatings;
/**
* The degree of item.(how many users has rated the item).
*/
private int[] itemDegrees;
/**
* The average rating of the current item.
*/
private double[] itemAverageRatings;
/**
* The first user start form 0. Let the first user has x ratings,the second user
* will start form x.
*/
private int[] userStartingIndices;
/**
* Number of non-neighbor objects.
*/
private int numNonNeighbors;
/**
* The radius (delta) for determining the neighborhood.
*/
private double radius;
数据的读入和处理:
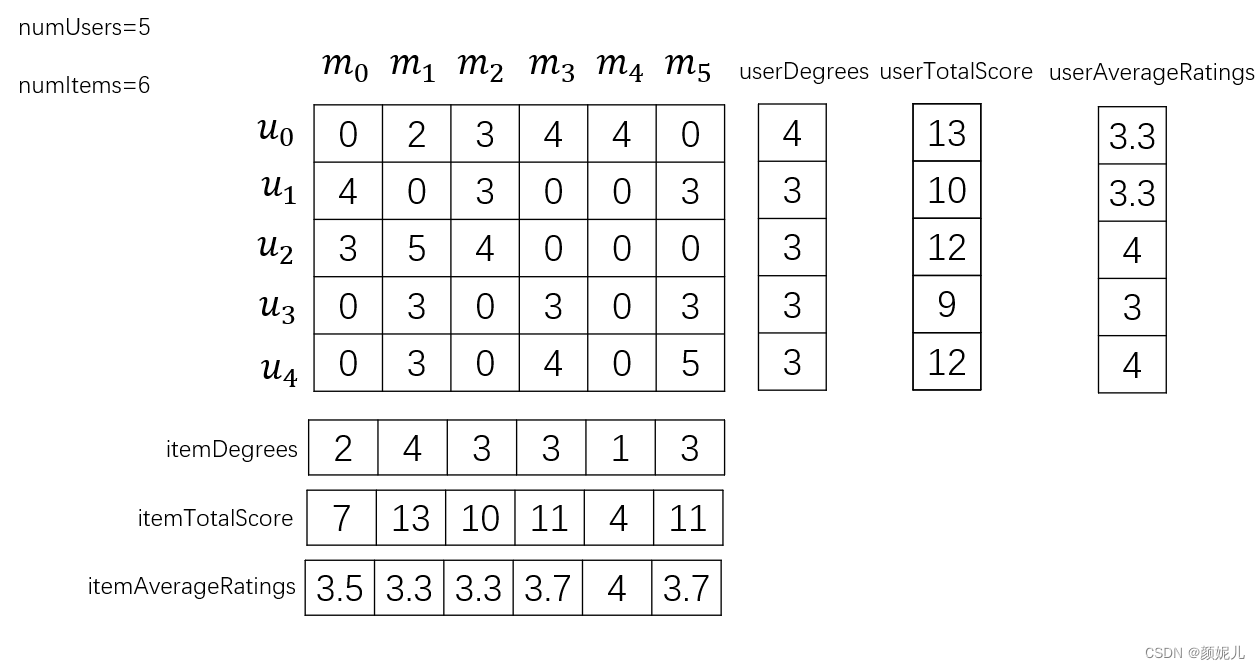
/**
*********************
* Construct the rating matrix.
*
* @param paraFilename The rating filename.
* @param paraNumbers The number of users.
* @param paraNumItems The number of items.
* @param paraNumRatings The number of ratings.
*********************
*/
public MBR(String paraFilename, int paraNumUsers, int paraNumItems, int paraNumRatings) throws Exception {
// Step 1. Initialize these arrays.
numItems = paraNumItems;
numUsers = paraNumUsers;
numRatings = paraNumRatings;
userDegrees = new int[numUsers];
userStartingIndices = new int[numUsers + 1];
userAverageRatings = new double[numUsers];
itemDegrees = new int[numItems];
compressedRatingMatrix = new int[numRatings][3];
itemAverageRatings = new double[numItems];
predictions = new double[numRatings];
System.out.println("Rating " + paraFilename);
// Step 2. Read the data file.
