目录
一、什么是堆
二叉树一般可以使用两种结构存储,一种是顺序存储,另一种是链式存储,顺序存储本质上就是用数组来存储,但是一般顺序存储只适合表示完全二叉树,因为非完全二叉树使用顺序存储会产生空间上的浪费,完全二叉树也更适合使用顺序结构存储。完全二叉树就是一种特殊的二叉树结构,也就是除了最后一层之外,其他层的结点个数一定达到最大,如果最后一层结点的个数也达到最大,则称为满二叉树,满二叉树是一种特殊的完全二叉树。而接下来要讲的堆,也是一种特殊的完全二叉树,同样使用顺序结构存储。
堆分为小根堆和大根堆。小根堆是每个父亲节点的数据必须小于其孩子结点的数据,因此最上面的根结点必然是最小的;大根堆则是每个父亲节点的数据必须大于其孩子结点的数据,因此最上面的根结点必然是最大的。
二、堆结构的实现
Heap.h文件
由于大根堆和小根堆要实现的功能一致,因此Heap.h文件如下,且往后不再赘述
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
//堆的结构
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* arr;
int size; //有效数据个数
int capacity; //空间大小
}HP;
//堆的初始化
void HPInit(HP* php);
//插入数据
void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x);
//判空
bool HPEmpty(HP* php);
//出堆
void HPPop(HP* php);
//取堆顶数据
HPDataType HPTop(HP* php);
//求size
int HPsize(HP* php);
//打印
void HPPrint(HP* php);
//堆的销毁
void HPDestroy(HP* php);1.小根堆
Heap.c文件
#include"Heap.h"
//初始化堆
void HPInit(HP* php)
{
php->arr = NULL;
php->capacity = php->size = 0;
}
//两数交换函数
void swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* arr, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
//小堆:< (小的上位)
//大堆:> (大的上位)
if (arr[child] < arr[parent])
{
//调整
swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else {
break;
}
}
//时间复杂度O(logn)
}
//插入数据
void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{
assert(php);
//判断空间是否足够
if (php->capacity == php->size)
{
int newCapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * php->capacity;
HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(HPDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail!");
exit(1);
}
php->arr = tmp;
php->capacity = newCapacity;
}
php->arr[php->size] = x;
//插入数据后需要调整——保证插入后还是一个堆结构
//向上调整
AdjustUp(php->arr, php->size);
php->size++;
}
//判空
bool HPEmpty(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->size == 0;
}
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* arr, int parent, int n)
{
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < n)
{
//大堆:<
//小堆:>
