kmeans
Finds centers of clusters and groups input samples around the clusters.
-
C++: double kmeans(InputArray data, int K, InputOutputArray bestLabels, TermCriteria criteria, int attempts, int flags, OutputArray centers=noArray() )
-
Python: cv2.kmeans(data, K, criteria, attempts, flags[, bestLabels[, centers]]) → retval, bestLabels, centers
-
C: int cvKMeans2(const CvArr* samples, int cluster_count, CvArr* labels, CvTermCriteria termcrit, int attempts=1, CvRNG* rng=0, int flags=0, CvArr* _centers=0, double*compactness=0 )
-
Python: cv.KMeans2(samples, nclusters, labels, termcrit, attempts=1, flags=0, centers=None) → float
-
Parameters: - samples – Floating-point matrix of input samples, one row per sample.
- data – Data for clustering.
- cluster_count – Number of clusters to split the set by.
- K – Number of clusters to split the set by.
- labels – Input/output integer array that stores the cluster indices for every sample.
- criteria – The algorithm termination criteria, that is, the maximum number of iterations and/or the desired accuracy. The accuracy is specified as criteria.epsilon. As soon as each of the cluster centers moves by less than criteria.epsilon on some iteration, the algorithm stops.
- termcrit – The algorithm termination criteria, that is, the maximum number of iterations and/or the desired accuracy.
- attempts – Flag to specify the number of times the algorithm is executed using different initial labellings. The algorithm returns the labels that yield the best compactness (see the last function parameter).
- rng – CvRNG state initialized by RNG().
- flags –
Flag that can take the following values:
- KMEANS_RANDOM_CENTERS Select random initial centers in each attempt.
- KMEANS_PP_CENTERS Use kmeans++ center initialization by Arthur and Vassilvitskii [Arthur2007].
- KMEANS_USE_INITIAL_LABELS During the first (and possibly the only) attempt, use the user-supplied labels instead of computing them from the initial centers. For the second and further attempts, use the random or semi-random centers. Use one of KMEANS_*_CENTERS flag to specify the exact method.
- centers – Output matrix of the cluster centers, one row per each cluster center.
- _centers – Output matrix of the cluster centers, one row per each cluster center.
- compactness – The returned value that is described below.
The function kmeans implements a k-means algorithm that finds the centers of cluster_count clusters and groups the input samples around the clusters. As an output,  contains a 0-based cluster index for the sample stored in the
contains a 0-based cluster index for the sample stored in the  row of the samples matrix.
row of the samples matrix.
The function returns the compactness measure that is computed as

