渐变分为线性渐变和径向渐变需要用到cairo.Pattern类
cairo.Pattern
Patterns are the paint with which cairo draws. The primary use of patterns is as the source for all cairo drawing operations, although they can also be used as masks, that is, as the brush too.
A cairo Pattern is created by using one of the PatternType constructors listed below, or implicitly through Context.set_source_() methods.
Pattern is the abstract base class from which all the other pattern classes derive. It cannot be instantiated directly.
class cairo.Pattern
get_extend()
Returns: the current extend strategy used for drawing the Pattern.
Return type: int
Gets the current extend mode for the Pattern. See EXTEND attributes for details on the semantics of each extend strategy.
get_matrix()
Returns: a new Matrix which stores a copy of the Pattern’s transformation matrix
set_extend(extend)
Parameters: extend – an EXTEND describing how the area outside of the Pattern will be drawn
Sets the mode to be used for drawing outside the area of a Pattern.
The default extend mode is cairo.EXTEND_NONE for SurfacePattern and cairo.EXTEND_PAD for Gradient Patterns.
set_matrix(matrix)
Parameters: matrix – a Matrix
Sets the Pattern’s transformation matrix to matrix. This matrix is a transformation from user space to pattern space.
When a Pattern is first created it always has the identity matrix for its transformation matrix, which means that pattern space is initially identical to user space.
Important: Please note that the direction of this transformation matrix is from user space to pattern space. This means that if you imagine the flow from a Pattern to user space (and on to device space), then coordinates in that flow will be transformed by the inverse of the Pattern matrix.
For example, if you want to make a Pattern appear twice as large as it does by default the correct code to use is:
matrix = cairo.Matrix(xx=0.5,yy=0.5)
pattern.set_matrix(matrix)Meanwhile, using values of 2.0 rather than 0.5 in the code above would cause the Pattern to appear at half of its default size.
Also, please note the discussion of the user-space locking semantics of Context.set_source.
class SolidPattern(Pattern)
class cairo.SolidPattern(red, green, blue, alpha=1.0)
Parameters:
red (float) – red component of the color
green (float) – green component of the color
blue (float) – blue component of the color
alpha (float) – alpha component of the color
Returns:
a new SolidPattern
Raises :
MemoryError in case of no memory
Creates a new SolidPattern corresponding to a translucent color. The color components are floating point numbers in the range 0 to 1. If the values passed in are outside that range, they will be clamped.
get_rgba()
Returns: (red, green, blue, alpha) a tuple of float
Gets the solid color for a SolidPattern.
New in version 1.4.
class SurfacePattern(Pattern)
class cairo.SurfacePattern(surface)
Parameters: surface – a cairo Surface
Returns: a newly created SurfacePattern for the given surface.
Raises : MemoryError in case of no memory.
get_filter()
Returns: the current FILTER used for resizing the SurfacePattern.
get_surface()
Returns: the Surface of the SurfacePattern.
New in version 1.4.
set_filter(filter)
Parameters: filter – a FILTER describing the filter to use for resizing the Pattern
Note that you might want to control filtering even when you do not have an explicit Pattern object, (for example when using Context.set_source_surface()). In these cases, it is convenient to use Context.get_source() to get access to the pattern that cairo creates implicitly. For example:
context.set_source_surface(image, x, y)
surfacepattern.set_filter(context.get_source(), cairo.FILTER_NEAREST)class Gradient(Pattern)
Gradient is an abstract base class from which other Pattern classes derive. It cannot be instantiated directly.
class cairo.Gradient
add_color_stop_rgb(offset, red, green, blue)
Parameters:
offset (float) – an offset in the range [0.0 .. 1.0]
red (float) – red component of color
green (float) – green component of color
blue (float) – blue component of color
Adds an opaque color stop to a Gradient pattern. The offset specifies the location along the gradient’s control vector. For example, a LinearGradient’s control vector is from (x0,y0) to (x1,y1) while a RadialGradient’s control vector is from any point on the start circle to the corresponding point on the end circle.
The color is specified in the same way as in Context.set_source_rgb().
If two (or more) stops are specified with identical offset values, they will be sorted according to the order in which the stops are added, (stops added earlier will compare less than stops added later). This can be useful for reliably making sharp color transitions instead of the typical blend.
add_color_stop_rgba(offset, red, green, blue, alpha)
Parameters:
offset (float) – an offset in the range [0.0 .. 1.0]
red (float) – red component of color
green (float) – green component of color
blue (float) – blue component of color
alpha (float) – alpha component of color
Adds an opaque color stop to a Gradient pattern. The offset specifies the location along the gradient’s control vector. For example, a LinearGradient’s control vector is from (x0,y0) to (x1,y1) while a RadialGradient’s control vector is from any point on the start circle to the corresponding point on the end circle.
