首先申明,这不是我写的,只是我根据学习资料进行整理加上自己的理解!
Python中的内存管理是通过包含所有Object和数据结构的私有堆来实现的。而对私有堆的控制和管理有Python memory manager 实现。
At the lowest level, a raw memory allocator ensures that there is enough room in the private heap for storing all Python-related data by interacting with the memory manager of the operating system.
On top of the raw memory allocator, several object-specific allocators operate on the same heap and implement distinct memory management policies adapted to the peculiarities of every object type.
The Python memory manager thus delegates some of the work to the object-specific allocators, but ensures that the latter operate within the bounds of the private heap.
Python中对堆得管理是通过解释器本事来实现的。用户并没有权利控制它,即使他能够直接将对象的指针指向某个内存块,但是对堆空间的分配实际由pytho的内存管理器通过Python/C的API函数来实现。
Python中的内存管理接口:
-
void* PyMem_Malloc ( size_t n )
- Allocates n bytes and returns a pointer of type void* to the allocated memory, or NULL if the request fails. Requesting zero bytes returns a distinct non- NULL pointer if possible, as if PyMem_Malloc(1)() had been called instead. The memory will not have been initialized in any way.
-
void* PyMem_Realloc ( void *p , size_t n )
- Resizes the memory block pointed to by p to n bytes. The contents will be unchanged to the minimum of the old and the new sizes. If p is NULL , the call is equivalent to PyMem_Malloc(n)() ; else if n is equal to zero, the memory block is resized but is not freed, and the returned pointer is non- NULL . Unless p is NULL , it must have been returned by a previous call to PyMem_Malloc() or PyMem_Realloc() . If the request fails, PyMem_Realloc() returns NULL and p remains a valid pointer to the previous memory area.
-
void PyMem_Free ( void *p )
- Frees the memory block pointed to by p , which must have been returned by a previous call to PyMem_Malloc() or PyMem_Realloc() . Otherwise, or if PyMem_Free(p)() has been called before, undefined behavior occurs. If p is NULL , no operation is performed.
The following type-oriented macros are provided for convenience. Note that TYPE refers to any C type.
-
TYPE* PyMem_New ( TYPE, size_t n )
- Same as PyMem_Malloc() , but allocates (n * sizeof(TYPE)) bytes of memory. Returns a pointer cast to TYPE* . The memory will not have been initialized in any way.
-
TYPE* PyMem_Resize ( void *p , TYPE, size_t n )
- Same as PyMem_Realloc() , but the memory block is resized to (n * sizeof(TYPE)) bytes. Returns a pointer cast to TYPE* . On return, p will be a pointer to the new memory area, or NULL in the event of failure. This is a C preprocessor macro; p is always reassigned. Save the original value of p to avoid losing memory when handling errors.
-
void PyMem_Del ( void *p )
- Same as PyMem_Free() .
In addition, the following macro sets are provided for calling the Python memory allocator directly, without involving the C API functions listed above. However, note that their use does not preserve binary compatibility across Python versions and is therefore deprecated in extension modules.
PyMem_MALLOC() , PyMem_REALLOC() , PyMem_FREE() .
PyMem_NEW() , PyMem_RESIZE() , PyMem_DEL() .
Python中内存管理的层次结构:
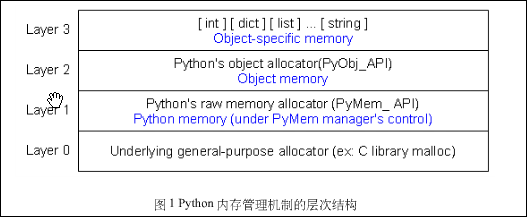
第0层是与操作系统密切相关的,用c来实现,实际上后三层还是有python管理。
另外为了提高程序的执行效率,python用来两套机制来调用c的lib 函数。一种是用宏实现,第二种是使用函数。
使用宏的好处是为了避免一次函数调用的开销,提高执行效率,而使用函数是为了便于扩展。
推荐一篇阅读:http://www.docin.com/p-6969952.html
我自己也没看完,太长了,而且现在处于初学水平,貌似太早了























 4717
4717

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










