什么是 Assistants API
顾名思义就是助手 API, 你可以在 OpenAI 官网添加一个智能体,这个智能体就是 assistant,如何想集成这个 assistant 到你的应用中就是通过 Assistants API。本质上就是接口调用。
Assistants API 的特点
- 创建和管理 assistant,每个 assistant 有独立的配置
- 支持无限长的多轮对话,对话历史保存在 OpenAI 的服务器上
- 通过自有向量数据库支持基于文件的 RAG
- 支持 Code Interpreter
- 在沙箱里编写并运行 Python 代码
- 自我修正代码
- 可传文件给 Code Interpreter
- 支持 Function Calling
- 支持在线调试的 Playground
即将具备的能力:
- 支持 DALL·E
- 支持图片消息
- 支持自定义调整 RAG 的配置项
收费:
- 按 token 收费。无论多轮对话,还是 RAG,所有都按实际消耗的 token 收费
- 如果对话历史过多超过大模型上下文窗口,会自动放弃最老的对话消息
- 文件按数据大小和存放时长收费。1 GB 向量存储 一天收费 0.10 美元
- Code interpreter 跑一次 $0.03
接下来直接进入正题,先介绍 AssistantsAPI,然后通多实例展示
安装 openai
pip install openai
创建一个 Assistant
可以在代码用创建
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
from openai import OpenAI
load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
client = OpenAI()
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
name="Food Assistant",
instructions="你是美食家,擅长美食,擅长美食的问答,你负责回答与美食相关的问题。",
model="gpt-4o"
)也可以到官网去手动创建:https://platform.openai.com/playground?mode=assistant
对话历史 Thread
注意,这里的 thread 不是我们程序员理解的那个线程的概念,这里是报错对话历史的工具
- Threads 里保存的是对话历史,即 messages
- 一个 assistant 可以有多个 thread
- 一个 thread 可以有无限条 message
- 一个用户与 assistant 的多轮对话历史可以维护在一个 thread 里
创建方式:
# 创建 thread
thread = client.beta.threads.create()我们写一个函数用来打印生成的对象里面到底有些什么属性
import json
def show_json(obj):
"""把任意对象用排版美观的 JSON 格式打印出来"""
print(json.dumps(
json.loads(obj.model_dump_json()),
indent=4,
ensure_ascii=False
))接下来打印一下这个 thread
show_json(thread)
输出:
{
"id": "thread_UmmMZHrQy6QHpguE4YoKUlia",
"created_at": 1718886745,
"metadata": {},
"object": "thread",
"tool_resources": {
"code_interpreter": null,
"file_search": null
}
}给对话历史加上标记
前面说了,thread 是用来保存对话历史的,那么不同的用户应该会有不同的对话历史,如何给 thread 做好标记呢?答案就是 metadata
thread = client.beta.threads.create(
metadata={"fullname": "IT民工老包", "username": "bj"}
)
show_json(thread)
输出:
{
"id": "thread_ZO9PbLBA4sHJdsseshprusi",
"created_at": 1718896823,
"metadata": {
"fullname": "IT民工老包",
"username": "bj"
},
"object": "thread",
"tool_resources": {
"code_interpreter": null,
"file_search": null
}
}thread.id 可以保存到数据库
thread.id 是可以保存到应用数据库中,当用户发起下一次的对话时,可以通过 thread.id 获取到原先创建的 thread 对象:
thread = client.beta.threads.retrieve(thread.id)
show_json(thread)
输出:
{
"id": "thread_ZO9PbLBA4sHJdsseshprusi",
"created_at": 1718896823,
"metadata": {
"fullname": "IT民工老包",
"username": "bj"
},
"object": "thread",
"tool_resources": {
"code_interpreter": null,
"file_search": null
}
}其他的方法:
threads.modify()修改 thread 的metadata和tool_resourcesthreads.retrieve()获取 threadthreads.delete()删除 thread。
用户消息添加
thread 是消息历史,我们可以往 thread 添加用户消息来实现对话,就跟在 ChatGPT 输入框中输入消息一样,只是现在我们是通过代码实现
message = client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id, # message 必须归属于一个 thread
role="user", # 取值是 user 或者 assistant。但 assistant 消息会被自动加入,我们一般不需要自己构造
content="你都能做什么?",
)
show_json(message)
输出:
{
"id": "msg_gsVBEkeRHXdpOmMwxGApkLVU",
"assistant_id": null,
"attachments": [],
"completed_at": null,
"content": [
{
"text": {
"annotations": [],
"value": "你能做什么?"
