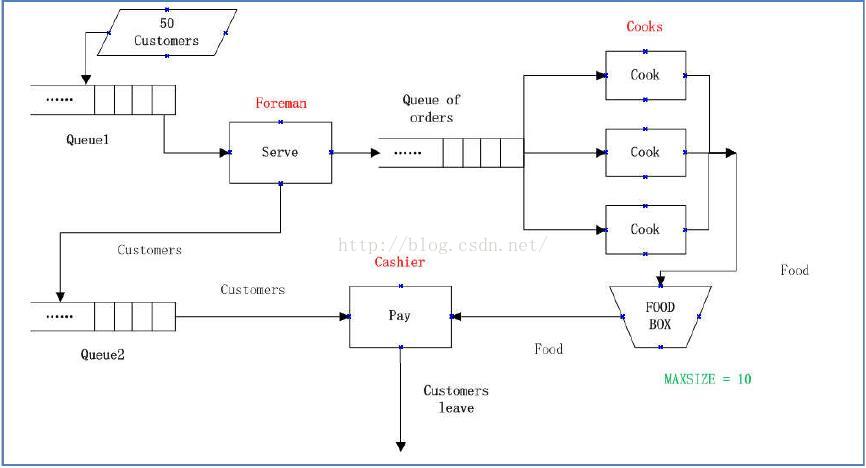
【问题描述】
Fast-food restaurant problem: Design, implement and test a solution for
the IPC problem specified below. Suppose we have the following scenario:
50 customers successively come to a fast-food restaurant to buy some food. They have
different IDs.
The intervals between two customers are random: 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 minutes.
Customers join in one FIFO queue after arriving at the restaurant, called queue1, and
wait to be served by the foreman one by one.
To serve customers, the foreman asks customers to order dishes one by one, writes
them down in papers and submits these orders with customer IDs. After that,
customers will be de-queued from queue1 and join in another queue called queue2,
waiting for their dishes.
There are 3 cooks, and each one can undertake one order at a time. As long as they are
idle and there are any orders, they will undertake them and finish them.
Each cook can finish one order in a random time: 3, 4 or 5 minutes.
Each order corresponds to a meal, which may contain several dishes. But for simplicity,
you can just call it a "dish".
Each dish(meal) has the same ID as the corresponding order.
All the dishes will be put in a box with a limited size to keep warm. The box can contain
at most 10 dishes(meals).
The cashier will take the dishes from the box one by one and offer them to
corresponding customers. For the sake of simplicity, you can also see the box as a
queue.
The cashier calls out the dish ID, and finds the corresponding customer. This customer
pays the money and the cashier offers the dishes at the same time. For simplicity, you
can suppose either action prior to the other.
Since time to cook dishes is not equal, the queue2 is not an FIFO queue.
To save time, one second in the program represents one minute in this scenario.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tips:
The customers can be expressed by only 2 threads instead of 50 ones because at the
same time only one customer will be served in one queue. On the contrary, 3 cooks can
work simultaneously, so three threads generated from the same copy of thread_cooks()
function are needed.
To send wake-up signal to the three cook threads, the "pthread_cond_broadcast"
function is needed.
In the implemented code we use the "malloc" function to build each queue. Moreover,
we set the size of each queue to be 50 except the box, which is equal to the total
number of customers. So customer "i" will be stored exactly at the location "i", and no
element will be moved.The size of food box should exactly be 10.
