神经网路算法Neural Network
神经网络包含输入层input layer、隐藏层hidden layer、输出层output layer三部分。多层神经网络中常用的优化参数算法,backpropagation/反向传播算法。
多层神经网络结构如图:
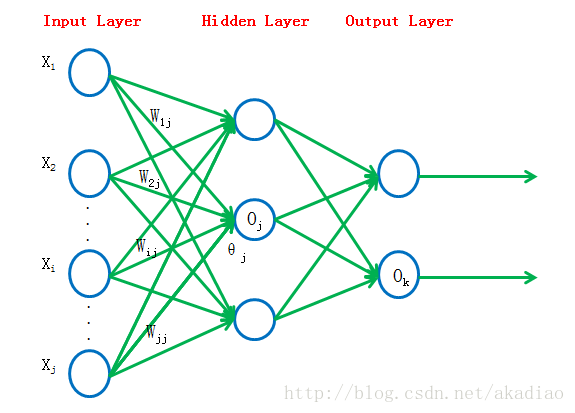
其中隐藏层通常有多层组成;
神经网络中每个节点i的输入为:
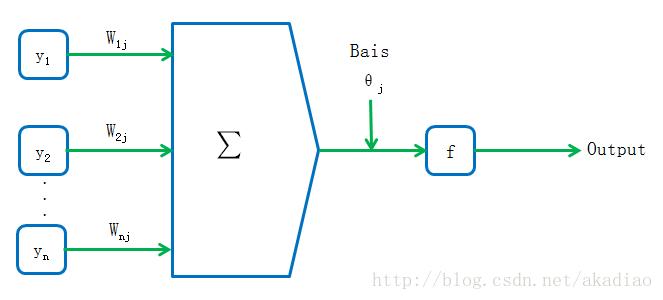
在节点处进行非线性化处理:
f为激活函数,常用的形式有:tanh(x) 和 Sigmoid(x)
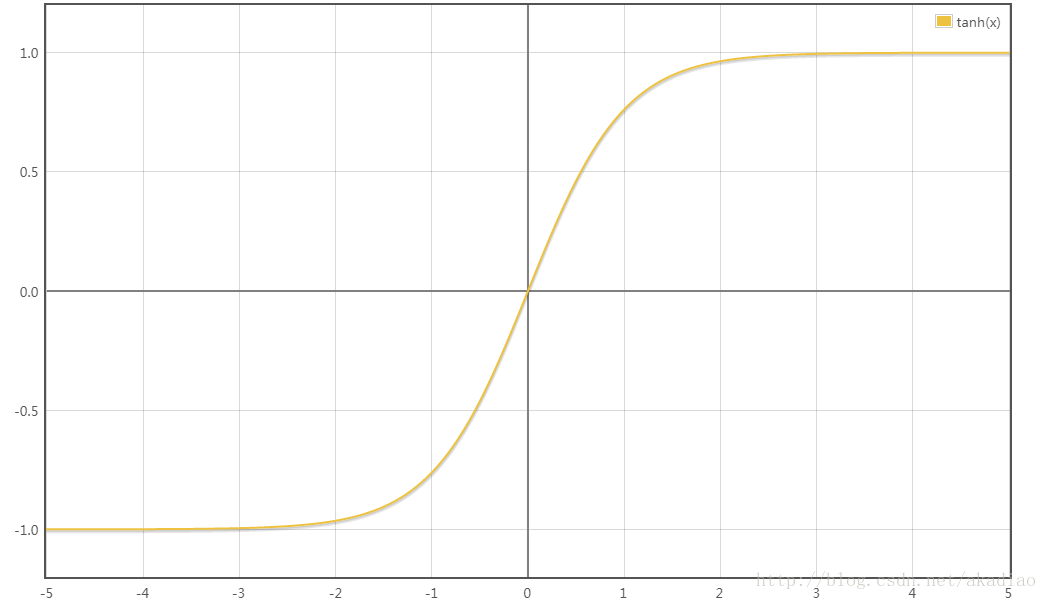
tanh(x)函数:
tanh(x)函数图像为:
tanh(x)导数形式为:
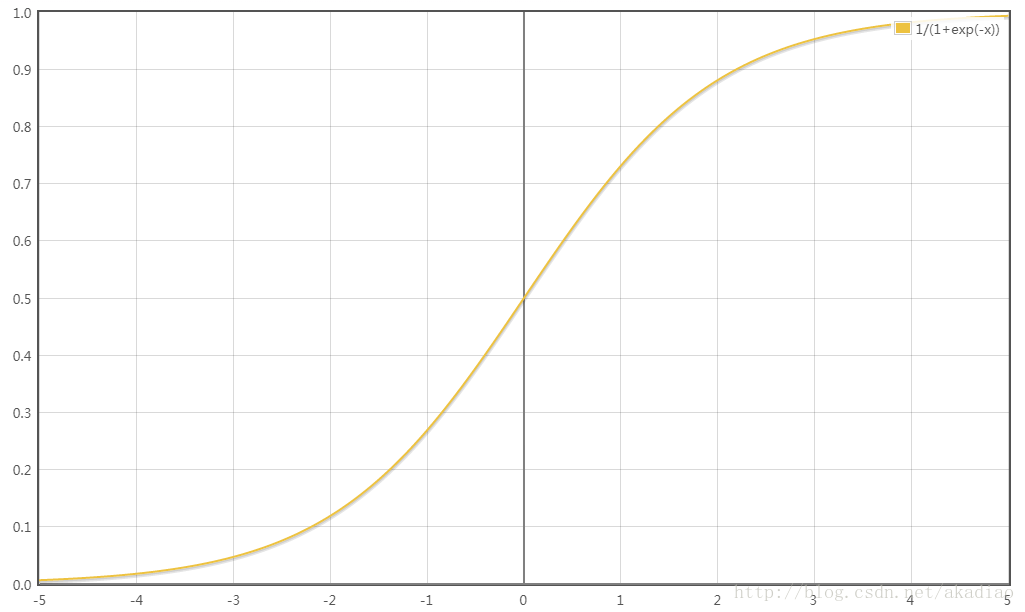
Sigmoid(x)函数:
Sigmoid(x)函数图像为:
Sigmoid(x)导数形式为:
选择Sigmoid函数作为激活函数时,则
对于输出层反向传递的误差为:
对于隐藏层反向传递的误差为:
权重w的更新方式为:
Bias的更新方式为:
Python实现:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8-*-
# #Neural Network算法
import numpy as np
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
# #tanh()导数
def tanh_deriv(x):
return 1.0 -np.tanh(x)*np.tanh(x)
def logistic(x):
return 1/(1 + np.exp(-x))
# #logistic()导数
def logistic_derivative(x):
return logistic(x)*(1 - logistic(x))
# #定义类NeuralNetwork
class NeuralNetwork:
# #__init__ 构造函数 self相当于this当前类的指针
def __init__(self, layers, activation = 'tanh'):
"""
:param layers:a list 包含几个数表示有几层;数值表示对应层的神经元个数;
:param activation: 指定函数;默认为tanh函数;
"""
if activation == 'logistic':
self.activation = logistic
self.activation_deriv = logistic_derivative
elif activation == 'tanh':
self.activation = tanh
self.activation_deriv = tanh_deriv
self.weights = [] # 初始化weights
for i in range(1, len(layers)-1):
self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i - 1] + 1,layers[i] + 1)) - 1)*0.25)