if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] > arr[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
//大堆:>
//小堆:<
if (arr[child] < arr[parent])
{
//调整
swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
//时间复杂度O(logn)
}
//出堆——堆顶
void HPPop(HP* php)
{
assert(!HPEmpty(php));
//堆顶与堆尾交换 0 php->size-1
swap(&php->arr[0], &php->arr[php->size - 1]);
//将换到堆尾的元素删除
php->size--;
//需要保证还是堆结构
//向下调整
AdjustDown(php->arr, 0, php->size);
}
//取堆顶数据
HPDataType HPTop(HP* php)
{
assert(!HPEmpty(php));
return php->arr[0];
}
//求size
int HPsize(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->size;
}
//打印
void HPPrint(HP* php)
{
for (int i = 0; i < php->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", php->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//堆的销毁
void HPDestroy(HP* php)
{
if (php->arr)
free(php->arr);
php->arr = NULL;
php->capacity = php->size = 0;
}2.大根堆
Heap.c文件
#include"Heap.h"
//初始化堆
void HPInit(HP* php)
{
php->arr = NULL;
php->capacity = php->size = 0;
}
//两数交换函数
void swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* arr, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
//小堆:< (小的上位)
//大堆:> (大的上位)
if (arr[child] > arr[parent])
{
//调整
swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else {
break;
}
}
//时间复杂度O(logn)
}
//插入数据
void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{
assert(php);
//判断空间是否足够
if (php->capacity == php->size)
{
int newCapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * php->capacity;
HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(HPDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail!");
exit(1);
}
php->arr = tmp;
php->capacity = newCapacity;
}
php->arr[php->size] = x;
//插入数据后需要调整——保证插入后还是一个堆结构
//向上调整
AdjustUp(php->arr, php->size);
php->size++;
}
//判空
bool HPEmpty(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->size == 0;
}
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* arr, int parent, int n)
{
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < n)
{
//大堆:<
//小堆:>