File tempFile = new File(paraFilename);
if (!tempFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("File " + paraFilename + " does not exists.");
System.exit(0);
} // Of if
BufferedReader tempBufReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(tempFile));
String tempString;
String[] tempStrArray;
int tempIndex = 0;
userStartingIndices[0] = 0;
userStartingIndices[numUsers] = numRatings;
while ((tempString = tempBufReader.readLine()) != null) {
// Each line has three values
tempStrArray = tempString.split(",");
compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0] = Integer.parseInt(tempStrArray[0]);
compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][1] = Integer.parseInt(tempStrArray[1]);
compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][2] = Integer.parseInt(tempStrArray[2]);
userDegrees[compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0]]++;
itemDegrees[compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][1]]++;
if (tempIndex > 0) {
// Starting to read the data of a new user.
if (compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0] != compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex - 1][0]) {
userStartingIndices[compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0]] = tempIndex;
} // Of if
} // Of if
tempIndex++;
} // Of while
tempBufReader.close();
double[] tempUserTotalScore = new double[numUsers];
double[] tempItemTotalScore = new double[numItems];
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempUserTotalScore[compressedRatingMatrix[i][0]] += compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
tempItemTotalScore[compressedRatingMatrix[i][1]] += compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < numUsers; i++) {
userAverageRatings[i] = tempUserTotalScore[i] / userDegrees[i];
} // Of fir i
for (int i = 0; i < numItems; i++) {
itemAverageRatings[i] = tempItemTotalScore[i] / itemDegrees[i];
} // Of fir i
}// Of the constructor
设置 δ \delta δ值得方法:
/**
********************
* Set the radius(delta).
*
* @param paraRadius The given radius.
*********************
*/
public void setRadius(double paraRadius) {
if (paraRadius > 0) {
radius = paraRadius;
} else {
radius = 0.1;
} // Of if
}// Of setRadius