【我的解答】
header.h
#ifndef H_header
#define H_header
#define RED "\033[1;32;31m"
#define GREEN "\033[1;32;32m"
#define BLUE "\033[1;32;34m"
#define YELLOW "\033[1;33m"
#define WHITE "\033[1;37m"
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
extern int max_number_of_customers; //The total number of customers in this program
extern sem_t number_of_customers_in_queue1, number_of_customers_in_queue2;
extern pthread_mutex_t mutex_queue1, mutex_queue2; //To make sure each role gets access to both queues of customers mutually exclusively
extern struct customer{ int id; } *queue_customer_1, *queue_customer_2;
extern int number_of_customers_waiting_in_queue1; //A variable which is just used to test conditional variable
extern pthread_mutex_t mutex_of_order; //To make sure each role gets access to the queue of orders mutually exclusively
extern struct order{ int id; } *queue_order;
extern pthread_cond_t cond_customers_in_queue1; //If no customers are in queue1, the foreman will block himself
extern int number_of_orders_to_be_finished; //A variable which is just used to test conditional variable
extern pthread_mutex_t mutex_of_dishes;
extern pthread_cond_t cond_orders, cond_rooms_for_dishes;
extern int dishes_full, dishes_empty;
extern struct dishes{ int id; } *queue_dishes;
extern int number_of_orders_received;
extern pthread_mutex_t mutex_dishes_offered_id;
extern pthread_cond_t cond_dishes, cond_payment, cond_offer;
extern int dishes_offered_id;
extern void Initialize();
extern void Destroy();
#endifheader.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "header.h"
int max_number_of_customers = 50;
sem_t number_of_customers_in_queue1, number_of_customers_in_queue2;
pthread_mutex_t mutex_queue1, mutex_queue2; //To make sure each role gets access to both queues of customers mutually exclusively
struct customer *queue_customer_1, *queue_customer_2;
int number_of_customers_waiting_in_queue1 = 0; //A variable which is just used to test conditional variable
pthread_mutex_t mutex_of_order; //To make sure each role gets access to the queue of orders mutually exclusively
struct order *queue_order;
pthread_cond_t cond_customers_in_queue1; //If no customers are in queue1, the foreman will block himself
int number_of_orders_to_be_finished = 0; //A variable which is just used to test conditional variable
pthread_mutex_t mutex_of_dishes;
pthread_cond_t cond_orders, cond_rooms_for_dishes;
int dishes_full = 0, dishes_empty = 10;
struct dishes *queue_dishes;
int number_of_orders_received = 0;
pthread_mutex_t mutex_dishes_offered_id;
pthread_cond_t cond_dishes, cond_payment, cond_offer;
int dishes_offered_id = -1;
void Initialize(){
/*Initialize semaphores, mutexes and conditional variables*/
int returnvalue;
returnvalue = sem_init(&number_of_customers_in_queue1, 0, 0);
if(returnvalue == -1){
printf("Semaphore number_of_customers_in_queue1 initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = sem_init(&number_of_customers_in_queue2, 0, 0);
if(returnvalue == -1){
printf("Semaphore number_of_customers_in_queue2 initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_queue1, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Mutex mutex_queue1 initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_queue2, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Mutex mutex_queue2 initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_of_order, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Mutex mutex_of_order initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_of_dishes, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Mutex mutex_of_dishes initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_dishes_offered_id, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Mutex mutex_dishes_offered_id initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_cond_init(&cond_customers_in_queue1, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Condition variable cond_customers_in_queue1 initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_cond_init(&cond_orders, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Condition variable cond_orders initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_cond_init(&cond_rooms_for_dishes, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Condition variable cond_rooms_for_dishes initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_cond_init(&cond_dishes, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Condition variable cond_dishes initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_cond_init(&cond_payment, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Condition variable cond_payment initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
returnvalue = pthread_cond_init(&cond_offer, 0);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Condition variable cond_offer initialization failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
/*Initialize queues*/
queue_customer_1 = (struct customer*)malloc(sizeof(struct customer) * 50);
queue_customer_2 = (struct customer*)malloc(sizeof(struct customer) * 50);
queue_order = (struct order*)malloc(sizeof(struct order) * 50);
queue_dishes = (struct dishes*)malloc(sizeof(struct dishes) * 10);
int i = 0;
for(;i < 50;i ++){
queue_customer_1[i].id = queue_customer_2[i].id = queue_order[i].id = -1;
if(i < 10)queue_dishes[i].id = -1;
}
}
void Destroy(){
sem_destroy(&number_of_customers_in_queue1);
sem_destroy(&number_of_customers_in_queue2);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_queue1);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_queue2);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_of_order);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_of_dishes);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_dishes_offered_id);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_customers_in_queue1);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_orders);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_rooms_for_dishes);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_dishes);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_payment);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_offer);
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "header.h"
#include "Customer.h"
#include "Foreman.h"
#include "Cooks.h"
#include "Cashier.h"
main(){
Initialize();
pthread_t customers_come_and_provide_order, customers_pay_and_go, foreman, cook1, cook2, cook3, cashier;
pthread_create(&customers_come_and_provide_order, 0, thread_customers_come, 0);
pthread_create(&customers_pay_and_go, 0, thread_customers_go, 0);
pthread_create(&foreman, 0, thread_foreman, 0);
pthread_create(&cook1, 0, thread_cooks, 0);
pthread_create(&cook2, 0, thread_cooks, 0);
pthread_create(&cook3, 0, thread_cooks, 0);
pthread_create(&cashier, 0, thread_cashier, 0);
int returnvalue = pthread_join(customers_pay_and_go, NULL);
if(returnvalue != 0){
printf("Errors!\n");
exit(-1);
}
printf(WHITE "All customers have left!\n");
Destroy();
return;
}Foreman.h
#include "header.h"
void *thread_foreman();Foreman.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define random(x) (rand() % x)
#include "header.h"
#include "Foreman.h"
void *thread_foreman(){
int count=0;
//the foreman must serve 50 customers before he stops working.
for (; count<max_number_of_customers; count++)
{
//Get the exclusive access to 'queue_customer_1', foreman works only if here comes a new customer.
