Spring 基于注解的配置
从 Spring 2.5 开始就可以使用注解来配置依赖注入。而不是采用 XML 来描述一个 bean 连线,你可以使用相关类,方法或字段声明的注解,将 bean 配置移动到组件类本身。
- 注解:就是一个类,使用@注解名称
- 开发中:使用注解 取代 xml配置文件。
创建Bean
@Component取代<bean class="">
@Component(“id”) 取代 <bean id="" class="">
web开发,提供3个@Component注解衍生注解(功能一样)取代<bean class="">
- @Repository :dao层
- @Service:service层
- @Controller:web层
注解使用前提,添加命名空间,让spring扫描含有注解类
- 配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 组件扫描,扫描含有注解的类 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.cc.study.annotation"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
- schema命名空间

- User
@Component("userId")
public class User {
private String username;
private Address address;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
- 测试
@Test
public void demo01(){
String xmlPath = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("userId");
System.out.println(user);
}
结果发现报错了,报错如下:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
at org.springframework.asm.ClassReader.<init>(Unknown Source)
at org.springframework.asm.ClassReader.<init>(Unknown Source)
at org.springframework.asm.ClassReader.<init>(Unknown Source)
at org.springframework.core.type.classreading.SimpleMetadataReader.<init>(SimpleMetadataReader.java:52)
at org.springframework.core.type.classreading.SimpleMetadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(SimpleMetadataReaderFactory.java:80)
at org.springframework.core.type.classreading.CachingMetadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(CachingMetadataReaderFactory.java:101)
at org.springframework.core.type.classreading.SimpleMetadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(SimpleMetadataReaderFactory.java:76)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.getImports(ConfigurationClassParser.java:298)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.getImports(ConfigurationClassParser.java:300)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.getImports(ConfigurationClassParser.java:300)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClassParser.java:230)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClassParser.java:153)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.parse(ConfigurationClassParser.java:130)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.processConfigBeanDefinitions(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.java:285)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.java:223)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(AbstractApplicationContext.java:630)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:461)
at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:139)
at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:83)
at com.cc.study.annotation.TestAnnotation.demo01(TestAnnotation.java:16)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:44)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:15)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:41)
at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:20)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:76)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:50)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:193)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:52)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:191)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:42)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:184)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:236)
at org.junit.runner.JUnitCore.run(JUnitCore.java:157)
at com.intellij.junit4.JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.startRunnerWithArgs(JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.java:117)
at com.intellij.junit4.JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.startRunnerWithArgs(JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.java:42)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.JUnitStarter.prepareStreamsAndStart(JUnitStarter.java:262)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.JUnitStarter.main(JUnitStarter.java:84)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain.main(AppMain.java:147)
然后我试了一下把Spring的版本改成4.0,把JDK改为1.8即可
<dependencies>
<!-- 4个核心(beans、core、context、expression) -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-beans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-expression -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
测试结果:
依赖注入
依赖注入,给私有字段设置,也可以给setter方法设置
普通值注入
使用@Value
- User
@Component("userId")
public class User {
@Value("Kevin")
private String username;
private Address address;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
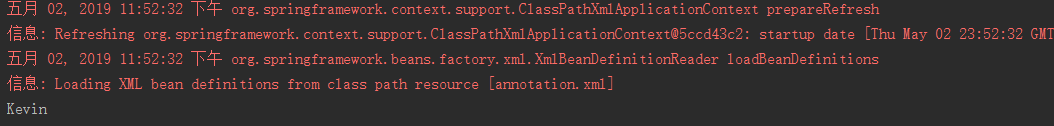
- 测试
@Test
public void demo02(){
String xmlPath = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("userId");
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
}
引用值注入
方式1:按照【类型】注入
@Autowired
- Address
@Component
public class Address {
@Value("北京")
private String addr;
@Value("112")
private String tel;
public String getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(String addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
}
- User
@Component("userId")
public class User {
@Value("Kevin")
private String username;
@Autowired
private Address address;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
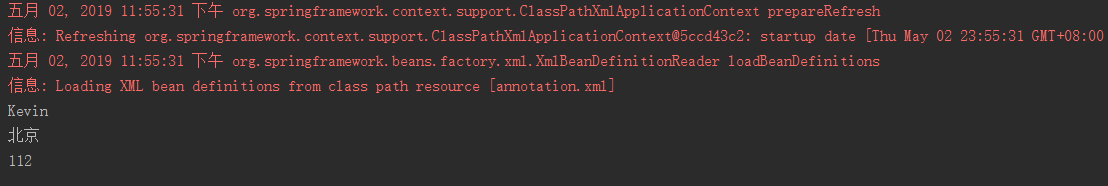
- 测试
@Test
public void demo03(){
String xmlPath = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("userId");
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
System.out.println(user.getAddress().getAddr());
System.out.println(user.getAddress().getTel());
}
方式2:按照【名称】注入1
@Autowired
@Qualifier(“名称”)
- Address
@Component("addressId")
public class Address {
@Value("北京")
private String addr;
@Value("112")
private String tel;
public String getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(String addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
}
- User
@Component("userId")
public class User {
@Value("Kevin")
private String username;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("addressId")
private Address address;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
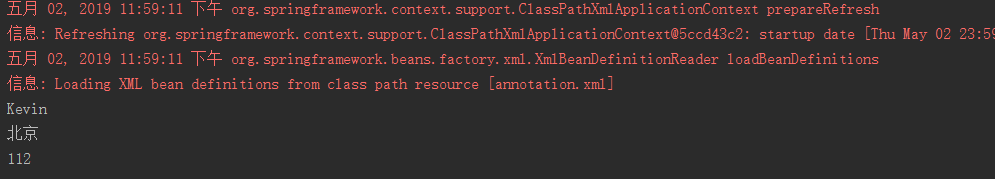
- 测试
@Test
public void demo03(){
String xmlPath = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("userId");
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
System.out.println(user.getAddress().getAddr());
System.out.println(user.getAddress().getTel());
}
方式3:按照【名称】注入2
@Resource(name=“名称”)
- User
@Component("userId")
public class User {
@Value("Kevin")
private String username;
@Resource(name = "addressId")
private Address address;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
- 测试
@Test
public void demo03(){
String xmlPath = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("userId");
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
System.out.println(user.getAddress().getAddr());
System.out.println(user.getAddress().getTel());
}

生命周期
初始化:@PostConstruct
销毁:@PreDestroy
- User
@Component("userId")
public class User {
@Value("Kevin")
private String username;
@Resource(name = "addressId")
private Address address;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("初始化");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("销毁");
}
}
- 测试
@Test
public void demo04(){
String xmlPath = "annotation.xml";
AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("userId");
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
System.out.println(user.getAddress().getAddr());
System.out.println(user.getAddress().getTel());
applicationContext.close();
}

作用域
@Scope(“prototype”) 多例
- User
@Component("userId")
@Scope("prototype")
public class User {
@Value("Kevin")
private String username;
@Resource(name = "addressId")
private Address address;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("初始化");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("销毁");
}
}
- 测试
@Test
public void demo05(){
String xmlPath = "annotation.xml";
AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
User user1 = (User) applicationContext.getBean("userId");
User user2 = (User) applicationContext.getBean("userId");
System.out.println(user1);
System.out.println(user2);
}























 1753
1753











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








