一、简介
这里使用CUDA实现一种计算计算点云与点云之间的欧式距离,其思路很简单,就是计算每个点到另一个点集之间的最小距离,最终保存结果到一个数组中,通过这种方式可以快速的计算出点云与点云之间的距离,这里充分利用CUDA的并行机制,并使用色带显示距离的远近关系。
二、实现代码
ComputeDistances.cuh
#ifndef COMPUTE_DISTANCES_GPU_CUH
#define COMPUTE_DISTANCES_GPU_CUH
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
// 主机端函数声明
void computeDisByGpu(std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>& points1, std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>& points2, std::vector<float>& dis1, std::vector<float>& dis2);
int getCudaDeviceCount();
#endif // COMPUTE_DISTANCES_GPU_CUH
CalculateDistances.cu
#include "ComputeDistances.cuh"
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
// CPU和GPU端都可以使用
struct Point3f
{
float x, y, z;
// 构造函数
__host__ __device__ Point3f() : x(0), y(0), z(0) {}
__host__ __device__ Point3f(float px, float py, float pz) : x(px), y(py), z(pz) {}
// 向量加法
__host__ __device__ Point3f operator+(const Point3f& p) const {
return Point3f(x + p.x, y + p.y, z + p.z);
}
// 向量减法
__host__ __device__ Point3f operator-(const Point3f& p) const {
return Point3f(x - p.x, y - p.y, z - p.z);
}
// 标量乘法
__host__ __device__ Point3f operator*(float s) const {
return Point3f(x * s, y * s, z * s);
}
// 向量叉乘
__host__ __device__ Point3f Cross(const Point3f& p) const {
return Point3f(y * p.z - z * p.y, z * p.x - x * p.z, x * p.y - y * p.x);
}
// 向量点乘
__host__ __device__ float Dot(const Point3f& p) const {
return (x * p.x + y * p.y + z * p.z);
}
// 向量模
__host__ __device__ float Module() const {
return sqrtf(x * x + y * y + z * z);
}
};
__global__ void calculateDistances(Point3f* points1, Point3f* points2,
float* dis1, float* dis2, int num1, int num2)
{
// 通过 blockIdx.x 和 threadIdx.x 计算当前线程的索引 idx
// ,然后分别对 points1 和 points2 中的每个点,计算它们到另一个点云中所有点的最小距离
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (idx < num1)
{
float minDistance = INFINITY;
for (int i = 0; i < num2; ++i)
{
float distance = (points1[idx] - points2[i]).Module();
if (distance < minDistance) {
minDistance = distance;
}
}
dis1[idx] = minDistance;
}
if (idx < num2)
{
float minDistance = INFINITY;
for (int i = 0; i < num1; ++i)
{
float distance = (points2[idx] - points1[i]).Module();
if (distance < minDistance) {
minDistance = distance;
}
}
dis2[idx] = minDistance;
}
}
void computeDisByGpu(std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>& points1, std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>& points2, std::vector<float>& dis1, std::vector<float>& dis2)
{
int maxNum = std::max(points1.size(), points2.size());
int num1 = points1.size();
int num2 = points2.size();
Point3f* d_points1;
Point3f* d_points2;
float* d_dis1;
float* d_dis2;
// 分配GPU设备内存
cudaMalloc(&d_points1, points1.size() * sizeof(Point3f));
cudaMalloc(&d_points2, points2.size() * sizeof(Point3f));
cudaMalloc(&d_dis1, points1.size() * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&d_dis2, points2.size() * sizeof(float));
// 复制数据到设备