self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i] + 1,layers[i + 1])) - 1)*0.25)
# #X为数据集,每一行为一个实例;y为label;抽取X中的一个样本进行更新,循环epochs次
def fit(self, X, y, learning_rate=0.2, epochs=10000):
# #确定X至少是二维的数据
X = np.atleast_2d(X)
# #初始化temp为1;与X同行数,列数比X多1
temp = np.ones([X.shape[0], X.shape[1]+1])
temp[:, 0:-1] = X
X = temp
# #转换y的数据类型
y = np.array(y)
# #每次循环从X中随机抽取1行,对神经网络进行更新
for k in range(epochs):
i = np.random.randint(X.shape[0])
# #取X中的1行,即一个实例放入a中
a = [X[i]]
for l in range(len(self.weights)):
# # a与weights内积
a.append(self.activation(np.dot(a[l], self.weights[l])))
# #实际的标记值减去标签值
error = y[i] - a[-1]
deltas = [error * self.activation_deriv(a[-1])]
# #反向
for l in range(len(a) - 2, 0, -1):
deltas.append(deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T)*self.activation_deriv(a[l]))
deltas.reverse()
for i in range(len(self.weights)):
layer = np.atleast_2d(a[i])
# #权重的更新
delta =np.atleast_2d(deltas[i])
self.weights[i] += learning_rate * layer.T.dot(delta)
def predict(self,x):
x = np.array(x)
temp = np.ones(x.shape[0] + 1)
temp[0:-1] = x
a = temp
for l in range(0, len(self.weights)):
a = self.activation(np.dot(a,self.weights[l]))
return a
写入NeuralNetwork.py文件。
示例1、调用NeuralNetwork中的算法,查看Neural Network算法实现效果:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# #Neural Network算法实例
from NeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork
import numpy as np
