Getting Started
Example( 和热相关的):
fever
Breathe on to warm up
Thermal expansion(anomalous expansion of water,低温时,晶格lattice变成六边形,水密度降低、体积膨胀)
the hydrological cycle(the water cyle、the vapor cycle)
Gas stove
ice melt
chocolate melt
Chameleon(靠身体感知周围的温度、阳光、湿度而变色)
anomalous expansion of water and lattice(水膨胀与晶格)
(
H
2
O
H_2O
H2O的密度变化)

冰融化时,Crystal Structure发生变化(六边形->矩形)。

Most substances expand when they get hot and contract when they get cold.
(对水下生命的意义)
Fortunately for the fish , water does not keep contracting. As it cools from 4 ℃ to 0℃, the water expands. This means that the colder water is less dense than the water below it and so it remains at the top. This water continues to cool and eventuallyfreezes. The ice forms at the top of the pond, not the bottom. This means fish can survive in the water
beneath the ice. This property of water is called the anomalous expansion of water.
Unlike most substances,water is less dense as a solid(ice) than it is as liquid.
Most substance are more dense when they are solid and so do not float.
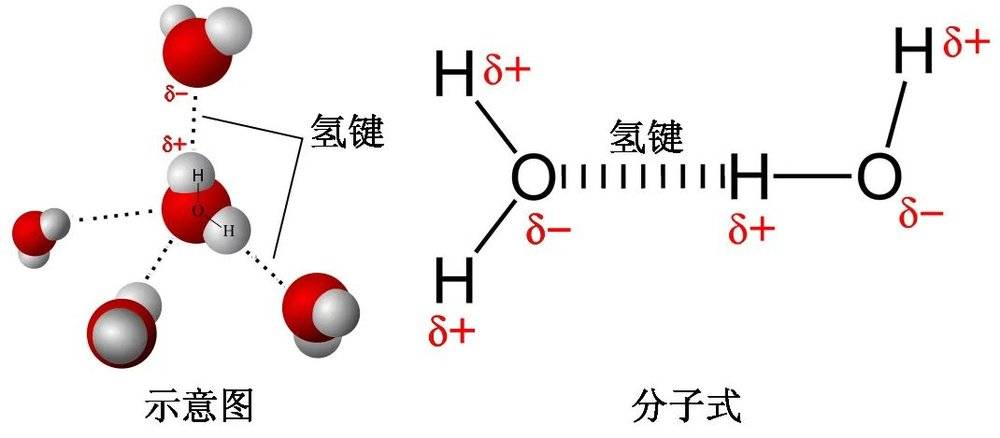
hydrogen bonds(氢键,课本中提到了这个单词,示意如下)
Most substances-solid,liquids and gases - expand when their temperature rises.
This is called thermal expansion.
Thermal expansion happens because the particles gain energy and move faster, push each other further apart.
10.1-Thermal Expansion(热胀冷缩)
The expansion of solids
四个案例:



轮毂(轮子里面的骨架)外面再套一个轮子,热的时候套入,冷缩的时候紧贴
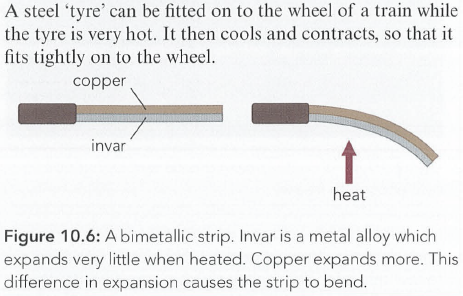
Activity 10.1


低温膨胀的物质有:
水(4°C以下)、锑、铋、镓和青铜等物质
Consequences of expansion

图解如下 :

The expansion of liquids
Examples
案例1:

另外举例水银温度计

汞在常温下是颗粒状。对于细小的管道不容易通过。

由于水银在室温下是颗粒状,所以缩喉工艺(下方管道很细小)让水银温度计在冷缩时无法下降,需要用力甩几下,才能通过缩喉处。
案例2:

由于太热导致的膨胀会让玻璃裂开,所以pyrex指的是一种耐温玻璃(热胀系数比较小)
The expansion of gases
We can explain this using the kinetic model of matter.

