车道线检测基础任务(Python实现)
基础任务: 车道线检测
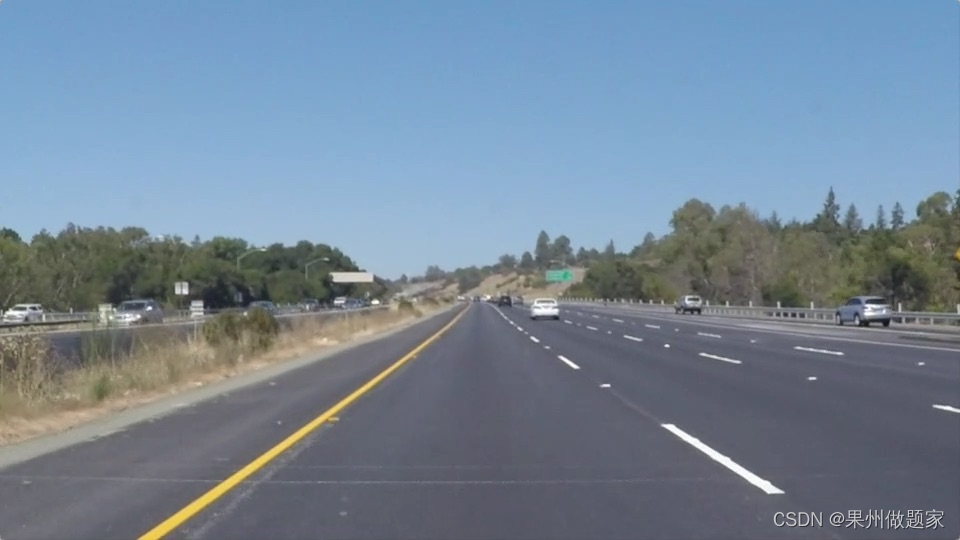

基础任务:实际公路的车道线检测。
任务内容:
1. 在所提供的公路图片上检测出车道线并标记:

2. 在所提供的公路视频上检测出车道线并标记。
解决方案:
要检测出当前车道,就是要检测出左右两条车道直线。由于无人车一直保持在当前车道,那么无人车上的相机拍摄的视频中,车道线的位置应该基本固定在某一个范围内:
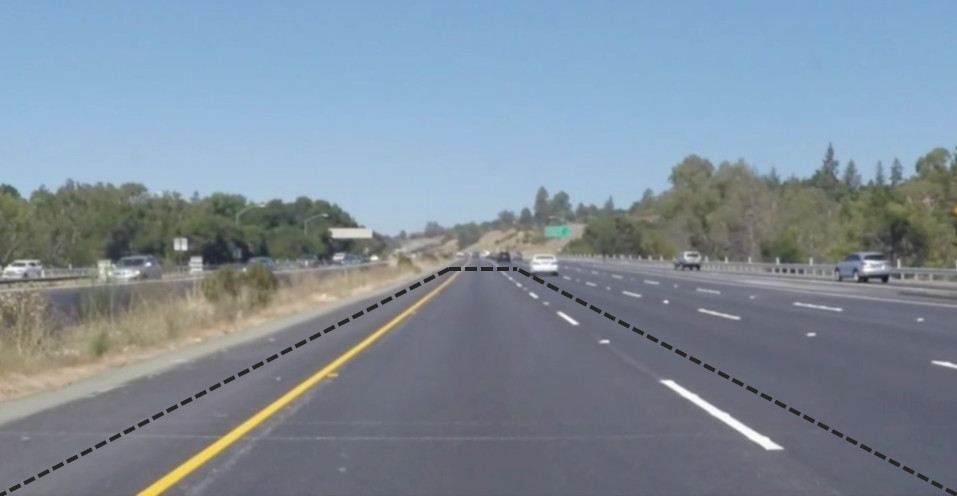

如果我们手动把这部分ROI区域抠出来,就会排除掉大部分干扰。接下来检测直线肯定是用霍夫变换,但ROI区域内的边缘直线信息还是很多,考虑到只有左右两条车道线,一条斜率为正,一条为负,可将所有的线分为两组,每组再通过均值或最小二乘法拟合的方式确定唯一一条线就可以完成检测。总体步骤如下:
- 灰度化
- 高斯模糊
- Canny边缘检测
- 不规则ROI区域截取
- 霍夫直线检测
- 车道计算
对于视频来说,只要一幅图能检查出来,合成下就可以了,问题不大。
1.图像预处理
灰度化和滤波操作是大部分图像处理的必要步骤。灰度化不必多说,因为不是基于色彩信息识别的任务,所以没有必要用彩色图,可以大大减少计算量。而滤波会削弱图像噪点,排除干扰信息。另外,根据前面学习的知识,边缘提取是基于图像梯度的,梯度对噪声很敏感,所以平滑滤波操作必不可少。

这次的代码我们分模块来写,规范一点。其中process_an_image()是主要的图像处理流程:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
