等待与通知模式实现一个简单的连接池,直接上代码
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* 使用等待通知实现一个简单的数据库连接池
*
* @author ckj
*
*/
public class DbPool {
/* 定义一个容器用做数据库连接池,由于数据库连接多做获取与释放操作所有选用LinkedList,池化技术与队列技术会在后续章节演示 */
public LinkedList<Connection> connectionPool = new LinkedList<Connection>();
public DbPool(int poolSize) {
if (poolSize > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
connectionPool.addLast( new Connection());
}
}
}
/* 归还连接,使用完连接后将连接重新放入池中 */
/* 使用notifyAll 通知等待线程获取 */
public void reConnection(Connection connection) {
if (connection != null) {
synchronized (connectionPool) {
// 将连接放到最后
connectionPool.addLast(connection);
connectionPool.notifyAll();
}
}
}
/**
* 获取连接 1、连接池中有连接直接返回 2、连接池中无连接切设置等待时间为负数 wait无限等待 3、连接池中无连接切设置等待时间 wait
* 按设置时间等待,被唤醒后需要如果没有抢到锁则重新计算等待时间,重新等待
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public Connection getConnection(long expireMills) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (connectionPool) {
// 连接池中无连接切设置等待时间为负数 wait无限等待
if (expireMills < 0) {
while (connectionPool.isEmpty()) {
connectionPool.wait();
}
return connectionPool.removeFirst();
} else {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis() + expireMills;
long waitTime = expireMills;
while (connectionPool.isEmpty() && waitTime > 0) {
connectionPool.wait(waitTime);
// 重新计算
waitTime = time - System.currentTimeMillis();
}
Connection connection = null;
if (!connectionPool.isEmpty()) {
// 从头部获取连接
connection = connectionPool.removeFirst();
}
return connection;
}
}
}
class Connection {
}
}
测试代码:测试代码中使用到了一些并发工具类,后续章节会说明
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import com.ckj.concurrent.DbPool.Connection;
/**
* 1、初始化线程池大小 2、模拟多线程测试拿取线程池
*
* @author ckj
*
*/
public class DbPoolTest {
static DbPool pool = new DbPool(10);
static CountDownLatch latch; // 并发工具类,闭锁,模拟多线程并发测试
static class PoolTest implements Runnable {
int count;
AtomicInteger success;
AtomicInteger error;
public PoolTest(int count, AtomicInteger success, AtomicInteger error) {
this.count = count;
this.success = success;
this.error = error;
}
public void run() {
while (count > 0) {
try {
// 获取线程池
Connection connection = pool.getConnection(1000);
if (connection != null) {
try {
// 模拟业务代码执行
Thread.sleep(100);
} finally {
// TODO: handle finally clause
pool.reConnection(connection);
success.incrementAndGet();
}
} else {
error.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "等待超时!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
count--;
}
}
latch.countDown(); // 执行闭锁
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
latch = new CountDownLatch(50);
AtomicInteger success = new AtomicInteger();// 原子类计数器:统计可以拿到连接的线程(后续会介绍到)
AtomicInteger error = new AtomicInteger();// 原子类计数器:统计没有拿到连接的线程(后续会介绍到)
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new PoolTest(20, success, error));
thread.start();
}
latch.await();
System.out.println("总共尝试了: " + (50 * 20));
System.out.println("拿到连接的次数: " + success);
System.out.println("没能连接的次数: " + error);
}
注:在做测试的时候遇到了一个有趣的问题:
当代码执行到 pool.reConnection(connection); 之后发现下一句不执行了 也就是这句success.incrementAndGet(),当时找了半天结果发现是 DbPool 中的notifyAll(),没有加上对象导致的,在此记录一下,需要谨记wait/notify 的使用范式;
/* 归还连接,使用完连接后将连接重新放入池中 */
/* 使用notifyAll 通知等待线程获取 */
public void reConnection(Connection connection) {
if (connection != null) {
synchronized (connectionPool) {
// 将连接放到最后
connectionPool.addLast(connection);
//使用错误:应该按照范式 对象.notifyAll()
notifyAll();
}
}
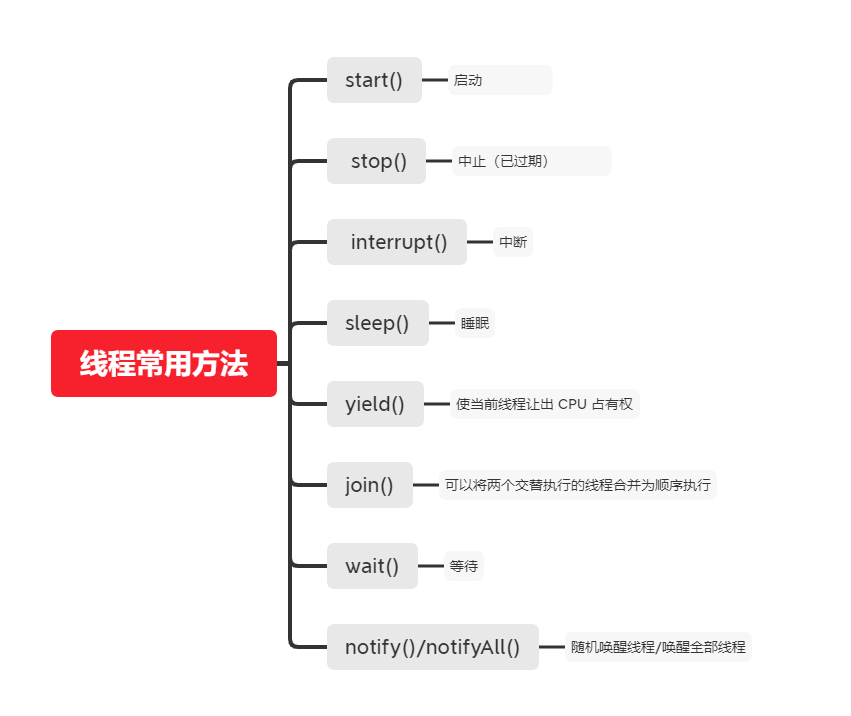
} 在网上找到了一个总结线程协作的流程图,感觉总结的相当到位。

抛出一个问题:
yield() 、sleep()、wait()、notify()等方法对锁有何影响?






















 222
222











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