# #2个输入,2层神经网络,1个输出
nn = NeuralNetwork([2,2,1],'tanh')
X = np.array([[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]])
y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0])
nn.fit(X, y)
for i in [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]:
print i, nn.predict(i)输出结果:
[0, 0] [ 0.00873859]
[0, 1] [ 0.99834637]
[1, 0] [ 0.99827345]
[1, 1] [ 0.01632346]可以设置一个threshold(如0.5)即可知四个的分类为[0, 1, 1, 0]。
示例、调用NeuralNetwork中的算法和sklearn中自带的手写数字数据集,查看Neural Network算法实现效果:
# !/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# #手写数字数据集分类
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,classification_report
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from NeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# #交叉验证
# from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
# #下载数据集
digits = load_digits()
# #将特征量放入X
X = digits.data
# #将标签值放入y
y =digits.target
# #预处理:将X标准化到0/1之间;
X -= X.min()
X /= X.max()
# #实例化一个神经网络;64个像素点,10个输出类别,通常隐藏层层数要比输入节点多一些
nn = NeuralNetwork([64, 100, 10], 'logistic')
# #将数据集分为训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)
# #将label数据转换为符合sklearn库的输入要求{即,数字对应位为1其余为0}
labels_train = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_train)
labels_test = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_test)
print "start fitting"
# #循环3000次
nn.fit(X_train, labels_train,epochs=3000)
predictions = []
for i in range(X_test.shape[0]):