if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] < arr[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
//大堆:>
//小堆:<
if (arr[child] > arr[parent])
{
//调整
swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
//时间复杂度O(logn)
}
//出堆——堆顶
void HPPop(HP* php)
{
assert(!HPEmpty(php));
//堆顶与堆尾交换 0 php->size-1
swap(&php->arr[0], &php->arr[php->size - 1]);
//将换到堆尾的元素删除
php->size--;
//需要保证还是堆结构
//向下调整
AdjustDown(php->arr, 0, php->size);
}
//取堆顶数据
HPDataType HPTop(HP* php)
{
assert(!HPEmpty(php));
return php->arr[0];
}
//求size
int HPsize(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->size;
}
//打印
void HPPrint(HP* php)
{
for (int i = 0; i < php->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", php->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//堆的销毁
void HPDestroy(HP* php)
{
if (php->arr)
free(php->arr);
php->arr = NULL;
php->capacity = php->size = 0;
}三、堆排序
1.基于堆的结构排序
升序:建小堆,打印堆顶结点后,头结点和尾结点互换然后删除掉尾结点,达到删除头结点的效果,然后向下调整重新得到新的小堆结构,再重复以上操作,就能打印出从小到大升序的元素。
降序:建大堆,其余的操作同理
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
//定义堆结构
typedef struct Heap
{
int* HeapArr;
int size;
int capacity;
} HP;
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
void HeapSort(int* arr, int sz, HP* hp)
{
//初始化堆
hp->HeapArr = NULL;
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
//插入
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
if (hp->capacity == hp->size)
{
//增容
int newCapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * hp->capacity;
int* tmp = (int*)realloc(hp->HeapArr, newCapacity * sizeof(int));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail!");
exit(1);
}
hp->HeapArr = tmp;
hp->capacity = newCapacity;
}
hp->HeapArr[hp->size] = arr[i];
//确保插入后仍是堆结构,故向上调整
int child = hp->size;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (hp->HeapArr[child] < hp->HeapArr[parent])
{
//调整
Swap(&hp->HeapArr[child], &hp->HeapArr[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else {
break;
}
}
hp->size++;//有效个数增加
}
