kaggle中预测的get started项目,原文链接。
看原文可以入门特征工程,这里主要说可视化部分,用到matplotlib和seaborn。
导库增加
import seaborn as sns
from scipy.stats import norm
from scipy import stats
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler基本信息
获取列名
.cloumns 获取DataFrame的所有列名
df_train.columns输出
Index(['Id', 'MSSubClass', 'MSZoning', 'LotFrontage', 'LotArea', 'Street',
'Alley', 'LotShape', 'LandContour', 'Utilities', 'LotConfig',
'LandSlope', 'Neighborhood', 'Condition1', 'Condition2', 'BldgType',
'HouseStyle', 'OverallQual', 'OverallCond', 'YearBuilt', 'YearRemodAdd',
'RoofStyle', 'RoofMatl', 'Exterior1st', 'Exterior2nd', 'MasVnrType',
'MasVnrArea', 'ExterQual', 'ExterCond', 'Foundation', 'BsmtQual',
'BsmtCond', 'BsmtExposure', 'BsmtFinType1', 'BsmtFinSF1',
'BsmtFinType2', 'BsmtFinSF2', 'BsmtUnfSF', 'TotalBsmtSF', 'Heating',
'HeatingQC', 'CentralAir', 'Electrical', '1stFlrSF', '2ndFlrSF',
'LowQualFinSF', 'GrLivArea', 'BsmtFullBath', 'BsmtHalfBath', 'FullBath',
'HalfBath', 'BedroomAbvGr', 'KitchenAbvGr', 'KitchenQual',
'TotRmsAbvGrd', 'Functional', 'Fireplaces', 'FireplaceQu', 'GarageType',
'GarageYrBlt', 'GarageFinish', 'GarageCars', 'GarageArea', 'GarageQual',
'GarageCond', 'PavedDrive', 'WoodDeckSF', 'OpenPorchSF',
'EnclosedPorch', '3SsnPorch', 'ScreenPorch', 'PoolArea', 'PoolQC',
'Fence', 'MiscFeature', 'MiscVal', 'MoSold', 'YrSold', 'SaleType',
'SaleCondition', 'SalePrice'],
dtype='object')
获取列信息