o = nn.predict(X_test[i])
# #选择1个概率最大的作为预测结果
predictions.append(np.argmax(o))
# #呈现预测结果矩阵
print confusion_matrix(y_test, predictions)
# #打印出预测准确度的度量结果
print classification_report(y_test, predictions)
打印结果:
start fitting
[[36 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 46 0 0 1 0 2 0 4 1]
[ 0 1 52 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 38 0 1 0 1 1 1]
[ 1 3 0 0 38 0 0 0 1 0]
[ 0 0 0 1 1 40 0 0 0 0]
[ 1 0 0 0 0 0 46 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 53 1 0]
[ 0 5 1 0 0 0 1 1 28 0]
[ 0 1 0 4 1 1 0 0 0 35]]
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.95 0.97 0.96 37
1 0.82 0.85 0.84 54
2 0.98 0.98 0.98 53
3 0.88 0.90 0.89 42
4 0.90 0.88 0.89 43
5 0.95 0.95 0.95 42
6 0.94 0.98 0.96 47
7 0.96 0.98 0.97 54
8 0.80 0.78 0.79 36
9 0.95 0.83 0.89 42
avg / total 0.92 0.92 0.92 450
Hierarchical Clustering 层次聚类
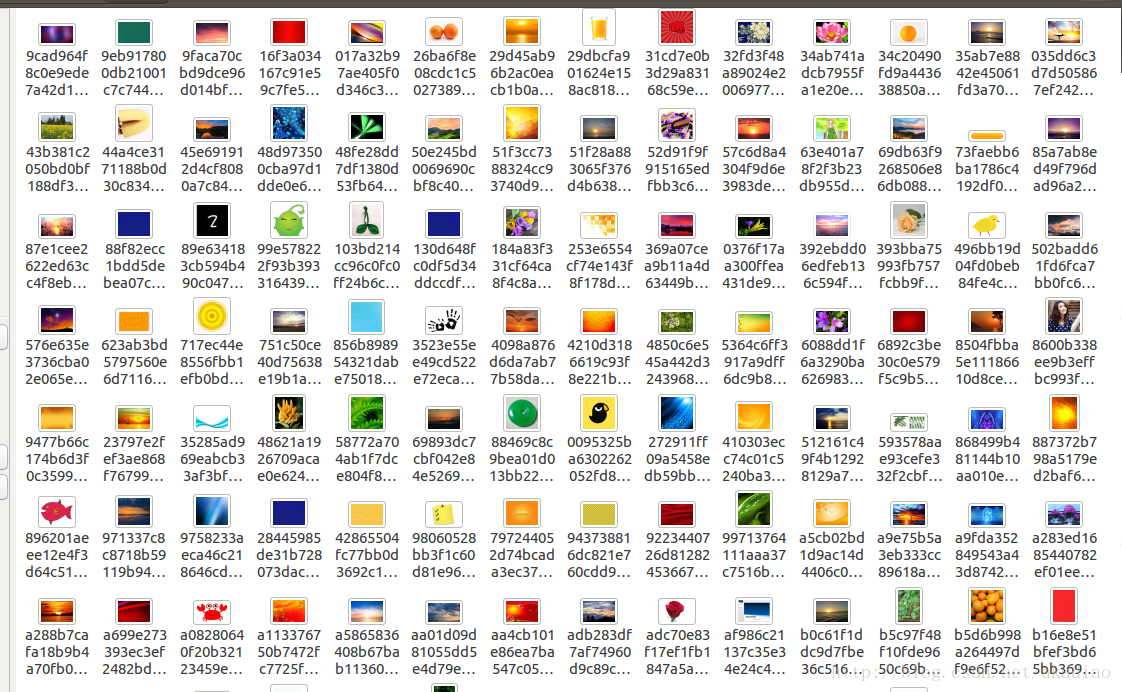
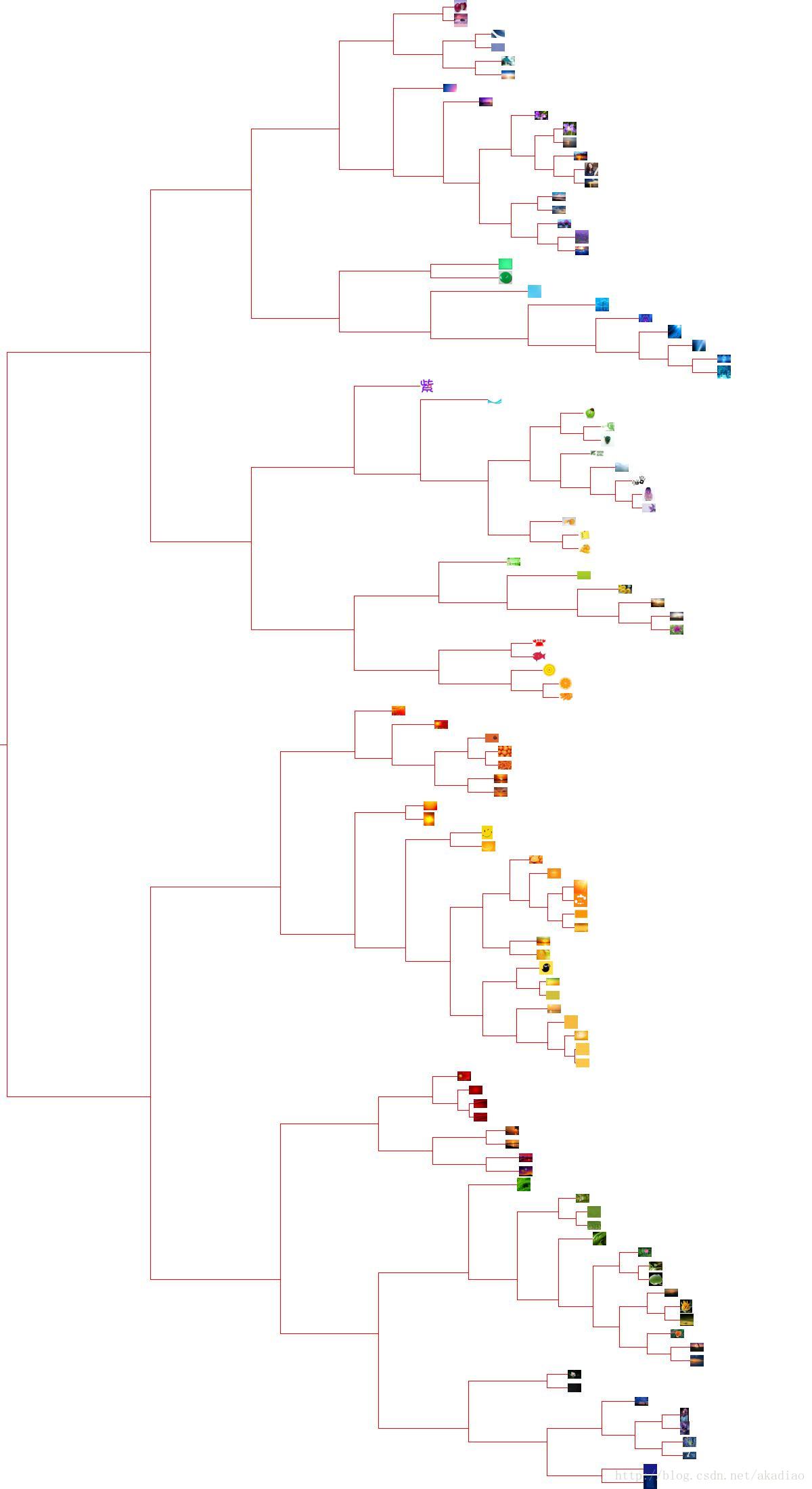
利用层次聚类以图像颜色对图片进行聚类:
其中’map’文件夹中放入110张jpg格式的图片.
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
from clustering import hcluster
from clustering import getheight
from clustering import getdepth
import numpy as np
import os
def drawdendrogram(clust, imlist, jpeg= 'clusters.jpg'):
h = getheight(clust)*20
w = 1200
depth = getdepth(clust)
scaling = float(w - 150)/depth
img = Image.new('RGB', (w, h), (255, 255, 255))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.line((0, h/2, 10, h/2), fill=(255, 0, 0))
