匈牙利算法原理与Python实现
今天学习一个新的算法-匈牙利算法,用于聚类结果分析,先用图表示我当前遇到的问题:
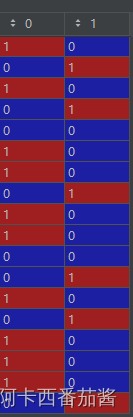
这两列值是我用不同算法得到的聚类结果,从肉眼可以看出第一列聚类为0的结果在第二列中对应的值为1.
为了使得两聚类结果可比,我需要将第二列的聚类结果做一次数据映射。当然这只是一个非常简单的情况,如果出现3类及以上就会变得复杂。
那么匈牙利的算法原理是啥?
如何利用python实现,下面我将简略翻译这篇文章,如果有词不达意的地方,请批评指正~ Hungarian Algorithm Introduction & Python Implementation | by Eason | Python in Plain English
这位大佬真的写的很详细!谢谢 Eason 的分享!
正文
在这篇文章中,我将介绍如何使用匈牙利方法来解决线性赋值问题,并提供我个人的Python代码解决方案。
那么…什么是线性分配问题?
线性分配问题表示需要在有限的资源下使可用资源最大化(或支出最小化)。例如,下面是一个二维矩阵,每一行代表一个不同的供应商,每一列代表雇用他们生产一个特定产品的成本。每个供应商只能专门生产其中一种产品。换句话说,矩阵中的每一列和每一行只能选择一个元素,而且所选元素的总和必须是最小的(成本支出最小)。
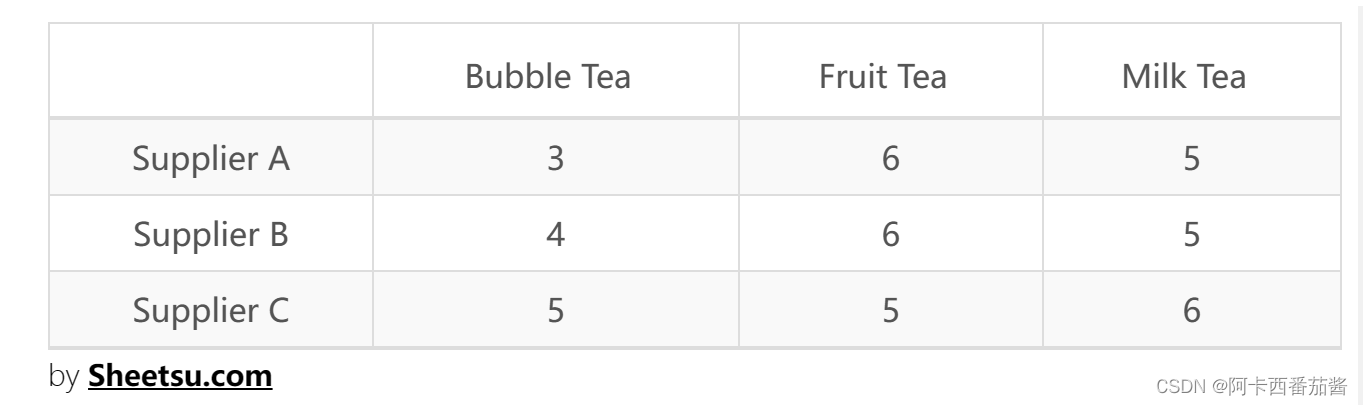
这是一个简单的例子。通过尝试可能的组合,我们可以看到最小的总和是13,所以供应商A供应 Bubble tea,供应商B供应milk tea,而供应商C供应 fruit tea。然而,这样的尝试并不遵循明确的规则,在应用于大型任务时就会变得低效。
因此,下一节将逐步介绍匈牙利算法,该算法可应用于线性分配问题。
匈牙利算法和Python代码的步骤
在本节中,我们将展示如何使用匈牙利算法来解决线性赋值问题并找到矩阵中的最小组合。当然,匈牙利算法也可以用来寻找最大组合。
import numpy as np
cost_matrix = np.random.randint(10,size=(5, 5))
print(f"The cost matrix is:\n", cost_matrix)
如果我们想找到最大的总和,我们可以反过来做。
要解决的矩阵被看作是利润矩阵,矩阵中的最大值被设定为所有商品的共同价格。
成本矩阵是由利润矩阵减去最大值得到的。
最后,将成本矩阵代入匈牙利算法,得到最小化的组合。
然后重新映射回利润矩阵,得到最大的总和值和组合结果。
import numpy as np
# The matrix who you want to find the maximum sum
profit_matrix = np.random.randint(10,size=(5, 5))
# Using the maximum value of the profit_matrix to get the corresponding cost_matrix
max_value = np.max(profit_matrix)
#Using the cost matrix to find which positions are the answer
cost_matrix = max_value - profit_matrix
