tensorflow 1.14.0, 提供远程访问 tensorboard 服务的方法
第一步生成 events 文件:
在上一篇demo的基础上加了一句,如下,
tf.summary.FileWriter("./tmp/summary", graph=sess1.graph)
hello_tensorboard_remote.py
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2'
def tf114_demo():
a = 3
b = 4
c = a + b
print("a + b in py =",c)
a_t = tf.constant(3)
b_t = tf.constant(4)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("TensorFlow add a_t + b_t =", c_t)
with tf.Session() as sess:
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value= ", c_t_value)
return None
def graph_demo():
a_t = tf.constant(3)
b_t = tf.constant(4)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("TensorFlow add a_t + b_t =", c_t)
default_g = tf.get_default_graph()
print("default_g:\n",default_g)
print("a_t g:", a_t.graph)
print("c_t g:", c_t.graph)
with tf.Session() as sess:
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value= ", c_t_value)
print("sess g:", sess.graph)
new_g = tf.Graph()
with new_g.as_default():
a_new = tf.constant(20)
b_new = tf.constant(30)
c_new = a_new + b_new
print("c_new:", c_new)
print("a_new g:",a_new.graph)
print("b_new g:",c_new.graph)
with tf.Session() as sess1:
c_t_value = sess1.run(c_t)
# print("c_new_value:", c_new_value)
print("sess1 g:", sess1.graph)
tf.summary.FileWriter("./tmp/summary", graph=sess1.graph)
with tf.Session(graph=new_g) as new_sess:
c_new_value = new_sess.run((c_new))
print("c_new_value:", c_new_value)
print("new_sess graph properties:", new_sess.graph)
# return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
# tf114_demo()
graph_demo()
运行 tensorflow1 的 app:
python3 hello_tensorboard_remote.py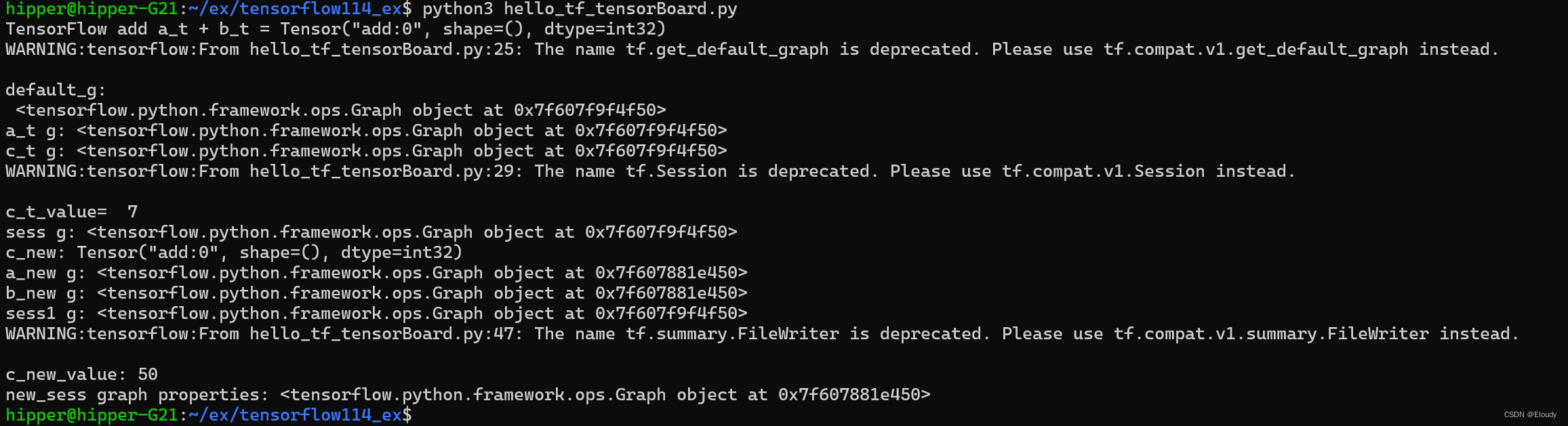
ls ./tmp/summary/ 启动 tensorboard 网络服务:
tensorboard --logdir="./tmp/summary" --port 67896789是自己选定的端口号,尝试任选;
运行状态如下:

远程访问tensorboard:
在同一个网络内的主机网页浏览器的地址栏中输入:
http://10.208.14.37:6789效果如下,显示出来了示例中非常简单的一个计算图:
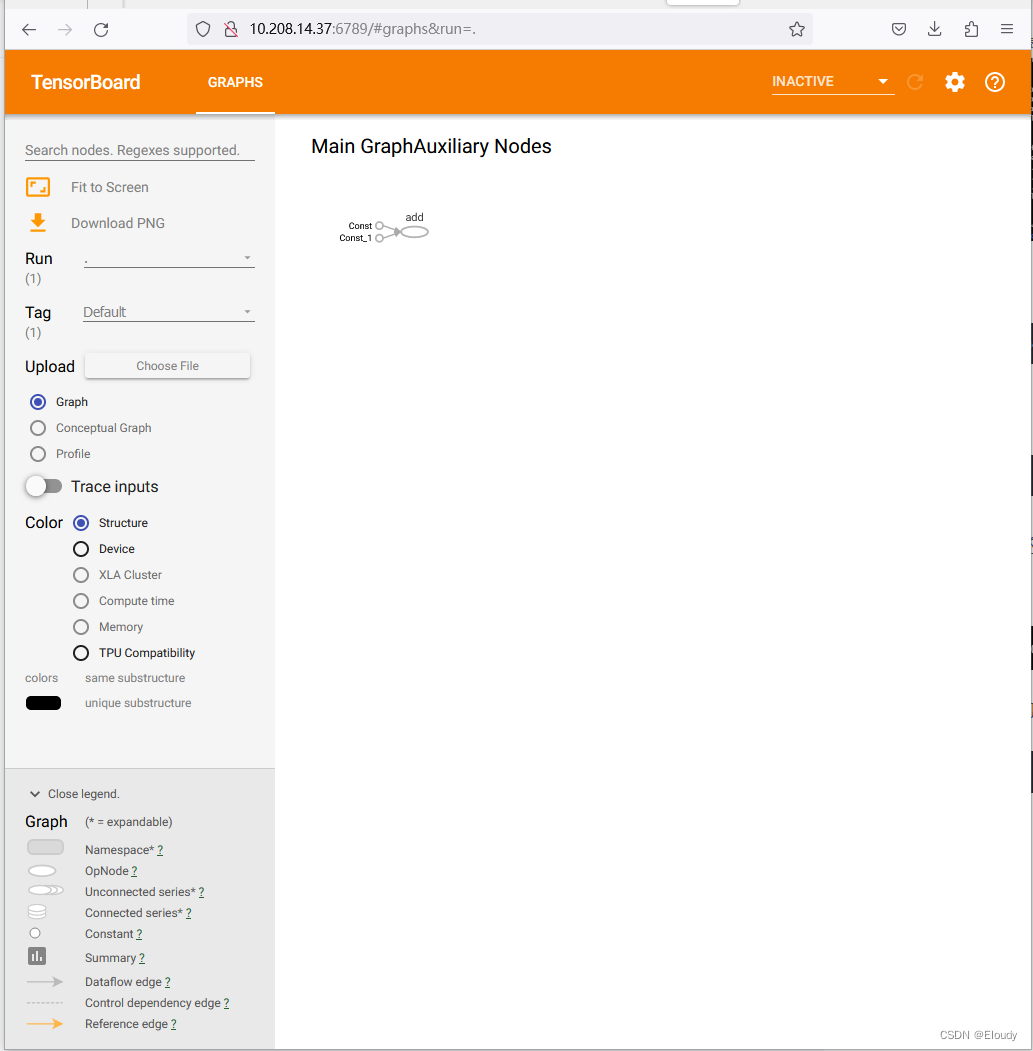
如果是本机访问,则在地址栏里输入
http://127.0.0.1:6006
demo03 convolutional_network_raw.py
tf.summary.FileWriter("./tmp/summary", graph=sess.graph)
""" Convolutional Neural Network.