基于item-based recommendation测试图示:
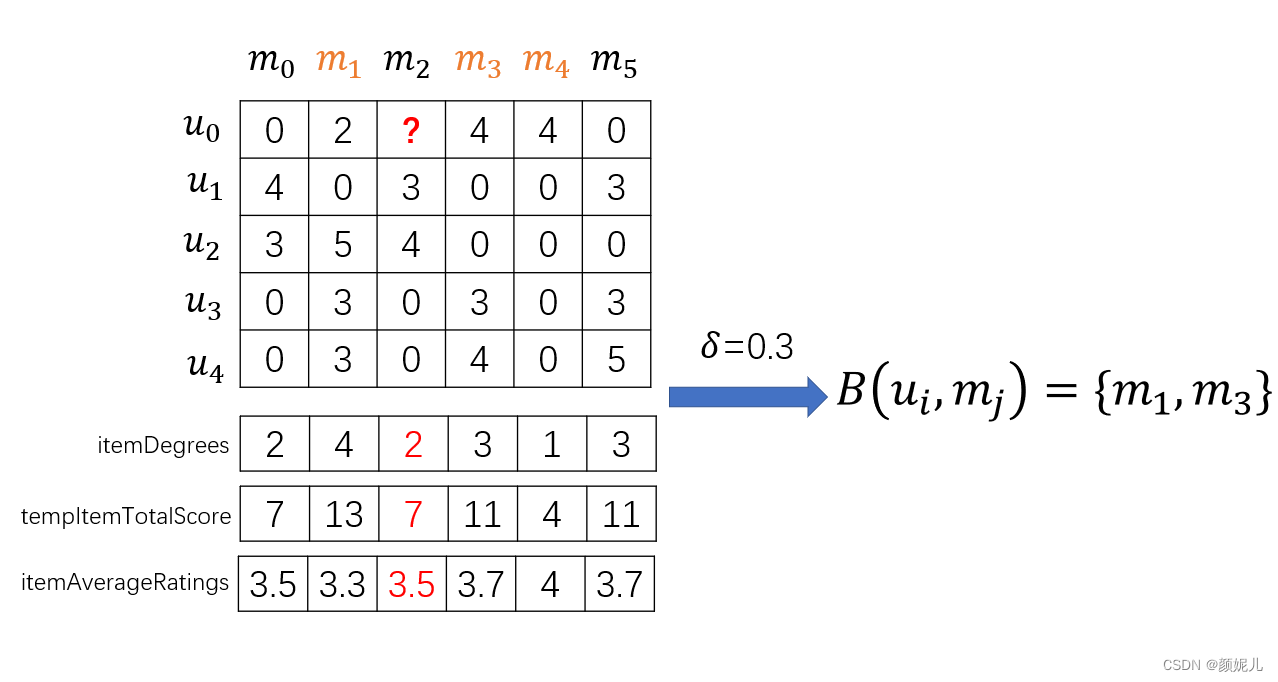
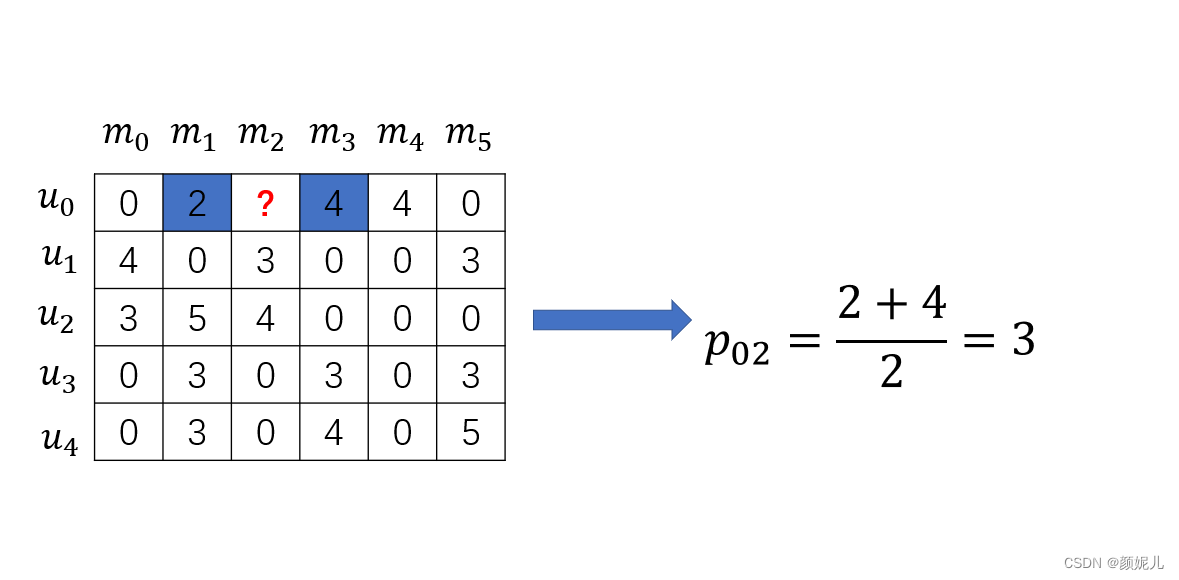
这里的测试方法是每次在原有数据集中“扣”出一个数据用来预测,剩下的数据作为训练集。
/**
********************
* Leave-one-out prediction. The predicted values are stores in predictions.
*
* @see predictions
*********************
*/
public void leaveOneOutPrediction() {
double tempItemAverageRating;
// Make each line of the code shorter.
int tempUser, tempItem, tempRating;
System.out.println("\r\nLeaveOneOutPrediction for radius " + radius);
numNonNeighbors = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempUser = compressedRatingMatrix[i][0];
tempItem = compressedRatingMatrix[i][1];
tempRating = compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
// Step 1. Recompute average rating of the current item.
tempItemAverageRating = (itemAverageRatings[tempItem] * itemDegrees[tempItem] - tempRating)
/ (itemDegrees[tempItem] - 1);
// Step 2. Recompute neighbors,at the same time obtain the ratings of neighbors.
int tempNeighbors = 0;
double tempTotal = 0;
int tempComparedItem;
for (int j = userStartingIndices[tempUser]; j < userStartingIndices[tempUser + 1]; j++) {
tempComparedItem = compressedRatingMatrix[j][1];
if (tempItem == tempComparedItem) {
continue;// Ignore itself.
} // Of if
if (Math.abs(tempItemAverageRating - itemAverageRatings[tempComparedItem]) < radius) {
tempTotal += compressedRatingMatrix[j][2];
tempNeighbors++;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// Step 3. Predict as the average value of neighbors.
if (tempNeighbors > 0) {
predictions[i] = tempTotal / tempNeighbors;
} else {
predictions[i] = DEFAULT_RATING;
numNonNeighbors++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
}// Of leaveOneOutPrediction
算法性能评价的两种方式:设:预测实例个数为
k
k
k,数组
p
p
p[]保存预测值,则:
M
A
E
=
∑
i
k
−
1
∣
p
i
−
r
i
,
2
∣
k
R
S
M
E
=
(
∑
i
k
−
1
∣
p
i
−
r
i
,
2
∣
2
k
)
1
2
\begin{matrix} &MAE=\frac{\sum_i^{k-1}|p_{i}-r_{i,2}|}{k}\\ &RSME=\begin{pmatrix}\frac{\sum_i^{k-1}|p_{i}-r_{i,2}|^2}{k}\end{pmatrix}^\frac{1}{2} \end{matrix}
MAE=k∑ik−1∣pi−ri,2∣RSME=(k∑ik−1∣pi−ri,2∣2)21
MAE能很好地反映预测值误差的实际情况;
RSME可以用来很亮预测值与真实值之间的偏差。
/**
********************
* Compute the MAE based on the deviation of each leave-one-out.