print(f"The profit matrix is:\n", profit_matrix, f"\nThe cost matrix is:\n", cost_matrix)
按照上面的步骤,你可以随机生成成本矩阵或利润矩阵。
接下来,我们将进入匈牙利算法的介绍,为了便于说明,下面的章节将使用下图所示的成本矩阵进行说明。我们将使用匈牙利算法来解决成本矩阵的线性分配问题,并找到相应的最小和。
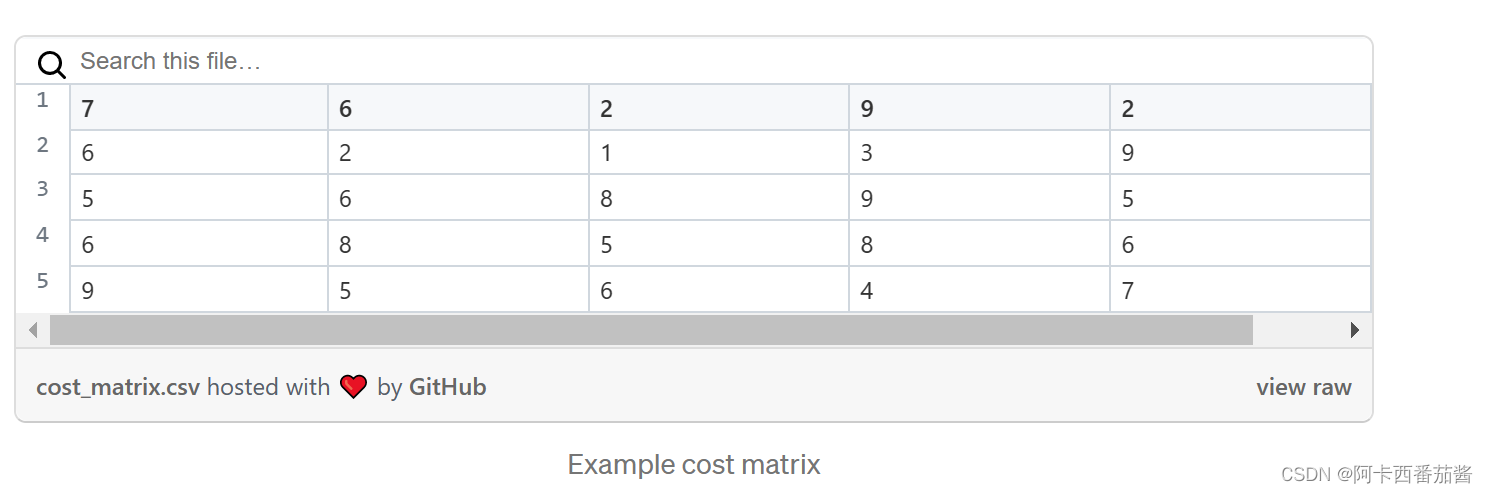
步骤1:每一列和每一行减去其内部最小值
首先,每一列和每一行必须减去其内部最小值。减去最小值后,成本矩阵将看起来像这样。
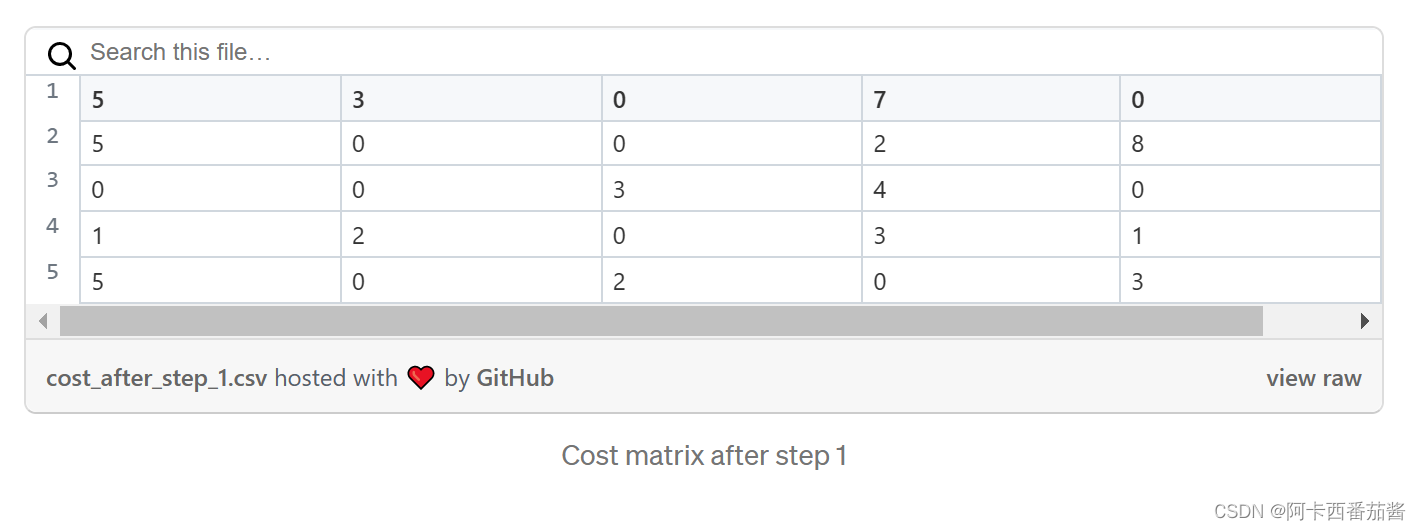
当前实现的代码:
import numpy as np
def hungarian_algorithm(mat):
dim = mat.shape[0]
cur_mat = mat
#Step 1 - Every column and every row subtract its internal minimum
for row_num in range(mat.shape[0]):
cur_mat[row_num] = cur_mat[row_num] - np.min(cur_mat[row_num])
for col_num in range(mat.shape[1]):
cur_mat[:,col_num] = cur_mat[:,col_num] - np.min(cur_mat[:,col_num])
def main():
#The matrix who you want to find the maximum sum
cost_matrix = np.array([[7, 6, 2, 9, 2],
[6, 2, 1, 3, 9],
[5, 6, 8, 9, 5],
[6, 8, 5, 8, 6],
[9, 5, 6, 4, 7]])
ans_pos = hungarian_algorithm(cost_matrix.copy())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
步骤2-1: Min_zero_row函数的实现
首先,我们需要找到零元素最少的那一行。因此,我们可以将前面的矩阵转换成布尔矩阵(0→真,其他→假)。
import numpy as np
#Transform the matrix to boolean matrix(0 = True, others = False)
zero_bool_mat = (cur_mat == 0)
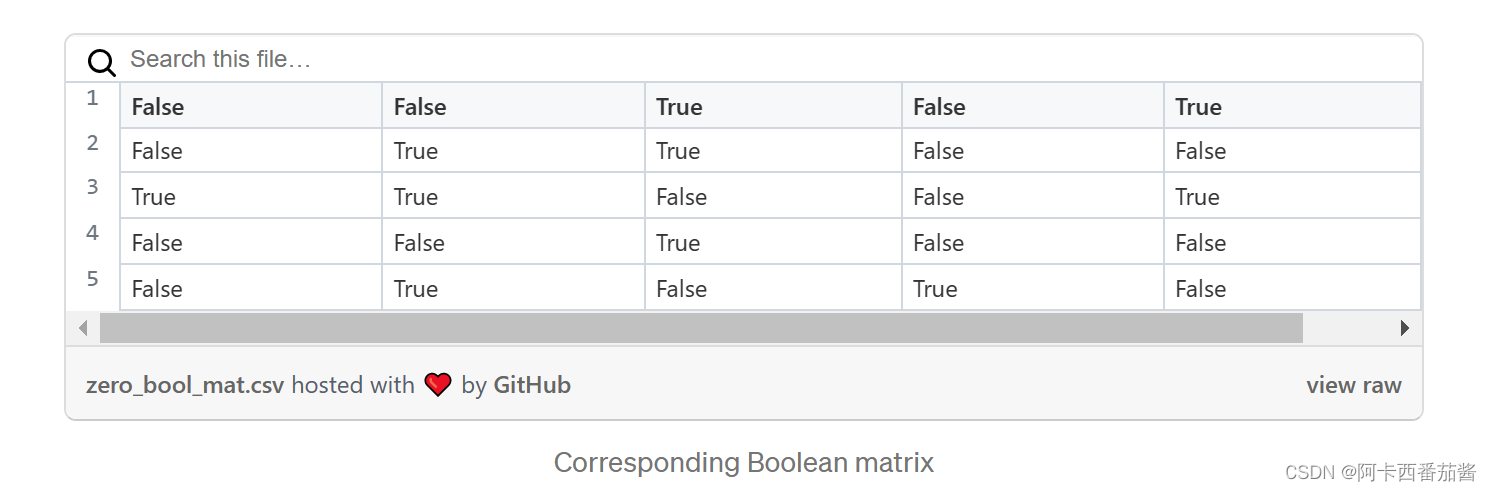
因此,我们可以使用 "min_zero_row "函数来找到相应的行。
# zero_mat = boolean, mark_zero = blank list
def min_zero_row(zero_mat, mark_zero):
'''
The function can be splitted into two steps:
#1 The function is used to find the row which containing the fewest 0.