# 高斯滤波核大小
blur_ksize = 5
# Canny边缘检测高低阈值
canny_lth = 50
canny_hth = 150
def process_an_image(img):
# 1. 灰度化、滤波和Canny
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
blur_gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (blur_ksize, blur_ksize), 1)
edges = cv2.Canny(blur_gray, canny_lth, canny_hth)
return edges
if __name__ == "__main__":
img = cv2.imread('lane.jpg')
img0 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
im0=Image.fromarray(img0)
display(im0)
result = process_an_image(img)
im=Image.fromarray(result)
display(im)
处理前的图片:

处理后的图片:
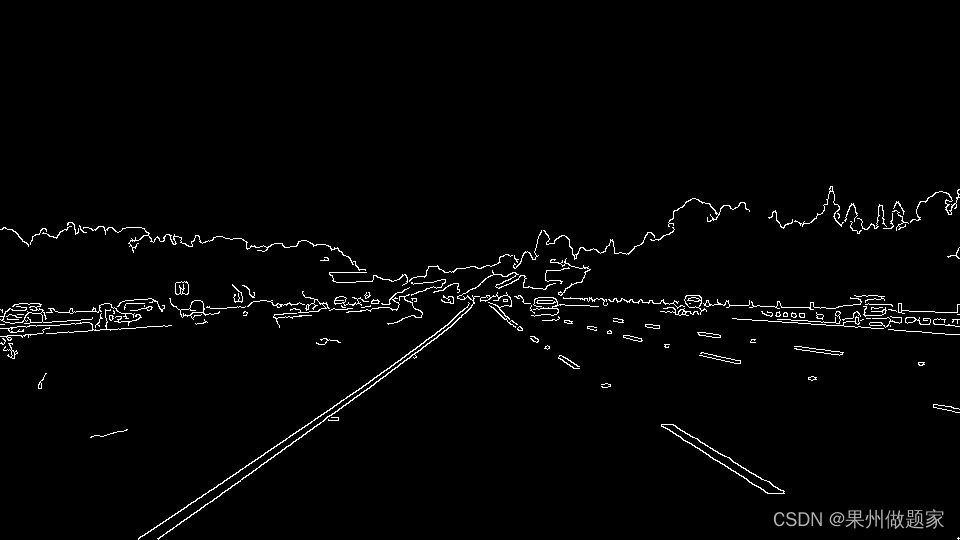

2.ROI截取
按照前面描述的方案,只需保留边缘图中的红线部分区域用于后续的霍夫直线检测,其余都是无用的信息:
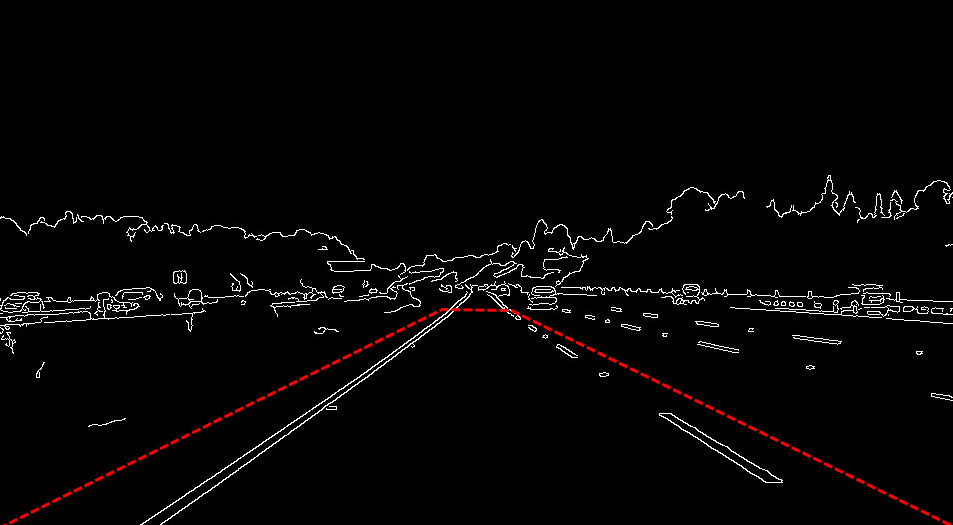
如何实现呢?
