一、多线程
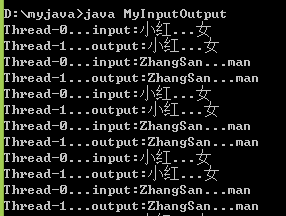
1、代码:MyInputOutput.java
/*
Input姓名、性别,Output输出。
*/
class Res
{
String name;
String sex;
boolean flag = false;
}
class Input implements Runnable
{
Res r = new Res();
Input(Res r) //初始化资源
{
this.r = r;
}
public void run()
{
int x = 0;
while(true)
{
synchronized(r) //Input和Output要是同一把锁(即对象r)
{
if(r.flag)
try{r.wait();}catch(Exception e){}
if(x == 0)
{
r.name = "小红";
r.sex = "女";
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "..." + "input:" + r.name + "..." + r.sex);
}
else
{
r.name = "ZhangSan";
r.sex = "man";
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "..." + "input:" + r.name + "..." + r.sex);
}
x = (x + 1) % 2;
r.flag = true;
r.notify();
}
}
}
}
class Output implements Runnable
{
Res r = new Res();
Output(Res r)
{
this.r = r;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
//-------------------------------------为什么这里一句话也要同步?-------
synchronized(r)
{
if(!r.flag)
try{r.wait();}catch(Exception e){}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "..." + "output:" + r.name + "..." + r.sex);
r.flag = false;
r.notify();
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
}
}
}
class MyInputOutput
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Res r = new Res();
Input in = new Input(r);
Output out = new Output(r);
Thread t1 = new Thread(in);
Thread t2 = new Thread(out);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
/*
wait:
notify();
notifyAll();
都使用在同步中,因为要对持有监视器(锁)的线程操作。
所以要使用在同步中,因为只有同步才具有锁。
等待和唤醒必须是同一个锁。
而锁可以是任意对象,所以可以被任意对象调用的方法定义Object类中。
*/代码:MyInputOutput.java 对上面代码的优化(只是格式上的优化,内容没变)
class Res
{
private String name;
private String sex;
private boolean flag = false;
public synchronized void set(String name, String sex) //非静态同步函数的对象是this
{
if(flag)
try{this.wait();}catch(Exception e){}
//else //不能有else了
//{
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "..." + "input:" + name + "..." + sex);
//}
flag = true;
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void out()
{
if(!flag)
try{this.wait();}catch(Exception e){}
//else
//{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "..." + "output:" + name + "..." + sex);
//}
flag = false;
this.notify();
}
}
class Input implements Runnable
{
private Res r = new Res();
Input(Res r)
{
this.r = r;
}
public void run()
{
int x = 0;
while(true)
{
if(x == 0)
{
r.set("小红", "女");
}
else
{
r.set("ZhangSan", "man");
}
x = (x + 1) % 2;
}
}
}
class Output implements Runnable
{
private Res r = new Res();
Output(Res r)
{
this.r = r;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
r.out();
}
}
}
class MyInputOutput
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Res r = new Res();
new Thread(new Input(r)).start();
new Thread(new Output(r)).start();
}
}
2、代码:MyProducerConsumer.java 跟MyInputOutput.java差不多
/*
一个生产者,一个消费者
*/
class Resource
{
private String name;
private int count = 1;
private boolean flag = false;
public synchronized void set(String name)
{
if(flag)
try
{
this.wait();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
this.name = name + "--" + count++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...生产者..." + this.name); //这个this. 不能省(因为this.name和name同名了)
flag = true;
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void out()
{
if(!flag)
try
{
this.wait();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---消费者------" + name); //为什么这里name前的this. 省了后面一样跟着count,跟上面那个不是一样的吗?
flag = false;
this.notify();
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable
{
private Resource res;
Producer(Resource res)
{
this.res = res;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
res.set("小笼包");
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable
{
private Resource res;
Consumer(Resource res)
{
this.res = res;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
res.out();
}
}
}
class MyProducerConsumer
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Resource res = new Resource();
Producer pro = new Producer(res);
Consumer con = new Consumer(res);
Thread t1 = new Thread(pro);
Thread t2 = new Thread(con);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
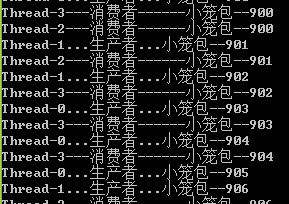
如果多创建几个线程,就会出现如下图所示的情况:
解决这个问题:代码:MyProducerConsumer.java
/*
多个生产者,多个消费者
*/
class Resource
{
private String name;
private int count = 1;
private boolean flag = false;
public synchronized void set(String name)
{
//if(flag)
while(flag) //1、这里改成while,就不会出现生产了两个,才被消费掉的情况了,但是会卡住(死锁了吧)
try
{
this.wait();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
this.name = name + "--" + count++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...生产者..." + this.name); //这个this. 不能省(因为this.name和name同名了)
flag = true;
this.notifyAll(); //2、唤醒所有的就不会卡在那不走了
}
public synchronized void out()
{
//if(!flag)
while(!flag)
try
{
this.wait();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---消费者------" + name); //为什么这里name前的this. 省了后面一样跟着count,跟上面那个不是一样的吗?
flag = false;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable
{
private Resource res;
Producer(Resource res)
{
this.res = res;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
res.set("小笼包");
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable
{
private Resource res;
Consumer(Resource res)
{
this.res = res;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
res.out();
}
}
}
class MyProducerConsumer
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Resource res = new Resource();
Producer pro = new Producer(res);
Consumer con = new Consumer(res);
Thread t1 = new Thread(pro);
Thread t2 = new Thread(pro);
Thread t3 = new Thread(con);
Thread t4 = new Thread(con);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}























 331
331

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