#2 Select the zero number on the row, and then marked the element corresponding row and column as False
'''
#Find the row
min_row = [99999, -1]
for row_num in range(zero_mat.shape[0]):
if np.sum(zero_mat[row_num] == True) > 0 and min_row[0] > np.sum(zero_mat[row_num] == True):
min_row = [np.sum(zero_mat[row_num] == True), row_num]
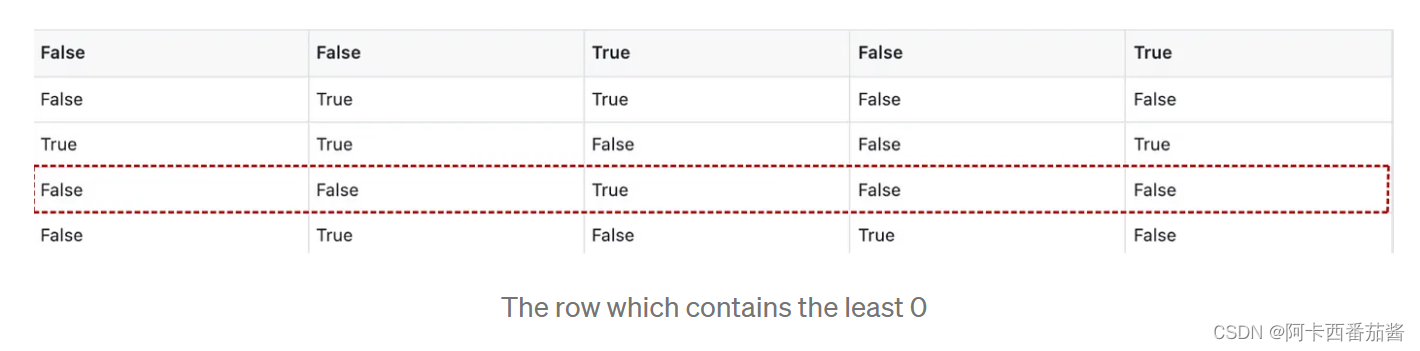
第三,标记相应行上的任何0元素,并整理其行和列(将布尔矩阵上的元素转换为False)。该元素的坐标被存储在mark_zero中。
# zero_mat = boolean matrix, mark_zero = blank list
def min_zero_row(zero_mat, mark_zero):
'''
The function can be splitted into two steps:
#1 The function is used to find the row which containing the fewest 0.
#2 Select the zero number on the row, and then marked the element corresponding row and column as False
'''
#Find the row
min_row = [99999, -1]
for row_num in range(zero_mat.shape[0]):
if np.sum(zero_mat[row_num] == True) > 0 and min_row[0] > np.sum(zero_mat[row_num] == True):
min_row = [np.sum(zero_mat[row_num] == True), row_num]
# Marked the specific row and column as False
zero_index = np.where(zero_mat[min_row[1]] == True)[0][0]
mark_zero.append((min_row[1], zero_index))
zero_mat[min_row[1], :] = False
zero_mat[:, zero_index] = False
因此,布尔矩阵将看起来像这样:
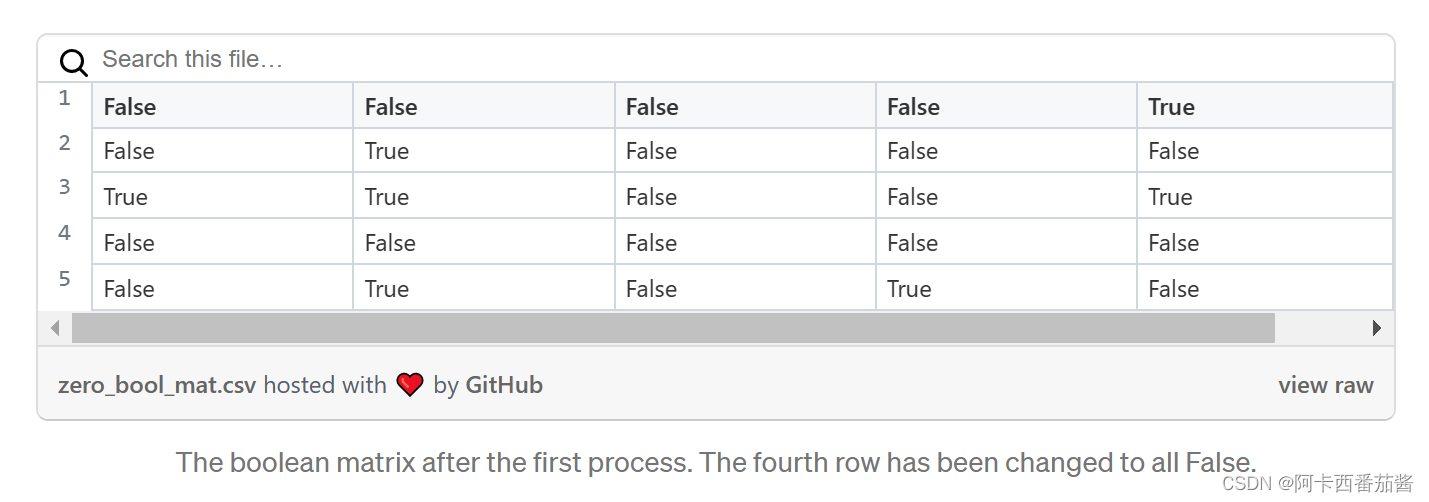
这个过程要重复几次,直到布尔矩阵中的元素都是假的。下图显示了它们被标记的顺序。