cudaMemcpy(d_points1, points1.data(), points1.size() * sizeof(Point3f), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_points2, points2.data(), points2.size() * sizeof(Point3f), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
dim3 blockSize(256);
dim3 gridSize((maxNum + blockSize.x - 1) / blockSize.x);
calculateDistances <<<gridSize, blockSize>>>(d_points1, d_points2, d_dis1, d_dis2, num1, num2);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
dis1.resize(num1);
dis2.resize(num2);
cudaMemcpy(dis1.data(), d_dis1, num1 * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaMemcpy(dis2.data(), d_dis2, num2 * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(d_points1);
cudaFree(d_points2);
cudaFree(d_dis1);
cudaFree(d_dis2);
}
int getCudaDeviceCount()
{
int count;
cudaGetDeviceCount(&count);
return count;
}
ColorRamp.h
#ifndef ColorRamp_H
#define ColorRamp_H
#include <array>
#include <vector>
class ColorRamp
{
public:
typedef std::array<unsigned char, 3> Color; //
typedef std::pair<double, Color> Step; //
ColorRamp()
{
m_steps.push_back(std::make_pair(0, Color{ 192, 192, 255 }));
m_steps.push_back(std::make_pair(0.2, Color{ 0, 0, 255 }));
m_steps.push_back(std::make_pair(0.4, Color{ 0, 255, 0 }));
m_steps.push_back(std::make_pair(0.6, Color{ 255, 255, 0 }));
m_steps.push_back(std::make_pair(0.8, Color{ 255, 0, 0 }));
m_steps.push_back(std::make_pair(1.0, Color{ 128, 0, 0 }));
}
//
Color get(double value) const
{
if (value < 0.0f) value = 0.0f;
if (value > 1.0f) value = 1.0f;
std::size_t idx = 0;
while (m_steps[idx + 1].first < value)
++idx;
double v0 = m_steps[idx].first;
double v1 = m_steps[idx + 1].first;
const Color& c0 = m_steps[idx].second;
const Color& c1 = m_steps[idx + 1].second;
double ratio = (value - v0) / (v1 - v0);
Color out;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
out[i] = static_cast<unsigned char>((1 - ratio) * c0[i] + ratio * c1[i]);
return out;
}
private:
std::vector<Step> m_steps;
};
#endif // ColorRamp_H
main.cpp
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <Eigen/Core>
// 引入CUDA相关头文件
#include "ComputeDistances.cuh"
#include "ColorRamp.h"
// 使用PCL读取点云并转换为Eigen::Vector3f的格式
void convertPCLToEigen(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pcl_cloud, std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>& eigen_points) {
eigen_points.clear();
for (const auto& point : pcl_cloud->points)
{
eigen_points.emplace_back(point.x, point.y, point.z);
}
}
int main()
{
// ---------------------------------------读取数据----------------------------------
const std::string fileName1 = R"(C:\Users\23547\Desktop\TEST\data\DemoICPPointClouds\cloud_bin_0.pcd)";
const std::string fileName2 = R"(C:\Users\23547\Desktop\TEST\data\DemoICPPointClouds\cloud_bin_2.pcd)";
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud1(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(fileName1, *cloud1) == -1) {
std::cerr << "Couldn't read file cloud1.pcd" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 加载第二个点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud2(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(fileName2, *cloud2) == -1) {