.describe()用于获取DataFrame某列的基本信息
df_train['SalePrice'].describe()输出
count 1460.000000
mean 180921.195890
std 79442.502883
min 34900.000000
25% 129975.000000
50% 163000.000000
75% 214000.000000
max 755000.000000
Name: SalePrice, dtype: float64
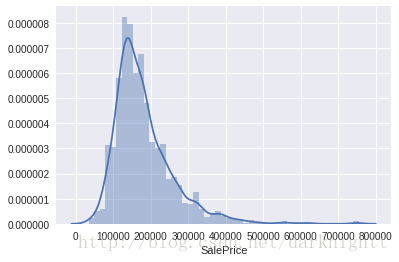
直方图
用seaborn画直方图
sns.displot(df_train['SalePrice'])偏度和峰度
.skew() 获取偏度
.kurt() 获取峰度
print("Skewness: %f" % df_train['SalePrice'].skew())
print("Kurtosis: %f" % df_train['SalePrice'].kurt())输出
Skewness: 1.882876
Kurtosis: 6.536282
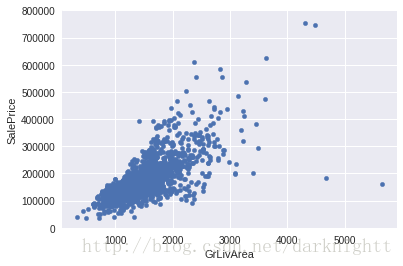
散点图
- 以特征GrLivArea为X轴,预测对象SalePrice为Y轴,观察相关性,如是否有线性关系
var = 'GrLivArea'
data = pd.concat([df_train['SalePrice'], df_train[var]], axis=1)
data.plot.scatter(x=var, y='SalePrice', ylim=(0,800000));- 用seaborn的
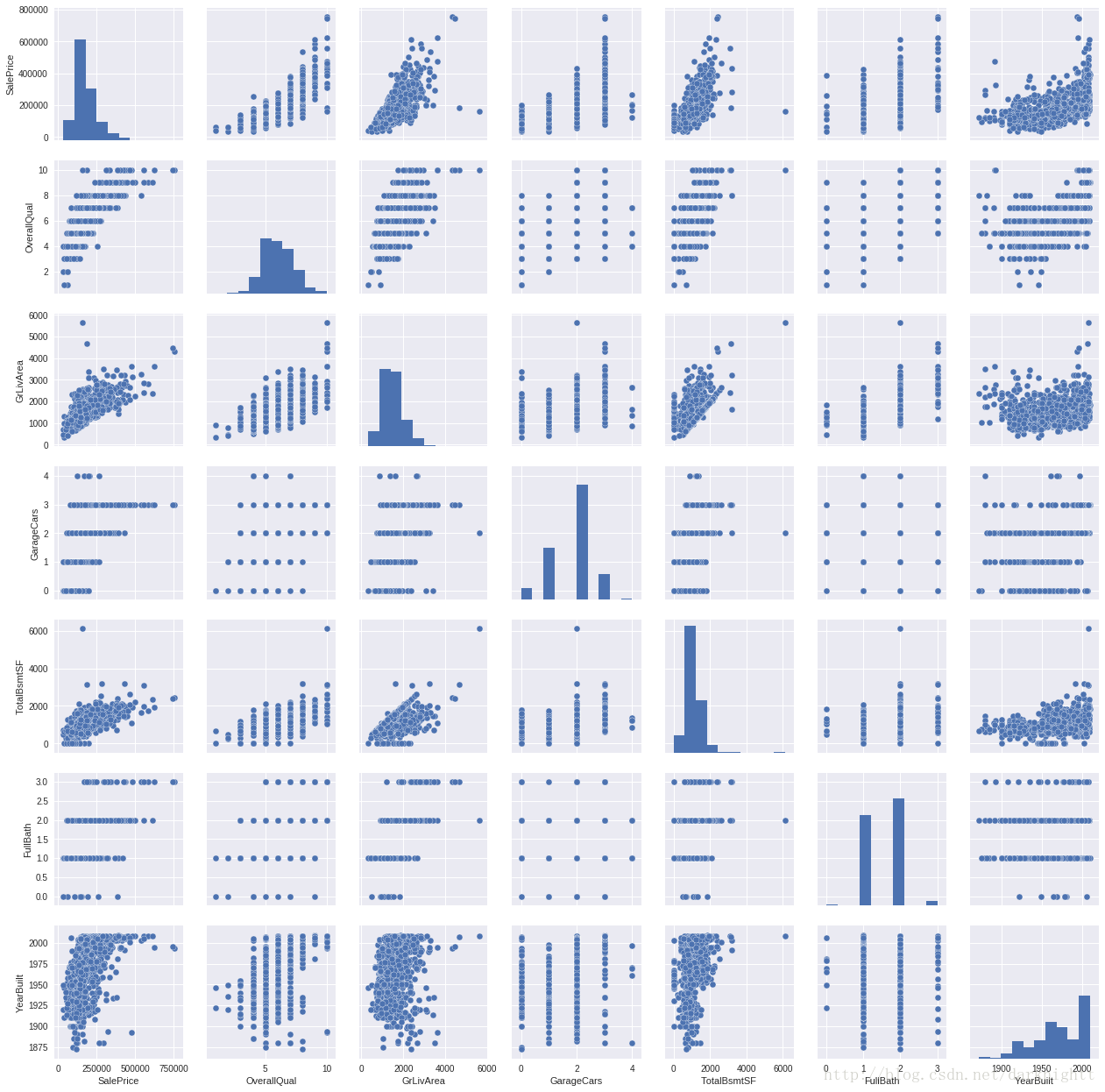
.pairplot()画很多散点图
sns.set()
cols = ['SalePrice', 'OverallQual', 'GrLivArea', 'GarageCars', 'TotalBsmtSF', 'FullBath', 'YearBuilt']
sns.pairplot(df_train[cols], size = 2.5)
plt.show();盒图
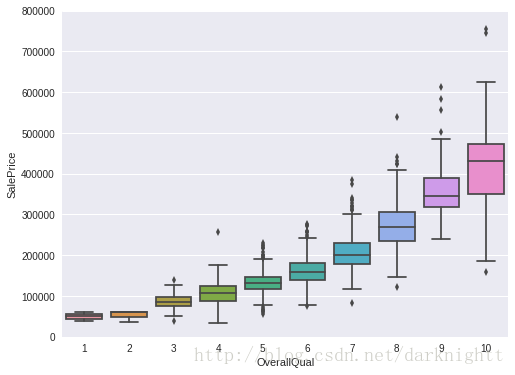
用seaborn的.boxplot() 方法画盒图,观察特征OverallQual与SalePrice的关系
var = 'OverallQual'
data = pd.concat([df_train['SalePrice'], df_train[var]], axis=1)
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
fig = sns.boxplot(x=var, y="SalePrice", data=data)
fig.axis(ymin=0, ymax=800000);热图
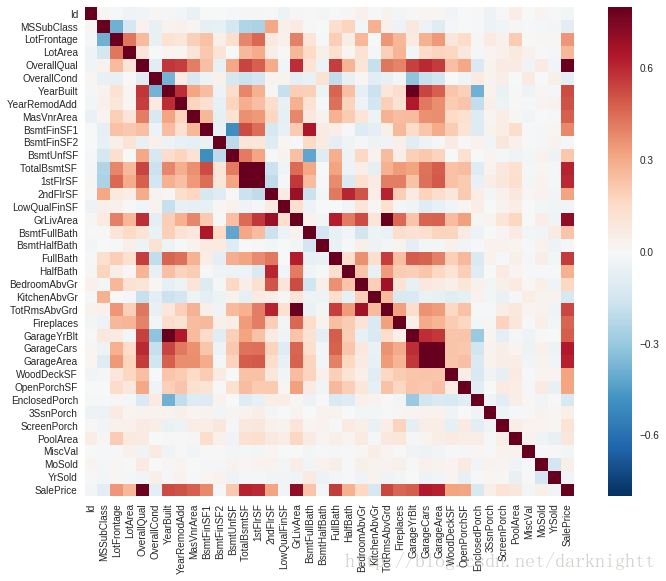
seaborn库的.heatmap() 方法
协方差矩阵热图,颜色越深代表相关性越强
corrmat = df_train.corr()