我们可以创建一个梯形的mask掩膜,然后与边缘检测结果图混合运算,掩膜中白色的部分保留,黑色的部分舍弃。梯形的四个坐标需要手动标记:

def process_an_image(img):
# 1. 灰度化、滤波和Canny
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
blur_gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (blur_ksize, blur_ksize), 1)
edges = cv2.Canny(blur_gray, canny_lth, canny_hth)
# 2. 标记四个坐标点用于ROI截取
rows, cols = edges.shape
points = np.array([[(0, rows), (460, 325), (520, 325), (cols, rows)]])
# [[[0 540], [460 325], [520 325], [960 540]]]
roi_edges = roi_mask(edges, points)
return roi_edges
def roi_mask(img, corner_points):
# 创建掩膜
mask = np.zeros_like(img)
cv2.fillPoly(mask, corner_points, 255)
masked_img = cv2.bitwise_and(img, mask)
return masked_img
if __name__ == "__main__":
img = cv2.imread('lane.jpg')
result = process_an_image(img)
cv2.imwrite('lane_detection_masked_roi_edges.jpg',result)
im=Image.fromarray(result)
display(im)
这样,结果图"roi_edges"应该是:
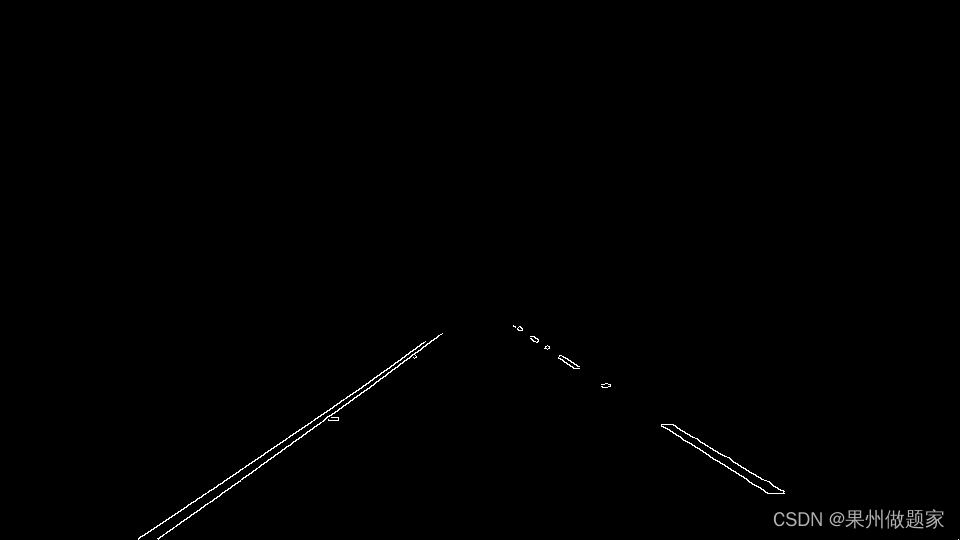
3.霍夫直线提取
为了方便后续计算直线的斜率,我们使用统计概率霍夫直线变换(因为它能直接得到直线的起点和终点坐标)。霍夫变换的参数比较多,可以放在代码开头,便于修改:
# 霍夫变换参数
rho = 1
theta = np.pi / 180
threshold = 15
min_line_len = 40
max_line_gap = 20
def process_an_image(img):
# 1. 灰度化、滤波和Canny
# 2. 标记四个坐标点用于ROI截取
# 3. 霍夫直线提取
drawing, lines = hough_lines(roi_edges, rho, theta, threshold, min_line_len, max_line_gap)
def hough_lines(img, rho, theta, threshold, min_line_len, max_line_gap):
# 统计概率霍夫直线变换
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(img, rho, theta, threshold, minLineLength=min_line_len, maxLineGap=max_line_gap)
# 新建一副空白画布
drawing = np.zeros((img.shape[0], img.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
draw_lines(drawing, lines) # 画出直线检测结果
return drawing, lines
def draw_lines(img, lines, color=[255, 0, 0], thickness=1):
for line in lines:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line:
cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, thickness)
draw_lines()是用来画直线检测的结果,效果如下:
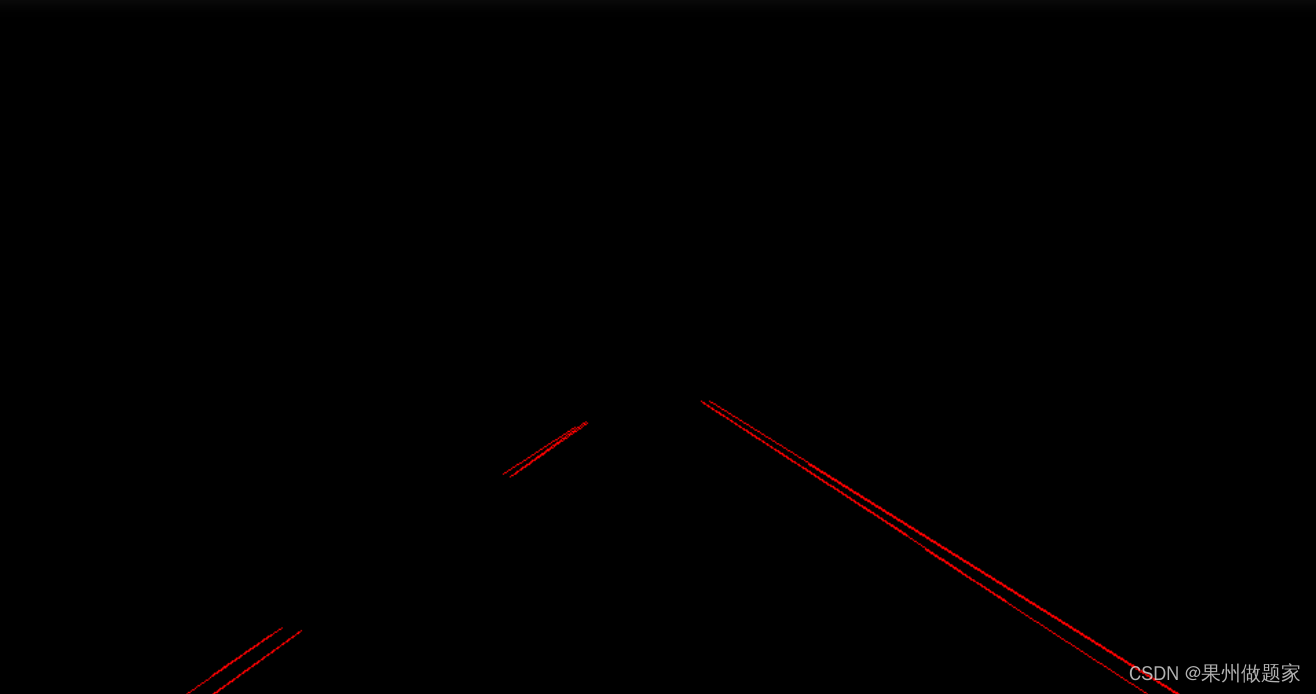

对本例的这张测试图来说,如果打印出直线的条数print(len(lines)),应该是有15条。
4.车道计算
这部分应该算是本次挑战任务的核心内容了:前面通过霍夫变换得到了多条直线的起点和终点,我们的目的是通过某种算法只得到左右两条车道线。
第一步、根据斜率正负划分某条线是左车道还是右车道。
斜 率 = y 2 − y 1 x 2 − x 1 ( ≤ 0 : 左 , > 0 : 右 ) 斜率=\frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}(\leq0:左,>0:右) 斜率=x2−x1y2−y1(≤0:左,>0:右)