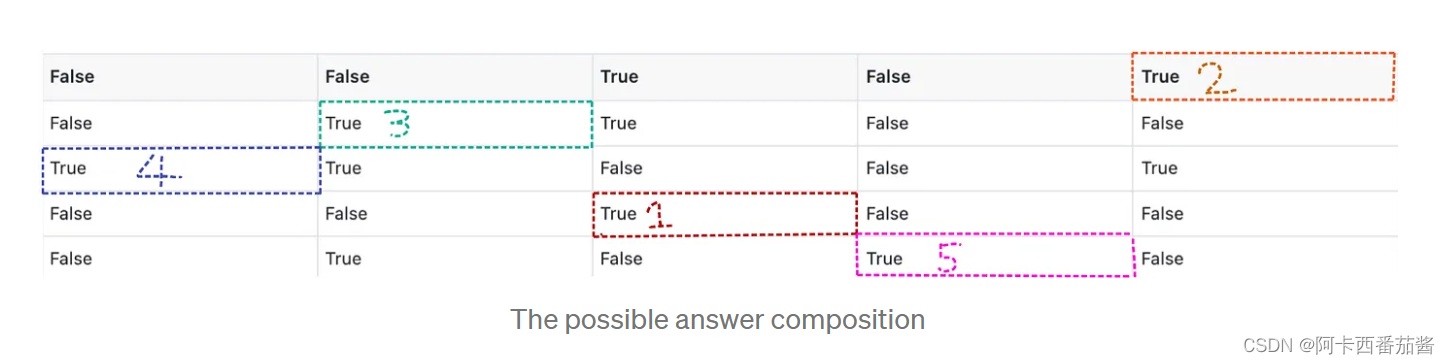
步骤2-2. Mark_matrix函数的实现
从步骤2-1得到Zero_mat后,我们可以根据一定的规则检查并标记矩阵。整个规则可以分解成几个步骤。
- 标记不包含被标记的0元素的行,并在non_marked_row中存储行索引;
- 搜索non_marked_row元素,并找出相应列中是否有未标记的0元素;
- 将列索引存储在marked_cols中;
- 比较存储在marked_zero和marked_cols中的列索引;
- 如果存在一个匹配的列索引,那么相应的行索引就会被保存到non_marked_rows中;
- 接下来,不在non_marked_row中的行索引被保存在marked_rows中;
最后,整个mark_matrx函数结束,然后返回mark_zero, marked_rows, marked_cols。这时,我们就可以根据返回的信息来决定结果。
def mark_matrix(mat):
'''
Finding the returning possible solutions for LAP problem.
'''
#Transform the matrix to boolean matrix(0 = True, others = False)
cur_mat = mat
zero_bool_mat = (cur_mat == 0)
zero_bool_mat_copy = zero_bool_mat.copy()
#Recording possible answer positions by marked_zero
marked_zero = []
while (True in zero_bool_mat_copy):
min_zero_row(zero_bool_mat_copy, marked_zero)
#Recording the row and column indexes seperately.
marked_zero_row = []
marked_zero_col = []
for i in range(len(marked_zero)):
marked_zero_row.append(marked_zero[i][0])
marked_zero_col.append(marked_zero[i][1])
#step 2-2-1
non_marked_row = list(set(range(cur_mat.shape[0])) - set(marked_zero_row))
marked_cols = []
check_switch = True
while check_switch:
check_switch = False
for i in range(len(non_marked_row)):
row_array = zero_bool_mat[non_marked_row[i], :]