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 9))
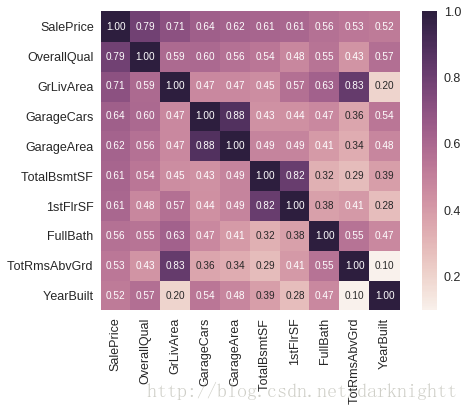
sns.heatmap(corrmat, vmax=.8, square=True);选取与SalePrice相关系数最高的10个特征作热图,显示相关系数
k = 10 #number of variables for heatmap
cols = corrmat.nlargest(k, 'SalePrice')['SalePrice'].index
cm = np.corrcoef(df_train[cols].values.T)
sns.set(font_scale=1.25)
hm = sns.heatmap(cm, cbar=True, annot=True, square=True, fmt='.2f', annot_kws={'size': 10}, yticklabels=cols.values, xticklabels=cols.values)
plt.show()缺失值
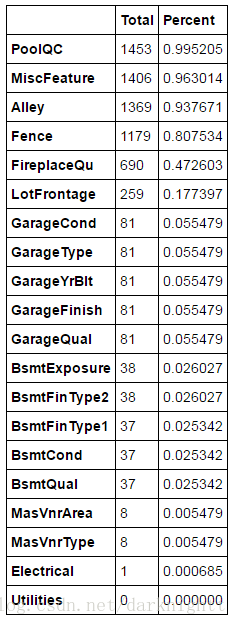
计算各特征对应缺失值占比,返回前20的情况
total = df_train.isnull().sum().sort_values(ascending=False)
percent = (df_train.isnull().sum()/df_train.isnull().count()).sort_values(ascending=False)
missing_data = pd.concat([total, percent], axis=1, keys=['Total', 'Percent'])
missing_data.head(20)离群点
单变量分析
首先用标准化(标准化不会改变数据相对分布的特性)把数据转变成正态分布,分别查看最大和最小的十个值
saleprice_scaled = StandardScaler().fit_transform(df_train['SalePrice'][:,np.newaxis]);
low_range = saleprice_scaled[saleprice_scaled[:,0].argsort()][:10]
high_range= saleprice_scaled[saleprice_scaled[:,0].argsort()][-10:]
print('outer range (low) of the distribution:')
print(low_range)
print('\nouter range (high) of the distribution:')
print(high_range)输出
outer range (low) of the distribution:
[[-1.83820775]
[-1.83303414]
[-1.80044422]
[-1.78282123]
[-1.77400974]
[-1.62295562]
[-1.6166617 ]
[-1.58519209]