Build and train a convolutional neural network with TensorFlow.
This example is using the MNIST database of handwritten digits
(http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/)
Author: Aymeric Damien
Project: https://github.com/aymericdamien/TensorFlow-Examples/
"""
from __future__ import division, print_function, absolute_import
import tensorflow as tf
# Import MNIST data
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/tmp/data/", one_hot=True)
# Training Parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
num_steps = 200
batch_size = 128
display_step = 10
# Network Parameters
num_input = 784 # MNIST data input (img shape: 28*28)
num_classes = 10 # MNIST total classes (0-9 digits)
dropout = 0.75 # Dropout, probability to keep units
# tf Graph input
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, num_input])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, num_classes])
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # dropout (keep probability)
# Create some wrappers for simplicity
def conv2d(x, W, b, strides=1):
# Conv2D wrapper, with bias and relu activation
x = tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, strides, strides, 1], padding='SAME')
x = tf.nn.bias_add(x, b)
return tf.nn.relu(x)
def maxpool2d(x, k=2):
# MaxPool2D wrapper
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, k, k, 1], strides=[1, k, k, 1],
padding='SAME')
# Create model
def conv_net(x, weights, biases, dropout):
# MNIST data input is a 1-D vector of 784 features (28*28 pixels)
# Reshape to match picture format [Height x Width x Channel]
# Tensor input become 4-D: [Batch Size, Height, Width, Channel]
x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
# Convolution Layer
conv1 = conv2d(x, weights['wc1'], biases['bc1'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
conv1 = maxpool2d(conv1, k=2)
# Convolution Layer
conv2 = conv2d(conv1, weights['wc2'], biases['bc2'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
conv2 = maxpool2d(conv2, k=2)
# Fully connected layer
# Reshape conv2 output to fit fully connected layer input
fc1 = tf.reshape(conv2, [-1, weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]])
fc1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['wd1']), biases['bd1'])
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1)
# Apply Dropout
fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1, dropout)
# Output, class prediction
out = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['out']), biases['out'])
return out
# Store layers weight & bias
weights = {
# 5x5 conv, 1 input, 32 outputs
'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 1, 32])),
# 5x5 conv, 32 inputs, 64 outputs
'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 32, 64])),
# fully connected, 7*7*64 inputs, 1024 outputs
'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7*7*64, 1024])),
# 1024 inputs, 10 outputs (class prediction)
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, num_classes]))
}
biases = {
'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([32])),
'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64])),
'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([num_classes]))
}
# Construct model
logits = conv_net(X, weights, biases, keep_prob)
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
# Define loss and optimizer
loss_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=logits, labels=Y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss_op)
# Evaluate model
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
# Initialize the variables (i.e. assign their default value)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Start training
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
# Run the initializer
sess.run(init)
for step in range(1, num_steps+1):
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
# Run optimization op (backprop)
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={X: batch_x, Y: batch_y, keep_prob: 0.8})
if step % display_step == 0 or step == 1:
# Calculate batch loss and accuracy
loss, acc = sess.run([loss_op, accuracy], feed_dict={X: batch_x,
Y: batch_y,
keep_prob: 1.0})
print("Step " + str(step) + ", Minibatch Loss= " + \
"{:.4f}".format(loss) + ", Training Accuracy= " + \
"{:.3f}".format(acc))
print("Optimization Finished!")