The color is specified in the same way as in Context.set_source_rgb().
If two (or more) stops are specified with identical offset values, they will be sorted according to the order in which the stops are added, (stops added earlier will compare less than stops added later). This can be useful for reliably making sharp color transitions instead of the typical blend.
class LinearGradient(Gradient)
class cairo.LinearGradient(x0, y0, x1, y1)
Parameters:
x0 (float) – x coordinate of the start point
y0 (float) – y coordinate of the start point
x1 (float) – x coordinate of the end point
y1 (float) – y coordinate of the end point
Returns:
a new LinearGradient
Raises :
MemoryError in case of no memory
Create a new LinearGradient along the line defined by (x0, y0) and (x1, y1). Before using the Gradient pattern, a number of color stops should be defined using Gradient.add_color_stop_rgb() or Gradient.add_color_stop_rgba()
Note: The coordinates here are in pattern space. For a new Pattern, pattern space is identical to user space, but the relationship between the spaces can be changed with Pattern.set_matrix()
get_linear_points()
Returns: (x0, y0, x1, y1) - a tuple of float
x0: return value for the x coordinate of the first point
y0: return value for the y coordinate of the first point
x1: return value for the x coordinate of the second point
y1: return value for the y coordinate of the second point
Gets the gradient endpoints for a LinearGradient.
New in version 1.4.
class RadialGradient(Gradient)
class cairo.RadialGradient(cx0, cy0, radius0, cx1, cy1, radius1)
Parameters:
cx0 (float) – x coordinate for the center of the start circle
cy0 (float) – y coordinate for the center of the start circle
radius0 (float) – radius of the start circle
cx1 (float) – x coordinate for the center of the end circle
cy1 (float) – y coordinate for the center of the end circle
radius1 (float) – radius of the end circle
Returns:
the newly created RadialGradient
Raises :
MemoryError in case of no memory
Creates a new RadialGradient pattern between the two circles defined by (cx0, cy0, radius0) and (cx1, cy1, radius1). Before using the gradient pattern, a number of color stops should be defined using Gradient.add_color_stop_rgb() or Gradient.add_color_stop_rgba().
Note: The coordinates here are in pattern space. For a new pattern, pattern space is identical to user space, but the relationship between the spaces can be changed with Pattern.set_matrix().
get_radial_circles()
Returns: (x0, y0, r0, x1, y1, r1) - a tuple of float
x0: return value for the x coordinate of the center of the first circle
y0: return value for the y coordinate of the center of the first circle
r0: return value for the radius of the first circle
x1: return value for the x coordinate of the center of the second circle
y1: return value for the y coordinate of the center of the second circle
r1: return value for the radius of the second circle
Gets the Gradient endpoint circles for a RadialGradient, each specified as a center coordinate and a radius.
New in version 1.4.