for j in range(row_array.shape[0]):
#step 2-2-2
if row_array[j] == True and j not in marked_cols:
#step 2-2-3
marked_cols.append(j)
check_switch = True
for row_num, col_num in marked_zero:
#step 2-2-4
if row_num not in non_marked_row and col_num in marked_cols:
#step 2-2-5
non_marked_row.append(row_num)
check_switch = True
#step 2-2-6
marked_rows = list(set(range(mat.shape[0])) - set(non_marked_row))
return(marked_zero, marked_rows, marked_cols)
如果我们使用示例成本矩阵,相应的marked_zero、marked_rows和marked_cols如下。
marked_zero: [(3, 2), (0, 4), (1, 1), (2, 0), (4, 3)]
marked_rows:[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
marked_cols: []
第3步:识别结果
在这一步,如果mark_rows和mark_cols的长度之和等于成本矩阵的长度,就意味着线性赋值问题的解决方案已经被成功找到,mark_zero存储了解决方案的坐标。幸运的是,在示例矩阵中,我们第一次就找到了答案。因此,我们可以跳到第5步,计算出解。
然而,一切都不是一帆风顺的。大多数情况下,我们不会在第一次尝试时就找到答案,比如下面这个矩阵。
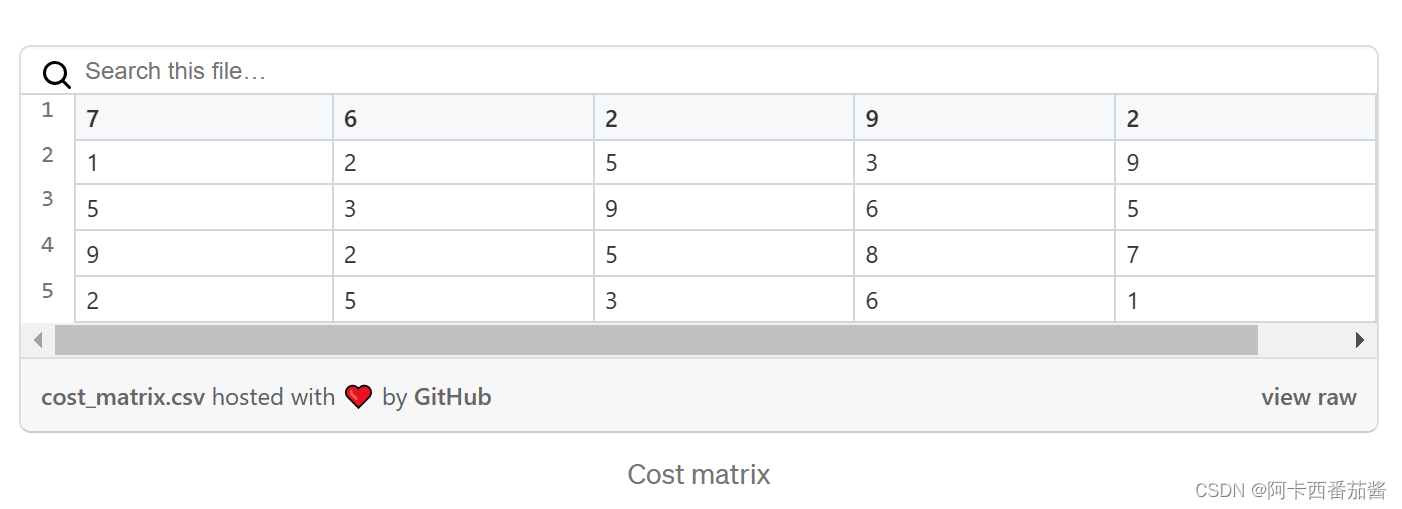
经过步骤1和2,相应的矩阵、标记的行和标记的列如下:
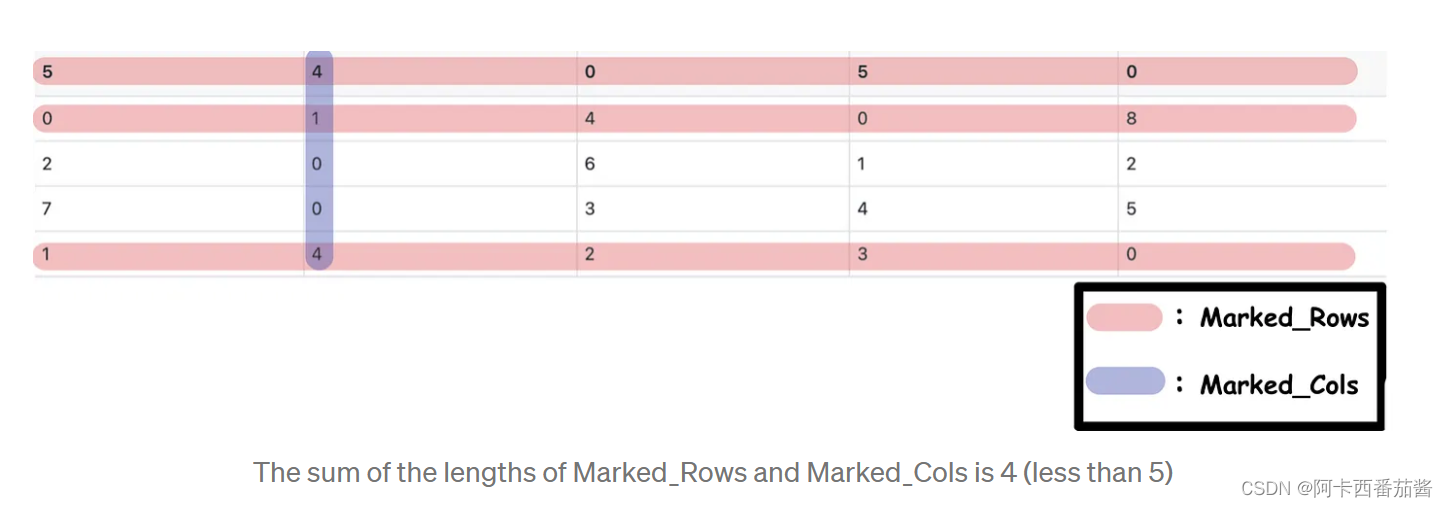
很明显,长度之和小于矩阵的长度。这时,我们需要进入第4步来调整矩阵。
def hungarian_algorithm(mat):
dim = mat.shape[0]
cur_mat = mat
#Step 1 - Every column and every row subtract its internal minimum
for row_num in range(mat.shape[0]):
cur_mat[row_num] = cur_mat[row_num] - np.min(cur_mat[row_num])
for col_num in range(mat.shape[1]):
cur_mat[:,col_num] = cur_mat[:,col_num] - np.min(cur_mat[:,col_num])
