写在前面
由于我是半路出身,半导体学的磕磕绊绊,零基础靠着死记硬背三个月,模型搞的差不多了,今夜要攻克avalance这座大山!
1.雪崩模型的总体公式
1.1雪崩产生条件:空间电荷区宽度>电子/空穴两次碰撞电离之间的平均自由程,空间电荷区的宽度大于两次电离撞击之间的平均自由路径,就会发生电荷倍增,从而导致电击穿。
(Electron–hole pair production due to avalanche generation (impact ionization) requires acertain threshold field strengthand the possibility of acceleration, that is, wide space chargeregions. If the width of a space charge region is greater than the mean free path between twoionizing impacts, charge multiplication occurs, which can cause electrical breakdown. Thereciprocal of the mean free path is called theionization coefficient α. With these coefficientsfor electrons and holes, the generation rate can be expressed as:)
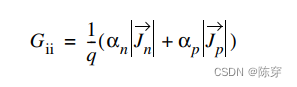
是电子、空穴的平均自由程的倒数;Jn/Jp为电子空穴电流密度。
1.2雪崩模型组成:电离系数模型(van
Overstraeten—de Man, Okuto—Crowell, Lackner, University of Bologna, the new University of]
Bologna, and Hatakeyama. )+雪崩驱动模型(GradQuasiFermi,
Eparallel, CarrierTempDrive, and ElectricField )
1.3雪崩模型的总体用法:Recombination{ avalanche (电离系数模型 驱动力模型 能带依赖模型(可加可不加))}
默认电离系数模型:Overstraeten–de Man model
默认驱动力模型:GradQuasiFermi
参考下文即可理解

The following example selects the default van Overstraeten–de Man model for the electronimpact ionization process with a driving force derived from electron temperature, and selectsthe Okuto–Crowell model for holes using the default driving force based on GradQuasiFermi:
Physics {
Recombination(eAvalanche(CarrierTempDrive) hAvalanche(Okuto)...)
}
Avalanche generation is switched on by using the keyword Avalanchein the Recombination statement in the Physics section. The keywords eAvalanche and hAvalanchespecify separate models or driving forces for the electron and hole ionizationcoefficients, respectively.
1.4雪崩模型的结果观察-电子、空穴的电离率与碰撞系数

2.我的仿真问题-一直被忽略的!!
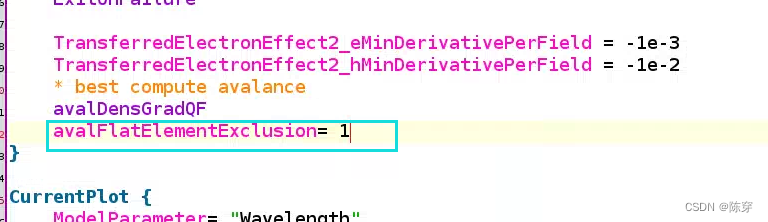
为了优化网格,math里面可以忽略角度偏小的网格角度,但不得超过2度,我之前都是直接忽略60度以下的了。
The value to be used for AvalFlatElementExclusion must not exceed 1–2°. Otherwise, too manyelements may be excluded from theavalanche generation, causing a shift in breakdown voltage to highervalues.
3.高场下常用的模型:vanOverstraeten – de Man Model
3.1公式+参数控制(调参方法)
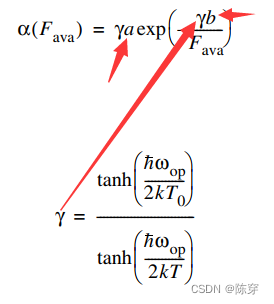
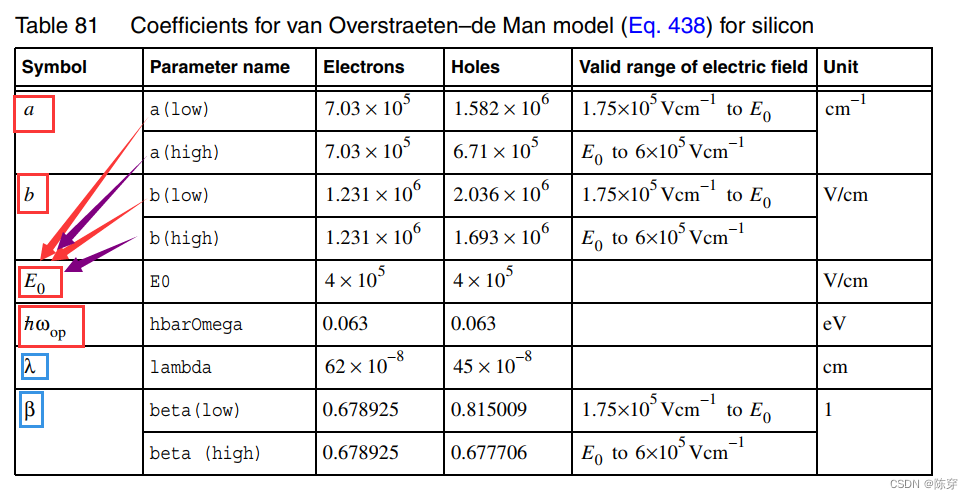
是电子、空穴的平均自由程的倒数,由三个参数决定:a、b、r。
调参方法: 修改.par文件中的 vanOverstraetendeMan.其中红色的是常规不考虑Bang gapDependence情况下的设置方法。