std::cerr << "Couldn't read file cloud2.pcd" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 将PCL点云转换为Eigen::Vector3f的格式
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> points1, points2;
convertPCLToEigen(cloud1, points1);
convertPCLToEigen(cloud2, points2);
// 存储结果的容器
std::vector<float> dis1, dis2;
// 调用CUDA函数进行距离计算
computeDisByGpu(points1, points2, dis1, dis2);
//---------------------------------------可视化----------------------------------
float minVal = std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
float maxVal = -std::numeric_limits<float>::min();
for (float d : dis1)
{
if (minVal > d) minVal = d;
if (maxVal < d) maxVal = d;
}
for (float d : dis2)
{
if (minVal > d) minVal = d;
if (maxVal < d) maxVal = d;
}
ColorRamp cr;
float range = maxVal - minVal;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr cloudRGB1(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
cloudRGB1->resize(dis1.size());
for (int i = 0; i < dis1.size(); ++i)
{
double value = (dis1[i] - minVal) / range;
ColorRamp::Color color = cr.get(value);
cloudRGB1->points[i].x = cloud1->points[i].x;
cloudRGB1->points[i].y = cloud1->points[i].y;
cloudRGB1->points[i].z = cloud1->points[i].z;
cloudRGB1->points[i].r = color[0];
cloudRGB1->points[i].g = color[1];
cloudRGB1->points[i].b = color[2];
}
cloudRGB1->width = cloudRGB1->size();
cloudRGB1->height = 1;
cloudRGB1->is_dense = true;
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("cloud1.pcd", *cloudRGB1);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr cloudRGB2(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
cloudRGB2->resize(dis2.size());
for (int i = 0; i < dis2.size(); ++i)
{
double value = (dis2[i] - minVal) / range;
ColorRamp::Color color = cr.get(value);
cloudRGB2->points[i].x = cloud2->points[i].x;
cloudRGB2->points[i].y = cloud2->points[i].y;
cloudRGB2->points[i].z = cloud2->points[i].z;
cloudRGB2->points[i].r = color[0];
cloudRGB2->points[i].g = color[1];
cloudRGB2->points[i].b = color[2];
}
cloudRGB2->width = cloudRGB2->size();
cloudRGB2->height = 1;
cloudRGB2->is_dense = true;
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("cloud2.pcd", *cloudRGB2);
auto ShowPointCloud = [](pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr cloud1
, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr cloud2)
{
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("Windows"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>(cloud1, "cloud1");
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>(cloud2, "cloud2");
viewer->spin();
};
ShowPointCloud(cloudRGB1, cloudRGB2);
return 0;
}
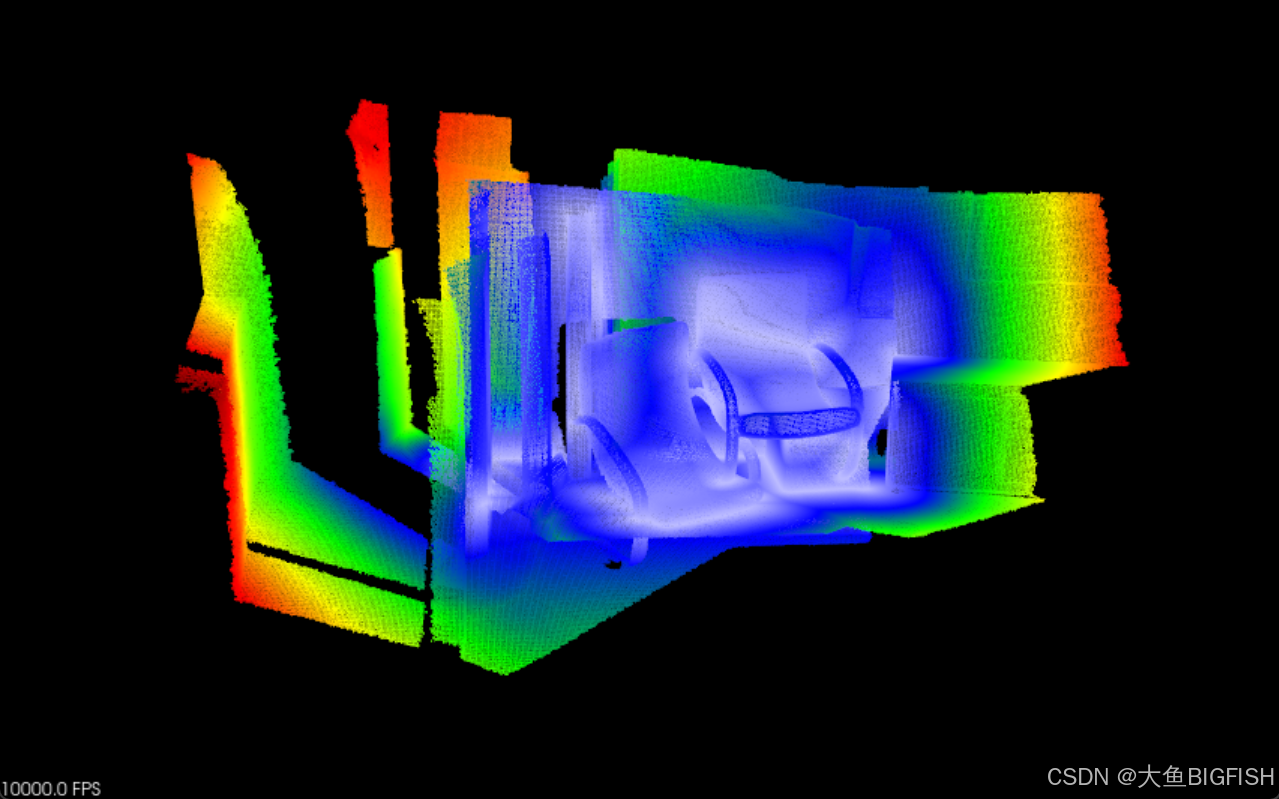
三、实现效果
参考资料
[1]https://bigfish.blog.csdn.net/article/details/141615277?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502























 73
73

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