drawnode(draw, clust, 10, int(h/2), scaling, imlist, img)
img.save(jpeg)
def drawnode(draw,clust,x,y,scaling,imlist,img):
if clust.id < 0:
h1 = getheight(clust.left)*20
h2 = getheight(clust.right)*20
top = y - (h1 + h2)/2
bottom = y + (h1 + h2)/2
ll = clust.distance * scaling
# 若不是叶子节点则画线
draw.line((x, top + h1/2, x, bottom - h2/2), fill=(255, 0, 0))
draw.line((x, top + h1/2, x + ll, top + h1/2), fill=(255, 0, 0))
draw.line((x, bottom - h2/2, x + ll, bottom - h2/2), fill=(255, 0, 0))
drawnode(draw, clust.left, x + ll, top + h1/2, scaling, imlist, img)
drawnode(draw, clust.right, x + ll, bottom - h2/2, scaling, imlist, img)
else:
nodeim = Image.open(imlist[clust.id])
# 画出缩略图
nodeim.thumbnail((20, 20))
ns = nodeim.size
print x,y - ns[1]//2
print x + ns[0]
print
img.paste(nodeim, (int(x), int(y - ns[1]//2), int(x + ns[0]),int(y + ns[1] - ns[1]//2)))
imlist = []
folderPath = r'map'
for filename in os.listdir(folderPath):
if os.path.splitext(filename)[1] == '.jpg':
imlist.append(os.path.join(folderPath, filename))
n = len(imlist)
print n
features = np.zeros((n, 3))
for i in range(n):
im = np.array(Image.open(imlist[i]))
R = np.mean(im[:, :, 0].flatten())
G = np.mean(im[:, :, 1].flatten())
B = np.mean(im[:, :, 2].flatten())
features[i] = np.array([R, G, B])
tree = hcluster(features)
drawdendrogram(tree, imlist, jpeg='map.jpg')
在clustering.py文件中编写层次聚类所使用的类及函数.