课本中Figure10.10中的滑翔翼的举例错误,上升原理并非通过空气热胀冷缩。
Comparing solids,liquids and gases
●Solids expand least when they are heated. Some, such as Pyrex glass and invar metal alloy, have been designed to expand as little as possible
●Liquids generally(≠always,存在反例)expand more than solids.
●Gases expand even more than liquids.
Exception(例外,这里的例外是想说明个别液体也可以膨胀很快)
There are some exceptions to this. For example, liqþid paraffin expands very rapidly on heating. Petrol
(gasoline) is stored in cool underground tanks. If a motorist fills their tank on a hot day, the petrol will heat up and expand. This can cause the fuel to overflow when it expands.
(固体)When a material expands, its particles (atoms or molecules) do not get any bigger. However, they have more energy, so they can move around more and take up more space. It is difficult for the particles of a solid to push their neighbours aside, so a solid does not expand much.
(气体)When a gas is heated, its particles move about more rapidly, and it is easy for them to push the walls of their container further apart, so that the gas takes up.
10.2-Specific heat capacity(比热容)
Energy and temperature
Internal energy(内能) includes both the kinetic energy of the particles and chemical potential energy of the bonds between them.
Energy and temperature are not the same thing.The internal energy
of an object is the total energy of all its particles.
Example:
A cup of tea may have a higher temperature than a bath of warm water,but the energy stored in the bath water is much greater as there are many more water particles.(烫的不一定比凉的总内能大)

Heating water causes the water particles to gain kinetic energy and speed up.It takes more energy to raise the temperature of a large amount of a water because more particles need to have their speed changed.(比热容大,加热费劲)
c
=
Δ
E
m
Δ
θ
c=\frac{\Delta E}{m\Delta \theta}
c=mΔθΔE
(
单位
:
J
/
(
k
g
℃
)
)
(单位:J/(kg℃))
(单位:J/(kg℃))
注意不要写成
J
/
k
g
℃
J/kg℃
J/kg℃
The meaing of specific heat capacity

Values of specific heat capacity for a variety of materials are different.
Table10.1中要注意,water和sea water的specific heat capacity是不一样的
考虑“海水-沙子”情境,水的specific heat capacity很高,沙子的specific heat capacity很低,
那么,那么sea water的specific heat capacity就是在water和sand的specific heat capacity之间。(这样便于记忆)
The specific heat capacity of water
it takes a lot of energy to heat up water
hot water takes a long time to cool down.
Example:
The consequences of this can be seen in our climates In the hot months of summer, the land warms up quickly
(low specific heat capacity) while the sea warms up only slowly. In the winter, the sea cools gradually while the
land cools rapidly. People who live a long way from the sea (in the continental interior of North America or Eurasia, for example) experience freezing winters and very hot summers. People who live on islands and in coastal areas (such as western Europe) are protected from climatic extremes because the sea acts as a store of heat in the winter, and stays relatively cool in the Summer
(比热容解释地面随气候变化温差大,岛国人民四周被海洋围绕,冬暖夏凉)
Experiment Skill 10.2

①水不能子啊100℃附近,以及0℃附近,也不适合再4℃以下测量(晶格发生变化)
②水不能刚好满(容易溢出)
accuracy of your answer(specific heat capacity)
power pack同时在加热heater、thermometer、water,所以测出来的specific heat capacity不准确。
10.3-Changing state(状态改变曲线)

change solid into liquid
①break bonds(potential energy) between molecules or atoms
②overcome the attraction btween the particles.
The boiling and melting points of a substance change if the air pressure changes.
Water has a melting point if 0℃ and a boiling point of 100℃ at standard atmospheric pressure.
This is the pressure at sea level which is about 101.32kPa or 1atmosphere.
At altitude,water boils at a lower temperature.
Investigating a change of state(状态改变特例)