*********************
*/
public double computeMAE() throws Exception {
double tempTotalError = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
tempTotalError += Math.abs(predictions[i] - compressedRatingMatrix[i][2]);
} // Of for i
return tempTotalError / predictions.length;
}// Of computeMAE
/**
********************
* Compute the RSME based on the deviation of each leave-one-out.
*********************
*/
public double computeRSME() throws Exception {
double tempTotalError = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
tempTotalError += (predictions[i] - compressedRatingMatrix[i][2])
* (predictions[i] - compressedRatingMatrix[i][2]);
} // Of for i
double tempAverage = tempTotalError / predictions.length;
return Math.sqrt(tempAverage);
}// Of computeRSME
主函数:
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MBR tempRecommender = new MBR("F:/sampledata-main/movielens-943u1682m.txt", 943, 1682, 100000);
for (double tempRadius = 0.2; tempRadius < 0.6; tempRadius += 0.1) {
tempRecommender.setRadius(tempRadius);
tempRecommender.leaveOneOutPrediction();
double tempMAE = tempRecommender.computeMAE();
double tempRSME = tempRecommender.computeRSME();
System.out.println("Radius = " + tempRadius + ", MAE = " + tempMAE + ", RSME = " + tempRSME
+ ", numNonNeighbors = " + tempRecommender.numNonNeighbors);
} // Of for tempRadius
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
} // Of try
}// Of main
运行结果:

补充:user-based recommendation

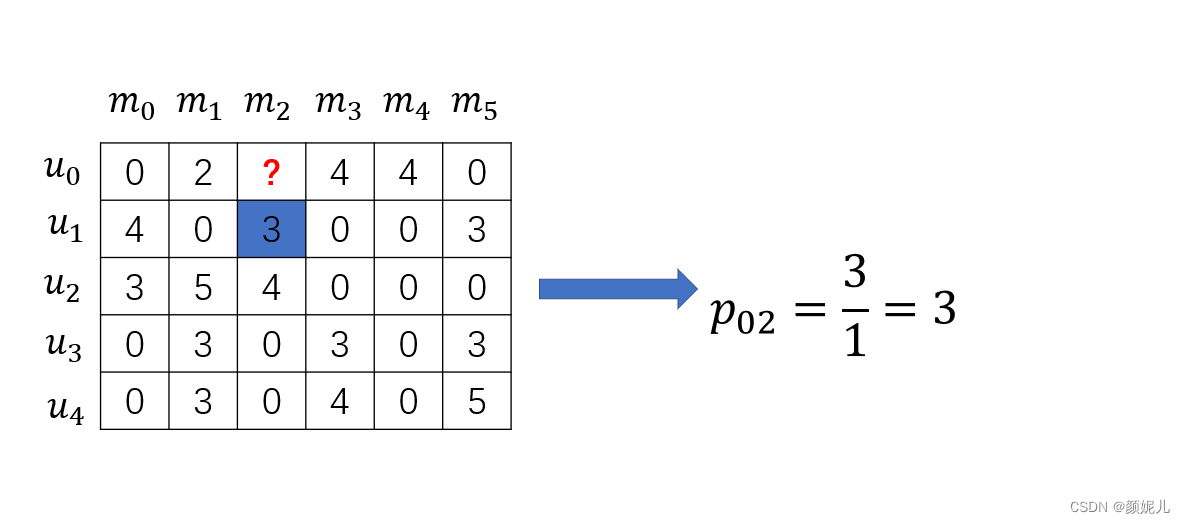
不然发现,就是将原有矩阵转置后进行同样操作,但由于矩阵采用的是压缩矩阵,我直接便利了所有数据,不出意外的很慢很慢~
/**
********************
* Leave-one-out prediction. The predicted values are stores in predictions.
*
* @see predictions
*********************
*/
public void leaveOneOutPrediction2() {
double tempUserAverageRating;
// Make each line of the code shorter.
int tempUser, tempItem, tempRating;
System.out.println("\r\nLeaveOneOutPrediction2 for radius " + radius);
numNonNeighbors = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempUser = compressedRatingMatrix[i][0];
tempItem = compressedRatingMatrix[i][1];
tempRating = compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
// Step 1. Recompute average rating of the current item.
tempUserAverageRating = (userAverageRatings[tempUser] * userDegrees[tempUser] - tempRating)
/ (userDegrees[tempUser] - 1);
// Step 2. Recompute neighbors,at the same time obtain the ratings of neighbors.
