摘要
本文深入剖析Deep-Live-Cam的系统架构设计,从整体架构、核心模块、数据流、性能优化等多个维度进行详细讲解。通过系统化的分析和实践案例,帮助开发者深入理解Deep-Live-Cam的设计理念和实现方案。
1. 系统整体架构
1.1 架构概览
1.2 模块职责
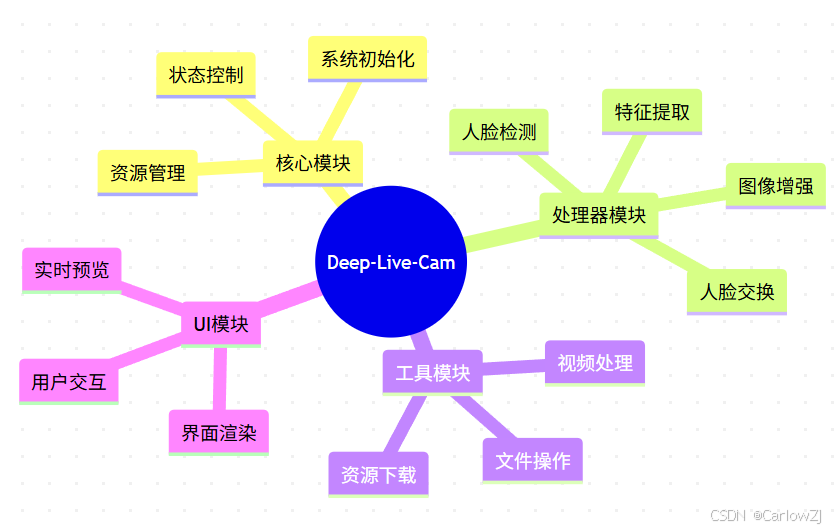
mindmap
root((Deep-Live-Cam))
核心模块
系统初始化
资源管理
状态控制
处理器模块
人脸检测
特征提取
人脸交换
图像增强
工具模块
视频处理
文件操作
资源下载
UI模块
界面渲染
用户交互
实时预览
2. 核心模块设计
2.1 Core模块
# core.py核心实现
class DeepLiveCam:
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化Deep-Live-Cam核心
"""
self.execution_providers = []
self.frame_processors = []
self.globals = {}
def initialize(self):
"""
系统初始化
"""
# 设置执行环境
self._setup_environment()
# 初始化处理器
self._init_processors()
# 加载模型
self._load_models()
def _setup_environment(self):
"""
配置执行环境
"""
# 设置线程数
os.environ['OMP_NUM_THREADS'] = '1'
# 设置日志级别
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
def _init_processors(self):
"""
初始化处理器
"""
for processor in self.frame_processors:
processor.pre_check()
processor.pre_start()
2.2 Face Analyser模块
# face_analyser.py核心实现
class FaceAnalyser:
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化人脸分析器
"""
self.model = None
self.face_detector = None
def initialize(self):
"""
初始化模型
"""
# 加载人脸检测模型
self.face_detector = insightface.app.FaceAnalysis(
name='buffalo_l',
providers=self.execution_providers
)
# 准备检测器
self.face_detector.prepare(
ctx_id=0,
det_size=(640, 640)
)
def detect_faces(self, frame):
"""
检测人脸
:param frame: 输入帧
:return: 检测到的人脸列表
"""
return self.face_detector.get(frame)
3. 处理器模块设计
3.1 Face Swapper模块
# face_swapper.py核心实现
class FaceSwapper:
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化人脸交换器
"""
self.model = None
self.thread_lock = threading.Lock()
def initialize(self):
"""
初始化模型
"""
with self.thread_lock:
if self.model is None:
model_path = os.path.join(
self.models_dir,
"inswapper_128_fp16.onnx"
)
self.model = insightface.model_zoo.get_model(
model_path,
providers=self.execution_providers
)
def swap_face(self, source_face, target_face, frame):
"""
执行人脸交换
:param source_face: 源人脸
:param target_face: 目标人脸
:param frame: 输入帧
:return: 处理后的帧
"""
return self.model.get(
frame,
target_face,
source_face,
paste_back=True
)
3.2 Face Enhancer模块
# face_enhancer.py核心实现
class FaceEnhancer:
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化人脸增强器
"""
self.model = None
self.thread_semaphore = threading.Semaphore()
def initialize(self):
"""
初始化模型
"""
model_path = os.path.join(
self.models_dir,
"GFPGANv1.4.pth"
)
# 选择设备
device = self._select_device()
# 初始化模型
self.model = gfpgan.GFPGANer(
model_path=model_path,
upscale=1,
device=device
)
def enhance_face(self, frame):
"""
增强人脸
:param frame: 输入帧
:return: 增强后的帧
"""
with self.thread_semaphore:
_, _, enhanced_frame = self.model.enhance(
frame,
paste_back=True
)
return enhanced_frame
4. 数据流设计
4.1 视频处理流程
4.2 人脸处理流程
5. 性能优化
5.1 内存优化
# memory_optimization.py
class MemoryOptimizer:
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化内存优化器
"""
self.max_memory = 16 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 # 16GB
def optimize(self):
"""
执行内存优化
"""
# 限制TensorFlow内存使用
gpus = tensorflow.config.experimental.list_physical_devices('GPU')
for gpu in gpus:
tensorflow.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu, True)
# 设置进程内存限制
if platform.system().lower() == 'windows':
import ctypes
kernel32 = ctypes.windll.kernel32
kernel32.SetProcessWorkingSetSize(
-1,
ctypes.c_size_t(self.max_memory),
ctypes.c_size_t(self.max_memory)
)
5.2 GPU加速
# gpu_acceleration.py
class GPUAccelerator:
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化GPU加速器
"""
self.device_priority = []
def select_device(self):
"""
选择最佳设备
"""
if torch.cuda.is_available():
if self._is_tensorrt_available():
return torch.device("cuda"), "TensorRT+CUDA"
return torch.device("cuda"), "CUDA"
elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
return torch.device("mps"), "MPS"
return torch.device("cpu"), "CPU"
6. 最佳实践
6.1 开发建议
-
模块化设计
- 保持模块独立性
- 定义清晰的接口
- 实现可扩展性
-
性能优化
- 使用GPU加速
- 优化内存使用
- 实现多线程处理
-
错误处理
- 完善的异常处理
- 日志记录
- 状态监控
6.2 部署建议
-
环境配置
- 使用虚拟环境
- 安装必要依赖
- 配置GPU驱动
-
资源管理
- 监控内存使用
- 控制GPU占用
- 优化磁盘空间
7. 常见问题
7.1 性能问题
-
CPU使用率过高
- 原因:未启用GPU加速
- 解决:检查CUDA配置
-
内存占用过大
- 原因:缓存未及时清理
- 解决:实现内存优化机制
7.2 集成问题
-
模型加载失败
- 原因:模型文件缺失
- 解决:检查模型路径
-
GPU加速失效
- 原因:驱动版本不匹配
- 解决:更新GPU驱动
8. 总结
本文详细介绍了Deep-Live-Cam的系统架构设计,包括:
- 整体架构设计
- 核心模块实现
- 数据流设计
- 性能优化方案
- 最佳实践建议
- 常见问题解决方案
9. 参考资料
10. 扩展阅读
- 深度学习模型部署
- 实时视频处理技术
- GPU加速原理
- 系统架构设计模式























 802
802

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