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
//确保堆不为空
assert(hp->size != 0);
//打印堆顶元素
printf("%d ", hp->HeapArr[0]);
//交换堆顶和堆尾元素后删除堆尾元素,达到删除原堆顶元素的效果
Swap(&hp->HeapArr[0], &hp->HeapArr[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;
//确保交换并删除后仍为堆结构,故向下调整
int parent = 0;
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < hp->size)
{
if (child + 1 < hp->size && hp->HeapArr[child] > hp->HeapArr[child + 1])
{
//择小而上
child++;
}
if (hp->HeapArr[child] < hp->HeapArr[parent])
{
Swap(&hp->HeapArr[child], &hp->HeapArr[parent]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
if (hp->HeapArr)
free(hp->HeapArr);
hp->HeapArr = NULL;
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
int main()
{
HP hp;
int arr[10] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("请输入第%d个数:", i + 1);
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
//堆排序——升序
HeapSort(arr, sz, &hp);
return 0;
}输出结果如下
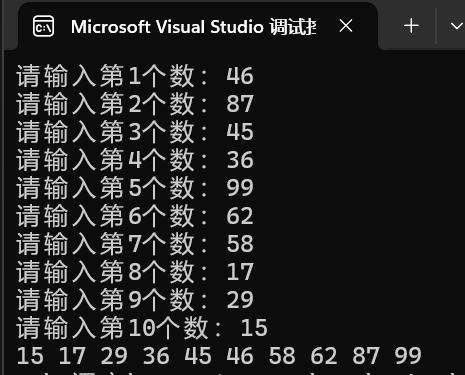
2.基于堆的思想排序
升序:建大堆,将给定好的原数组(假设内含n个元素,下面的代码案例中假设n=10)直接调整为大堆,然后让首位和末位的元素互换,就可以将最大的元素置于末位,再对前n-1个元素重新再调整为大堆,再将首元素和第n-1个元素互换,就能将次大的元素置于倒数第二个位置。重复此操作即可得到升序的数组
降序:建小堆,思路同理
#include<stdio.h>
//交换函数
void swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(int* arr, int parent, int n)
{
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] < arr[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
if (arr[parent] < arr[child])
{
swap(&arr[parent], &arr[child]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("请输入第%d个数:", i + 1);
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
//建大堆——升序
for (int i = (10 - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
//从最小且最后的一棵子树开始向下调整
//对自下而上的子树一一调整
AdjustDown(arr, i, 10);
}
int n = 10;
while (n > 1)
{
//将首尾元素互换,最大的元素放在数组末位
swap(&arr[0], &arr[n - 1]);
n--;
//再将前面9个元素调整成大堆,重复以上操作即可获得升序数组
AdjustDown(arr, 0, n);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}输出结构如下
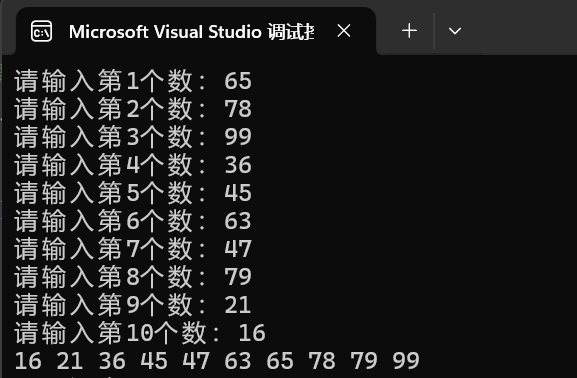
四、调整堆需要的时间复杂度
1.向下调整
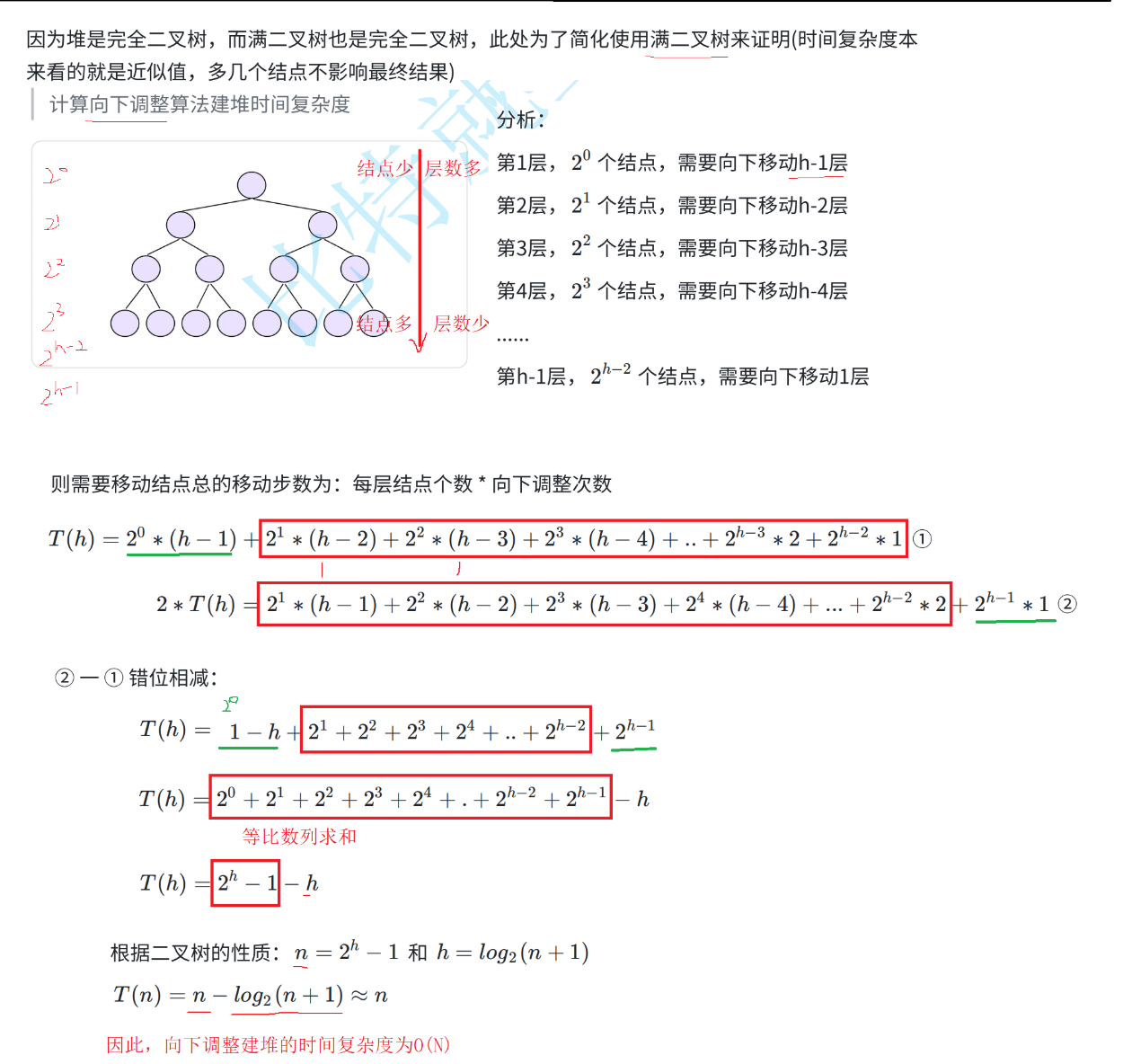