zero_count = 0
while zero_count < dim:
#Step 2 & 3
ans_pos, marked_rows, marked_cols = mark_matrix(cur_mat)
zero_count = len(marked_rows) + len(marked_cols)
if zero_count < dim:
cur_mat = adjust_matrix(cur_mat, marked_rows, marked_cols)
return ans_pos
第4步:调整矩阵
在步骤4中,我们要把步骤1之后的矩阵放入Adjust_Matrix函数中。以步骤3中的后一个矩阵为例,Adjust_Matrix中要修改的矩阵是:
整个函数可以分成三个步骤。
为不在标记的行和不在标记的列中的元素找到最小值。因此,我们可以发现最小值是1。
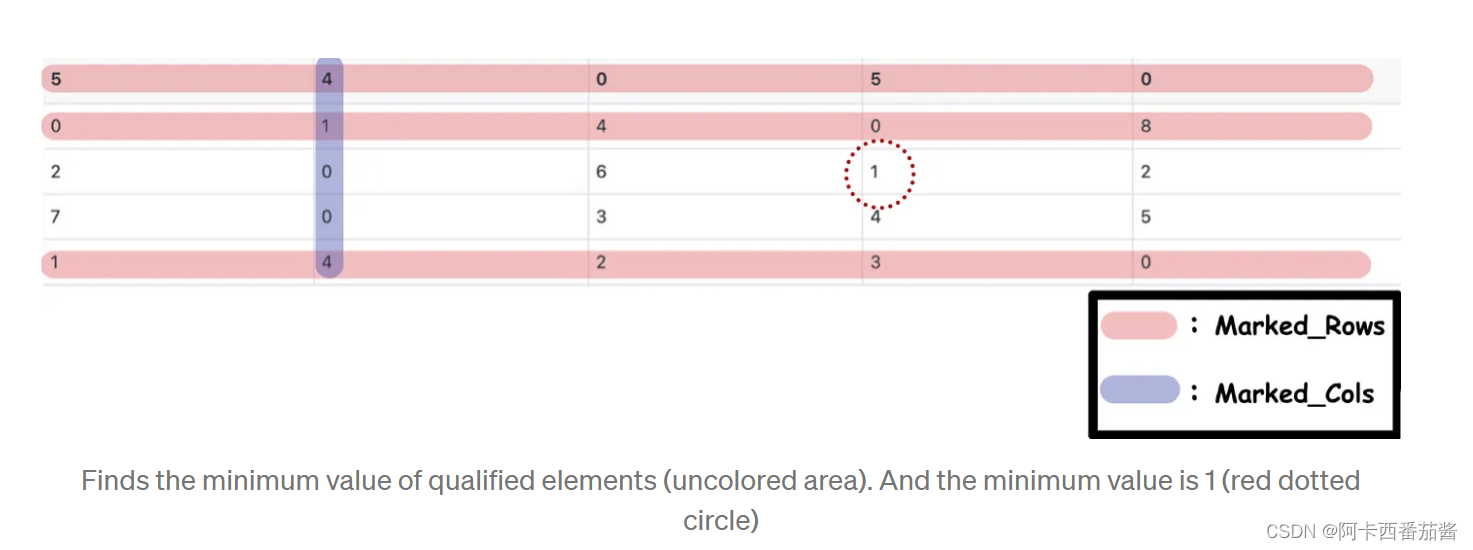
def adjust_matrix(mat, cover_rows, cover_cols):
cur_mat = mat
non_zero_element = []
#Step 4-1 Find the minimum value
for row in range(len(cur_mat)):
if row not in cover_rows:
for i in range(len(cur_mat[row])):
if i not in cover_cols:
non_zero_element.append(cur_mat[row][i])
min_num = min(non_zero_element)
- 从上一步得到的最小值中减去不在标记的行和标记的列中的元素。
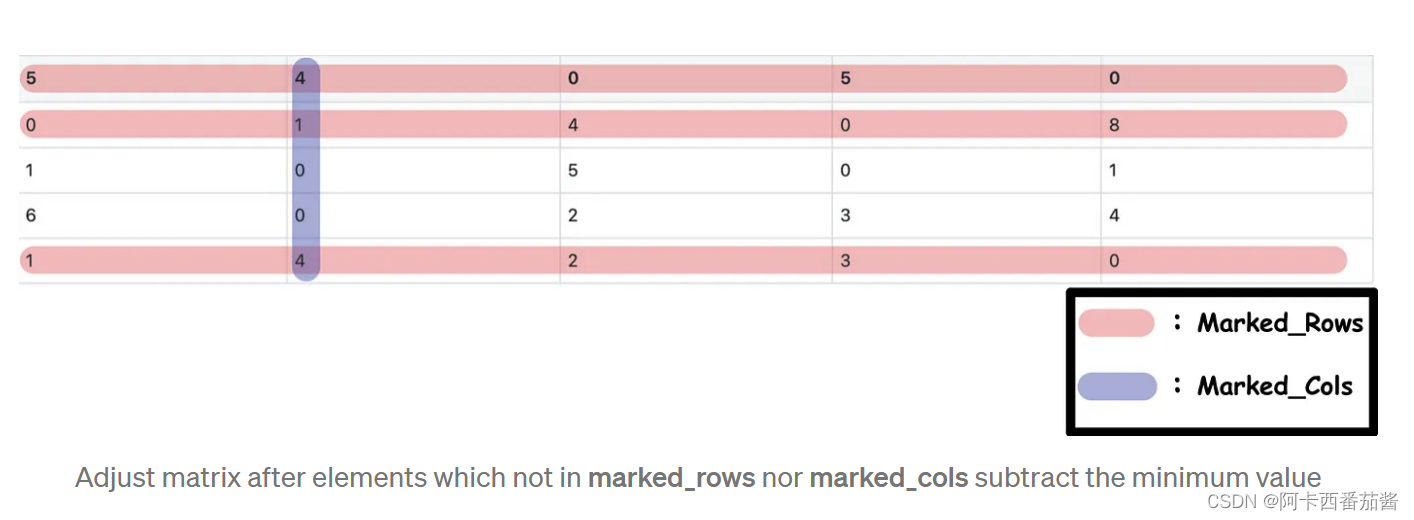
def adjust_matrix(mat, cover_rows, cover_cols):
cur_mat = mat
non_zero_element = []
#Step 4-1
for row in range(len(cur_mat)):
if row not in cover_rows:
for i in range(len(cur_mat[row])):
if i not in cover_cols:
non_zero_element.append(cur_mat[row][i])
min_num = min(non_zero_element)
#Step4-2
for row in range(len(cur_mat)):
if row not in cover_rows:
for i in range(len(cur_mat[row])):
if i not in cover_cols:
cur_mat[row, i] = cur_mat[row, i] - min_num
- 将marked_rows中的元素,也就是marked_cols中的元素,加到步骤4-1得到的最小值。