},
"type": "text"
}
],
"created_at": 1719195090,
"incomplete_at": null,
"incomplete_details": null,
"metadata": {
"fullname": "IT民工老包",
"username": "baoj2010"
},
"object": "thread.message",
"role": "user",
"run_id": null,
"status": null,
"thread_id": "thread_rRqbAUhg6Pate2p9wv9fe8wN"
}当然创建消息可以在 thread create 的时候就以参数的方式传入也可以
thread = client.beta.threads.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "你好",
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "有什么可以帮您?",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "你是谁?",
},
]
)其他函数:
threads.messages.retrieve()获取 messagethreads.messages.update()更新 message 的metadatathreads.messages.list()列出给定 thread 下的所有 messages具体文档参考:https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/messages
开始对话
创建 run
用户每输入一次消息就需要让 gpt 跑一次,这就是 run
run 需要手动创建,需要关联上 thread 以及 assistant
run = client.beta.threads.runs.create_and_poll(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant.id,
)
获取消息:
if run.status == 'completed':
messages = client.beta.threads.messages.list(
thread_id=thread.id
)
show_json(messages)
else:
print(run.status)
输出:
{
"data": [
{
"id": "msg_eSObrKHxiYJZTW4a51u0cjCn",
"assistant_id": "asst_MKmn4iLMrb8EMKgJiUW3tmlk",
"attachments": [],
"completed_at": null,
"content": [
{
"text": {
"annotations": [],
"value": "作为一个美食家,我可以为你提供以下服务:\n\n1. **食谱推荐**:根据你的口味和需求,提供适合的食谱。\n2. **烹饪技巧**:分享各类烹饪技巧和注意事项,帮助你提升厨艺。\n3. **食材介绍**:详细介绍各种食材的特点、选购技巧以及使用方法。\n4. **餐厅推荐**:根据你的偏好,推荐优质的餐厅或美食场所。\n5. **美食文化**:分享不同文化中的美食习俗和独特的食品风味。\n6. **饮食健康建议**:提供营养搭配建议,帮助你在享受美食的同时保持健康。\n\n如果你有任何美食相关的问题,随时告诉我!"
},
"type": "text"
}
],
"created_at": 1719196342,
"incomplete_at": null,
"incomplete_details": null,
"metadata": [],
"object": "thread.message",
"role": "assistant",
"run_id": "run_oMiWMqVnKvTzQUahuJdWEr2V",
"status": null,
"thread_id": "thread_bdj1G6SBwGkWzoHXYlrU91Mm"
},
{
"id": "msg_OFKFvgFo9UYGHN0SyDvTo63I",
"assistant_id": null,
"attachments": [],
"completed_at": null,
"content": [
{
"text": {
"annotations": [],
"value": "你能做什么?"
},
"type": "text"
}
],
"created_at": 1719196340,
"incomplete_at": null,
"incomplete_details": null,
"metadata": {
"fullname": "IT民工老包",
"username": "baoj2010"
},
"object": "thread.message",
"role": "user",
"run_id": null,
"status": null,
"thread_id": "thread_bdj1G6SBwGkWzoHXYlrU91Mm"
}
],
"object": "list",
"first_id": "msg_eSObrKHxiYJZTW4a51u0cjCn",
"last_id": "msg_OFKFvgFo9UYGHN0SyDvTo63I",
"has_more": false
}
run 的状态
run 的底层是一个异步调用,意味着 ta 不等大模型处理完就返回了,所以我们通过 run.status 来确定大模型的工作状况,来判定下一步该干什么。
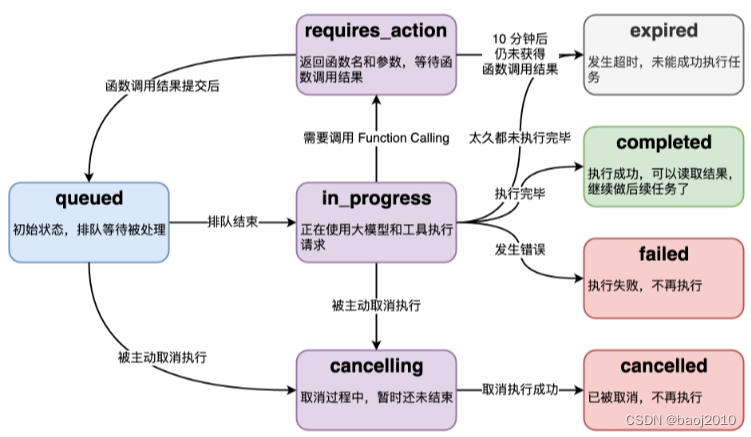
流式运行
from openai import AssistantEventHandler
class EventHandler(AssistantEventHandler):
def on_text_created(self, text: Text) -> None:
"""响应输出创建事件"""
print(f"\nassistant > ", end="\n", flush=True)
def on_text_delta(self, delta: TextDelta, snapshot: Text) -> None:
"""响应输出生成的流片段"""
print(delta.value, end="", flush=True)再来添加一条消息:
# 添加新一轮的 user message
message = client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
role="user",
content="番茄炒鸡蛋怎么做?",
)
# 使用 stream 接口并传入 EventHandler
with client.beta.threads.runs.stream(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant_id,
event_handler=EventHandler(),
) as stream:
stream.until_done()
输出:
run 的其他函数
threads.runs.list()列出 thread 归属的 runthreads.runs.retrieve()获取 runthreads.runs.update()修改 run 的 metadatathreads.runs.cancel()取消in_progress状态的 run
更强的功能
创建 Assistant 时声明 Code_Interpreter
load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
client = OpenAI()
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
name="Food Assistant",
instructions="你是人工智能助手。你可以通过代码回答很多数学问题。",