经验之谈:再次强调,斜率计算是在图像坐标系下,所以斜率正负/左右跟平面坐标有区别。
第二步、迭代计算各直线斜率与斜率均值的差,排除掉差值过大的异常数据。
注意这里迭代的含义,意思是第一次计算完斜率均值并排除掉异常值后,再在剩余的斜率中取均值,继续排除……这样迭代下去。
第三步、最小二乘法拟合左右车道线。
经过第二步的筛选,就只剩下可能的左右车道线了,这样只需从多条直线中拟合出一条就行。拟合方法有很多种,最常用的便是最小二乘法,它通过最小化误差的平方和来寻找数据的最佳匹配函数。
具体来说,假设目前可能的左车道线有6条,也就是12个坐标点,包括12个x和12个y,我们的目的是拟合出这样一条直线:
f ( x i ) = a x i + b f(x_i) = ax_i+b f(xi)=axi+b
使得误差平方和最小:
E = ∑ ( f ( x i ) − y i ) 2 E=\sum(f(x_i)-y_i)^2 E=∑(f(xi)−yi)2
Python中可以直接使用np.polyfit()进行最小二乘法拟合。
def process_an_image(img):
# 1. 灰度化、滤波和Canny
# 2. 标记四个坐标点用于ROI截取
# 3. 霍夫直线提取
# 4. 车道拟合计算
draw_lanes(drawing, lines)
# 5. 最终将结果合在原图上
result = cv2.addWeighted(img, 0.9, drawing, 0.2, 0)
return result
def draw_lanes(img, lines, color=[255, 0, 0], thickness=8):
# a. 划分左右车道
left_lines, right_lines = [], []
for line in lines:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line:
k = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
if k < 0:
left_lines.append(line)
else:
right_lines.append(line)
if (len(left_lines) <= 0 or len(right_lines) <= 0):
return
# b. 清理异常数据
clean_lines(left_lines, 0.1)
clean_lines(right_lines, 0.1)
# c. 得到左右车道线点的集合,拟合直线
left_points = [(x1, y1) for line in left_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
left_points = left_points + [(x2, y2) for line in left_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
right_points = [(x1, y1) for line in right_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
right_points = right_points + [(x2, y2) for line in right_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
left_results = least_squares_fit(left_points, 325, img.shape[0])
right_results = least_squares_fit(right_points, 325, img.shape[0])
# 注意这里点的顺序
vtxs = np.array([[left_results[1], left_results[0], right_results[0], right_results[1]]])
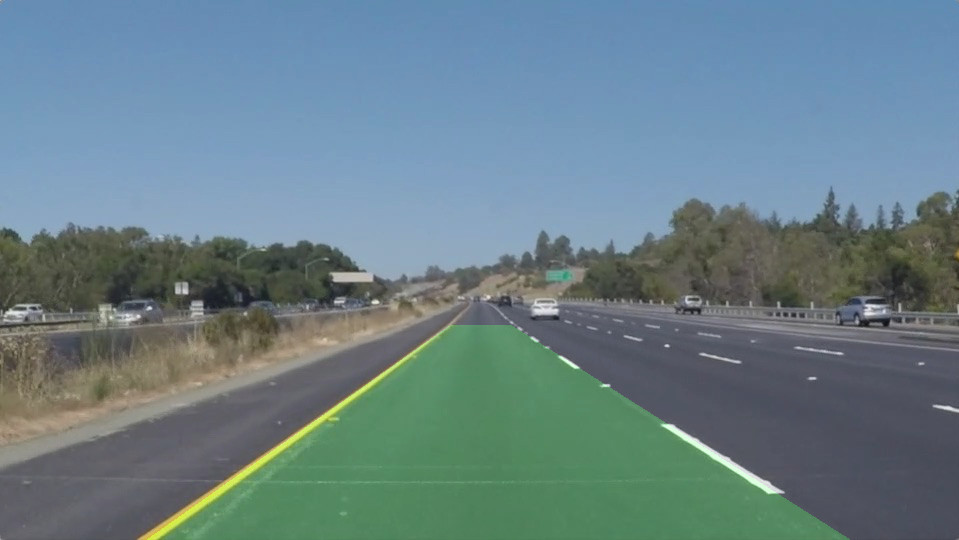
# d. 填充车道区域
cv2.fillPoly(img, vtxs, (0, 255, 0))
# 或者只画车道线
# cv2.line(img, left_results[0], left_results[1], (0, 255, 0), thickness)
# cv2.line(img, right_results[0], right_results[1], (0, 255, 0), thickness)
def clean_lines(lines, threshold):
# 迭代计算斜率均值,排除掉与差值差异较大的数据
slope = [(y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) for line in lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