sem_wait(&number_of_customers_in_queue1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_queue1);
//Serve one customer waiting in the queue1
queue_customer_1[count].id=-1;
number_of_customers_waiting_in_queue1 --;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_queue1);
printf(BLUE "The foreman starts serving customer %d!\n", count+1);
//Get the exclusive access to 'queue_customer_2'
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_queue2);
queue_customer_2[count].id=count+1; //The customer joins queue2
sem_post(&number_of_customers_in_queue2);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_queue2);
//Get the exclusive access to 'queue_order'
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_of_order);
queue_order[count].id=count+1; //add a new order to the 'queue_order'
number_of_orders_to_be_finished++; //Cooks have a new task to be finished!
number_of_orders_received=count+1;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond_orders); //Tell all three cooks to catch the new order.
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_of_order);
printf(BLUE "Customer %d has left queue1 and joined in queue2! And his order has been submitted to cooks!\n", count+1);
}
}Customer.h
#include "header.h"
void *thread_customers_come();
void *thread_customers_go();Customer.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define random(x) (rand() % x)
#include "header.h"
#include "Customer.h"
void *thread_customers_come(){
int count = 0;
while(count < max_number_of_customers){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_queue1); //Get the exclusive access to 'queue_customer_1' and 'number_of_customers_waiting_in_queue1'
queue_customer_1[count].id = count + 1; //Allocate an ID when each customer is generated
sem_post(&number_of_customers_in_queue1);
number_of_customers_waiting_in_queue1 ++; //Add 1 to the semaphore and the testing varaible
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_queue1);
printf(RED "One customer comes and joins in the queue1! ID:%d\n", queue_customer_1[count].id);
count ++;
sleep(random(5) + 1); //The next customer will come in 1-5 minute(s)
}
}
void *thread_customers_go(){
int count = 0;
while(count < max_number_of_customers){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_dishes_offered_id); //Get the access to 'dishes_offered_id' exclusively
pthread_cond_wait(&cond_offer, &mutex_dishes_offered_id); //Wait for the cashier to announce the id and offer the dishes
printf(RED "The dishes id is %d, and the cashier is ready to receive money and offer dishes!\n", dishes_offered_id);
/*Find the customer which the dishes belong to*/
sem_wait(&number_of_customers_in_queue2); //Cut down the number firstly; If this line is between 'pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_queue2);' and 'pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_queue2);', it may block forever
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_queue2);
int i = 0;
for(;i < 50;i ++){
if(queue_customer_2[i].id == dishes_offered_id){
/*Delete the customer from queue_2*/
queue_customer_2[i].id = -1;
break;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_queue2);
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_payment); //The customer pay his money, and wake up the cashier
printf(RED "Customer %d has paid and got his dishes! He's going to leave!\n", dishes_offered_id);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_dishes_offered_id);
count ++;
}
}
#include "header.h"
void *thread_cooks();
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define random(x) (rand() % x)
#include "header.h"
#include "Cooks.h"
void *thread_cooks(){
while (1)
{
//Cooks stop working only if customers reserved have reached the maximum number and there is no more order to be finished at the moment
if (number_of_orders_received==max_number_of_customers && number_of_orders_to_be_finished==0) break;
//Get the exclusive access to 'queue_order'
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_of_order);
//Cooks wait for orders to be finished and try to get one if there is any
while (number_of_orders_to_be_finished==0) pthread_cond_wait(&cond_orders, &mutex_of_order);
if (number_of_orders_to_be_finished>0)
{
//Catch one order in the queue_order in random
int i=0;
for (; i<number_of_orders_received; i++) if (queue_order[i].id>0) break;
int getId=queue_order[i].id;
queue_order[i].id=-1;
number_of_orders_to_be_finished --; //One order has been received by the cook
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_of_order);
printf(YELLOW "Order %d has been received by one cook!\n", getId);
//Finish the order in 3,4 or 5 minutes
int temps[3]={3, 4, 5};
sleep( temps[random(3)] );
printf(YELLOW "Order %d has been finished!\n", getId);
//Get the exclusive access to 'queue_dishes'
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_of_dishes);
//Waiting for room available in the box to put the dish that has been finished by the cook
while (dishes_empty==0) pthread_cond_wait(&cond_rooms_for_dishes, &mutex_of_dishes);
if (dishes_empty>0)
{
//Choose one space available in random to put the dish
for (i=0; i<10; i++) if (queue_dishes[i].id<0) break;
queue_dishes[i].id=getId;
dishes_empty--; dishes_full++;
//Tell the cashier that here comes a new dish and that it should wake up if it is sleeping
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_dishes);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_of_dishes);
}
}
}
}
#include "header.h"
void *thread_cashier();Cashier.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define random(x) (rand() % x)
#include "header.h"
#include "Cashier.h"
void *thread_cashier(){
int count=0;
//the cashier must serve 50 customers before he stops working.