4.基于流体力学模型的雪崩产生模型(Avalanche Generation With Hydrodynamic Transport)
4.1模型公式+调参方法
如果使用流体力学模型,则雪崩的默认驱动力从GradQuasiFermi转换为ElectricField
如果使用流体动力传输模型,默认驱动力 Favae 等于从载流子温度得到的有效场 Eeff。将局部载流子温度转换为有效场 Eeff 的通常方法由代数方程描述:
未修正的方程:

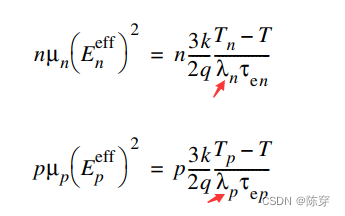
修正后的方程以及如何激活关闭
通过传统转换公式公式 469 和公式 470 可以通过在同一雪崩系数部分指定
参数 Y,, = 0, Y,, = 0 激活。
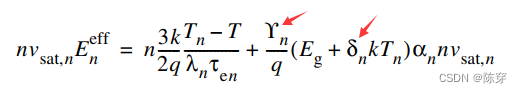
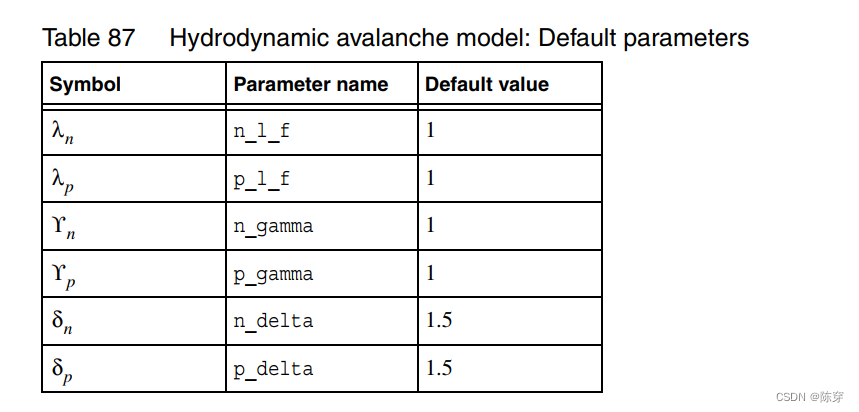
 模型参数设置:调整.par中的 avalanceFactors参数即可
模型参数设置:调整.par中的 avalanceFactors参数即可
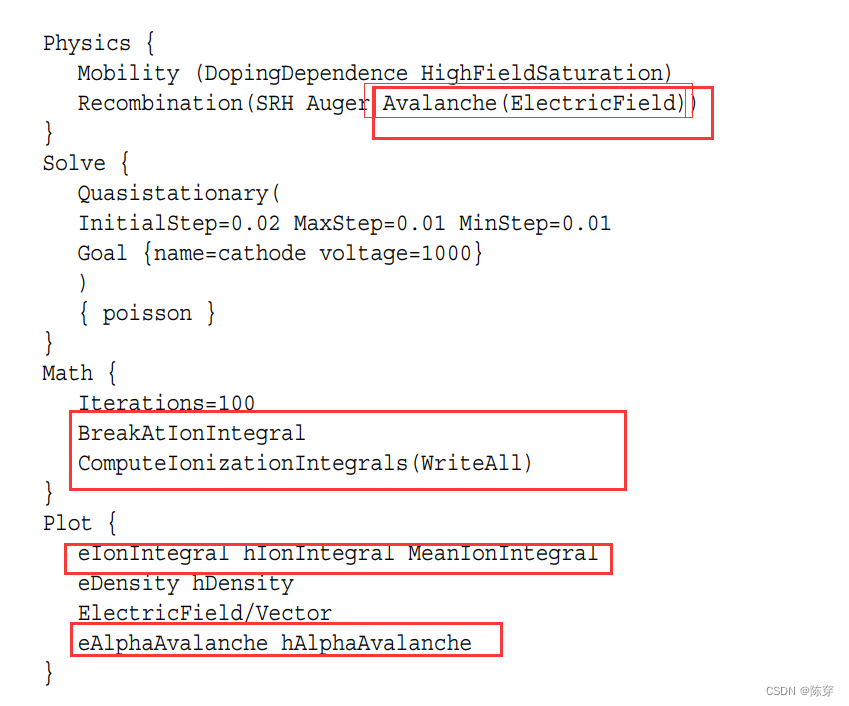
5.如何基于系统自带模型进行雪崩分析(Approximate Breakdown Analysis)
5.1雪崩击穿的条件与分析
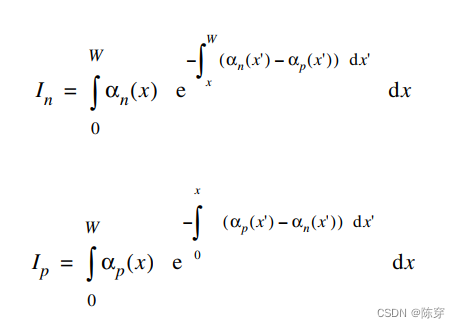
其中、
分别是电子和空穴的电离系数,W 是耗尽区的宽度。积分沿着穿过耗尽区的场线进行。如果电离积分等于 1,就会发生雪崩击穿。上述两个公式分别描述的是电子注入(电子初级电流)和空穴注入。由于这些击穿标准并不依赖于电流密度,因此击穿分析可以计算泊松方程和电离积分。在耗尽区准费米级恒定的假设下,只需计算泊松方程和电离积分即可。
5.2操作方法
Physics+Math+Plot






















 2576
2576











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