while len(lines) > 0:
mean = np.mean(slope)
diff = [abs(s - mean) for s in slope]
idx = np.argmax(diff)
if diff[idx] > threshold:
slope.pop(idx)
lines.pop(idx)
else:
break
def least_squares_fit(point_list, ymin, ymax):
# 最小二乘法拟合
x = [p[0] for p in point_list]
y = [p[1] for p in point_list]
# polyfit第三个参数为拟合多项式的阶数,所以1代表线性
fit = np.polyfit(y, x, 1)
fit_fn = np.poly1d(fit) # 获取拟合的结果
xmin = int(fit_fn(ymin))
xmax = int(fit_fn(ymax))
return [(xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax)]
这段代码比较多,请每个步骤单独来看。最后得到的是左右两条车道线的起点和终点坐标,可以选择画出车道线,这里我们直接填充了整个区域:
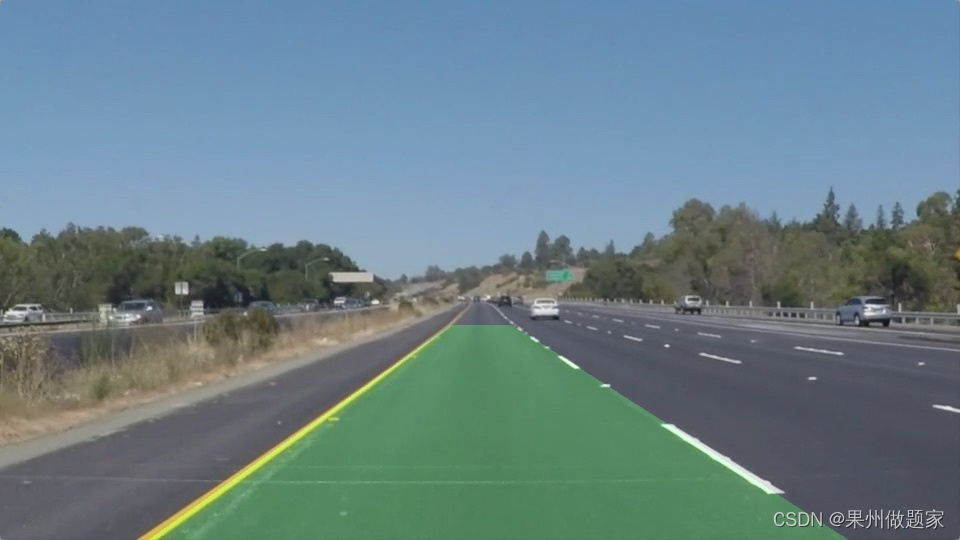

完整代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
# 高斯滤波核大小
blur_ksize = 5
# Canny边缘检测高低阈值
canny_lth = 50
canny_hth = 150
# 霍夫变换参数
rho = 1
theta = np.pi / 180
threshold = 15
min_line_len = 40
max_line_gap = 20
def process_an_image(img):
# 1. 灰度化、滤波和Canny
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
blur_gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (blur_ksize, blur_ksize), 1)
edges = cv2.Canny(blur_gray, canny_lth, canny_hth)
# 2. 标记四个坐标点用于ROI截取
rows, cols = edges.shape
points = np.array([[(0, rows), (460, 325), (520, 325), (cols, rows)]])
# [[[0 540], [460 325], [520 325], [960 540]]]
roi_edges = roi_mask(edges, points)
# 3. 霍夫直线提取
drawing, lines = hough_lines(roi_edges, rho, theta,
threshold, min_line_len, max_line_gap)
# 4. 车道拟合计算
draw_lanes(drawing, lines)
# 5. 最终将结果合在原图上
result = cv2.addWeighted(img, 0.9, drawing, 0.2, 0)
return result
def roi_mask(img, corner_points):
# 创建掩膜
mask = np.zeros_like(img)
cv2.fillPoly(mask, corner_points, 255)
masked_img = cv2.bitwise_and(img, mask)
return masked_img
def hough_lines(img, rho, theta, threshold, min_line_len, max_line_gap):
# 统计概率霍夫直线变换
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(img, rho, theta, threshold,
minLineLength=min_line_len, maxLineGap=max_line_gap)
# 新建一副空白画布
drawing = np.zeros((img.shape[0], img.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 画出直线检测结果
# draw_lines(drawing, lines)
return drawing, lines
def draw_lines(img, lines, color=[0, 0, 255], thickness=1):
for line in lines:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line:
cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, thickness)
def draw_lanes(img, lines, color=[255, 0, 0], thickness=8):
# a. 划分左右车道
left_lines, right_lines = [], []
for line in lines:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line:
k = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
if k < 0:
left_lines.append(line)
else:
right_lines.append(line)
if (len(left_lines) <= 0 or len(right_lines) <= 0):
return
# b. 清理异常数据
clean_lines(left_lines, 0.1)
clean_lines(right_lines, 0.1)
# c. 得到左右车道线点的集合,拟合直线
left_points = [(x1, y1) for line in left_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
left_points = left_points + [(x2, y2)
for line in left_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
right_points = [(x1, y1)
for line in right_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
right_points = right_points + \
[(x2, y2) for line in right_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
left_results = least_squares_fit(left_points, 325, img.shape[0])
right_results = least_squares_fit(right_points, 325, img.shape[0])
# 注意这里点的顺序
vtxs = np.array(
[[left_results[1], left_results[0], right_results[0], right_results[1]]])
# d.填充车道区域
cv2.fillPoly(img, vtxs, (0, 255, 0))
# 或者只画车道线
# cv2.line(img, left_results[0], left_results[1], (0, 255, 0), thickness)
# cv2.line(img, right_results[0], right_results[1], (0, 255, 0), thickness)
def clean_lines(lines, threshold):
# 迭代计算斜率均值,排除掉与差值差异较大的数据
slope = [(y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
for line in lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
while len(lines) > 0:
mean = np.mean(slope)
diff = [abs(s - mean) for s in slope]
idx = np.argmax(diff)
if diff[idx] > threshold:
slope.pop(idx)
lines.pop(idx)
else:
break
def least_squares_fit(point_list, ymin, ymax):
# 最小二乘法拟合
x = [p[0] for p in point_list]
y = [p[1] for p in point_list]
# polyfit第三个参数为拟合多项式的阶数,所以1代表线性
fit = np.polyfit(y, x, 1)
fit_fn = np.poly1d(fit) # 获取拟合的结果
xmin = int(fit_fn(ymin))
xmax = int(fit_fn(ymax))
return [(xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax)]
if __name__ == "__main__":
img = cv2.imread('test_pictures/lane.jpg')