for (; count<max_number_of_customers; count++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_of_dishes); //Get the exclusive access to 'queue_dishes'
//waiting for the cook to finish cooking if there is not any dish
while (dishes_full==0) pthread_cond_wait(&cond_dishes, &mutex_of_dishes);
//get one of the dishes in the box in random
int i=0;
for (; i<10; i++) if (queue_dishes[i].id>0) break;
int getId=queue_dishes[i].id;
queue_dishes[i].id=-1;
dishes_full--; dishes_empty++;
//tell the cooks that there is now space available
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_rooms_for_dishes);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_of_dishes);
printf(GREEN "The dishes of order %d has been passed to the cashier!\n", getId);
//Get the exclusive access to 'dishes_offered_id'
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_dishes_offered_id);
dishes_offered_id=getId;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_offer); //tell the customer_go() that the cashier has offered one dish
printf(GREEN "The cashier takes out the dishes of customer %d and offer them to the customer!\n", getId);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond_payment, &mutex_dishes_offered_id); //waiting for the corresponding customer to pay
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_dishes_offered_id);
}
}MakeFile
Question4: Question4.o header.o Customer.o Foreman.o Cooks.o Cashier.o
gcc -o Question4 Question4.o header.o Customer.o Foreman.o Cooks.o Cashier.o -pthread
Question4.o: header.h Customer.h Foreman.h Cooks.h Cashier.h
header.o: header.h
Customer.o: header.h Customer.h
Foreman.o: header.h Foreman.h
Cooks.o: header.h Cooks.h
Cashier.o: header.h Cashier.h
clean:
rm Question4 Question4.o header.o Customer.o Foreman.o Cooks.o Cashier.o【运行结果】
由于50个客户的运行结果太长,这里截取开头、中间、结尾的结果作说明。








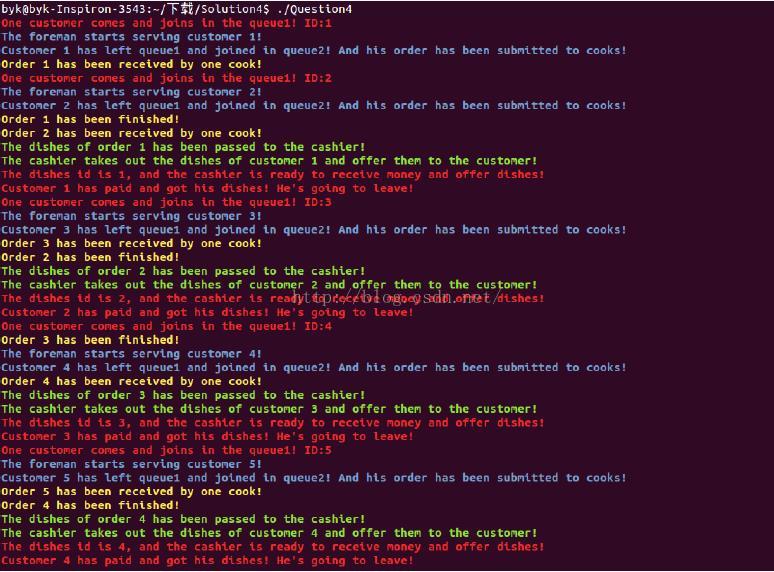
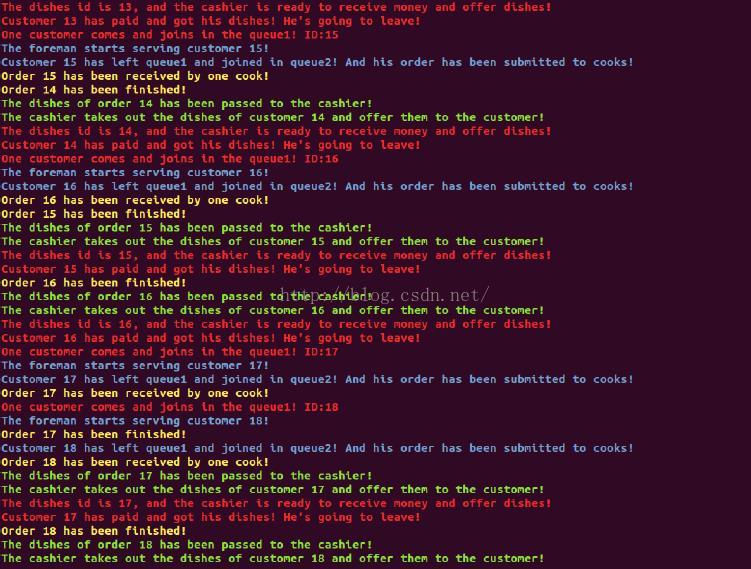















 964
964

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