tools=[{"type": "code_interpreter"}],
model="gpt-4o"
)在回调中添加 code_interpreter 的事件响应
class EventHandler(AssistantEventHandler):
def on_text_created(self, text: Text) -> None:
print(f"\nassistant > ", end="\n", flush=True)
def on_text_delta(self, delta: TextDelta, snapshot: Text) -> None:
print(delta.value, end="", flush=True)
def on_tool_call_created(self, tool_call: ToolCall) -> None:
print(f"\nassistant > {tool_call.type}", flush=True)
def on_tool_call_delta(self, delta: ToolCallDelta, snapshot: ToolCall) -> None:
if delta.type == "code_interpreter":
if delta.code_interpreter.input:
print(delta.code_interpreter.input, end="", flush=True)
if delta.code_interpreter.outputs:
print(f"\n\noutput > ", flush=True)
for output in delta.code_interpreter.outputs:
if output.type == "logs":
print(f"\n{output.logs}", flush=True)尝试一下
thread = client.beta.threads.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "用代码计算斐波那契数列的第 20 位"
}
]
)
with client.beta.threads.runs.stream(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant.id,
event_handler=EventHandler()
) as stream:
stream.until_done()输出:
assistant >
斐波那契数列(Fibonacci sequence)是由意大利数学家莱昂纳多·斐波那契在他的《计算之书》中首先引入的。这个数列从0和1开始,接下来的每一项都是前两项之和。其一般形式为:
\[ F(0) = 0 \]
\[ F(1) = 1 \]
\[ F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2) \]让我们用一个简单的 Python 函数来计算斐波那契数列的第 20 位。
assistant > code_interpreter
def fibonacci(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
else:
a, b = 0, 1
for _ in range(2, n + 1):
a, b = b, a + b
return b# 计算斐波那契数列的第 20 位
fibonacci_20 = fibonacci(20)
fibonacci_20
assistant >
斐波那契数列的第 20 位是 6765。
Process finished with exit code 0
自愧不如,比我写得好
操作文件
load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
client = OpenAI()
# 上传文件到 OpenAI
file = client.files.create(
file=open("D:/abcd.csv", "rb").read(),
purpose="assistants"
)
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
name="CodeInterpreterWithFileDemo",
instructions="你是数据分析师,按要求分析数据。",
model="gpt-4o",
tools=[{"type": "code_interpreter"}],
tool_resources={
"code_interpreter": {
"file_ids": [file.id] # 为 code_interpreter 关联文件
}
}
)
thread = client.beta.threads.create()
while 1:
print("=====已知文件:abcd.csv")
query = input("一致文件user > 请输入你的问题:")
message = client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
role="user",
content=query
)
with client.beta.threads.runs.stream(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant.id,
event_handler=EventHandler() # 用前面定义好的
) as stream:
stream.until_done()其他文件相关函数
client.files.list()列出所有文件client.files.retrieve()获取文件对象client.files.delete()删除文件client.files.content()读取文件内容
Function Calling
接下来就不演示了,直贴代码,兄弟们遇到问题可以私信我
定义 assistant
load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
client = OpenAI()
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
instructions="你叫瓜瓜。你是天气助手。每次回答问题前,你要拆解问题并输出一步一步的思考过程。",
model="gpt-4o",
tools=[
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "query_weather",
"description": "用于查看天气信息。Function输入必须是一个城市名。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名"
}
},
"required": [
"city"
]
}
}
}
]
)自定义函数
def query_weather(city):
if city == "上海":
res = {
"temperature": 25,
"condition": "Sunny"
}
elif city == "北京":
res = {
"temperature": 19,
"condition": "Rainy"
}
else:
res = {
"temperature": 20,
"condition": "Windy"
}
return json.dumps(res)
context = {
"query_weather": query_weather
}添加回调事件响应
class EventHandler(AssistantEventHandler):
def on_text_created(self, text) -> None:
"""响应回复创建事件"""
print(f"\nassistant > ", end="", flush=True)
def on_text_delta(self, delta, snapshot):
"""响应输出生成的流片段"""
print(delta.value, end="", flush=True)