[-1.58519209]
[-1.57269236]]
outer range (high) of the distribution:
[[ 3.82758058]
[ 4.0395221 ]
[ 4.49473628]
[ 4.70872962]
[ 4.728631 ]
[ 5.06034585]
[ 5.42191907]
[ 5.58987866]
[ 7.10041987]
[ 7.22629831]]
可以发现,Low range值偏离原点并且都比较相近,High range离远点较远,7.很可能是异常值
双变量分析
以GrLivArea为X轴,SalePrice为y轴画散点图
var = 'GrLivArea'
data = pd.concat([df_train['SalePrice'], df_train[var]], axis=1)
data.plot.scatter(x=var, y='SalePrice', ylim=(0,800000));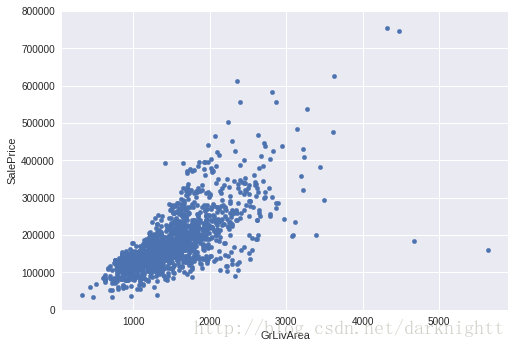
从图中看出二者很可能有线性关系,则图中右下方的两个点作为异常值舍弃
df_train.sort_values(by = 'GrLivArea', ascending = False)[:2]
df_train = df_train.drop(df_train[df_train['Id'] == 1299].index)
df_train = df_train.drop(df_train[df_train['Id'] == 524].index)正态化
scipy库中stats对象的.probplot() 方法拟合一个高斯正态分布,以SalePrice为例
sns.distplot(df_train['SalePrice'], fit=norm);
fig = plt.figure()
res = stats.probplot(df_train['SalePrice'], plot=plt)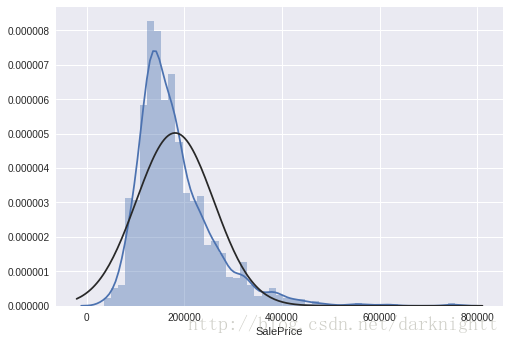
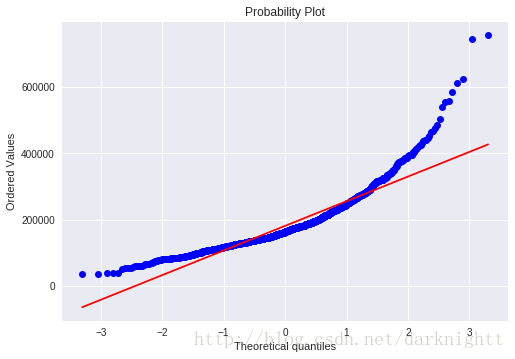
可以看到数据呈正偏态分布,现在我们想把它转变成正太分布。统计学里面一个常用的做法就是对SalePrice的取log。
df_train['SalePrice'] = np.log(df_train['SalePrice'])
sns.distplot(df_train['SalePrice'], fit=norm);
fig = plt.figure()
res = stats.probplot(df_train['SalePrice'], plot=plt)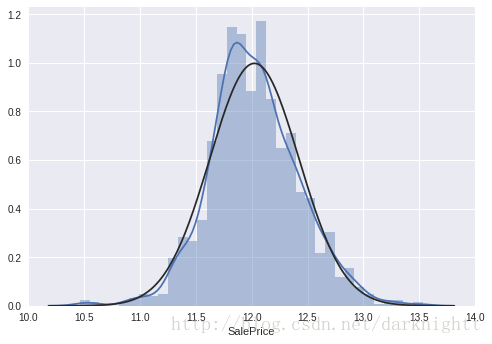
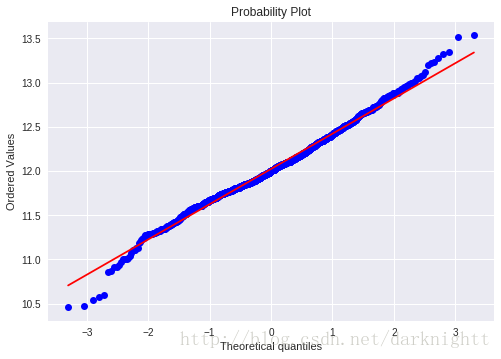
可以看到对SalePrice做了log变换之后近似于正态分布了






















 3021
3021

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