result = process_an_image(img)
img0 = cv2.cvtColor(np.hstack((img, result)), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
im=Image.fromarray(img0)
display(im)

5.视频处理
搞定了一张图,视频也就没什么问题了,关键就是视频帧的提取和合成,为此,我们要用到Python的视频编辑包moviepy:
pip install moviepy
另外还需要ffmpeg,首次运行moviepy时会自动下载,也可手动下载。
# 开头导入moviepy
from moviepy.editor import VideoFileClip
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 高斯滤波核大小
blur_ksize = 5
# Canny边缘检测高低阈值
canny_lth = 50
canny_hth = 150
# 霍夫变换参数
rho = 1
theta = np.pi / 180
threshold = 15
min_line_len = 40
max_line_gap = 20
def process_an_image(img):
# 1. 灰度化、滤波和Canny
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
blur_gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (blur_ksize, blur_ksize), 1)
edges = cv2.Canny(blur_gray, canny_lth, canny_hth)
# 2. 标记四个坐标点用于ROI截取
rows, cols = edges.shape
points = np.array([[(0, rows), (460, 325), (520, 325), (cols, rows)]])
# [[[0 540], [460 325], [520 325], [960 540]]]
roi_edges = roi_mask(edges, points)
# 3. 霍夫直线提取
drawing, lines = hough_lines(roi_edges, rho, theta,
threshold, min_line_len, max_line_gap)
# 4. 车道拟合计算
draw_lanes(drawing, lines)
# 5. 最终将结果合在原图上
result = cv2.addWeighted(img, 0.9, drawing, 0.2, 0)
return result
def roi_mask(img, corner_points):
# 创建掩膜
mask = np.zeros_like(img)
cv2.fillPoly(mask, corner_points, 255)
masked_img = cv2.bitwise_and(img, mask)
return masked_img
def hough_lines(img, rho, theta, threshold, min_line_len, max_line_gap):
# 统计概率霍夫直线变换
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(img, rho, theta, threshold,
minLineLength=min_line_len, maxLineGap=max_line_gap)
# 新建一副空白画布
drawing = np.zeros((img.shape[0], img.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 画出直线检测结果
# draw_lines(drawing, lines)
return drawing, lines
def draw_lines(img, lines, color=[0, 0, 255], thickness=1):
for line in lines:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line:
cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, thickness)
def draw_lanes(img, lines, color=[255, 0, 0], thickness=8):
# a. 划分左右车道
left_lines, right_lines = [], []
for line in lines:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line:
k = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