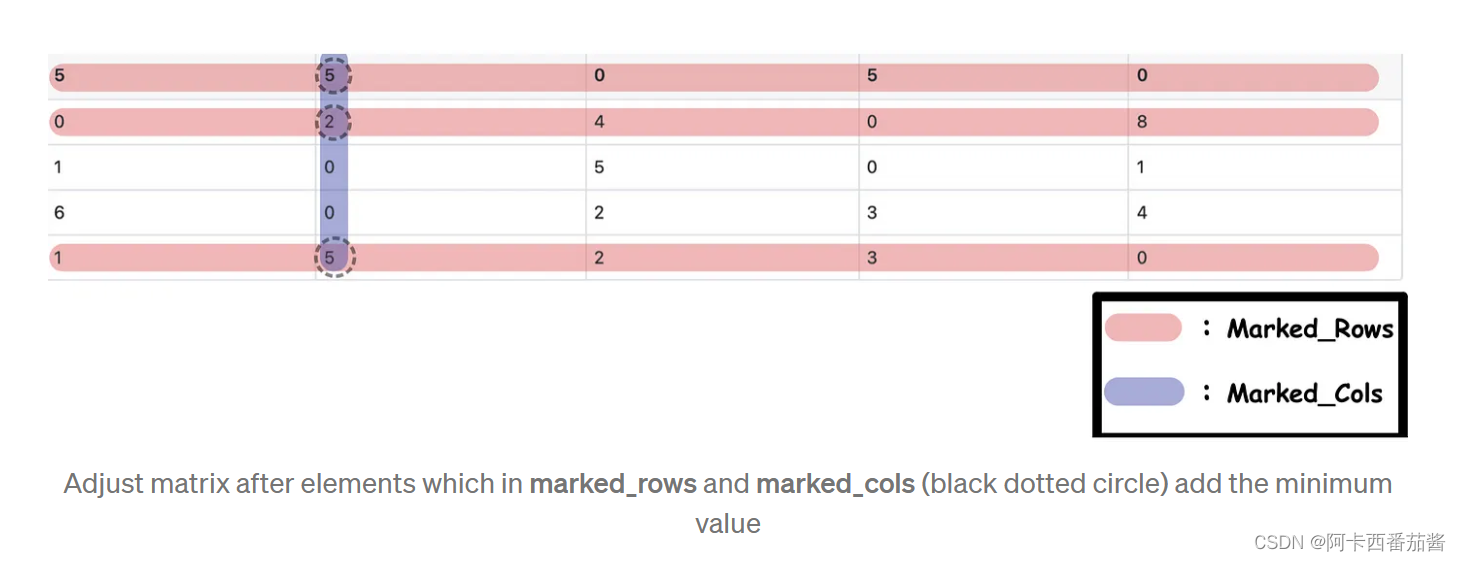
def adjust_matrix(mat, cover_rows, cover_cols):
cur_mat = mat
non_zero_element = []
#Step 4-1
for row in range(len(cur_mat)):
if row not in cover_rows:
for i in range(len(cur_mat[row])):
if i not in cover_cols:
non_zero_element.append(cur_mat[row][i])
min_num = min(non_zero_element)
#Step 4-2
for row in range(len(cur_mat)):
if row not in cover_rows:
for i in range(len(cur_mat[row])):
if i not in cover_cols:
cur_mat[row, i] = cur_mat[row, i] - min_num
#Step 4-3
for row in range(len(cover_rows)):
for col in range(len(cover_cols)):
cur_mat[cover_rows[row], cover_cols[col]] = cur_mat[cover_rows[row], cover_cols[col]] + min_num
return cur_mat
返回调整后的矩阵,重复步骤2和步骤3,直到条件满足进入步骤5的要求。
第5步:计算答案
使用存储在mark_zero中的元素组成,可以计算出线性赋值问题的最小值和最大值。
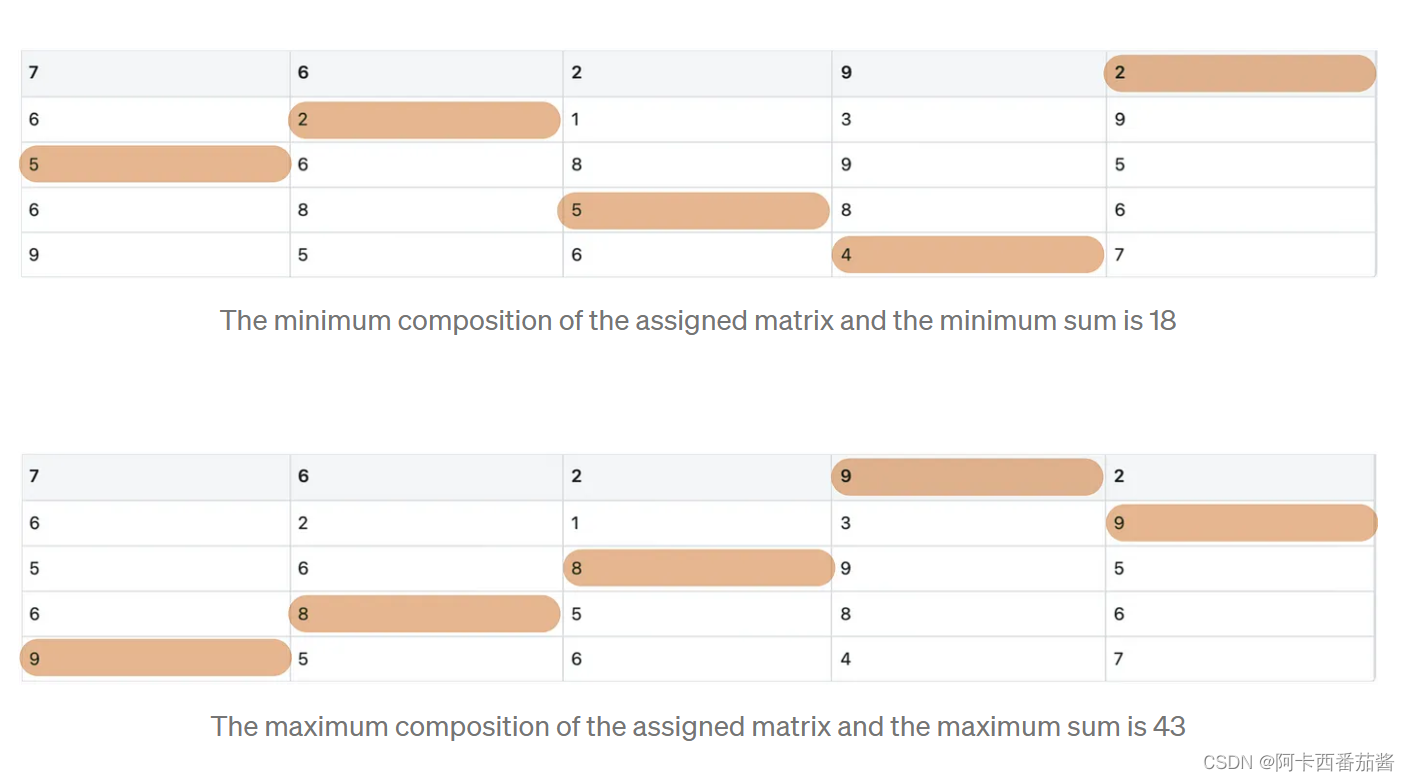
Answer_Calculator函数的代码如下:
def ans_calculation(mat, pos):
total = 0
ans_mat = np.zeros((mat.shape[0], mat.shape[1]))
for i in range(len(pos)):
total += mat[pos[i][0], pos[i][1]]
ans_mat[pos[i][0], pos[i][1]] = mat[pos[i][0], pos[i][1]]
return total, ans_mat
结论
完整的代码如下,如果你有任何问题,请让我知道~
import numpy as np
def min_zero_row(zero_mat, mark_zero):
'''
The function can be splitted into two steps:
#1 The function is used to find the row which containing the fewest 0.