int tempNeighbors = 0;
double tempTotal = 0;
int tempComparedItem;
for (int j = 0; j < numUsers; j++) {
if (j == tempUser)
continue;
for (int k = userStartingIndices[j]; k < userStartingIndices[j + 1]; k++) {
tempComparedItem = compressedRatingMatrix[k][1];
if (tempComparedItem == tempItem
&& Math.abs(tempUserAverageRating - userAverageRatings[j]) < radius) {
tempTotal += compressedRatingMatrix[k][2];
tempNeighbors++;
} // Of if
} // Of for k
} // Of for j
// Step 3. Predict as the average value of neighbors.
if (tempNeighbors > 0) {
predictions[i] = tempTotal / tempNeighbors;
} else {
predictions[i] = DEFAULT_RATING;
numNonNeighbors++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
}// Of leaveOneOutPrediction2
运行结果:
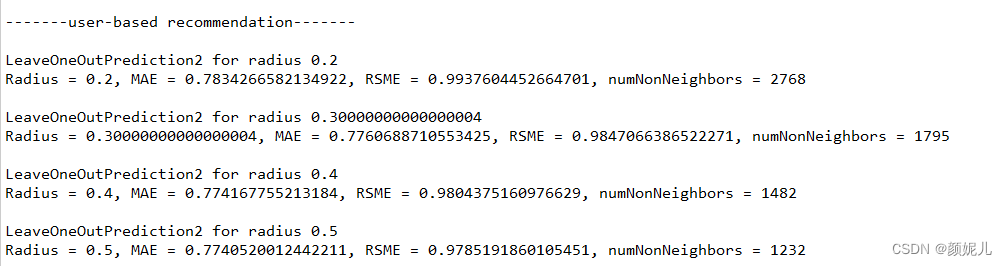
补充:
上面咱们说到了user-based recommendation就是用同样的方式处理转置矩阵,下面补充了压缩矩阵的转置代码:
/**
********************
* Transform the compressed matrix.
*********************
*/
public void transformMatrix() {
int[][] resultMatrix = new int[numRatings][3];
int[] tempItemCounts = new int[numItems];
int[] tempPointIndex = new int[numItems];
int[] tempItemStartingIndices = new int[numItems + 1];
// Count the number of every item.
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempItemCounts[compressedRatingMatrix[i][1]]++;
} // Of for i
// Get every item's starting index and initial the point array.
tempPointIndex[0] = 0;
tempItemStartingIndices[0] = 0;
tempItemStartingIndices[numItems] = numRatings;
for (int i = 1; i < numItems; i++) {
tempPointIndex[i] = tempItemCounts[i - 1] + tempPointIndex[i - 1];
tempItemStartingIndices[i] = tempPointIndex[i];
} // Of for i
// Transform the matrix.
int tempIndex;
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempIndex = tempPointIndex[compressedRatingMatrix[i][1]];
resultMatrix[tempIndex][0] = compressedRatingMatrix[i][1];
resultMatrix[tempIndex][1] = compressedRatingMatrix[i][0];
resultMatrix[tempIndex][2] = compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
tempPointIndex[compressedRatingMatrix[i][1]]++;
} // Of for i
// Swap the value between users and items.
int tempArray[], tempValue;
double tempAvarageArray[];
compressedRatingMatrix = resultMatrix;
userStartingIndices = tempItemStartingIndices;
tempArray = userDegrees;
userDegrees = itemDegrees;
itemDegrees = tempArray;
tempValue = numUsers;
numUsers = numItems;
numItems = tempValue;
tempAvarageArray = userAverageRatings;
userAverageRatings = itemAverageRatings;
itemAverageRatings = tempAvarageArray;
// leaveOneOutPrediction();
}// Of transformMatrix
这是打印的转置压缩矩阵一个测试用例,可以帮助理解:

测试数据:
0,0,2
0,3,5
0,4,1
1,0,1
1,2,3
2,1,4
2,3,3
在主函数中调用:
System.out.println("\r\n-------user-based recommendation by transform -------");
tempRecommender.transformMatrix();
for (double tempRadius = 0.2; tempRadius < 0.6; tempRadius += 0.1) {
tempRecommender.setRadius(tempRadius);
tempRecommender.leaveOneOutPrediction();
double tempMAE = tempRecommender.computeMAE();
double tempRSME = tempRecommender.computeRSME();
System.out.println("Radius = " + tempRadius + ", MAE = " + tempMAE + ", RSME=" + tempRSME
+ ", numNonNeighbors = " + tempRecommender.numNonNeighbors);
} // Of for tempRadius
运行结果和上图一样,但更快:























 1227
1227











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