if k < 0:
left_lines.append(line)
else:
right_lines.append(line)
if (len(left_lines) <= 0 or len(right_lines) <= 0):
return
# b. 清理异常数据
clean_lines(left_lines, 0.1)
clean_lines(right_lines, 0.1)
# c. 得到左右车道线点的集合,拟合直线
left_points = [(x1, y1) for line in left_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
left_points = left_points + [(x2, y2)
for line in left_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
right_points = [(x1, y1)
for line in right_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
right_points = right_points + \
[(x2, y2) for line in right_lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
left_results = least_squares_fit(left_points, 325, img.shape[0])
right_results = least_squares_fit(right_points, 325, img.shape[0])
# 注意这里点的顺序
vtxs = np.array(
[[left_results[1], left_results[0], right_results[0], right_results[1]]])
# d.填充车道区域
cv2.fillPoly(img, vtxs, (0, 255, 0))
# 或者只画车道线
# cv2.line(img, left_results[0], left_results[1], (0, 255, 0), thickness)
# cv2.line(img, right_results[0], right_results[1], (0, 255, 0), thickness)
def clean_lines(lines, threshold):
# 迭代计算斜率均值,排除掉与差值差异较大的数据
slope = [(y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
for line in lines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line]
while len(lines) > 0:
mean = np.mean(slope)
diff = [abs(s - mean) for s in slope]
idx = np.argmax(diff)
if diff[idx] > threshold:
slope.pop(idx)
lines.pop(idx)
else:
break
def least_squares_fit(point_list, ymin, ymax):
# 最小二乘法拟合
x = [p[0] for p in point_list]
y = [p[1] for p in point_list]
# polyfit第三个参数为拟合多项式的阶数,所以1代表线性
fit = np.polyfit(y, x, 1)
fit_fn = np.poly1d(fit) # 获取拟合的结果
xmin = int(fit_fn(ymin))
xmax = int(fit_fn(ymax))
return [(xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax)]
# 主函数:
if __name__ == "__main__":
output = 'my_output.mp4' #输出视频文件
clip = VideoFileClip("cv2_yellow_lane.mp4") #输入视频文件
out_clip = clip.fl_image(process_an_image)
out_clip.write_videofile(output, audio=False)
处理前视频:
v
处理后视频:
车道线检测处理结果视频2
完整代码及资源下载
https://download.csdn.net/download/baidu/85651043
























 2239
2239











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