#2 Select the zero number on the row, and then marked the element corresponding row and column as False
'''
#Find the row
min_row = [99999, -1]
for row_num in range(zero_mat.shape[0]):
if np.sum(zero_mat[row_num] == True) > 0 and min_row[0] > np.sum(zero_mat[row_num] == True):
min_row = [np.sum(zero_mat[row_num] == True), row_num]
# Marked the specific row and column as False
zero_index = np.where(zero_mat[min_row[1]] == True)[0][0]
mark_zero.append((min_row[1], zero_index))
zero_mat[min_row[1], :] = False
zero_mat[:, zero_index] = False
def mark_matrix(mat):
'''
Finding the returning possible solutions for LAP problem.
'''
#Transform the matrix to boolean matrix(0 = True, others = False)
cur_mat = mat
zero_bool_mat = (cur_mat == 0)
zero_bool_mat_copy = zero_bool_mat.copy()
#Recording possible answer positions by marked_zero
marked_zero = []
while (True in zero_bool_mat_copy):
min_zero_row(zero_bool_mat_copy, marked_zero)
#Recording the row and column positions seperately.
marked_zero_row = []
marked_zero_col = []
for i in range(len(marked_zero)):
marked_zero_row.append(marked_zero[i][0])
marked_zero_col.append(marked_zero[i][1])
#Step 2-2-1
non_marked_row = list(set(range(cur_mat.shape[0])) - set(marked_zero_row))
marked_cols = []
check_switch = True
while check_switch:
check_switch = False
for i in range(len(non_marked_row)):
row_array = zero_bool_mat[non_marked_row[i], :]
for j in range(row_array.shape[0]):
#Step 2-2-2
if row_array[j] == True and j not in marked_cols:
#Step 2-2-3
marked_cols.append(j)
check_switch = True
for row_num, col_num in marked_zero:
#Step 2-2-4
if row_num not in non_marked_row and col_num in marked_cols:
#Step 2-2-5
non_marked_row.append(row_num)
check_switch = True
#Step 2-2-6
marked_rows = list(set(range(mat.shape[0])) - set(non_marked_row))
return(marked_zero, marked_rows, marked_cols)
def adjust_matrix(mat, cover_rows, cover_cols):
cur_mat = mat
non_zero_element = []
#Step 4-1
for row in range(len(cur_mat)):
if row not in cover_rows:
for i in range(len(cur_mat[row])):
if i not in cover_cols:
non_zero_element.append(cur_mat[row][i])
min_num = min(non_zero_element)
#Step 4-2
for row in range(len(cur_mat)):
if row not in cover_rows:
for i in range(len(cur_mat[row])):
if i not in cover_cols:
cur_mat[row, i] = cur_mat[row, i] - min_num
#Step 4-3
for row in range(len(cover_rows)):
for col in range(len(cover_cols)):
cur_mat[cover_rows[row], cover_cols[col]] = cur_mat[cover_rows[row], cover_cols[col]] + min_num
return cur_mat
def hungarian_algorithm(mat):
dim = mat.shape[0]
cur_mat = mat
#Step 1 - Every column and every row subtract its internal minimum
for row_num in range(mat.shape[0]):
cur_mat[row_num] = cur_mat[row_num] - np.min(cur_mat[row_num])
for col_num in range(mat.shape[1]):
cur_mat[:,col_num] = cur_mat[:,col_num] - np.min(cur_mat[:,col_num])
zero_count = 0
while zero_count < dim:
#Step 2 & 3
ans_pos, marked_rows, marked_cols = mark_matrix(cur_mat)
zero_count = len(marked_rows) + len(marked_cols)
if zero_count < dim:
cur_mat = adjust_matrix(cur_mat, marked_rows, marked_cols)
return ans_pos
def ans_calculation(mat, pos):
total = 0
ans_mat = np.zeros((mat.shape[0], mat.shape[1]))
for i in range(len(pos)):
total += mat[pos[i][0], pos[i][1]]
ans_mat[pos[i][0], pos[i][1]] = mat[pos[i][0], pos[i][1]]
return total, ans_mat
def main():
'''Hungarian Algorithm:
Finding the minimum value in linear assignment problem.
Therefore, we can find the minimum value set in net matrix
by using Hungarian Algorithm. In other words, the maximum value
and elements set in cost matrix are available.'''
#The matrix who you want to find the minimum sum
cost_matrix = np.array([[7, 6, 2, 9, 2],
[6, 2, 1, 3, 9],
[5, 6, 8, 9, 5],
[6, 8, 5, 8, 6],
[9, 5, 6, 4, 7]])
ans_pos = hungarian_algorithm(cost_matrix.copy())#Get the element position.
ans, ans_mat = ans_calculation(cost_matrix, ans_pos)#Get the minimum or maximum value and corresponding matrix.
#Show the result
print(f"Linear Assignment problem result: {ans:.0f}\n{ans_mat}")
#If you want to find the maximum value, using the code as follows:
#Using maximum value in the cost_matrix and cost_matrix to get net_matrix
profit_matrix = np.array([[7, 6, 2, 9, 2],
[6, 2, 1, 3, 9],
[5, 6, 8, 9, 5],
[6, 8, 5, 8, 6],
[9, 5, 6, 4, 7]])
max_value = np.max(profit_matrix)
cost_matrix = max_value - profit_matrix
ans_pos = hungarian_algorithm(cost_matrix.copy())#Get the element position.
ans, ans_mat = ans_calculation(profit_matrix, ans_pos)#Get the minimum or maximum value and corresponding matrix.
#Show the result
print(f"Linear Assignment problem result: {ans:.0f}\n{ans_mat}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
翻译原文:Hungarian Algorithm Introduction & Python Implementation | by Eason | Python in Plain English
再次感谢 Eason!
后续我将出一期在聚类评估中如何使用匈牙利函数对聚类结果进行精确度分析。
整理不易,欢迎点赞关注支持~






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