The wax is hotter than its surroundings,so thermal energy is transferred to the surroundings.
As the temperature drops,there’s less difference between the temperature of the wax and its surroundings,so it cools more slowly.
Mercury(汞) is the only metal that is not solid at room temperature.
A mixture of substances may melt or boil over a range of temperatures.(混合物具有多沸点、溶点)
Example:
Candle wax
Dissolving things in water changes the boiling point and freezing point of the water.For example,salty water boils at a higher temperature than pure water and freezes at a lower temperature.(溶质改变沸点、溶点)
Not all substances melt or boil when they are heated.
Some burn,and others decompose(break down) into simpler substances before they have a chance to change state.
Example:
C
a
C
O
3
⇒
高温
C
a
O
+
C
O
2
CaCO_3\xRightarrow{高温}CaO+CO_2
CaCO3高温CaO+CO2🠙
C
u
(
O
H
)
2
⇒
加热
C
u
O
+
H
2
O
Cu(OH)_2\xRightarrow{加热}CuO+H_2O
Cu(OH)2加热CuO+H2O
Evaporation(蒸发的分子动能原理)
A liquid can change state without boiling.
Example:
After it rains,the puddle dry up even though the temperature is much lower than 100℃.The water from the puddles has evaporated.
A liquid evaporates more quickly as its temperature approaches its boiling point.That is why puddles disappear faster on a hot day than a cold day.
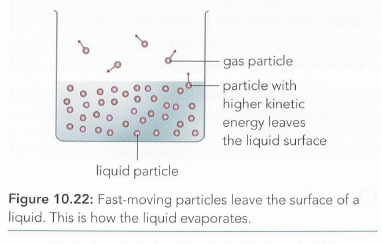
How can we use the kinetic molecular model of matter to explain evaporation? Imagine a beaker of water. The water will gradually evaporate. Figure 10.22 shows the particles that make up the water. The particles of the water are moving around, and some are moving fastcr than others. Some may be moving fast enough to escape
from the surface of the water. They become particles of water vapour in the air. In this way, all of the water particles may eventually escape from the beaker, and the
water will have evaporated. If the temperature of the liquid is higher, more of its particles will havc enough energy to escape. This means the liquid will evaporate more quickly. The hottest particles are most likely to escape as they have most energy. When they escape, the average energy of the remaining particles is less, so the liquid cools down.
Cooling by evaporation(蒸发降温)
If you get wet, perhaps in the rain or after swimming, you will notice that you can quickly get cold. The water
on your body is evaporating, and this cools you down. Why does evaporation make things cooler?
Look again at Figure 10.22. The particles that are ecscaping from the water are the fastest-moving ones. They are the particles with the most kinetic energy. This means that the particles that remain are those with
less energy. Now the particles of the liquid have less energy (on average) and so the temperature of the water
decreases. The water cools down.
Comparing evaporation and boiling(蒸发、沸点对比)
| boiling | evaporation | |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | boiling point | at all temperature |
| energy | kinetic energy of its particles must be increased | Evaporation happens when the most energetic particles escape so evaporation takes energy from the substance |
| location | throughout the liquid | at the surface |
| bubbles | a boiling liquid bubbles | a liquid can evaporate |
Speeding up evaporation(加速蒸发的3个条件)
1、Increasing the temperature
2、Increasing the surface area
3、Blowing air across the surface
Examples
①The sweat evaporates,causing thermal energy to flow from the skin
②The refrigerant liquid absorbs thermal energy from the fridge as it evaporate.
Project(小项目)
①best metal for a pan
low specific heat capacity
②good coolant for the cooling system
Non-combustible and non-explosive
Low toxicity
High specific heat capacity
Not easy to decompose
③different specific heat capacities of sand and water create sea breezes
The specific heat capacity of water is large, and the water in the ocean warms up slowly. In this way, the temperature of sand and gravel on land during the day is much higher than that of water in the ocean. Due to heat transfer, the temperature above land is significantly higher than that above the surface of the ocean. Due to the decrease in density of hot air, the hot air above the land rises, and the relatively cold air above the ocean surface flows to supplement it, forming a sea breeze that blows from the ocean to the land during the day. At night, the seawater and sand that have lost solar thermal radiation must cool down, and the temperature of sand and stone with smaller heat capacity drops even lower. In contrast, the temperature above land is lower than that above seawater. Due to convection, hot air with relatively high temperature above seawater rises, while cold air with relatively low temperature above land sand and gravel flows to the sea surface to supplement. This forms a land breeze that blows from the land to the ocean at night.
In the era without internal combustion engine power, fishermen who lived by the sea for a long time mastered the changing laws of sea and land winds. At dawn, setting sail with the help of the land breeze, to engage in deep-sea fishing operations far from the shore. In the afternoon, I returned with a full load under the sea breeze.
④which type of food store the most thermal energy and so stay hot the longest
Foods with higher heat capacity contain more water or fat.
However, it is important to note that while these types of foods may stay hot longer, they may not be the healthiest options due to their high water and fat content.
























 956
956

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