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8
from numpy import *
"""
层次聚类
"""
# 创建节点类及对应属性
class cluster_mode:
def __init__(self, vec, left = None, right = None, distance =0.0, id = None, count =1):
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.vec = vec
self.id = id
self.distance = distance
self.cont = count
def L2dist(v1 ,v2):
return sqrt(sum((v1 - v2)**2))
def L1dist(v1, v2):
return sum(abs(v1 - v2))
# 传入features为数据矩阵,每一行为一个实例点
def hcluster(features, distance = L2dist):
distances = {}
currentclustid = -1
# 每一点自成一类,按features的行数进行分类
clust = [cluster_mode(array(features[i]), id=i) for i in range(len(features))]
# 当类数大于1时继续循环
while len(clust) > 1:
# 初始化,取前两个点
lowestpair = (0, 1)
closest = distance(clust[0].vec, clust[1].vec)
for i in range(len(clust)):
for j in range(i+1, len(clust)):
if (clust[i].id, clust[j].id) not in distances:
distances[(clust[i].id, clust[j].id)] = distance(clust[i].vec, clust[j].vec)
d = distances[(clust[i].id, clust[j].id)]
# 若当前距离小于最小距离,则将当前距离作为closest
if d < closest:
closest = d
lowestpair = (i, j)
# 通过计算两两之间的平均值来衡量类之间的相似度
mergevec = [(clust[lowestpair[0]].vec[i] + clust[lowestpair[1]].vec[i]) / 2.0
for i in range(len(clust[0].vec))]
# 选最近的距离创建新的节点/类
newcluster = cluster_mode(array(mergevec), left= clust[lowestpair[0]],
right=clust[lowestpair[1]], distance= closest, id= currentclustid)
currentclustid -= 1
# 删除旧的clust并添加新的clust
del clust[lowestpair[1]]
del clust[lowestpair[0]]
clust.append(newcluster)
return clust[0]
# 通过设置阈值dist将cluster取出
def extract_clusters(clust, dist):
clusts = {}
# 若树状结构的distance比给定的阈值小,则直接返回
if clust.distance < dist:
return [clust]
# 若树状结构的distance大于给定阈值,则继续往下看左右的分支节点距离
else:
cl = []
cr = []
# 若节点不为None,则取出其dist,递归返回
if clust.left != None:
cl = extract_clusters(clust.left, dist= dist)
if clust.right != None:
cr = extract_clusters(clust.right, dist= dist)
return cl + cr
# 将cluster中的元素取出
def get_cluster_elements(clust):
if clust.id >= 0:
return [clust.id]
# 若id小于0,进行递归调用
else:
cl = []
cr = []
if clust.left != None:
cl = get_cluster_elements(clust.left)
if clust.right != None:
cr = get_cluster_elements(clust.right)
#
def printclust(clust, labels= None, n= 0):
for i in range(n): print ' ',
# 若当前的id小于0则,当前clust为支点
if clust.id < 0:
print '-'
# 若当前id大于等于0则表示当前节点为枝叶
else:
if labels == None: print clust.id
# 若不为None则打印出其id
else: print labels[clust.id]
# 通过递归的方法将左边和右边的分支都打印出来
if clust.left != None: printclust(clust.left, labels= labels, n= n+1)
if clust.right != None: printclust(clust.right, labels= labels, n= n+1)
# 获取树的高度
def getheight(clust):
# 若树没有左右支点,即只有一个原点,则返回树的高度为1
if clust.left== None and clust.right== None: return 1
# 否则返回左右分支的高度之和
return getheight(clust.left) + getheight(clust.right)
# 获取树的深度
def getdepth(clust):
# 若树没有左右支点,即只有一个原点,则返回树的深度为0
if clust.left== None and clust.right== None: return 0
# 否则返回左右分支的深度最大的一个加上distance
return max(getdepth(clust.left), getdepth(clust.right)) + clust.distance
输出结果为:
110
671.889031583 0
690.889031583
671.889031583 20
691.889031583
726.292592208 44
746.292592208
726.292592208 64
746.292592208
741.216242107 83
761.216242107
741.216242107 104
761.216242107
655.135915648 124
675.135915648
.
.
.
1009.04888336 2123
1029.04888336
1009.04888336 2145
1029.04888336
951.812241088 2163
971.812241088
951.812241088 2180
971.812241088








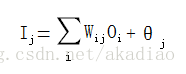
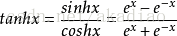
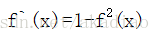
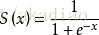
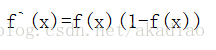
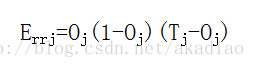
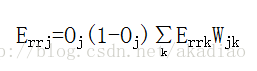
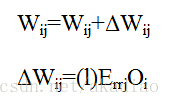















 132
132











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