def on_tool_call_created(self, tool_call):
"""响应工具调用"""
print(f"\nassistant > {tool_call.type}\n", flush=True)
def on_tool_call_delta(self, delta, snapshot):
"""响应工具调用的流片段"""
if delta.type == 'code_interpreter':
if delta.code_interpreter.input:
print(delta.code_interpreter.input, end="", flush=True)
if delta.code_interpreter.outputs:
print(f"\n\noutput >", flush=True)
for output in delta.code_interpreter.outputs:
if output.type == "logs":
print(f"\n{output.logs}", flush=True)
def on_event(self, event):
"""
响应 'requires_action' 事件
"""
if event.event == 'thread.run.requires_action':
run_id = event.data.id # 获取 run ID
self.handle_requires_action(event.data, run_id)
def handle_requires_action(self, data, run_id):
tool_outputs = []
for tool in data.required_action.submit_tool_outputs.tool_calls:
arguments = json.loads(tool.function.arguments)
print(
f"{tool.function.name}({arguments})",
flush=True
)
# 运行 function
tool_outputs.append({
"tool_call_id": tool.id,
"output": context[tool.function.name](**arguments)}
)
# 提交 function 的结果,并继续运行 run
self.submit_tool_outputs(tool_outputs, run_id)
def submit_tool_outputs(self, tool_outputs, run_id):
"""提交function结果,并继续流"""
print("=============test======", tool_outputs, run_id)
with client.beta.threads.runs.submit_tool_outputs_stream(
thread_id=self.current_run.thread_id,
run_id=self.current_run.id,
tool_outputs=tool_outputs,
event_handler=EventHandler(),
) as stream:
stream.until_done()
输出响应:
thread = client.beta.threads.create()
while True:
# 添加 user message
query = input("user:")
message = client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
role="user",
content=query,
)
# 使用 stream 接口并传入 EventHandler
with client.beta.threads.runs.stream(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant.id,
event_handler=EventHandler(),
) as stream:
stream.until_done()内置的 RAG 功能
创建 Vector Store, 上传文件
vector_store = client.beta.vector_stores.create(
name="MyVectorStore"
)将文件上传到 OpenAI 存储空间
file = client.files.create(
file=open("abcd.pdf", "rb").read(),
purpose="assistants"
)将文件添加到 Vector Store
vector_store_file = client.beta.vector_stores.files.create(
vector_store_id=vector_store.id,
file_id=file.id
)批量上传文件到 Vector Store
files = ['file1.pdf','file2.pdf']
file_batch = client.beta.vector_stores.file_batches.upload_and_poll(
vector_store_id=vector_store.id,
files=[open(filename, "rb").read() for filename in files]
)Vector store 和 vector store file 也有对应的
list,retrieve, 和delete等操作。具体文档参考:
- Vector store: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/vector-stores
- Vector store file: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/vector-stores-files
- Vector store file 批量操作: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/vector-stores-file-batches
RAG 被当成一种 tool
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
instructions="你是个问答机器人,你根据给定的知识回答用户问题。",
model="gpt-4o",
tools=[{"type": "file_search"}],
tool_resources={"file_search": {"vector_store_ids": [vector_store.id]}} # 指定检索源
)# 创建 thread
thread = client.beta.threads.create()
# 添加 user message
message = client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
role="user",
content="上海天气怎么样?",
)
# 使用 stream 接口并传入 EventHandler
with client.beta.threads.runs.stream(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant_id,
event_handler=EventHandler(),
) as stream:
stream.until_done()总结:Assistant 有 ta 的优缺点
优点:是方便,代码咔咔几行就能集成到自己的应用中了
缺点:不易控制,比如 LLM 死活不掉你的自定义方法的时候你是真没办法的
如果需要细粒度的控制就是 API + RAG,参考我之前的文章。






















 1705
1705











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