向下调整的时间复杂度为O(n)
2.向上调整
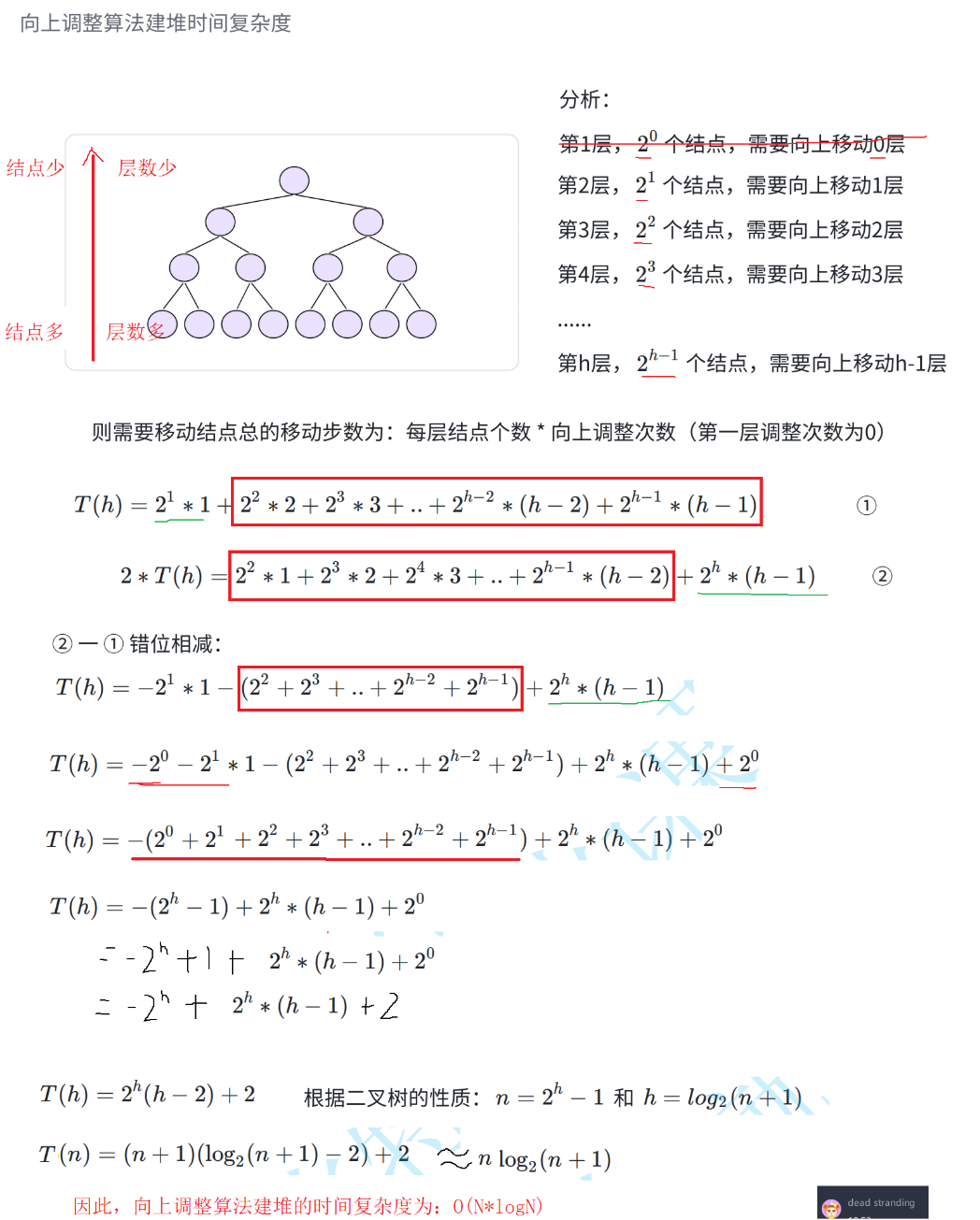
向上调整空间复杂度为O(nlogn)
五、TOP-K问题
求数据集合中前K个最大的元素或者最小的元素,一般情况下数据都比较大,下面假设数据集合中有十万个整型数据,求前K个最大的元素。
可以将这十万个数据放在数组里面然后建大堆依次取10次堆顶吗?理论上可以,但是存这么多数据到数组中不现实。要容纳如此庞大的数据,可以临时创建一个txt文件,然后随机生成十万个数据放入文件当中,再取文件中的前K个数据存放入数组中,然后对数组建小堆(如果要前K个最小的元素则建大堆),建好后开始遍历文件中的元素,如果有数据大于堆顶,则将堆顶替换,然后重新向下调整建堆,直到文件中的元素完全遍历,此时数组中的K个元素就是这十万个元素当中最大的K个元素。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
void CreateData()
{
//造数据
int n = 100000;
srand(time(NULL));
const char* file = "data.txt";
FILE* fin = fopen("file", "w");
if (fin == NULL)
{
perror("fopen error");
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x = (rand() + i) % 1000000;
fprintf(fin,"%d\n", x);
}
fclose(fin);
}
void swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(int* arr, int parent, int n)
{
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] > arr[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
if (arr[child] < arr[parent])
{
swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
void Topk()
{
int k = 0;
printf("请输入k的大小:");
scanf("%d", &k);
const char* fout = fopen("file", "r");
if (fout == NULL)
{
perror("perror fail!");
exit(1);
}
int* maxHeap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
if (maxHeap == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail!");
exit(2);
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
//读取前k个数据放入maxHeap数组中
fscanf(fout, "%d", &maxHeap[i]);
}
//向下调整——建小堆
for (int i = (k - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(maxHeap, i, k);
}
int x = 0;
//遍历文件的数据 与堆顶一一对比
while ((fscanf(fout, "%d", &x)) != EOF)
{
if (x > maxHeap[0])
{
maxHeap[0] = x;
AdjustDown(maxHeap, 0, k);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
printf("%d ", maxHeap[i]);
}
fclose(fout);
}
int main()
{
//CreateData();
Topk();
return 0;
}创造数据放入文件后应将造数据的函数注释,因为数据的创造是随机的,会使每一次运行得到的前K个数据不同,注释掉后可确保二次运行后的结果唯一性。





















 1336
1336

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