# Calculate accuracy for 256 MNIST test images
print("Testing Accuracy:", \
sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[:256],
Y: mnist.test.labels[:256],
keep_prob: 1.0}))
tf.summary.FileWriter("./tmp/summary", graph=sess.graph)$ python3 convolutional_network_raw.py
另一台网内的机器上访问结果:
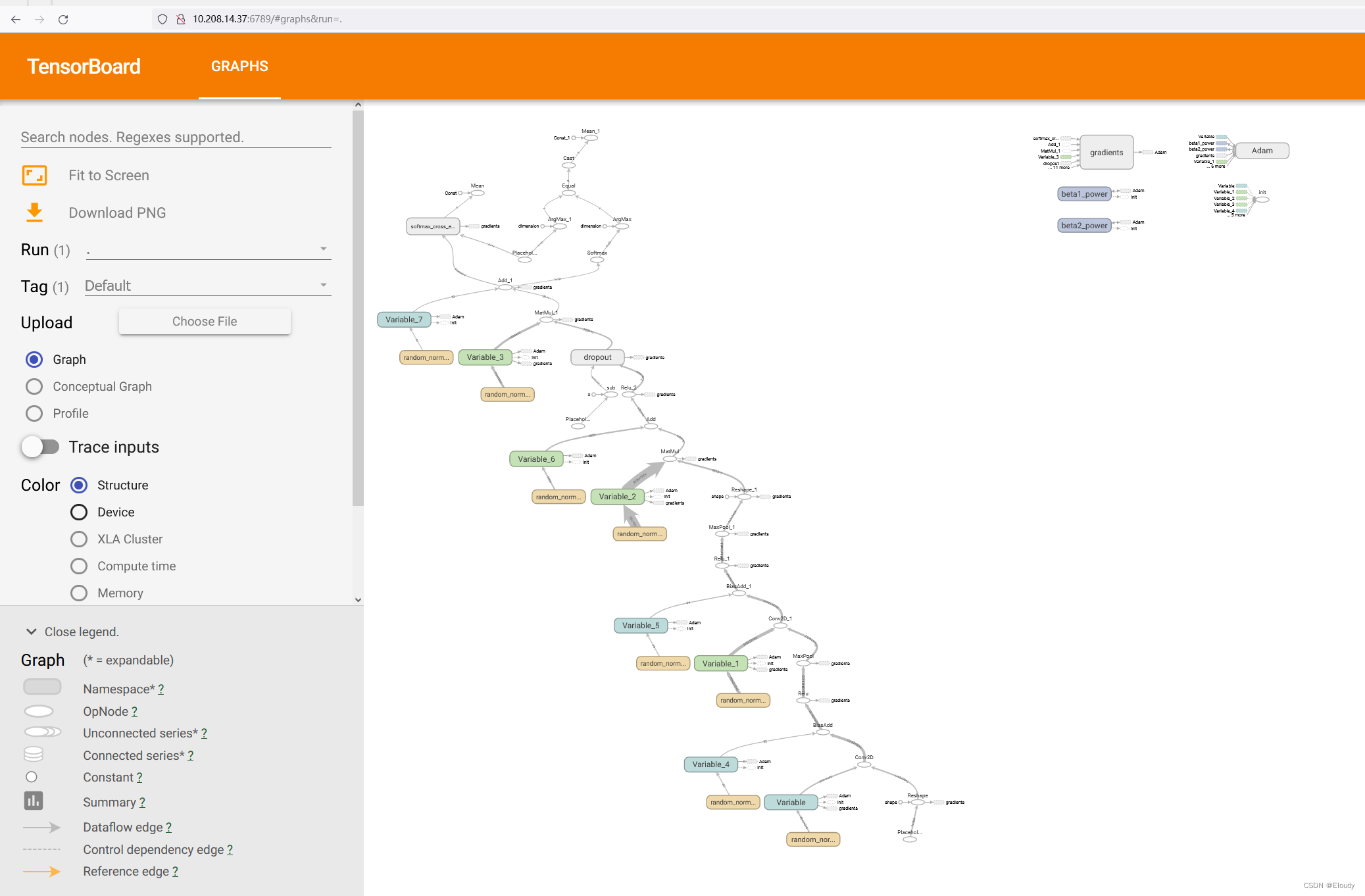





















 98
98











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