after every attempt. The best (minimum) value is chosen and the corresponding labels and the compactness value are returned by the function. Basically, you can use only the core of the function, set the number of attempts to 1, initialize labels each time using a custom algorithm, pass them with the ( flags = KMEANS_USE_INITIAL_LABELS ) flag, and then choose the best (most-compact) clustering.
Note
- An example on K-means clustering can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/kmeans.cpp
- (Python) An example on K-means clustering can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/python2/kmeans.py
Opencv Sample
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
// static void help()
// {
// cout << "\nThis program demonstrates kmeans clustering.\n"
// "It generates an image with random points, then assigns a random number of cluster\n"
// "centers and uses kmeans to move those cluster centers to their representitive location\n"
// "Call\n"
// "./kmeans\n" << endl;
// }
int main( int /*argc*/, char** /*argv*/ )
{
const int MAX_CLUSTERS = 5;
Scalar colorTab[] =
{
Scalar(0, 0, 255),
Scalar(0,255,0),
Scalar(255,100,100),
Scalar(255,0,255),
Scalar(0,255,255)
};
Mat img(500, 500, CV_8UC3);
RNG rng(12345);
for(;;)
{
int k, clusterCount = rng.uniform(2, MAX_CLUSTERS+1);
int i, sampleCount = rng.uniform(1, 1001);
Mat points(sampleCount, 1, CV_32FC2), labels;
clusterCount = MIN(clusterCount, sampleCount);
Mat centers(clusterCount, 1, points.type());
/* generate random sample from multigaussian distribution */
for( k = 0; k < clusterCount; k++ )
{
Point center;
center.x = rng.uniform(0, img.cols);
center.y = rng.uniform(0, img.rows);
Mat pointChunk = points.rowRange(k*sampleCount/clusterCount,
k == clusterCount - 1 ? sampleCount :
(k+1)*sampleCount/clusterCount);
rng.fill(pointChunk, CV_RAND_NORMAL, Scalar(center.x, center.y), Scalar(img.cols*0.05, img.rows*0.05));
}
randShuffle(points, 1, &rng);
kmeans(points, clusterCount, labels,
TermCriteria( CV_TERMCRIT_EPS+CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 10, 1.0),
3, KMEANS_PP_CENTERS, centers);
img = Scalar::all(0);
for( i = 0; i < sampleCount; i++ )
{
int clusterIdx = labels.at<int>(i);
Point ipt = points.at<Point2f>(i);
circle( img, ipt, 2, colorTab[clusterIdx], CV_FILLED, CV_AA );
}
imshow("clusters", img);
char key = (char)waitKey();
if( key == 27 || key == 'q' || key == 'Q' ) // 'ESC'
break;
}
return 0;
}
Opencv 图像分割
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include "opencv/cv.h"
#include "opencv/highgui.h"
#include "opencv/cxcore.h"
#define ClusterNum (6)
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat clustering(Mat src)
{
int row = src.rows;
int col = src.cols;
unsigned long int size = row*col;
Mat clusters(size, 1, CV_32SC1); //clustering Mat, save class label at every location;
//convert src Mat to sample srcPoint.
Mat srcPoint(size, 1, CV_32FC3);
Vec3f* srcPoint_p = (Vec3f*)srcPoint.data;//
Vec3f* src_p = (Vec3f*)src.data;
unsigned long int i;
for(i = 0;i < size; i++)
{
*srcPoint_p = *src_p;
srcPoint_p++;
src_p++;
}
Mat center(ClusterNum,1,CV_32FC3);
double compactness;//compactness to measure the clustering center dist sum by different flag
compactness = kmeans(srcPoint, ClusterNum, clusters,
cvTermCriteria (CV_TERMCRIT_EPS + CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 10, 0.1),ClusterNum,
KMEANS_PP_CENTERS , center);
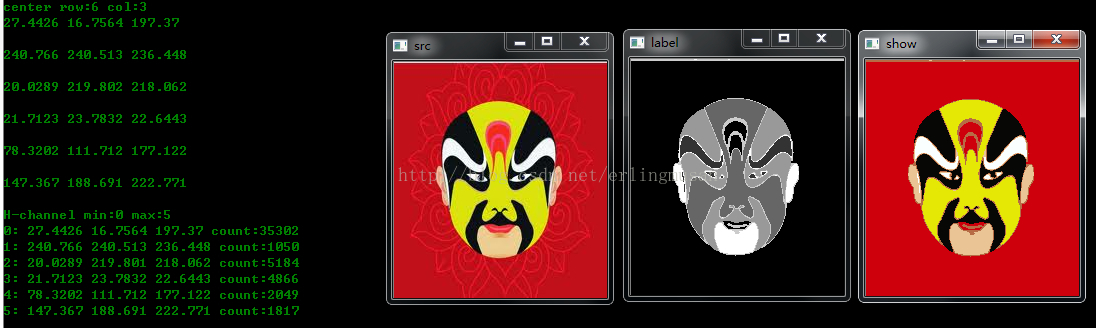
cout<<"center row:"<<center.rows<<" col:"<<center.cols<<endl;
for (int y = 0; y < center.rows; y++)
{
Vec3f* imgData = center.ptr<Vec3f>(y);
cout<<imgData->val[0]<<" "<<imgData->val[1]<<" "<<imgData->val[2]<<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
double minH,maxH;
minMaxLoc(clusters, &minH, &maxH); //remember must use "&"
cout<<"H-channel min:"<<minH<<" max:"<<maxH<<endl;
int* clusters_p = (int*)clusters.data;
//show label mat
Mat label(src.size(), CV_32SC1);
int* label_p = (int*)label.data;
//assign the clusters to Mat label
for(i = 0;i < size; i++)
{
*label_p = *clusters_p;
label_p++;
clusters_p++;
}
Mat label_show;
label.convertTo(label_show,CV_8UC1);
normalize(label_show,label_show,255,0,CV_MINMAX);
imshow("label",label_show);
map<int,int> count; //map<id,num>
map<int,Vec3f> avg; //map<id,color>
//compute average color value of one label
for (int y = 0; y < row; y++)
{
const Vec3f* imgData = src.ptr<Vec3f>(y);
int* idx = label.ptr<int>(y);
for (int x = 0; x < col; x++)
{
avg[idx[x]] += imgData[x];
count[idx[x]] ++;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < ClusterNum; i++)
{
avg[i] /= count[i];
if (avg[i].val[0]>0&&avg[i].val[1]>0&&avg[i].val[2]>0)
{
cout<<i<<": "<<avg[i].val[0]<<" "<<avg[i].val[1]<<" "<<avg[i].val[2]<<" count:"<<count[i]<<endl;
}
}
//show the clustering img;
Mat showImg(src.size(),CV_32FC3);
for (int y = 0; y < row; y++)
{
Vec3f* imgData = showImg.ptr<Vec3f>(y);
int* idx = label.ptr<int>(y);
for (int x = 0; x < col; x++)
{
int id = idx[x];
imgData[x].val[0] = avg[id].val[0];
imgData[x].val[1] = avg[id].val[1];
imgData[x].val[2] = avg[id].val[2];
}
}
normalize(showImg,showImg,1,0,CV_MINMAX);
imshow("show",showImg);
waitKey();
return label;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat img=imread(argv[1]);
imshow("src",img);
GaussianBlur(img,img,Size(3,3),0);
img.convertTo(img,CV_32FC3);
Mat pixId=clustering(img);
}






















 5161
5161

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