例子
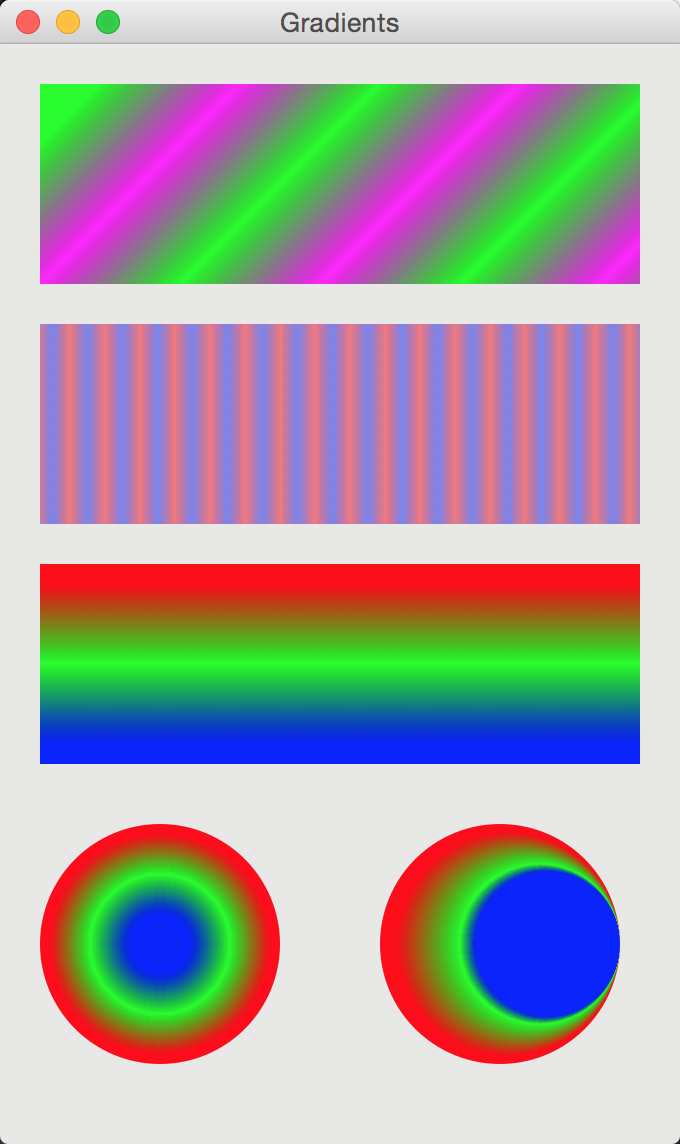
代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Created by xiaosanyu at 16/7/6
# section 145
TITLE = "Gradients"
DESCRIPTION = """
In computer graphics, gradient is a smooth blending of shades from light to dark
or from one colour to another. In 2D drawing programs and paint programs,
gradients are used to create colourful backgrounds and special effects as well as
to simulate lights and shadows.
"""
import gi
gi.require_version("Gtk", "3.0")
from gi.repository import Gtk, GLib
import cairo
class PyApp(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Gradients")
self.set_size_request(340, 550)
self.connect("destroy", Gtk.main_quit)
darea = Gtk.DrawingArea()
darea.connect("draw", self.draw)
self.add(darea)
self.show_all()
@staticmethod
def draw(widget, cr):
lg1 = cairo.LinearGradient(0.0, 0.0, 350.0, 350.0)
count = 1
i = 0.1
while i < 1.0:
if count % 2:
lg1.add_color_stop_rgba(i, 0, 1, 0, 1)
else:
lg1.add_color_stop_rgba(i, 1, 0, 1, 1)
i += 0.1
count += 1
cr.rectangle(20, 20, 300, 100)
cr.set_source(lg1)
cr.fill()
lg2 = cairo.LinearGradient(0.0, 0.0, 350.0, 0)
count = 1
i = 0.05
while i < 0.95:
if count % 2:
lg2.add_color_stop_rgba(i, 1, 0, 0, 0.5)
else:
lg2.add_color_stop_rgba(i, 0, 0, 1, 0.5)
i += 0.025
count += 1
cr.rectangle(20, 140, 300, 100)
cr.set_source(lg2)
cr.fill()
lg3 = cairo.LinearGradient(20.0, 260.0, 20.0, 360.0)
lg3.add_color_stop_rgba(0.1, 1, 0, 0, 1)
lg3.add_color_stop_rgba(0.5, 0, 1, 0, 1)
lg3.add_color_stop_rgba(0.9, 0, 0, 1, 1)
cr.rectangle(20, 260, 300, 100)
cr.set_source(lg3)
cr.fill()
lg4 = cairo.RadialGradient(80, 450, 60, 80, 450, 10)
lg4.add_color_stop_rgba(0.1, 1, 0, 0, 1)
lg4.add_color_stop_rgba(0.5, 0, 1, 0, 1)
lg4.add_color_stop_rgba(0.9, 0, 0, 1, 1)
cr.arc(80, 450, 60, 0, 2 * GLib.PI)
cr.set_source(lg4)
cr.fill()
lg4 = cairo.RadialGradient(250, 450, 60, 290, 450, 20)
lg4.add_color_stop_rgba(0.1, 1, 0, 0, 1)
lg4.add_color_stop_rgba(0.5, 0, 1, 0, 1)
lg4.add_color_stop_rgba(0.6, 0, 0, 1, 1)
cr.arc(250, 450, 60, 0, 2 * GLib.PI)
cr.set_source(lg4)
cr.fill()
def main():
PyApp()
Gtk.main()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()

























 2782
2782

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










